课后实践之mybash20155314
课后实践之mybash
实践要求
加分题-mybash的实现
- 使用fork,exec,wait实现mybash
- 写出伪代码,产品代码和测试代码
- 发表知识理解,实现过程和问题解决的博客(包含代码托管链接)
预备知识
关于bash
- Bash (GNU Bourne-Again Shell) 是大多数Linux系统以及Mac OS X默认的shell,它能运行于大多数类Unix风格的操作系统之上,甚至被移植到了Microsoft Windows上的Cygwin系统中,以实现Windows的POSIX虚拟接口。此外,它也被DJGPP项目移植到了MS-DOS上。
- bash的命令语法是Bourne shell命令语法的超集。数量庞大的Bourne shell脚本大多不经修改即可以在bash中执行,只有使用了Bourne的特殊变量或内置命令的脚本才需要修改。 bash的命令语法很多来自Korn shell (ksh) 和 C shell (csh), 例如命令行编辑,命令历史,目录栈,$RANDOM 和 $PPID 变量,以及POSIX的命令置换语法: $(...)。作为一个交互式的shell,按下TAB键即可自动补全已部分输入的程序名、文件名、变量名等等。
操作系统的核心
- 文件:字节序列
- 虚拟内存:字节数组,抽象出外设和主存
- 进程:操作系统对一个正在运行的程序的一种抽象
操作系统的功能
“管家婆”:管理各种硬件资源
“服务生” :提供接口
-->为用户提供shell(写代码)
-->为程序猿提供系统调用
关于进程
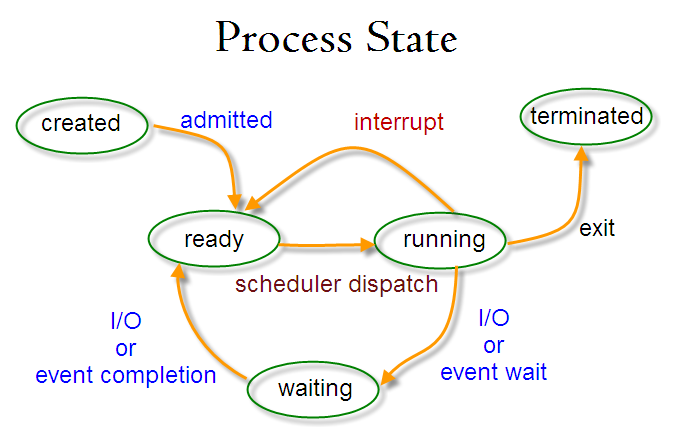
- 进程的状态:
- 创建(created)
- 执行(running)
- 就绪(ready)
- 阻塞(blocked)
- 终止(terminated)
- 进程的状态:
实践过程
准备工作
查询相关命令
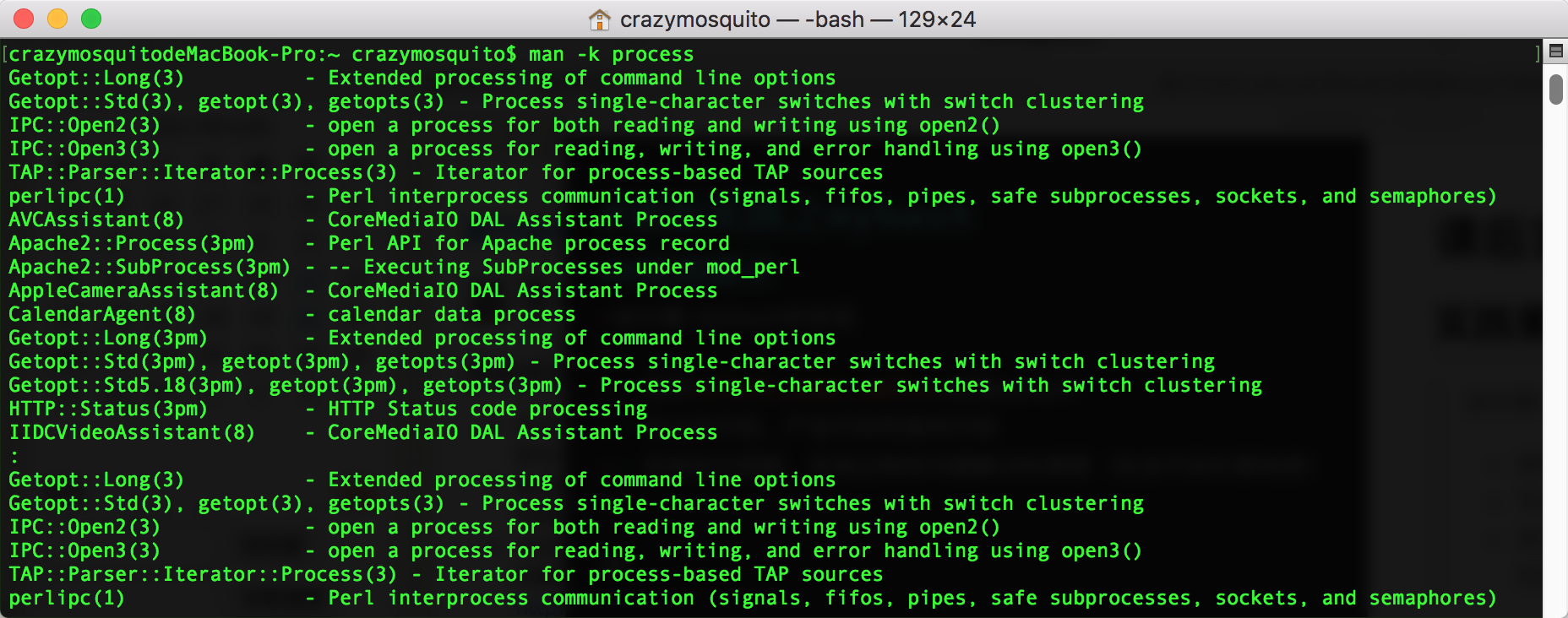
用
man -k process命令查看与进程(process)相关的命令,发现有很多很多:
再用
man -k process | grep 2命令进一步查看与系统调用相关的命令(参数2表示与系统调用有关),找到fork和wait命令:
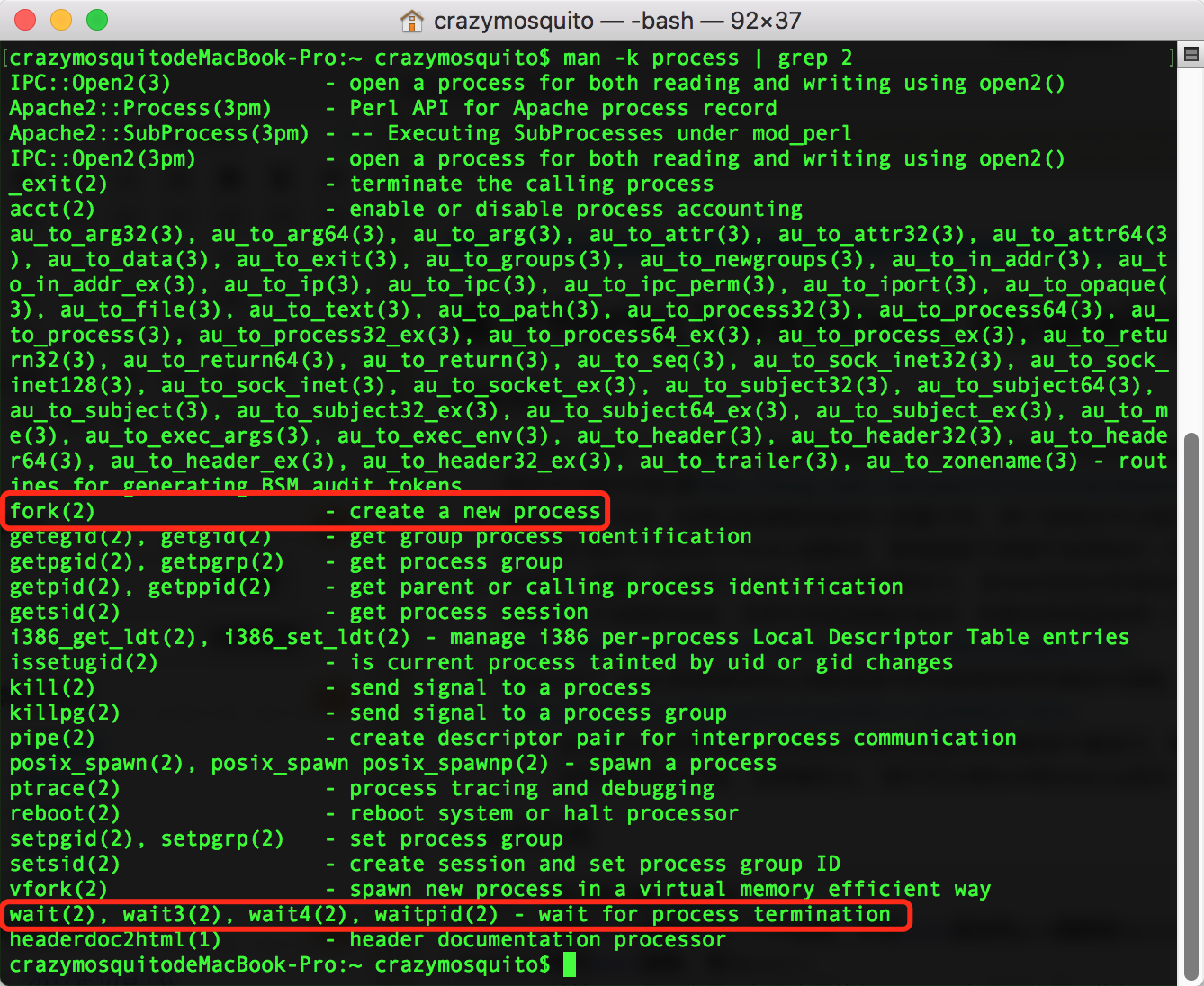
其描述为:fork(2) - create a child process
即fork命令用来创建一个子进程。
