HBase源码学习系列
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/cenyuhai/tag/hbase%E6%BA%90%E7%A0%81%E7%B3%BB%E5%88%97/ (mark)
hbase源码系列(十)HLog与日志恢复
HLog概述
hbase在写入数据之前会先写入MemStore,成功了再写入HLog,当MemStore的数据丢失的时候,还可以用HLog的数据来进行恢复,下面先看看HLog的图。
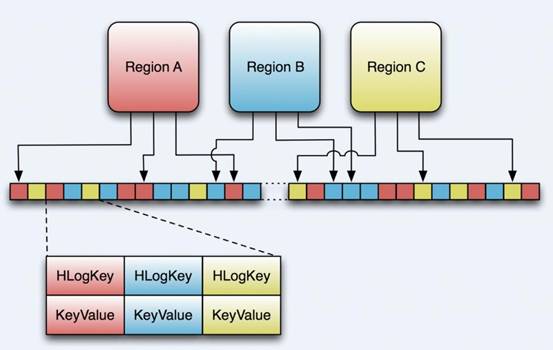
旧版的HLog是实际上是一个SequceneFile,0.96的已经使用Protobuf来进行序列化了。从Writer和Reader上来看HLog的都是Entry的,换句话说就是,它的每一条记录就是一个Entry。
class Entry implements Writable {
private WALEdit edit;
private HLogKey key;
}
所以上面那个图已经不准确了,HLogKey没变,但是Value缺不是KeyValue,而是WALEdit。
下面我们看看HLogKey的五要素,region、tableName、log的顺序、写入时间戳、集群id。

public HLogKey(final byte [] encodedRegionName, final TableName tablename,
long logSeqNum, final long now, List<UUID> clusterIds){
init(encodedRegionName, tablename, logSeqNum, now, clusterIds);
} protected void init(final byte [] encodedRegionName, final TableName tablename,
long logSeqNum, final long now, List<UUID> clusterIds) {
this.logSeqNum = logSeqNum;
this.writeTime = now;
this.clusterIds = clusterIds;
this.encodedRegionName = encodedRegionName;
this.tablename = tablename;
}

下面看看WALEdit的属性, 这里只列出来一个重要的,它是内部持有的一群KeyValue。。
public class WALEdit implements Writable, HeapSize {
......private final ArrayList<KeyValue> kvs = new ArrayList<KeyValue>();
HLog的具体实现类是FSHLog,一个Region Server有两个FSHLog,一个负责RS上面所有的用户region的日志,一个负责RS上面的META表的region的日志。
对于日志来说,我们关心的是它如何保证一致性和准确性,在需要它的时候可以发挥救命作用。
HLog同步
对于meta region的HLog写入之后,它会立即同步到硬盘,非meta表的region,它会先把Entry添加到一个队列里面等待同步。

while(!this.isInterrupted() && !closeLogSyncer.get()) {
try {
if (unflushedEntries.get() <= syncedTillHere) {
synchronized (closeLogSyncer) {
closeLogSyncer.wait(this.optionalFlushInterval);
}
}// 同步已经添加的entry
sync();
} catch (IOException e) {
LOG.error("Error while syncing, requesting close of hlog ", e);
requestLogRoll();
Threads.sleep(this.optionalFlushInterval);
}
}

它这里是有一个判断条件的,如果判断条件不成立就立即同步,等待this.optionalFlushInterval时间,默认的同步间隔是1000,它是通过参数hbase.regionserver.optionallogflushinterval设置。unflushedEntries是一个AtomicLong在写入entry的时候递增,syncedTillHere是一个volatile long,同步完成之后也是变大,因为可能被多个线程调用同步操作,所以它是volatile的,从条件上来看,如果没有日志需要同步就等待一秒再进行判断,如果有日志需要同步,也是立马就写入硬盘的,如果发生错误,就是调用requestLogRoll方法,进行回滚,这个回滚比较有意思,它是跑过去flush掉MemStore中的数据,把他们写入硬盘。
下面是回滚的方法。中间我忽略了几步,然后找到LogRoller中的这段代码。
byte [][] regionsToFlush = getWAL().rollWriter(rollLog.get());
if (regionsToFlush != null) {
for (byte [] r: regionsToFlush) scheduleFlush(r);
}
找出来需要flush的region,然后计划flush。

regions = findMemstoresWithEditsEqualOrOlderThan(this.outputfiles.firstKey(),
this.oldestUnflushedSeqNums); static byte[][] findMemstoresWithEditsEqualOrOlderThan(
final long walSeqNum, final Map<byte[], Long> regionsToSeqNums) {
List<byte[]> regions = null;
for (Map.Entry<byte[], Long> e : regionsToSeqNums.entrySet()) {
//逐个对比,找出小于已输出为文件的最小的seq id的region
if (e.getValue().longValue() <= walSeqNum) {
if (regions == null) regions = new ArrayList<byte[]>();
regions.add(e.getKey());
}
}
return regions == null ? null : regions
.toArray(new byte[][] { HConstants.EMPTY_BYTE_ARRAY });
}

