MapReduce笔记——技术点汇总
目录
· 概况
· 原理
· 容错机制
· API
· 概况
· Mapper类
· Reducer类
· 示例:连接
· 示例:二次排序
概况
1. 起源:一篇Google论文。
2. 特点
a) 开发简单:用户可不考虑进程通信、套接字编程,无需高深技巧,只需符合MapReduce编程模型。
b) 伸缩性:当集群资源无法满足计算需求时,可通过增加节点达到线性伸缩集群的目的。
c) 容错性:节点故障导致的作业失败,计算框架自动将作业安排到健康节点重新执行,直到任务完成。
3. MapReduce含义:MapReduce编程模型;MapReduce运行环境(YARN)。
4. 局限性
a) 执行速度慢:普通MapReduce作业一般分钟级别完成,复杂作业或数据量更大时可能花费一小时或更多。MapReduce通常时数据密集型作业,大量中间结果写到磁盘并通过网络传输,消耗大量时间。
b) 过于底层:与SQL相比,过于底层。对于习惯关心数据库的用户,或数据分析师,编写map和reduce函数无疑头疼。
c) 无法实现所有算法。
原理
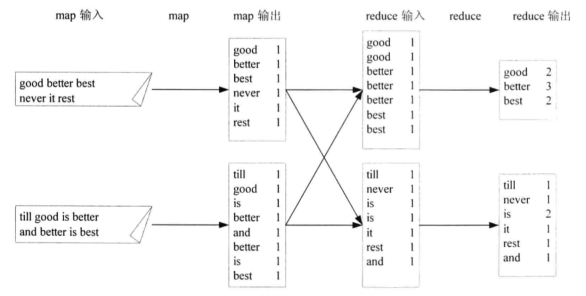
MapReduce编程模型
1. Map与Reduce起源:LISP和其他函数式编程语言中的古老映射和化简操作。
2. MapReduce操作数据最小单位:键值对。
3. MapReduce模型执行过程
(Key1, Value1) → (Key1, List<Value2>) → (Key3, Value3)
a) 将数据抽象为键值对形式作为map函数输入;
b) 经过map函数处理,生成一系列新键值对作为中间结果输出到本地;
c) 计算框架自动将中间结果按键聚合,并将键相同的数据分发到reduce函数,以键和对应指的集合作为reduce函数输入;
d) 经过reduce函数处理,生成一系列键值对作为最终输出。
4. WordCount举例
MapReduce过程
1. 过程描述:input、map、combine、reduce和output五个阶段,其中combine阶段不一定发生,map函数输出的中间结果被被分发到reduce函数的过程称为shuffle,shuffle阶段还会发生copy和sort。
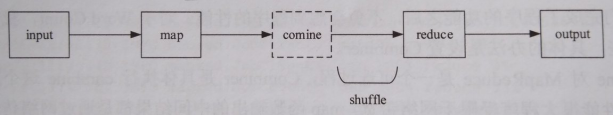
1. Map与Reduce任务:一个作业被分成Map和Reduce计算两个阶段,分别由一个或多个Map任务和Reduce任务组成。
2. input阶段
a) input过程:如果使用HDFS上文件作为MapReduce输入,计算框架以“org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.InputFormat”抽象类的子类“org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat”作为该文件的InputSplit,每个InputSplit作为一个Map任务的输入,再将InputSplit解析成键值对。
b) InputSplit对数据影响:InputSplit只在逻辑上对数据切分,不影响磁盘上存储的文件。
c) InputSplit包含信息:分片的元数据信息,包括起始位置、长度和所在节点列表等。
package org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input;
// ...
public class FileSplit extends InputSplit implements Writable {
// ...
/** Constructs a split with host information
*
* @param file the file name
* @param start the position of the first byte in the file to process
* @param length the number of bytes in the file to process
* @param hosts the list of hosts containing the block, possibly null
*/
public FileSplit(Path file, long start, long length, String[] hosts) {
this.file = file;
this.start = start;
this.length = length;
this.hosts = hosts;
}
// ...
