自动化特征工程—Featuretools
Featuretools是一个可以自动进行特征工程的python库,主要原理是针对多个数据表以及它们之间的关系,通过转换(Transformation)和聚合(Aggregation)操作自动生成新的特征。转换操作的对象是单一数据表的一列或多列(例如对某列取绝对值或者计算两列之差);聚合操作的对象是具有父子 (one-to-many)关系的两个数据表,通过对父表的某列进行归类(groupby)计算子表某列对应的统计值。下面通过几个简单的例子进行介绍,Featuretools在实际应用中的案例可以参考它的Github仓库。
1. 顾客交易记录,每个交易对应一个顾客,可分多次支付(需要求解的问题是关于顾客的)
- 建立数据
import featuretools as ft
import pandas as pd
### 构建简单的数据表
customers = pd.DataFrame({'customer_id':[1,2],})
transactions = pd.DataFrame({'transaction_id':[1,2,3,4,5], 'customer_id':[1,1,1,2,2], \
'amount':[3.,8.,6.,4.,9.]})
payments = pd.DataFrame({'payment_id':[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8], 'transaction_id':[1,1,2,3,3,4,4,5], \
'money':[3,7,6,5,8,2,4,7]})
### 建立数据表之间的关系
es = ft.EntitySet('example1')
es.entity_from_dataframe(dataframe=payments, entity_id='payments', index='payment_id')
es.entity_from_dataframe(dataframe=transactions, entity_id='transactions', index='transaction_id')
es.entity_from_dataframe(dataframe=customers, entity_id='customers', index='customer_id')
r1 = ft.Relationship(es['customers']['customer_id'], es['transactions']['customer_id'])
r2 = ft.Relationship(es['transactions']['transaction_id'], es['payments']['transaction_id'])
es = es.add_relationship(r1)
es = es.add_relationship(r2)
print(es)
- 生成新的特征
# 自定义primitive
# Featuretools内置了许多常用的primitive, 这里仅为了介绍Featuretools更多的特性
def plusOne(column): return column+1
plus_one = ft.primitives.make_trans_primitive(function=plusOne, input_types=[ft.variable_types.Numeric],\
return_type=ft.variable_types.Numeric)
def maximum(column): return max(column)
Maximum = ft.primitives.make_agg_primitive(function=maximum, input_types=[ft.variable_types.Numeric], \
return_type=ft.variable_types.Numeric)
# max_depth控制转换和聚合的次数
feature_matrix, feature_defs = ft.dfs(entityset=es, target_entity="customers", trans_primitives=[plus_one], \
agg_primitives=["sum", Maximum], max_depth=3)