wait(2),wait3(2),wait4(2),waitpid(2) - wait for process termination
即wait命令用来等待进程结束。
(后来发现只需查找与创建(create)进程相关的命令
man -k process | grep 2 | grep create就可一步到位,快速找到fork命令:
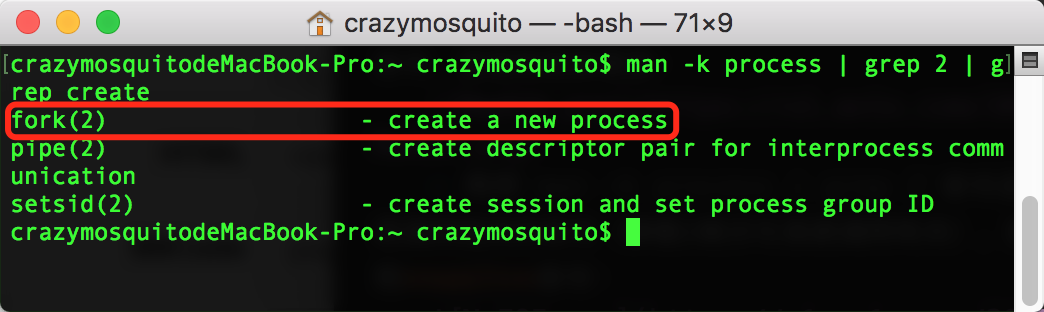 )
)用
man -k execute | grep 2命令找到execve命令:
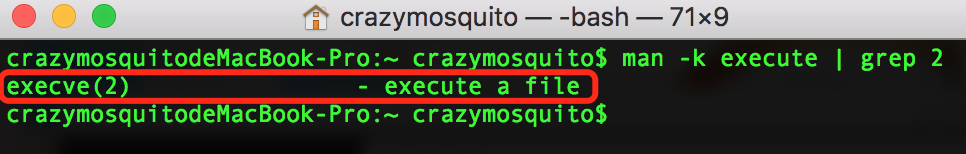
其描述为:execve(2) - execute a file
即execve命令用来执行文件。
模块分析:
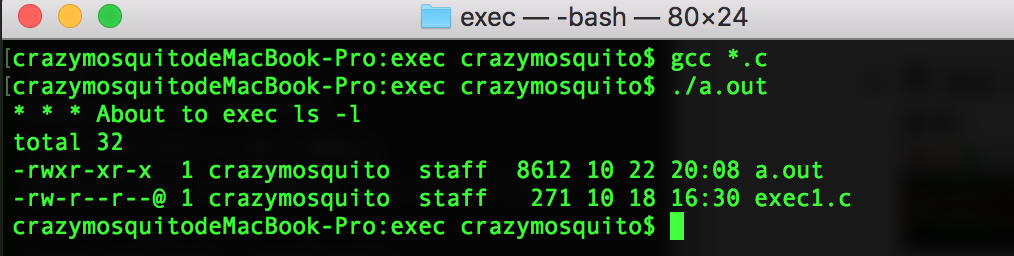
exec1.c:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h> int main() {
char *arglist[3]; arglist[0] = "ls";
arglist[1] = "-l";
arglist[2] = 0;//NULL
printf("* * * About to exec ls -l\n");
execvp("ls", arglist);
printf("* * * ls is done. bye"); return 0;
}
- 功能:
调用execvp()函数,用man命令查看该函数的用法为: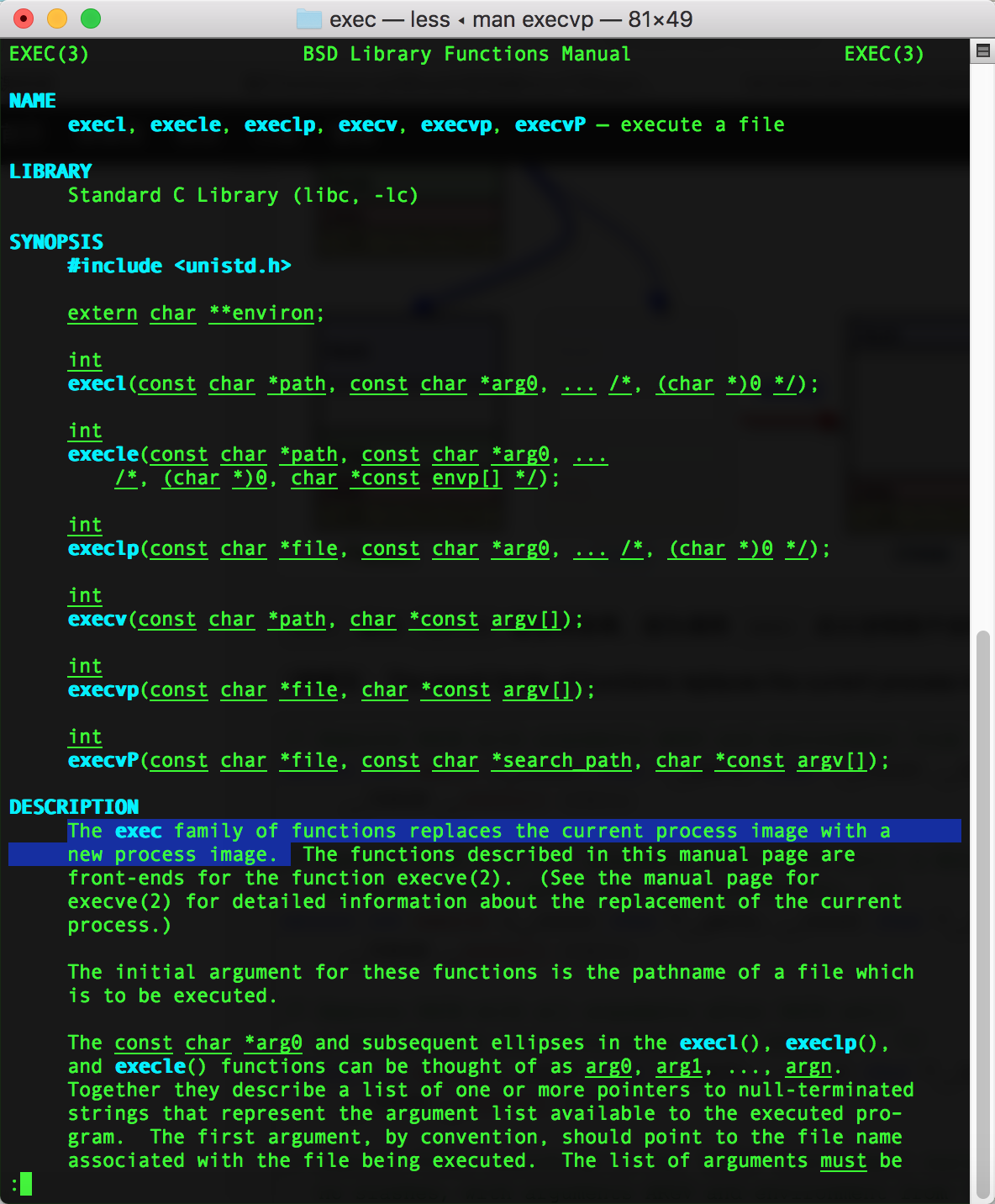
exec函数会将当前的进程替换为一个新的进程,这个新的进程可以由路径或者文件参数指定。 - 运行结果:
- 功能:
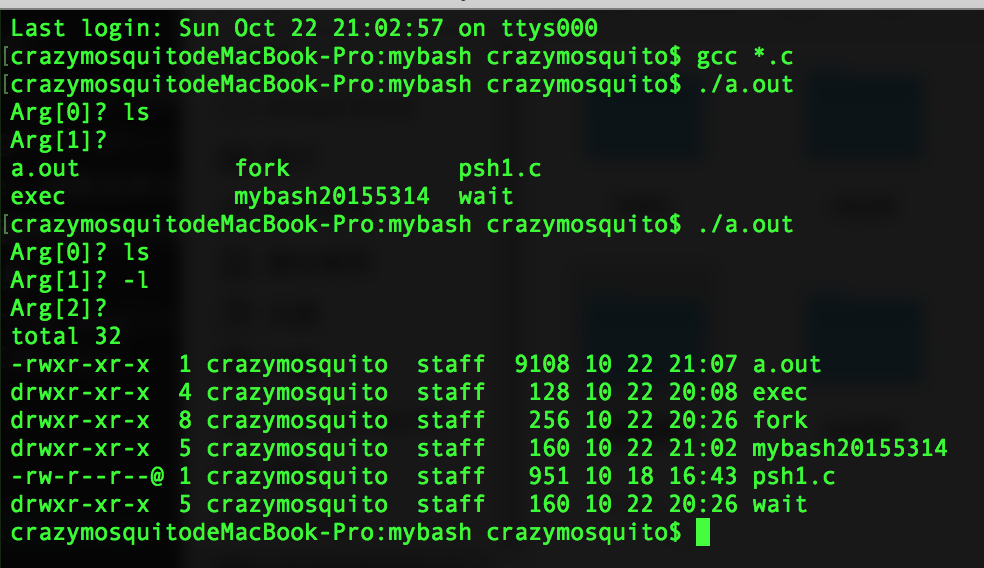
psh1.c:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h> #define MAXARGS 20
#define ARGLEN 100 int execute(char *arglist[]) {
execvp(arglist[0], arglist);
perror("execvp failed");
exit(1);
} char *makestring(char *buf) {
char *cp; buf[strlen(buf) - 1] = '\0';
cp = malloc(strlen(buf) + 1);