}
d) InputSplit大小计算:minSize取自mapred-site.xml参数“mapreduce.input.fileinputformat.split.minsize”,默认1;maxSize取自mapred-site.xml参数“mapreduce.input.fileinputformat.split.maxsize”,默认Long.MAX_VALUE;blockSize取自hdfs-site.xml参数“dfs.block.size”。所以,使用默认配置时,InputSplit大小为块大小。
package org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input;
// ...
public abstract class FileInputFormat<K, V> extends InputFormat<K, V> {
// ...
protected long computeSplitSize(long blockSize, long minSize,
long maxSize) {
return Math.max(minSize, Math.min(maxSize, blockSize));
}
// ...
}
e) input数量计算:文件大小÷InputSplit大小。
f) 对齐:任务调度时,优先考虑本节点的数据,如果本节点没有可处理的数据或还需其他节点数据,Map任务所在节点会从其他节点将数据网络传输给自己。当InputSplit大小大于块大小时,Map任务会从其他节点读取一部分数据,就无法实现完全数据本地化,所以InputSplit大小应等于块大小。
g) map函数输入:通过InputFormat.createRecordReader()方法将InputSplit解析为键值对。
package org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input;
// ...
public class TextInputFormat extends FileInputFormat<LongWritable, Text> {
// ...
@Override
public RecordReader<LongWritable, Text>
createRecordReader(InputSplit split,
TaskAttemptContext context) {
String delimiter = context.getConfiguration().get(
"textinputformat.record.delimiter");
byte[] recordDelimiterBytes = null;
if (null != delimiter)
recordDelimiterBytes = delimiter.getBytes(Charsets.UTF_8);
return new LineRecordReader(recordDelimiterBytes);
}
// ...
}
4. map阶段
a) 写缓冲区:map函数输出时,先写到内存环形缓冲区,并做一次预排序;每个Map任务都有一个环形缓冲区,大小取自mapred-site.xml参数“mapreduce.task.io.sort.mb”,默认100MB。
b) 缓冲区溢写磁盘:当环形缓冲区达到阀值(mapred-site.xml参数“mapreduce.map.sort.spill.percent”,默认0.80)时,一个后台线程将缓冲区内容溢写(spill)到磁盘mapred-site.xml参数“mapreduce.cluster.local.dir”指定的目录,默认${hadoop.tmp.dir}/mapred/local。
c) 溢写磁盘前排序:溢写磁盘前,线程根据数据要传送的Reducer对缓冲区数据分区(默认按键),每个分区内再按键排序。
d) Combiner:当已指定Combiner且溢写次数至少3次时,在溢写磁盘前执行Combiner;效果是对map函数输出的中间结果进行一次合并,作用与reduce函数一样;目的是降低中间结果数据量(中间结果要写磁盘且通过网络传至Reducer),提升运行效率。
e) 压缩:对中间结果压缩,目的与Combiner相同;mapred-site.xml参数“mapreduce.map.output.compress”,默认false,参数“mapreduce.map.output.compress.codec”。
|
压缩格式 |
算法 |
文件扩展名 |
可切分 |
codec类 |
说明 |
|
Deflate |
Deflate |
.deflate |
否 |
org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.DeflateCodec |
|
|
gzip |
Deflate |
.gz |
否 |
org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.GzipCodec |
|
|
bzip2 |
bzip2 |
.bz2 |
是 |
org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.BZip2Codec |
|
|
LZO |
LZOP |
.lzo |
否 |
com.hadoop.compression.lzo.LzopCodec |
|
|
Snappy |
Snappy |
.snappy |
否 |
org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.SnappyCodec |
高压缩、高速,推荐 |
f) 中间结果传输:中间结果通过HTTP方式传至Reducer,传输工作线程数配置mapred-site.xml参数“mapreduce.tasktracker.http.threads”,默认40。
5. shuffle阶段
a) copy:一个Reduce任务可能需多个Map任务输出,而每个Map任务完成时间很可能不同,当只要有一个Map任务完成,Reduce任务即开始复制其输出;复制线程数配置mapred-site.xml参数“mapreduce.reduce.shuffle.parallelcopies”,默认5。
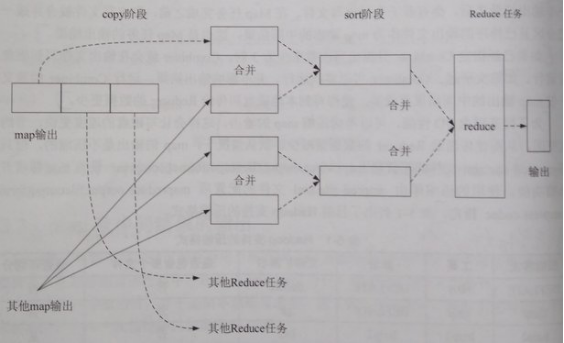
b) copy的缓冲区:如果map输出相当小,数据先被复制到Reducer所在节点的内存缓冲区(大小配置mapred-site.xml参数“mapreduce.reduce.shuffle.input.buffer.percent”,默认0.70),当内存缓冲区大小达到阀值(mapred-site.xml参数“mapreduce.reduce.shuffle.merge.percent”,默认0.66)或内存缓冲区文件数达到阀值(mapred-site.xml参数“mapreduce.reduce.merge.inmem.threshold”,默认1000)时,则合并后溢写磁盘。否则,map输出被复制到磁盘。
c) copy的合并:随复制到磁盘的文件增多,后台线程将其合并为更大、有序的文件,为后续合并节约时间。合并时,压缩的中间结果将在内存中解压缩。
