STL容器-deque-双端队列
注明:全部来自转载,供自己学习与复习使用
deque双向开口可进可出的容器
我们知道连续内存的容器不能随意扩充,因为这样容易扩充别人那去
deque却可以,它创造了内存连续的假象.
其实deque由一段一段构成 ,他是分段连续,而不是内存连续 当走向段的尾端时候自动跳到下一段 所以支持迭代器++ 操作,自动跳到下一段的方法由operator++实现
deque每次扩充 申请一个段
一 定义
头文件 #include <deque>
int main_0() {
//默认构造函数 创建一个空的deque
deque<int> c;
//拷贝构造
deque<int> c1(c);
//赋值拷贝
deque<int> c2 = c1;
//指定元素个数创建
deque<int> c3 (5,6);
for (auto i : c3) {
cout<< i << ",";
}
cout << "deque(个数, 元素)"<<endl;
//指定区间创建
deque<int> c4(c3.begin()+2, c3.begin()+3);
for (auto i : c4) {
cout<< i << ",";
}
cout << "deque(区间, 区间)"<<endl;
//指定初始化列表创建
deque<int> c5({2,3,4,5});
for (auto i : c5) {
cout<< i << ",";
}
cout << "deque({})"<<endl;
//指定初始化列表创建
deque<int> c6 = {2,3,4,5};
for (auto i : c6) {
cout<< i << ",";
}
cout << "deque = {}" <<endl;
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}
二 操作
int main()
{
deque<int> c = {1,2,3,4,5};
deque<int> c1; // 赋值初始化
c1.assign(c.begin(),c.end());
for (auto i: c1) {
cout<< i << ",";
}
cout << "assign()" <<endl; //在尾部插入
c1.push_back(6);
for (auto i: c1) {
cout<< i << ",";
}
cout << "push_back()" <<endl; //头插入
c1.push_front(0);
for (auto i: c1) {
cout<< i << ",";
}
cout << "push_front()" <<endl; //弹尾元素
c1.pop_back();
for (auto i: c1) {
cout<< i << ",";
}
cout << "pop_back()" <<endl; //弹头元素
c1.pop_front();
for (auto i: c1) {
cout<< i << ",";
}
cout << "pop_front()" <<endl; //指定位置插入元素
c1.insert(c1.begin()+3, 10);
for (auto i: c1) {
cout<< i << ",";
}
cout << "insert()" <<endl; //删除指定位置元素
c1.erase(c1.begin()+3);
for (auto i: c1) {
cout<< i << ",";
}
cout << "erase()" <<endl; //清空deque
c.clear();
for (auto i: c) {
cout<< i << ",";
}
cout << "clear()" <<endl; //构造