if (cp == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "no memory\n");
exit(1);
}
strcpy(cp, buf);
return cp;
} int main() {
char *arglist[MAXARGS + 1];
int numargs;
char argbuf[ARGLEN]; numargs = 0;
while (numargs < MAXARGS) {
printf("Arg[%d]? ", numargs);
if (fgets(argbuf, ARGLEN, stdin) && *argbuf != '\n')
arglist[numargs++] = makestring(argbuf);
else {
if (numargs > 0) {
arglist[numargs] = NULL;
execute(arglist);
numargs = 0;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
- 功能:一次性bash。
- 运行结果:
forkdemo1.c:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h> int main() {
int ret_from_fork, mypid;
mypid = getpid();
printf("Before: my pid is %d\n", mypid);
ret_from_fork = fork();
sleep(1);
printf("After: my pid is %d, fork() said %d\n", getpid(), ret_from_fork); return 0;
}
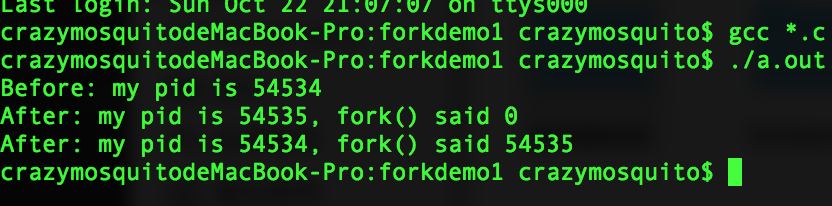
- 功能:即fork的功能,除pid之外复制(duplicate)出一个一模一样的子进程,如同克隆。
- 运行结果:
forkdemo2.c:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h> int main() {
printf("before:my pid is %d\n", getpid());
fork();
fork();
printf("after:my pid is %d\n", getpid()); return 0;
}