逐个对比,找出来未flush MemStore的比输出的文件的HLog流水号还小的region,当它准备flush MemStore之前会调用startCacheFlush方法来把region从oldestUnflushedSeqNums这个map当中去除,添加到已经flush的map当中。
从日志恢复
看过《HMaster启动过程》的童鞋都知道,如果之前有region失败的话,在启动之前会把之前的HLog进行split,把属于该region的为flush过的日志提取出来,然后生成一个新的HLog到recovered.edits目录下,中间的过程控制那块有点儿类似于snapshot的那种,在zk里面建立一个splitWAL节点,在这个节点下面建立任务,不一样的是,snapshot那块是自己处理自己的,这里是别人的闲事它也管,处理完了之后就更新这个任务的状态了,没有snapshot那么复杂的交互过程。
那啥时候会用到这个呢,在region打开的时候,我们从HRegionServer的openRegion方法一路跟踪,中间历经OpenMetaHandler,再到HRegion.openHRegion方法,终于在initializeRegionStores方法里面找到了那么一句话。
// 如果recovered.edits有日志的话,就恢复日志
maxSeqId = Math.max(maxSeqId, replayRecoveredEditsIfAny(
this.fs.getRegionDir(), maxSeqIdInStores, reporter, status));
高潮来了!!!

HLog.Reader reader = null;
try {
//创建reader读取hlog
reader = HLogFactory.createReader(fs, edits, conf);
long currentEditSeqId = -1;
long firstSeqIdInLog = -1;
long skippedEdits = 0;
long editsCount = 0;
long intervalEdits = 0;
HLog.Entry entry;
Store store = null;
boolean reported_once = false; try {//逐个读取
while ((entry = reader.next()) != null) {
HLogKey key = entry.getKey();
WALEdit val = entry.getEdit();
//实例化firstSeqIdInLog
if (firstSeqIdInLog == -1) {
firstSeqIdInLog = key.getLogSeqNum();
}
boolean flush = false;
for (KeyValue kv: val.getKeyValues()) {
// 从WALEdits里面取出kvs
if (kv.matchingFamily(WALEdit.METAFAMILY) ||
!Bytes.equals(key.getEncodedRegionName(),
this.getRegionInfo().getEncodedNameAsBytes())) {//是meta表的kv就有compaction
CompactionDescriptor compaction = WALEdit.getCompaction(kv);
if (compaction != null) {
//完成compaction未完成的事情,校验输入输出文件,完成文件替换等操作
completeCompactionMarker(compaction);
} skippedEdits++;
continue;
}
// 获得kv对应的store
if (store == null || !kv.matchingFamily(store.getFamily().getName())) {
store = this.stores.get(kv.getFamily());
}
if (store == null) {
// 应该不会发生,缺少它对应的列族
skippedEdits++;
continue;
}
// seq id小,呵呵,说明已经被处理过了这个日志
if (key.getLogSeqNum() <= maxSeqIdInStores.get(store.getFamily().getName())) {
skippedEdits++;
continue;
}
currentEditSeqId = key.getLogSeqNum();
// 这个就是我们要处理的日志,添加到MemStore里面就ok了
flush = restoreEdit(store, kv);
editsCount++;
}
//MemStore太大了,需要flush掉
if (flush) internalFlushcache(null, currentEditSeqId, status); }
} catch (IOException ioe) {
// 就是把名字改了,然后在后面加上".时间戳",这个有毛意思?
if (ioe.getCause() instanceof ParseException) {
Path p = HLogUtil.moveAsideBadEditsFile(fs, edits);
msg = "File corruption encountered! " +
"Continuing, but renaming " + edits + " as " + p;
} else {// 不知道是啥错误,抛错误吧,处理不了
throw ioe;
}
}
status.markComplete(msg);
return currentEditSeqId;
} finally {
status.cleanup();
if (reader != null) {
reader.close();
}
}