c1.emplace(c1.end(), 100);
for (auto i: c1) {
cout<< i << ",";
}
cout << "emplace()" <<endl; //头位置插入元素
c1.emplace_front(111);
for (auto i: c1) {
cout<< i << ",";
}
cout << "emplace_front()" <<endl; //尾位置插入元素
c1.emplace_back(111);
for (auto i: c1) {
cout<< i << ",";
}
cout << "emplace_back()" <<endl; //交换
c.swap(c1);
for (auto i: c) {
cout<< i << ",";
}
cout << "swap()" <<endl; int tmp;
tmp = c.front();
cout<<"第一个元素"<< tmp << endl; tmp = c.back();
cout<<"最后一个元素"<< tmp << endl; tmp = c.at(1);
cout<<"指定下标元素"<< tmp << endl; tmp = c[1];
cout<<"指定[]下标元素"<< tmp << endl; return 0;
}
三 内存
int main()
{
deque<int> c = {1,2,3,4,5}; //元素个数
cout<< "size(): " << c.size() <<endl; //重新设定deque大小 少退多补
c.resize(10, 5);
for(auto i : c)
{
cout << i <<",";
}
cout << "resize()" << endl; //最大容量
cout << "max_size(): " << c.max_size() <<endl; //是否为空
cout << "empty: " << c.empty() << endl; //清空内存
c.shrink_to_fit(); return 0;
}
五 与迭代器操作
int main()
{
deque<int> c = {1,2,3,4,5};
//指向第一个元素的迭代器
cout << *c.begin() << endl;
//指向最后一个元素的下一个位置的迭代器
cout << *c.end() << endl;
//反向deque的第一个元素的迭代器
cout << *c.rbegin() << endl;
//反向deque的第一个元素的上一个位置迭代器
cout << *c.rend() << endl;
//指向第一个元素的迭代器
cout << *c.cbegin() << endl;
//指向最后一个元素的下一个位置的迭代器
cout << *c.cend() << endl;
//反向deque的第一个元素的迭代器
cout << *c.crbegin() << endl;
//反向deque的第一个元素的上一个位置迭代器
cout << *c.crend() << endl; return 0;
}
Soource Code
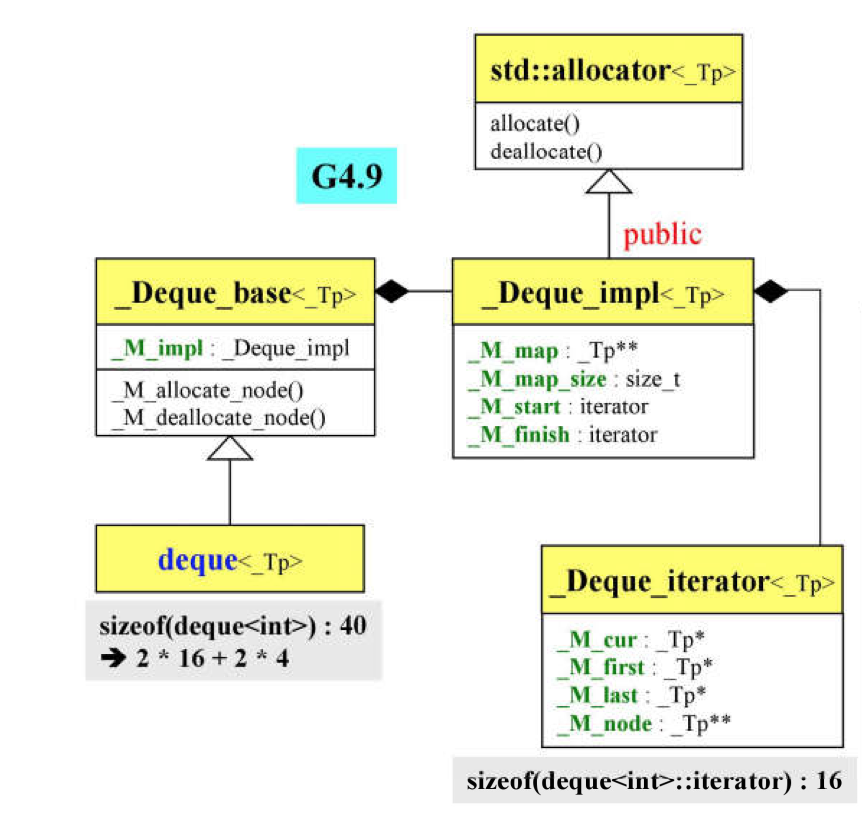
deque的类图如下,跟vector的类图结构相似
_Deque_base<_Tp>基类
template<typename _Tp, typename _Alloc>
class _Deque_base
{
...
struct _Deque_impl
: public _Tp_alloc_type
{
_Tp** _M_map;
size_t _M_map_size;
iterator _M_start;
iterator _M_finish;
}
...