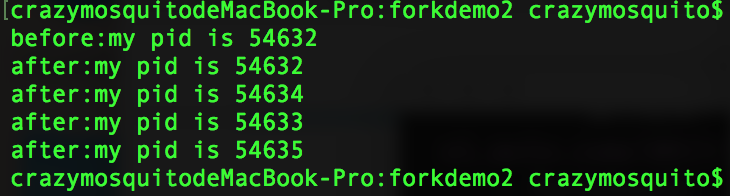
- 功能:调用2次fork会出现4个after,调用n次fork会出现2^n个after。
- 运行结果:
forkdemo3.c:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h> int main() {
int fork_rv; printf("Before: my pid is %d\n", getpid()); fork_rv = fork(); /* create new process */ if (fork_rv == -1) /* check for error */
perror("fork");
else if (fork_rv == 0) {
printf("I am the child. my pid=%d\n", getpid()); exit(0);
} else {
printf("I am the parent. my child is %d\n", fork_rv);
exit(0);
} return 0;
}
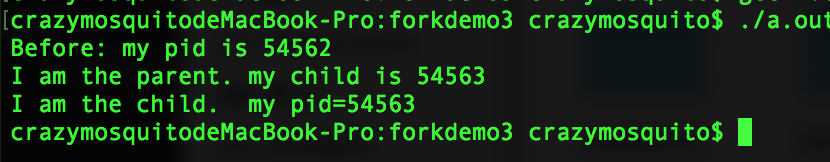
- 功能:通过
fork()的返回值来区分是父进程还是子进程:如果返回一个大于0的数(子进程的Pid)则为父进程;如果返回值为0则为子进程;如果返回值为负值则出错。 - 运行结果:
- 功能:通过
forkgdb.c:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h> int gi = 0; int main() {
int li = 0;
static int si = 0;
int i = 0; pid_t pid = fork();
if (pid == -1) {
exit(-1);
} else if (pid == 0) {
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
printf("child li:%d\n", li++);
sleep(1);
printf("child gi:%d\n", gi++);
printf("child si:%d\n", si++);
}
exit(0); } else {
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
printf("parent li:%d\n", li++);