d) sort:复制完成所有map输出后,合并map输出文件并归并排序。
e) sort的合并:将map输出文件合并,直至≤合并因子(mapred-site.xml参数“mapreduce.task.io.sort.factor”,默认10)。例如,有50个map输出文件,进行5次合并,每次将10个文件合并成一个文件,最后5个文件。
6. reduce阶段
a) reduce函数输入:经过shuffle的文件都是按键分区且有序,相同分区的文件调用一次reduce函数。
b) reduce函数输出:一般为HDFS。
7. 排序
a) MapReduce中的排序算法:快速排序、归并排序。
b) MapReduce发生的3次排序:map阶段的缓冲区排序(快速排序算法);map阶段溢写磁盘前,对溢写文件合并时的排序(归并排序算法);shuffle阶段的文件合并sort(归并排序算法)。
容错机制
1. 任务错误:对错误任务不断重试,直到总尝试次数超过N次认为彻底失败;Map任务、Reduce任务总尝试次数分别为mapred-site.xml参数“mapreduce.map.maxattempts”和“mapreduce.reduce.maxattempts”,默认均为4。
2. ApplicationMaster错误:通过YARN容错机制完成。
3. NodeManager错误:通过YARN容错机制完成。
4. ResourceManager错误:通过YARN容错机制完成。
API
概况
1. 新旧API
a) 旧API包:org.apache.hadoop.mapred
b) 新API包:org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce
2. Maven依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hadoop</groupId>
<artifactId>hadoop-client</artifactId>
<version>2.6.5</version>
</dependency>
WordCount示例
1. Mapper类
package mr.wordcount; import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper; public class TokenizerMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, IntWritable> { private final static IntWritable one = new IntWritable(1); private Text word = new Text(); @Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value,
Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, IntWritable>.Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
StringTokenizer stringTokenizer = new StringTokenizer(value.toString());
while (stringTokenizer.hasMoreTokens()) {
word.set(stringTokenizer.nextToken());
context.write(word, one);
}
} }
2. Reducer类
package mr.wordcount; import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer; public class IntSumReducer extends Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable> { private IntWritable result = new IntWritable(); @Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values,
Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable>.Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
int sum = 0;
for (IntWritable value : values) {
sum += value.get();
}
result.set(sum);
context.write(key, result);
} }
3. main方法
package mr.wordcount; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; public class WordCount { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
if (args.length != 2) {
System.err.println("Usage: wordcount <in> <out>");
System.exit(2);
} Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, "WordCount");
job.setJarByClass(WordCount.class);
job.setMapperClass(TokenizerMapper.class);
job.setCombinerClass(IntSumReducer.class);
job.setReducerClass(IntSumReducer.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(args[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1]));
System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
} }
4. 执行命令
hadoop jar wordcount.jar mr.wordcount.WordCount /test/wordcount/in /test/wordcount/out
hadoop fs -ls /test/wordcount/out
hadoop fs -cat /test/wordcount/out/part-r-
Writable接口
1. 职责:Hadoop序列化格式。
2. Hadoop序列化场景:IPC(进程间通信)、数据持久化。
3. 源码(2个重要方法)
package org.apache.hadoop.io;
// ...
public interface Writable {
/**
* Serialize the fields of this object to <code>out</code>.