}
_Deque_impl<_Tp>数据类
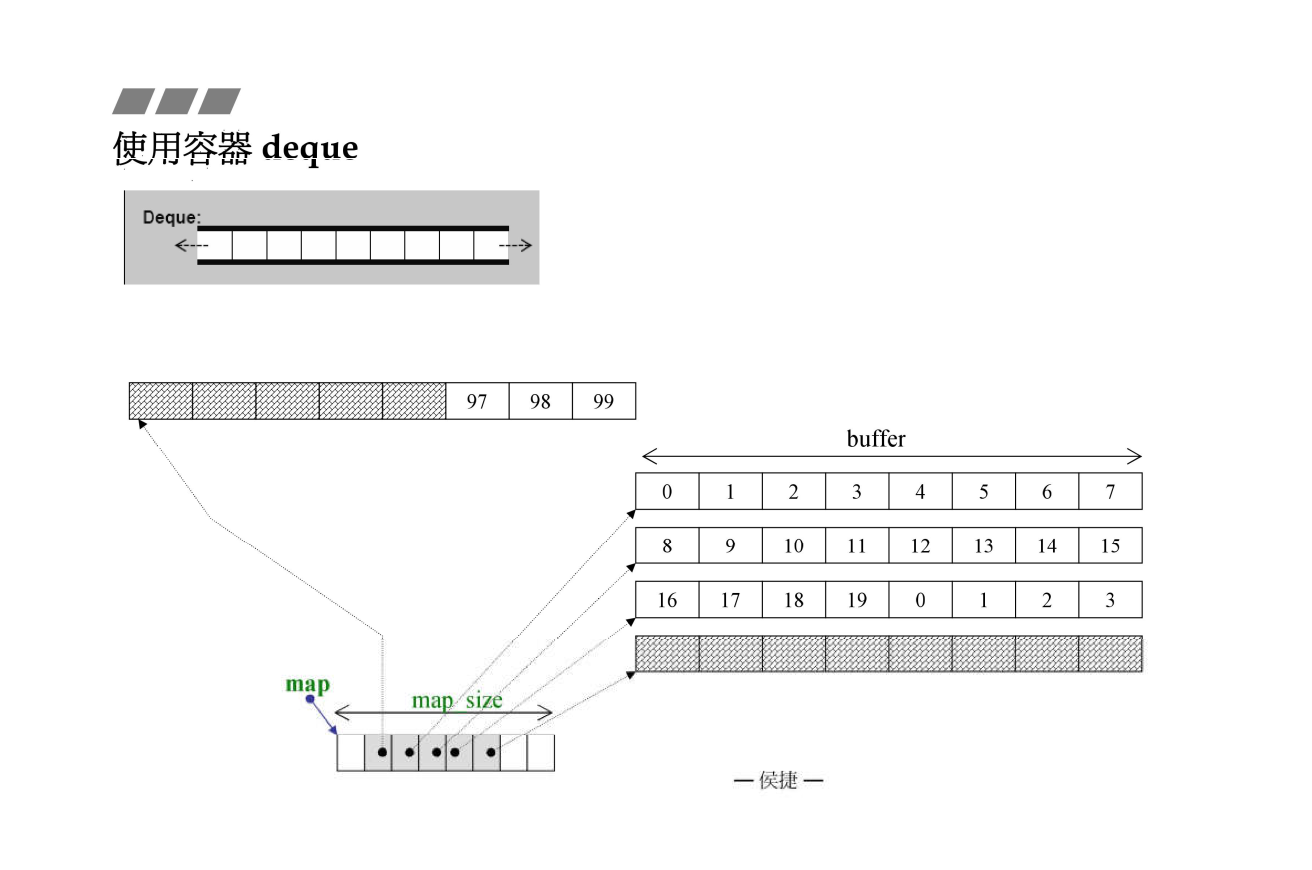
成员变量含义,如下图所示
_M_map指向存储 指向内存的指针 的连续内存
_M_map_size表示_M_map指向的内存大小(有多少个buffer)
_M_start指向_M_map指向内存起始点的迭代器
_M_finish指向_M_map指向内存结束点的迭代器
deque<_Tp>
template<typename _Tp, typename _Alloc = std::allocator<_Tp> >
class deque : protected _Deque_base<_Tp, _Alloc>
{
//成员变量含义与vector成员变量含义相似
public:
typedef _Tp value_type;
typedef typename _Tp_alloc_type::pointer pointer;
typedef typename _Tp_alloc_type::const_pointer const_pointer;
typedef typename _Tp_alloc_type::reference reference;
typedef typename _Tp_alloc_type::const_reference const_reference;
typedef typename _Base::iterator iterator;
typedef typename _Base::const_iterator const_iterator;
typedef std::reverse_iterator<const_iterator> const_reverse_iterator;
typedef std::reverse_iterator<iterator> reverse_iterator;
typedef size_t size_type;
typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type;
typedef _Alloc allocator_type;
...