printf("parent gi:%d\n", gi++);
sleep(1);
printf("parent si:%d\n", si++);
}
exit(0); }
return 0;
}
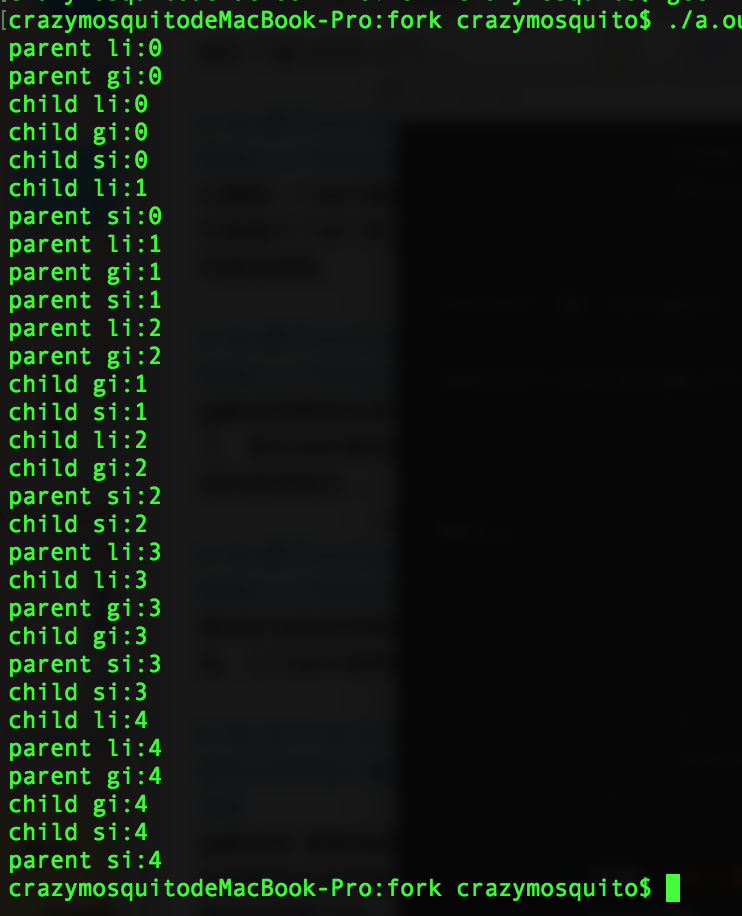
相关函数:
getpid():获得自己的pidgetppid():获得父进程的pidsleep():延迟指定数量的时间(作为函数参数,单位为s)
运行结果:
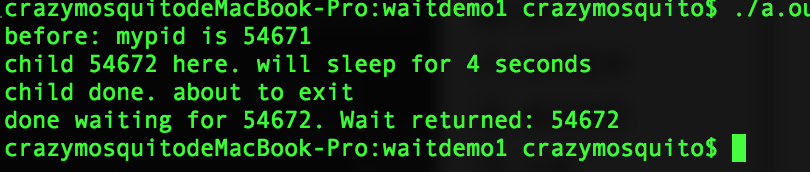
waitdemo1.c:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <unistd.h> #define DELAY 4 void child_code(int delay) {
printf("child %d here. will sleep for %d seconds\n", getpid(), delay);
sleep(delay);
printf("child done. about to exit\n");
exit(17);
} void parent_code(int childpid) {
int wait_rv = 0; /* return value from wait() */
wait_rv = wait(NULL);
printf("done waiting for %d. Wait returned: %d\n",
childpid, wait_rv);
} int main() {
int newpid;
printf("before: mypid is %d\n", getpid());
if ((newpid = fork()) == -1)
perror("fork");
else if (newpid == 0)
child_code(DELAY);
else
parent_code(newpid); return 0;
}
运行结果:
waitdemo2.c:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <unistd.h> #define DELAY 10 void child_code(int delay) {
printf("child %d here. will sleep for %d seconds\n", getpid(), delay);
sleep(delay);