print(feature_defs)以特征SUM(transactions.PLUSONE(MAXIMUM(payments.money)))为例,下图说明了对customer_id=1的顾客该特征是如何计算的:

2. 顾客交易记录,每个交易对应一个顾客,可分多次支付(需要求解的问题是关于交易的)
- 同上,仅改动一行代码:
feature_matrix, feature_defs = ft.dfs(entityset=es, target_entity="transactions", trans_primitives=[plus_one], \
agg_primitives=["sum", Maximum], max_depth=3)以特征customers.PLUSONE(SUM(payments.money))为例,下图说明了对transaction_id=1的交易该特征是如何计算的:

3. 顾客交易记录,每个交易对应一个顾客和一个商品(需要求解的问题是关于顾客的)
- 建立数据
customers = pd.DataFrame({'customer_id':[1,2],})
transactions = pd.DataFrame({'transaction_id':[1,2,3,4,5], 'customer_id':[1,1,1,2,2], \
'amount':[3.,8.,6.,4.,9.], 'product_id':[1,2,3,1,2]})
products = pd.DataFrame({'product_id':[1,2,3]})
### 建立数据表之间的关系
es = ft.EntitySet('example')
es.entity_from_dataframe(dataframe=products, entity_id='products', index='product_id')
es.entity_from_dataframe(dataframe=transactions, entity_id='transactions', index='transaction_id')
es.entity_from_dataframe(dataframe=customers, entity_id='customers', index='customer_id')
r1 = ft.Relationship(es['customers']['customer_id'], es['transactions']['customer_id'])
r2 = ft.Relationship(es['products']['product_id'], es['transactions']['product_id'])
es = es.add_relationship(r1)
es = es.add_relationship(r2)
print(es)
生成新的特征
def plusOne(column): return column+1
plus_one = ft.primitives.make_trans_primitive(function=plusOne, input_types=[ft.variable_types.Numeric],\
return_type=ft.variable_types.Numeric)
def maximum(column): return max(column)
Maximum = ft.primitives.make_agg_primitive(function=maximum, input_types=[ft.variable_types.Numeric], \
return_type=ft.variable_types.Numeric)
feature_matrix, feature_defs = ft.dfs(entityset=es, target_entity="customers", trans_primitives=[plus_one], \
agg_primitives=["sum", Maximum], max_depth=3)
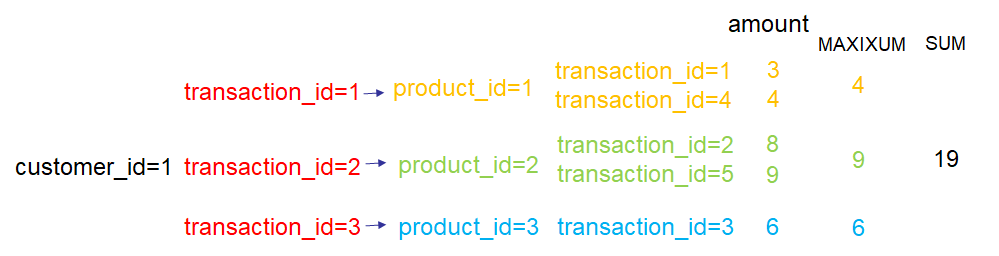
print(feature_defs)以特征SUM(transactions.products.MAXIMUM(transactions.amount))为例,下图说明了对customer_id=1的顾客该特征是如何计算的:
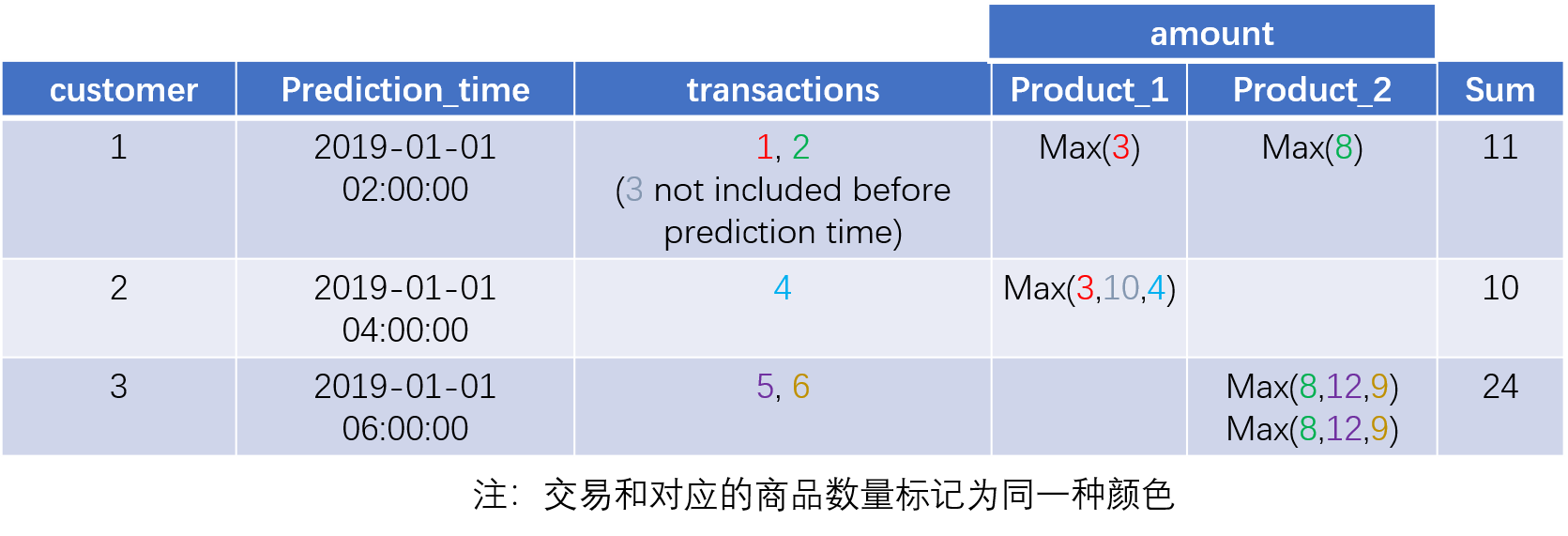
Featuretools的一个重要特性是可以在建立特征工程时自动考虑时间的影响,防止数据泄露。下面仍以一个简单的例子进行说明,同上仍为顾客交易记录,每个交易对应一个顾客和一个商品,但是需要求解的问题是关于顾客在某个时间点的情况。
- 建立数据
import featuretools as ft
import pandas as pd
### 构建交易数据表
transactions = pd.DataFrame({'transaction_id':[1,2,3,4,5,6], 'customer_id':[1,1,1,2,3,3], 'product_id':[1,2,1,1,2,2], \
'time':[pd.Timestamp('1/1/2019')+pd.Timedelta(x,'h') for x in [1,2,3,4,5,6]], \
'amount':[3., 8., 10., 4., 12., 9]}) #加入了交易时间
products = pd.DataFrame({'product_id':[1,2]})
### 对每个顾客,定义对应的预测时间
cutoff_times = pd.DataFrame({'customer_id':[1,2,3],'time':[pd.Timestamp('1/1/2019')+pd.Timedelta(x,'h') for x in [2,4,6]]})
### 从原始数据表中生成新的数据表并建立关系
es = ft.EntitySet('example')
es.entity_from_dataframe(dataframe=transactions, entity_id='transactions', index='transaction_id', time_index='time')
es.normalize_entity(base_entity_id='transactions', new_entity_id='customers',index='customer_id')
es.normalize_entity(base_entity_id='transactions', new_entity_id='products',index='product_id')
print(es)

- 生成新的特征
feature_matrix, feature_defs = ft.dfs(entityset=es, target_entity="customers", agg_primitives=["max","sum"], \
max_depth=3, cutoff_time=cutoff_times) #添加了cutoff_time这一参数
print(feature_defs)下图以特征SUM(transactions.products.MAX(transactions.amount))为例,说明建立特征时如何考虑了时间的影响
自动化特征工程—Featuretools的更多相关文章
- Auto-ML之自动化特征工程
1. 引言 个人以为,机器学习是朝着更高的易用性.更低的技术门槛.更敏捷的开发成本的方向去发展,且Auto-ML或者Auto-DL的发展无疑是最好的证明.因此花费一些时间学习了解了Auto-ML领域的 ...
- 如何用Python做自动化特征工程
机器学习的模型训练越来越自动化,但特征工程还是一个漫长的手动过程,依赖于专业的领域知识,直觉和数据处理.而特征选取恰恰是机器学习重要的先期步骤,虽然不如模型训练那样能产生直接可用的结果.本文作者将使用 ...
- 2022年Python顶级自动化特征工程框架⛵
作者:韩信子@ShowMeAI 机器学习实战系列:https://www.showmeai.tech/tutorials/41 本文地址:https://www.showmeai.tech/artic ...
- python 机器学习库 —— featuretools(自动特征工程)
文档:https://docs.featuretools.com/#minute-quick-start 所谓自动特征工程,即是将人工特征工程的过程自动化.以 featuretools 为代表的自动特 ...