//这个函数返回buffer大小
static size_t _S_buffer_size() _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
{ return __deque_buf_size(sizeof(_Tp)); }
}
//它的实现如下
#ifndef _GLIBCXX_DEQUE_BUF_SIZE
#define _GLIBCXX_DEQUE_BUF_SIZE 512
#endif
inline size_t
__deque_buf_size(size_t __size)
{ return (__size < _GLIBCXX_DEQUE_BUF_SIZE
? size_t(_GLIBCXX_DEQUE_BUF_SIZE / __size) : size_t(1)); }
/*
如果是deque<int>的话 上面的函数可以翻译成 4 < 512 ? size_t(512/4) " size_t(1)
结果就是512/4 = 128
那么每个buffer所含value_type的个数就128,即一个buffer能存128个int
deque<double> 的话就是512/8 = 64 那么每个buffer的所含个数就是64
如果>=512 就是每个buffer只能存1个 (class/array/struct)
*/
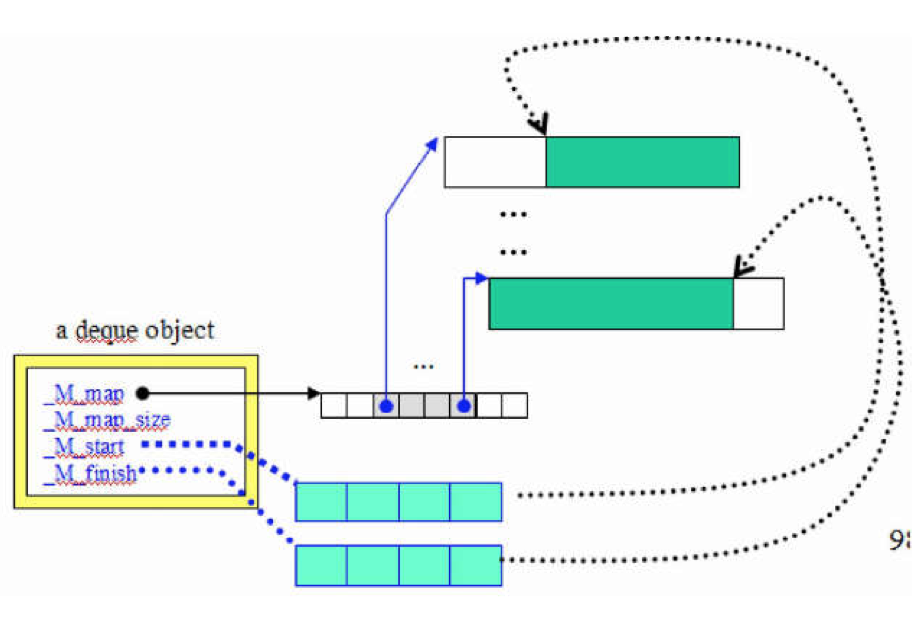
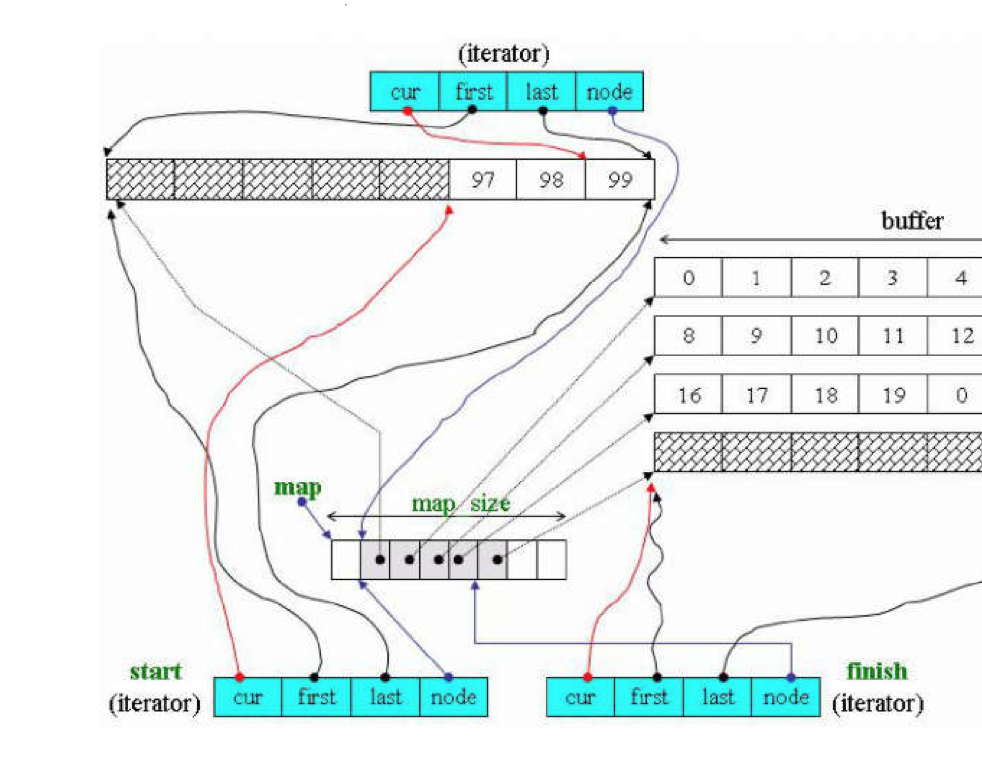
解析一个成员函数insert(),在解析之前介绍一下它的迭代器成员变量的含义
start 指向头的迭代器(_M_start)
finish 指向尾部的下一个位置的迭代器(_M_finish)
cur 指向当前元素
first 指向当前buffer内的第一个元素
last 指向单钱buffer的最后一个元素
node 指向当前buffer的指针
map_size node的个数
insert(const_iterator __position, value_type&& __x)
{ return emplace(__position, std::move(__x)); }
empalce()
template<typename _Tp, typename _Alloc>
template<typename... _Args>
typename deque<_Tp, _Alloc>::iterator
deque<_Tp, _Alloc>::
emplace(const_iterator __position, _Args&&... __args)
{
if (__position._M_cur == this->_M_impl._M_start._M_cur) //插入的位置是否在最前端
{
emplace_front(std::forward<_Args>(__args)...);
return this->_M_impl._M_start;
}
else if (__position._M_cur == this->_M_impl._M_finish._M_cur)//插入的位置在最尾端