*
* @param out <code>DataOuput</code> to serialize this object into.
* @throws IOException
*/
void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException;
/**
* Deserialize the fields of this object from <code>in</code>.
*
* <p>For efficiency, implementations should attempt to re-use storage in the
* existing object where possible.</p>
*
* @param in <code>DataInput</code> to deseriablize this object from.
* @throws IOException
*/
void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException;
}
4. 内置实现类
a) 包:org.apache.hadoop.io。
b) 类图
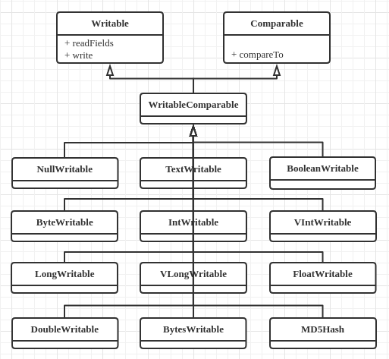
c) 与Java类型对照
|
Java类型 |
Writable实现 |
备注 |
|
null |
NullWritable |
序列化长度为0,充当占位符 |
|
String |
Text |
|
|
boolean |
BooleanWritable |
|
|
byte |
ByteWritable |
|
|
int |
IntWritable、VIntWritable |
V开头表示变长,否则定长 |
|
long |
LongWritable、VLongWritable |
V开头表示变长,否则定长 |
|
float |
FloatWritable |
|
|
double |
DoubleWritable |
5. 自定义实现类
import java.io.DataInput;
import java.io.DataOutput;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable; public class TextPair implements WritableComparable<TextPair> { private Text first; private Text second; public TextPair() {
this(new Text(), new Text());
} public TextPair(Text first, Text second) {
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
} public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
first.write(out);
second.write(out);
} public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
first.readFields(in);
second.readFields(in);
} // 用于MapReduce过程中的排序
public int compareTo(TextPair o) {
int result = first.compareTo(o.first);
if (result == 0) {
result = second.compareTo(o.second);
}
return result;
} public Text getFirst() {
return first;
} public void setFirst(Text first) {
this.first = first;
} public Text getSecond() {
return second;
} public void setSecond(Text second) {
this.second = second;
} }
Mapper类
1. 源码(4个重要方法)
package org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce;
// ...
public class Mapper<KEYIN, VALUEIN, KEYOUT, VALUEOUT> {
/**
* The <code>Context</code> passed on to the {@link Mapper} implementations.
*/
public abstract class Context
implements MapContext<KEYIN,VALUEIN,KEYOUT,VALUEOUT> {
}
/**
* Called once at the beginning of the task.
*/
protected void setup(Context context
) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// NOTHING
}
/**
* Called once for each key/value pair in the input split. Most applications
* should override this, but the default is the identity function.
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected void map(KEYIN key, VALUEIN value,
Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
context.write((KEYOUT) key, (VALUEOUT) value);
}
/**
* Called once at the end of the task.
*/
protected void cleanup(Context context
) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// NOTHING
}
/**
* Expert users can override this method for more complete control over the
* execution of the Mapper.
* @param context
* @throws IOException
*/
public void run(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
setup(context);
try {
while (context.nextKeyValue()) {
map(context.getCurrentKey(), context.getCurrentValue(), context);
}
} finally {
cleanup(context);
}
}
}
2. run方法:setup→map→cleanup的执行模板。
Reducer类
1. 源码
package org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce;
// ...
public class Reducer<KEYIN,VALUEIN,KEYOUT,VALUEOUT> {
/**
* The <code>Context</code> passed on to the {@link Reducer} implementations.
*/
public abstract class Context
implements ReduceContext<KEYIN,VALUEIN,KEYOUT,VALUEOUT> {
}
/**
* Called once at the start of the task.