printf("child done. about to exit\n");
exit(27);
} void parent_code(int childpid) {
int wait_rv;
int child_status;
int high_8, low_7, bit_7; wait_rv = wait(&child_status);
printf("done waiting for %d. Wait returned: %d\n", childpid, wait_rv); high_8 = child_status >> 8; /* 1111 1111 0000 0000 */
low_7 = child_status & 0x7F; /* 0000 0000 0111 1111 */
bit_7 = child_status & 0x80; /* 0000 0000 1000 0000 */
printf("status: exit=%d, sig=%d, core=%d\n", high_8, low_7, bit_7);
} int main() {
int newpid; printf("before: mypid is %d\n", getpid()); if ((newpid = fork()) == -1)
perror("fork");
else if (newpid == 0)
child_code(DELAY);
else
parent_code(newpid);
}
- 运行结果:
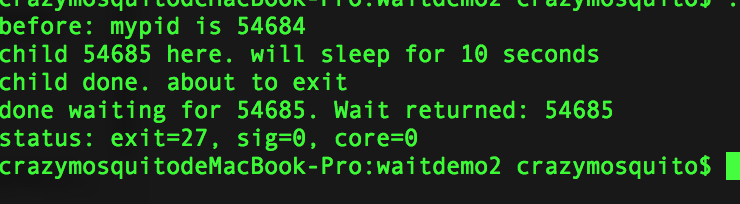
- 运行结果:
伪代码
mybash:for
{
用户输入命令;
fork;
spid:父进程
子进程:exec
}
我的代码
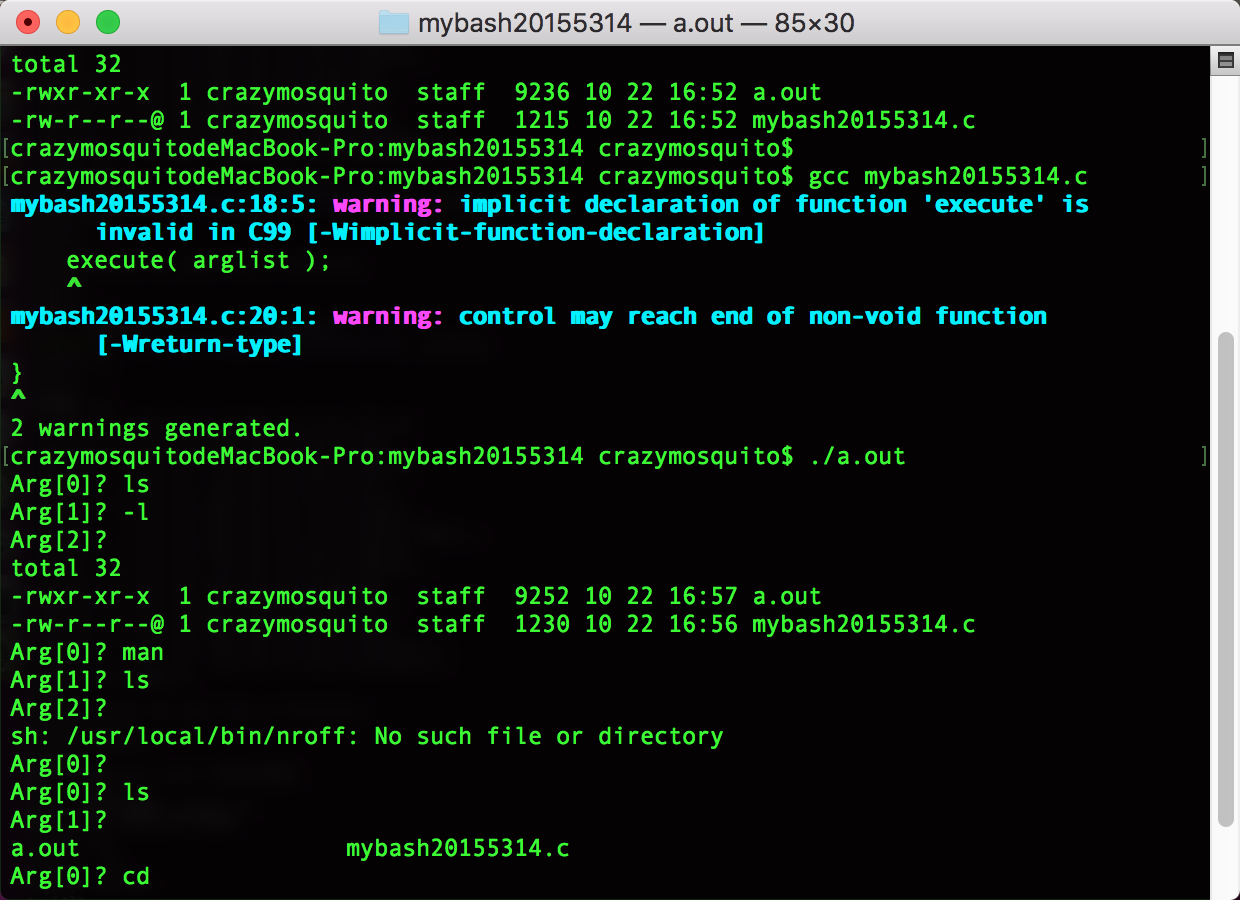
mybash20155314.c:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define MAXARGS 20
#define ARGLEN 100
int mybash20155314(char *arglist[])
{
int pc,pr;
pc=fork();
pr=wait(NULL);
if(pc==0) execute(arglist);
else return 0;
}
int execute(char *arglist[])
{
execvp(arglist[0],arglist);
perror("execvp failed");