{
emplace_back(std::forward<_Args>(__args)...);
iterator __tmp = this->_M_impl._M_finish;
--__tmp;//迭代器指向的是最尾端的下一个位置
return __tmp;
}
else
return _M_insert_aux(__position._M_const_cast(),
std::forward<_Args>(__args)...);
}
emplace_front()
template<typename _Tp, typename _Alloc>
template<typename... _Args>
void
deque<_Tp, _Alloc>::
emplace_front(_Args&&... __args)//插入在最前端
{
if (this->_M_impl._M_start._M_cur != this->_M_impl._M_start._M_first)//如果最前端的buffer内存够的话
{
this->_M_impl.construct(this->_M_impl._M_start._M_cur - 1,
std::forward<_Args>(__args)...);//直接在备用空间上构造元素
--this->_M_impl._M_start._M_cur;//调整cur
}
else //如过内存不够
_M_push_front_aux(std::forward<_Args>(__args)...);
} #if __cplusplus >= 201103L
template<typename... _Args>
void
deque<_Tp, _Alloc>::
_M_push_front_aux(_Args&&... __args)
#else
void
deque<_Tp, _Alloc>::
_M_push_front_aux(const value_type& __t)
#endif
{
_M_reserve_map_at_front();
*(this->_M_impl._M_start._M_node - 1) = this->_M_allocate_node();//申请空的头结点
__try
{
this->_M_impl._M_start._M_set_node(this->_M_impl._M_start._M_node
- 1); //改变start,令其指向新节点
this->_M_impl._M_start._M_cur = this->_M_impl._M_start._M_last - 1; ////改变cur,
#if __cplusplus >= 201103L
this->_M_impl.construct(this->_M_impl._M_start._M_cur,
std::forward<_Args>(__args)...);//复制
#else
this->_M_impl.construct(this->_M_impl._M_start._M_cur, __t);