*/
protected void setup(Context context
) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// NOTHING
}
/**
* This method is called once for each key. Most applications will define
* their reduce class by overriding this method. The default implementation
* is an identity function.
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected void reduce(KEYIN key, Iterable<VALUEIN> values, Context context
) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
for(VALUEIN value: values) {
context.write((KEYOUT) key, (VALUEOUT) value);
}
}
/**
* Called once at the end of the task.
*/
protected void cleanup(Context context
) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// NOTHING
}
/**
* Advanced application writers can use the
* {@link #run(org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer.Context)} method to
* control how the reduce task works.
*/
public void run(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
setup(context);
try {
while (context.nextKey()) {
reduce(context.getCurrentKey(), context.getValues(), context);
// If a back up store is used, reset it
Iterator<VALUEIN> iter = context.getValues().iterator();
if(iter instanceof ReduceContext.ValueIterator) {
((ReduceContext.ValueIterator<VALUEIN>)iter).resetBackupStore();
}
}
} finally {
cleanup(context);
}
}
}
2. run方法:setup→reduce→cleanup的执行模板。
Partitioner抽象类
1. 场景:控制shuffle,即控制中间结果分发的目的Reducer。
2. 源码
package org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce;
// ...
public abstract class Partitioner<KEY, VALUE> {
/**
* Get the partition number for a given key (hence record) given the total
* number of partitions i.e. number of reduce-tasks for the job.
*
* <p>Typically a hash function on a all or a subset of the key.</p>
*
* @param key the key to be partioned.
* @param value the entry value.
* @param numPartitions the total number of partitions.
* @return the partition number for the <code>key</code>.
*/
public abstract int getPartition(KEY key, VALUE value, int numPartitions);
}
3. 内置子类
a) org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.partition.HashPartitioner:按键的Hash值分区,默认。
package org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.partition;
// ...
public class HashPartitioner<K, V> extends Partitioner<K, V> {
/** Use {@link Object#hashCode()} to partition. */
public int getPartition(K key, V value,
int numReduceTasks) {
return (key.hashCode() & Integer.MAX_VALUE) % numReduceTasks;
}
}
b) org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.partition.TotalOrderPartitioner:按键分区,使得每个Reduce任务处理一个键连续区间(如1~1000、1000~2000……)的数据,最终输出是全局有序的;如果键对应的数据分布不均匀,则导致部分Reduce任务完成时间变长。
4. 自定义子类
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner; public class MyPartitioner extends Partitioner<Text, IntWritable> { @Override
public int getPartition(Text key, IntWritable value, int numReduceTasks) {
return ((new Boolean(value.get() > 10000)).hashCode() & Integer.MAX_VALUE) % numReduceTasks;
} }
// main方法设置Partitioner
job.setPartitionerClass(MyPartitioner.class);
WritableComparator接口
1. 场景:控制MapReduce过程中第2次和第3次排序的排序规则。
2. 内置实现类:org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparator。
3. 自定义实现类
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparator; public class MyWritableComparator extends WritableComparator { protected MyWritableComparator() {
super(IntWritable.class, true);
} @Override
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
public int compare(WritableComparable key1, WritableComparable key2) {
IntWritable x = (IntWritable) key1;
IntWritable y = (IntWritable) key2;
return (x.get() % 5 - y.get() % 5) > 0 ? 1 : -1;
} }
// main方法设置WritableComparator
job.setSortComparatorClass(MyWritableComparator.class);
job.setGroupingComparatorClass(MyWritableComparator.class);
示例:连接
1. 数据准备(一对多关系)
a) 学生信息
Jenny,00001
Hardy,00002
Bradley,00003
b) 选课信息
00001,Chinese
00001,Math
00002,Music
00002,Math
00003,Physic
2. 代码
a) Mapper类
package mr.join; import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileSplit; public class JoinMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, Text> { public static final String LEFT_PATH = "student_info"; public static final String RIGHT_PATH = "student_class_info"; public static final String LEFT_TABLE_FLAG = "l\u0001"; public static final String RIGHT_TABLE_FLAG = "r\u0001"; private Text outKey = new Text(); private Text outValue = new Text(); @Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value,
Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, Text>.Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String filePath = ((FileSplit) context.getInputSplit()).getPath().toString();
String tableFlag = null;
String joinKey = null;
String joinValue = null; if (filePath.contains(LEFT_PATH)) {
tableFlag = LEFT_TABLE_FLAG;
String[] values = value.toString().split(",");
joinKey = values[1];
joinValue = values[0]; } else if (filePath.contains(RIGHT_PATH)) {
tableFlag = RIGHT_TABLE_FLAG;
String[] values = value.toString().split(",");
joinKey = values[0];
joinValue = values[1];
} else {
return;
} outKey.set(joinKey);
outValue.set(tableFlag + joinValue);
context.write(outKey, outValue);
} }
b) Reducer类
package mr.join; import static mr.join.JoinMapper.LEFT_TABLE_FLAG;
import static mr.join.JoinMapper.RIGHT_TABLE_FLAG;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer; public class JoinReducer extends Reducer<Text, Text, Text, NullWritable> { private Text result = new Text(); @Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<Text> values,
Reducer<Text, Text, Text, NullWritable>.Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
Iterator<Text> iterator = values.iterator();
List<String> studentClassNames = new ArrayList<>();
String studentName = null; while (iterator.hasNext()) {
String value = iterator.next().toString();
if (value.startsWith(LEFT_TABLE_FLAG)) {
studentName = value.substring(LEFT_TABLE_FLAG.length());
} else if (value.startsWith(RIGHT_TABLE_FLAG)) {
studentClassNames.add(value.substring(RIGHT_TABLE_FLAG.length()));
}
}
// 笛卡尔积
for (String studentClassName : studentClassNames) {
result.set(studentName + "," + studentClassName);
context.write(result, NullWritable.get());
}
} }
c) main方法
package mr.join; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; public class Join { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, "Join");
job.setJarByClass(Join.class);
job.setMapperClass(JoinMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(JoinReducer.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class);
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path("/test/join/student_info"));
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path("/test/join/student_class_info"));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("/test/join/result"));
System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
} }
d) 执行命令
hadoop jar join.jar mr.join.Join
e) 结果
Jenny,Math
Jenny,Chinese
Hardy,Math
Hardy,Music
Bradley,Physic
示例:二次排序
1. 二次排序:key由两个字段组成,先第1个字段排序,在此基础上再按第2个字段排序。本示例实现先按第1个字段正序,再按第2个字段倒序,类似SQL的“order by column1 asc, column2 desc”。
2. 原理
a) map阶段后期:先调用job.setPartitionerClass()的类对map函数输出分区;每个分区内再调用job.setSortComparatorClass()的类对key排序;如果未设置job.setSortComparatorClass(),则调用key的compareTo()方法排序。
b) reduce阶段:先调用job.setSortComparatorClass()的类对key排序,再开始构造key对应的value迭代器,调用job.setGroupingComparatorClass()的类将key相同的value分到相同value迭代器。
3. 数据准备(column1、column2、column3)
4,3,h
4,2,g
4,1,e
3,4,b
2,7,c
2,3,a
3,1,f
3,3,j
3,2,i
3,3,d
4. 代码
a) Map key类
package mr.secondarysort; import java.io.DataInput;
import java.io.DataOutput;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable; public class CompositeKey implements WritableComparable<CompositeKey> { private Text column1 = new Text(); private Text column2 = new Text(); @Override
public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
column1.write(out);
column2.write(out);
} @Override
public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
column1.readFields(in);
column2.readFields(in);
} // 用于环形缓冲区排序
@Override
public int compareTo(CompositeKey o) {
// 仅按第1个字段排序
return column1.compareTo(o.column1);
} public Text getColumn1() {
return column1;
} public Text getColumn2() {
return column2;
} public void set(String column1, String column2) {
this.column1.set(column1);
this.column2.set(column2);
} }
b) Mapper类
package mr.secondarysort; import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper; public class SecondarySortMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, CompositeKey, Text> { private CompositeKey outKey = new CompositeKey(); private Text outValue = new Text(); @Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value,