exit(1);
}
char *makestring(char *buf)
{
char *cp;
buf[strlen(buf)-1] = '\0';
cp = malloc( strlen(buf)+1 );
if ( cp == NULL ){
fprintf(stderr,"no memory\n");
exit(1);
}
strcpy(cp, buf);
return cp;
}
int main() {
char *arglist[MAXARGS + 1];
int numargs;
char argbuf[ARGLEN];
numargs = 0;
while (numargs < MAXARGS) {
printf("Arg[%d]? ", numargs);
if (fgets(argbuf, ARGLEN, stdin) && *argbuf != '\n')
arglist[numargs++] = makestring(argbuf);
else {
if (numargs > 0) {
arglist[numargs] = NULL;
mybash20155314(arglist);
numargs = 0;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
运行结果
代码调试过程中遇到的问题
macOS High Sierra下终端man命令中文显示问题
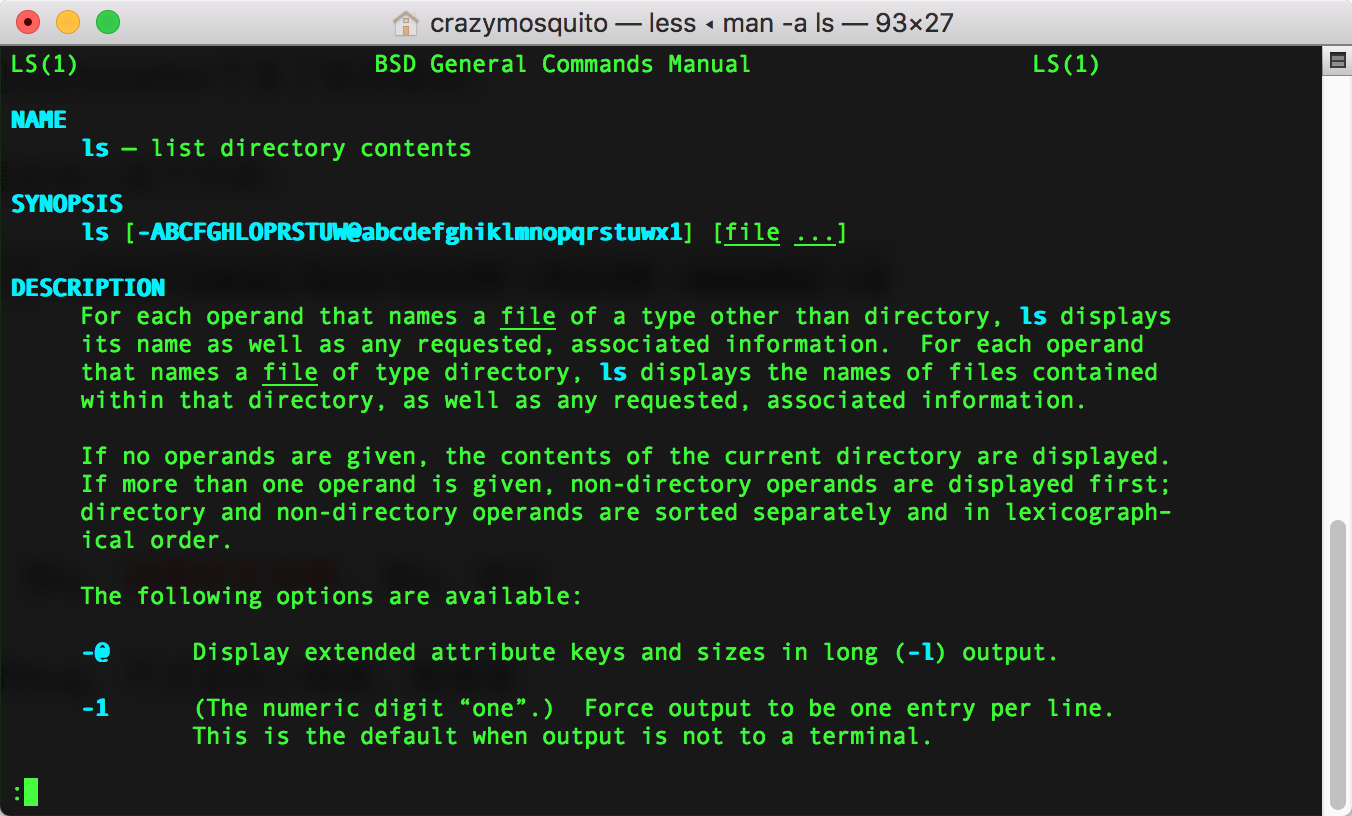
解决方法
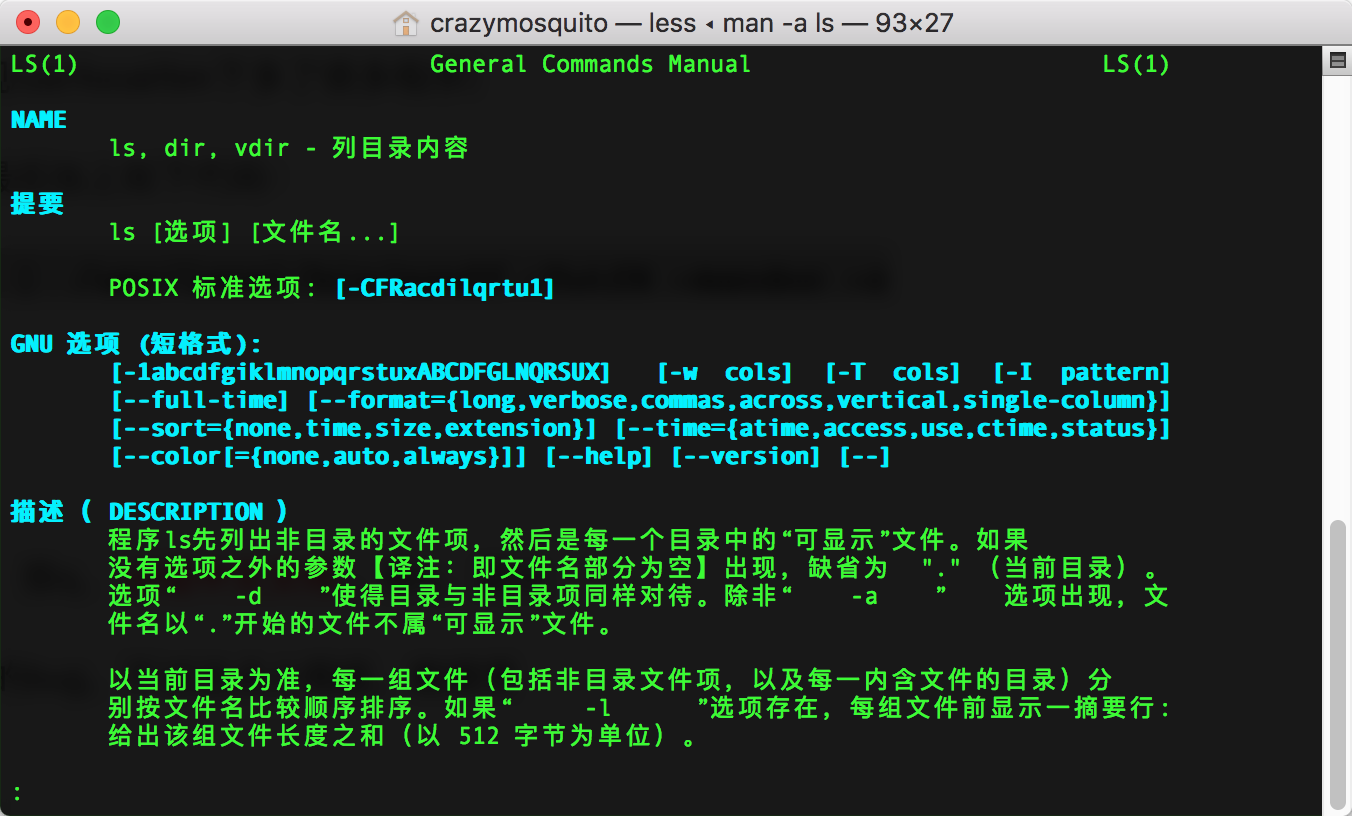
参考资料
- MAC下常用命令的中文帮助文档(man)
- MAC下常用命令的中文帮助文档(man) 出现错误
- 用vi修改文件,保存文件时,提示“readonly option is set”的解决方法
- linux 打造man中文帮助手册图解(man-pages-zh帮助页)
- [Mac入门]如何在Mac下显示Finder中的所有文件
- Linux 进程与信号的概念和操作 linux process and signals
课后实践之mybash20155314的更多相关文章
- 第3周课后实践·程序阅读(4)-利用引用訪问私有数据成员
/* * Copyright (c) 2015, 烟台大学计算机学院 * All rights reserved. * 文件名:test.cpp * 作 者:刘畅 * 完毕日期:2015年 3 月 2 ...