呵呵,读取recovered.edits下面的日志,符合条件的就加到MemStore里面去,完成之后,就把这些文件删掉。大家也看到了,这里通篇讲到一个logSeqNum,哪里都有它的身影,它实际上是FSHLog当中的一个递增的AtomicLong,每当往FSLog里面写入一条日志的时候,它都会加一,然后MemStore请求flush的时候,会调用FSLog的startCacheFlush方法,获取(logSeqNum+1)回来,然后写入到StoreFile的sequenceid字段,再次拿出来的时候,就遍历这个HStore下面的StoreFile的logSeqNum,取出来最大的跟它比较,小于它的都已经写过了,没必要再写了。
好了,HLog结束了,累死我了,要睡了。
HBase源码学习系列的更多相关文章
- JDK源码学习系列05----LinkedList
JDK源码学习系列05----LinkedList 1.LinkedList简介 LinkedList是基于双向链表实 ...
- JDK源码学习系列04----ArrayList
JDK源码学习系列04----ArrayList 1. ...
- JDK源码学习系列03----StringBuffer+StringBuilder
JDK源码学习系列03----StringBuffer+StringBuilder 由于前面学习了StringBuffer和StringBuilder的父类A ...
- JDK源码学习系列02----AbstractStringBuilder
JDK源码学习系列02----AbstractStringBuilder 因为看StringBuffer 和 StringBuilder 的源码时发现两者都继承了AbstractStringBuil ...
- JDK源码学习系列01----String
JDK源码学习系列01----String 写在最前面: 这是我JDK源码学习系列的第一篇博文,我知道 ...
- 源码学习系列之SpringBoot自动配置(篇一)
源码学习系列之SpringBoot自动配置源码学习(篇一) ok,本博客尝试跟一下Springboot的自动配置源码,做一下笔记记录,自动配置是Springboot的一个很关键的特性,也容易被忽略的属 ...
- 源码学习系列之SpringBoot自动配置(篇二)
源码学习系列之SpringBoot自动配置(篇二)之HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration 源码分析 继上一篇博客源码学习系列之SpringBoot自动配置(篇一)之后,本博客继续 ...
- SpringBoot源码学习系列之SpringMVC自动配置
目录 1.ContentNegotiatingViewResolver 2.静态资源 3.自动注册 Converter, GenericConverter, and Formatter beans. ...
- SpringBoot源码学习系列之异常处理自动配置
SpringBoot源码学习系列之异常处理自动配置 1.源码学习 先给个SpringBoot中的异常例子,假如访问一个错误链接,让其返回404页面 在浏览器访问: 而在其它的客户端软件,比如postm ...
随机推荐
- android-文字的处理-随心
一.计算文字的大小 String timeStr = "00:00"; int textWidth = (int)Layout.getDesiredWidth(timeStr, 0 ...
- es5 - array - push
/** * 参数:arr.push(element1, ..., elementN) * 作用:被添加到数组末尾的元素. * 当调用该方法时,新的 length 属性值将被返回. * 描述:push ...
- ES6 class 基本使用
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8&quo ...
- git gui :Updating the Git index failed. A rescan will be automatically started to res
这个是由于unix系统的换行符和windows的换行符不一致造成的结果.你在安装git的时候,设置了成使用LF,即unix换行符,可是你是在windows下进行文件编辑的,所以会出现上面的警告.其实这 ...
- Oracle url编码与解码
Oracle url编码与解码 CreateTime--2018年3月30日17:26:36 Author:Marydon 一.url编码 实现方式:utl_url.escape() 说明:utl ...
- 推荐算法——非负矩阵分解(NMF)
一.矩阵分解回想 在博文推荐算法--基于矩阵分解的推荐算法中,提到了将用户-商品矩阵进行分解.从而实现对未打分项进行打分. 矩阵分解是指将一个矩阵分解成两个或者多个矩阵的乘积.对于上述的用户-商品矩阵 ...
- ubuntu 命令行下查看网页 w3m
w3m localhost/index.php
- OCR 识别原理
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzA3MDExNzcyNA==&mid=402907292&idx=1&sn=889c4abcf576e24 ...
- tp数据库操作
1.常见的数据库操作//插入记录// $insert=Db::execute("insert into tp_user (username,password) values ('dome', ...
- Mysql 日期时间类型详解
MySQL 中有多种数据类型可以用于日期和时间的表示,不同的版本可能有所差异,表3-2 中列出了MySQL 5.0 中所支持的日期和时间类型. 这些数据类型的主要区别如下: * 如果要用来表示年月日 ...