- 手把手教你用Python实现自动特征工程
任何参与过机器学习比赛的人,都能深深体会特征工程在构建机器学习模型中的重要性,它决定了你在比赛排行榜中的位置. 特征工程具有强大的潜力,但是手动操作是个缓慢且艰巨的过程.Prateek Joshi,是 ...
- Python机器学习笔记 使用sklearn做特征工程和数据挖掘
特征处理是特征工程的核心部分,特征工程是数据分析中最耗时间和精力的一部分工作,它不像算法和模型那样式确定的步骤,更多的是工程上的经验和权衡,因此没有统一的方法,但是sklearn提供了较为完整的特征处 ...
- 谷歌大规模机器学习:模型训练、特征工程和算法选择 (32PPT下载)
本文转自:http://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/Xe3g2OSkE3BpIC2wdt5J-A 谷歌大规模机器学习:模型训练.特征工程和算法选择 (32PPT下载) 2017-01-26 ...
- 想搞机器学习,不会特征工程?你TM逗我那!
原文:http://dataunion.org/20276.html 作者:JasonDing1354 引言 在之前学习机器学习技术中,很少关注特征工程(Feature Engineering),然而 ...
- 使用sklearn做单机特征工程
目录 1 特征工程是什么?2 数据预处理 2.1 无量纲化 2.1.1 标准化 2.1.2 区间缩放法 2.1.3 标准化与归一化的区别 2.2 对定量特征二值化 2.3 对定性特征哑编码 2.4 缺 ...
随机推荐
- Python Ethical Hacking - BACKDOORS(4)
REVERSE_BACKDOOR - cd command Access file system: cd command changes current working directory. It h ...
- View Animation 运行原理解析
Android 平台目前提供了两大类动画,在 Android 3.0 之前,一大类是 View Animation,包括 Tween animation(补间动画),Frame animation(帧 ...
- git的几个常用基本操作
需求一:如何把stage中的修改还原到work dir中 这个需求很常见,也很重要,比如我先将当前work dir中的修改添加到stage中,然后又对work dir中的文件进行了修改,但是又后悔了, ...
- UVa 548 Tree(中序遍历+后序遍历)
给一棵点带权(权值各不相同,都是小于10000的正整数)的二叉树的中序和后序遍历,找一个叶子使得它到根的路径上的权和最小.如果有多解,该叶子本身的权应尽量小.输入中每两行表示一棵树,其中第一行为中序遍 ...
- Electron-vue 项目搭建
Electron 应用技术体系推荐 目录结构 demo(项目名称) ├─ .electron-vue(webpack配置文件) │ └─ build.js(生产环境构建代码) | └─ dev-cl ...
- 【mysql】- 锁篇(上)
回顾 问题 事务并发执行时可能带来各种问题,并发事务访问相同记录的情况大致可以划分为3种 读-读情况:即并发事务相继读取相同的记录 读取操作本身不会对记录有什么影响,并不会引起什么问题,所以允许这种情 ...
- 性能测试必备知识(5)- 深入理解“CPU 上下文切换”
做性能测试的必备知识系列,可以看下面链接的文章哦 https://www.cnblogs.com/poloyy/category/1806772.html 前言 上一篇文章中,举例了大量进程等待 CP ...
- Jarvisoj-web phpinfo
题目入口:http://web.jarvisoj.com:32784/ 一进来就看到源码 简单分析之后知道考点是反序列化,注意到了关键字session_start(),这个函数是用于创建会话.但具体如 ...
- 前端学习(一):Html
进击のpython ***** 前端学习--HTML HTML全称HyperText Mackeup Language,超文本标记语言 网页的超链接,图片,音频,视频都可以超文本 标记就相当于你在本子 ...
- 没想到 Hash 冲突还能这么玩,你的服务中招了吗?
背景 其实这个问题我之前也看到过,刚好在前几天,洪教授在某个群里分享的一个<一些有意思的攻击手段.pdf>,我觉得这个话题还是有不少人不清楚的,今天我就准备来“实战”一把,还请各位看官轻拍 ...