- 小垃圾myl的课后实践
#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> using namespace std; int main(){ ,flag=; printf(&quo ...
- 00java语法基础和课后实践
一:运行代码,并分析结果 代码1: package reserve; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Size ...
- 零基础python入门(1)
1.前景及准备 (1).python是一门简单易学且功能强大的编程语言.它拥有高效的高级数据结构,并且能用简单而又高效的方式进行面向对象的编程.python优雅的语法和动态的类型,再结合它的解释性,使 ...
- 20155216 2016-2017-2《Java程序设计》课程总结
20155216 2016-2017-2<Java程序设计>课程总结 (按顺序)每周作业链接汇总 预备作业1:简要内容:我对师生关系的见解 预备作业2:简要内容:有关C语言学习调查以及学习 ...
- 20155322 2017-2018-1 《信息安全系统设计》第五周 MyBash实现
#20155322 2017-2018-1<信息安全系统设计>第五周 MyBash实现 [博客目录] 实现要求 相关知识 bash fork exec wait 相关问题 fork返回两次 ...
- HTMl+CSS 模仿京东网登录页面
课后实践项目,仅页面效果,写博客纯属记录! 码云开源仓库地址:https://gitee.com/ynavc/jd 演示地址:https://ynavc.gitee.io/jd 效果图: 实现代码: ...
- 《Java 程序设计》课堂实践项目 课后学习总结
<Java 程序设计>课堂实践项目 课后学习总结 String类的使用(sort) 目录 Linux命令(sort) 课堂实践 课后思考 学习老师的代码之后的思考:int与Integer ...
- 《python编程:从入门到实践》课后习题及答案
转载: <Python编程:从入门到实践>课后习题及答案-码农之家 (xz577.com) <Python编程:从入门到实践>课后习题及答案 - 信德维拉 - 博客园 (cnb ...
随机推荐
- mysql 中 max_allowed_packet 查询和修改
mysql 会根据配置文件限制 server 接收的数据包的大小. 有时候大的插入和更新会被 max_allowed_packet 参数限制,报如下错误: Packet > ). You can ...
- Spring系列之——spring security
1 搭建springboot 2 配置pom依赖(springboot版本为2.1.3) <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.b ...
- SpringBoot配置——@PropertySource、@ImportResource、@Bean
@PropertySource:加载指定的配置文件 package com.hoje.springboot.bean; import org.springframework.beans.factory ...
- manven springmvc 项目中 slf4j 的配置使用(结合log4j 或者 logback)
前言:每个maven springmvc 都应该有日志功能,SLF4J(Simple logging facade for Java)就是一种日志规范,它提供了一个共通接口,可以适配多种不同的LOG实 ...
- IDEA 现有项目连接SVN
前言:有时会先搭建好系统,准备好所有配置文件及公共类,然后才会从IDEA中将代码放到SVN中,这里正好讲述了如何从现有代码连接到SVN. 首先将该项目启动SVN管理 然后关联对应SVN地址 右键项目名 ...
- 基于Udp的五子棋对战游戏
引言 本文主要讲述在局域网内,使用c#基于Udp协议编写一个对战的五子棋游戏.主要从Udp的使用.游戏的绘制.对战的逻辑这三个部分来讲解. 开发环境:vs2013,.Net4.0,在文章的末尾提供源代 ...
- Hackerrank GCD Product(莫比乌斯反演)
题意 题目链接 Sol 一道咕咕咕了好长时间的题 题解可以看这里 #include<bits/stdc++.h> #define LL long long using namespace ...
- centos 删除文件和目录
每次都记不住,发个文章记录一下.直接rm就可以了,不过要加两个参数-rf 即:rm -rf 目录名字-r 就是向下递归,不管有多少级目录,一并删除-f 就是直接强行删除,不作任何提示的意思 删除文件夹 ...
- html active属性
源代码 <div class="col-md-3"> <div class="list-group"> <a href=" ...
- 【node】用koa搭建一个增删改服务(一)
前文,vue分类里有一个日志demo的练习,这篇文章就是介绍针对日志demo的服务是怎么写的 一.koa搭建项目 1. npm init 2. npm install koa 二.建数据库 下面是项目 ...