Mapper<LongWritable, Text, CompositeKey, Text>.Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String valueString = value.toString();
String[] columns = valueString.split(",");
outKey.set(columns[0], columns[1]);
outValue.set(valueString);
context.write(outKey, outValue);
} }
c) Partitioner类
package mr.secondarysort; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner; public class SecondarySortPartitioner extends Partitioner<CompositeKey, Text> { @Override
public int getPartition(CompositeKey key, Text value, int numReduceTasks) {
return (key.getColumn1().hashCode() & Integer.MAX_VALUE) % numReduceTasks;
} }
d) SortComparator类
package mr.secondarysort; import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparator; // 用于二次排序
public class SortComparator extends WritableComparator { protected SortComparator() {
super(CompositeKey.class, true);
} @Override
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
public int compare(WritableComparable key1, WritableComparable key2) {
// 按两个字段排序
CompositeKey compositeKey1 = (CompositeKey) key1;
CompositeKey compositeKey2 = (CompositeKey) key2;
int result = compositeKey1.getColumn1().compareTo(compositeKey2.getColumn1());
if (result == 0) {
// 第2个字段倒序
result = -compositeKey1.getColumn2().compareTo(compositeKey2.getColumn2());
}
return result;
} }
e) GroupingComparator类
package mr.secondarysort; import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparator; // 用于对value分组
public class GroupingComparator extends WritableComparator { protected GroupingComparator() {
super(CompositeKey.class, true);
} @Override
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
public int compare(WritableComparable key1, WritableComparable key2) {
// 按第1个字段分组
CompositeKey compositeKey1 = (CompositeKey) key1;
CompositeKey compositeKey2 = (CompositeKey) key2;
return compositeKey1.getColumn1().compareTo(compositeKey2.getColumn1());
} }
f) Reducer类
package mr.secondarysort; import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Iterator;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer; public class SecondarySortReducer extends Reducer<CompositeKey, Text, Text, NullWritable> { private Text result = new Text(); @Override
protected void reduce(CompositeKey key, Iterable<Text> values,
Reducer<CompositeKey, Text, Text, NullWritable>.Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
Iterator<Text> iterator = values.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
result.set(iterator.next());
context.write(result, NullWritable.get());
}
} }
g) main方法
package mr.secondarysort; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; public class SecondarySort { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, "SecondarySort");
job.setJarByClass(SecondarySort.class);
job.setMapperClass(SecondarySortMapper.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(CompositeKey.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(Text.class);
job.setPartitionerClass(SecondarySortPartitioner.class);
job.setSortComparatorClass(SortComparator.class);
job.setGroupingComparatorClass(GroupingComparator.class);
job.setReducerClass(SecondarySortReducer.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class);
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path("/test/secondarysort/in"));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("/test/secondarysort/out"));
System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
} }
5. 执行命令
hadoop jar secondarysort.jar mr.secondarysort.SecondarySort
6. 结果
2,7,c
2,3,a
3,4,b
3,3,d
3,3,j
3,2,i
3,1,f
4,3,h
4,2,g
4,1,e
作者:netoxi
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/netoxi
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,未经同意须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接。欢迎指正与交流。
MapReduce笔记——技术点汇总的更多相关文章
- Hadoop笔记——技术点汇总
目录 · 概况 · Hadoop · 云计算 · 大数据 · 数据挖掘 · 手工搭建集群 · 引言 · 配置机器名 · 调整时间 · 创建用户 · 安装JDK · 配置文件 · 启动与测试 · Clo ...
- Spark SQL笔记——技术点汇总
目录 概述 原理 组成 执行流程 性能 API 应用程序模板 通用读写方法 RDD转为DataFrame Parquet文件数据源 JSON文件数据源 Hive数据源 数据库JDBC数据源 DataF ...
- Spark笔记——技术点汇总
目录 概况 手工搭建集群 引言 安装Scala 配置文件 启动与测试 应用部署 部署架构 应用程序部署 核心原理 RDD概念 RDD核心组成 RDD依赖关系 DAG图 RDD故障恢复机制 Standa ...
- Hive笔记——技术点汇总
目录 · 概况 · 手工安装 · 引言 · 创建HDFS目录 · 创建元数据库 · 配置文件 · 测试 · 原理 · 架构 · 与关系型数据库对比 · API · WordCount · 命令 · 数 ...
- JVM笔记——技术点汇总
目录 · 初步认识 · Java里程碑(关键部分) · 理解虚拟机 · Java虚拟机种类 · Java语言规范 · Java虚拟机规范 · 基本结构 · Java堆(Heap) · Java栈(St ...
- Netty笔记——技术点汇总
目录 · Linux网络IO模型 · 文件描述符 · 阻塞IO模型 · 非阻塞IO模型 · IO复用模型 · 信号驱动IO模型 · 异步IO模型 · BIO编程 · 伪异步IO编程 · NIO编程 · ...
- Redis笔记——技术点汇总
目录 · 特点 · 安装 · 数据库 · 服务器命令 · 数据类型及其操作命令 · 数据结构 · string · list · set · hash · zset · 发布与订阅 · 排序 · 事务 ...
- Java并发编程笔记——技术点汇总
目录 · 线程安全 · 线程安全的实现方法 · 互斥同步 · 非阻塞同步 · 无同步 · volatile关键字 · 线程间通信 · Object.wait()方法 · Object.notify() ...
- Storm笔记——技术点汇总
目录 概况 手工搭建集群 引言 安装Python 配置文件 启动与测试 应用部署 参数配置 Storm命令 原理 Storm架构 Storm组件 Stream Grouping 守护进程容错性(Dae ...
随机推荐
- mysql+keepalived 双主热备高可用
理论介绍:我们通常说的双机热备是指两台机器都在运行,但并不是两台机器都同时在提供服务.当提供服务的一台出现故障的时候,另外一台会马上自动接管并且提供服务,而且切换的时间非常短.MySQL双主复制,即互 ...
- SICP-1.7-递归函数
递归函数 函数内部直接或间接的调用函数自身 将复杂问题简单化 例子程序 def sum_digits(n): """Return the sum of the digit ...
- 关于MATLAB处理大数据坐标文件2017622
今天新提交了一次数据,总量达到10337个,本以为成绩会突飞猛进,没想到还是不如从前 但是已经找到人工鼠标轨迹的程序,有待完善,接下来兵分四路:找特征.决策树.完善人工轨迹程序,使其可以将生成的数据自 ...
- SQL Server事务的隔离级别和锁
背景 当用户并发尝试访问同一数据的时,SQL Server尝试用锁来隔离不一致的数据和使用隔离级别查询数据时控制一致性(数据该如何读取),说起锁就会联想到事务,事务是一个工作单元,包括查 ...
- Css3视频教程下载
本套教程主要讲解了大量的CSS3新功能,包括: 边框.圆角.背景.渐变.阴影.文本特效.2D/3D转换.过渡.动画.伪类元素的使用等,同时伴随了大量的实例制作,比如CSS3实现红心的制作,火焰字.多彩 ...
- Api接口通用安全策略及实现-OSS.Core
这篇文章一直说写,迟迟没有动手,这两天看到一些应用接口数据被别人爬虫.短信接口被人高频率请求攻击等案列,感觉简单概述分享一下接口安全验证还是有必要的.毕竟当下基本都以客户端应用为主,如果前期疏忽,发布 ...
- 静态变量和Session
静态变量: Application级别的,不同客户端访问同一个变量. Session:对于每个访问的客户端是独立的,都有一个唯一的SessionID.也就是说,不同客户端下,都可以有一个Session ...
- Mysql元数据分析
Mysql元数据分析 @(基础技术) 一.information_schema库 information_schema库中的表,保存的是Mysql的元数据. 官网元数据表介绍 InnoDB相关的表介绍 ...
- Java开源博客My-Blog之docker组件化修改
前言 5月13号上线了自己的个人博客,<Docker+SpringBoot+Mybatis+thymeleaf的Java博客系统开源啦>,紧接着也在github上开源了博客的代码,到现在为 ...
- Chrome浏览器扩展开发系列之八:Chrome扩展的数据存储
Google Chrome浏览器扩展可以使用如下任何一种存储机制: HTML5的localStorage API实现的本地存储(此处略) Google的chrome.storage.* API实现的浏 ...