#endif
}
__catch(...)
{
++this->_M_impl._M_start;
_M_deallocate_node(*(this->_M_impl._M_start._M_node - 1));
__throw_exception_again;
}
}
_M_insert_aux
#if __cplusplus >= 201103L
template<typename... _Args>
typename deque<_Tp, _Alloc>::iterator
deque<_Tp, _Alloc>::
_M_insert_aux(iterator __pos, _Args&&... __args)
{
value_type __x_copy(std::forward<_Args>(__args)...); // XXX copy
#else
typename deque<_Tp, _Alloc>::iterator
deque<_Tp, _Alloc>::
_M_insert_aux(iterator __pos, const value_type& __x)
{
value_type __x_copy = __x; // XXX copy
#endif
difference_type __index = __pos - this->_M_impl._M_start;//重在operator- 返回距起始端距离 安插点之前的元素个数
if (static_cast<size_type>(__index) < size() / 2)//若果插入点在整体内存的前半段,插入后整体内存前移
{
push_front(_GLIBCXX_MOVE(front()));//复制头buffer的一个元素
iterator __front1 = this->_M_impl._M_start;//取出头迭代器位置,和下一个节点的起始点
++__front1;
iterator __front2 = __front1;
++__front2;
__pos = this->_M_impl._M_start + __index;
iterator __pos1 = __pos;
++__pos1;
_GLIBCXX_MOVE3(__front2, __pos1, __front1);//front1 到 front2 这段区间内的前pos1个元素向前移动一个单位 (留出一个单位给将插入的的元素)
}
else
{
push_back(_GLIBCXX_MOVE(back()));
iterator __back1 = this->_M_impl._M_finish;
--__back1;
iterator __back2 = __back1;
--__back2;
__pos = this->_M_impl._M_start + __index;
_GLIBCXX_MOVE_BACKWARD3(__pos, __back2, __back1);
}
*__pos = _GLIBCXX_MOVE(__x_copy); //复制元素
return __pos;
}
既然说deque是模仿内存连续,实现这种功能的主要功臣是deque的迭代器,说道迭代器 那么我们一定会联想到迭代器的操作符重载,下面我主要介绍迭代器的操作符重载
operator* 这个比较好理解 返回cur指向的元素
reference
operator*() const _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
{ return *_M_cur; } pointer
operator->() const _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
{ return _M_cur; }
operator++()(前++)与operator++(int)
_Self&
operator++() _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
{
++_M_cur;
if (_M_cur == _M_last)//如果++到达该节点尾端
{
_M_set_node(_M_node + 1);//跳至下一个节点
_M_cur = _M_first;
}
return *this;
} _Self
operator++(int) _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
{
_Self __tmp = *this;
++*this;//调用前++
return __tmp;
}
operator--()与operator--(int)
_Self&
operator--() _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
{
if (_M_cur == _M_first)//如果--后到达头端
{
_M_set_node(_M_node - 1);//跳至前一个节点
_M_cur = _M_last;
}
--_M_cur;
return *this;
} _Self
operator--(int) _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
{
_Self __tmp = *this;
--*this;
return __tmp;
}
operator+=(itn) ,+,-=,-
_Self&
operator+=(difference_type __n) _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
{
const difference_type __offset = __n + (_M_cur - _M_first);//查找位置
if (__offset >= 0 && __offset < difference_type(_S_buffer_size()))//查找位置是否小于一个buffer的容量(在当前buffer内)
_M_cur += __n;
else
{
const difference_type __node_offset =
__offset > 0 ? __offset / difference_type(_S_buffer_size())
: -difference_type((-__offset - 1)
/ _S_buffer_size()) - 1;
_M_set_node(_M_node + __node_offset);//切换至正确buffer
_M_cur = _M_first + (__offset - __node_offset
* difference_type(_S_buffer_size()));
}
return *this;
}
_Self
operator+(difference_type __n) const _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
{
_Self __tmp = *this;
return __tmp += __n;//调用+=
}
_Self&
operator-=(difference_type __n) _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
{ return *this += -__n; }//调用+=
_Self
operator-(difference_type __n) const _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
{
_Self __tmp = *this;
return __tmp -= __n;
}
operator[],和_M_set_node
reference
operator[](difference_type __n) const _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
{ return *(*this + __n); }
/**
* Prepares to traverse new_node. Sets everything except
* _M_cur, which should therefore be set by the caller
* immediately afterwards, based on _M_first and _M_last.
*/
void
_M_set_node(_Map_pointer __new_node) _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT//切换至正确buffer
{
_M_node = __new_node;
_M_first = *__new_node;
_M_last = _M_first + difference_type(_S_buffer_size());
}
原文出处:
http://www.cnblogs.com/LearningTheLoad/p/7450948.html
STL容器-deque-双端队列的更多相关文章
- stl之deque双端队列容器
deque与vector很相似,不仅能够在尾部插入和删除元素,还能够在头部插入和删除. 只是当考虑到容器元素的内存分配策略和操作性能时.deque相对vector较为有优势. 头文件 #include ...
- STL标准库-容器-deque 双端队列
头文件: #include<deque> 常用操作: https://www.cnblogs.com/LearningTheLoad/p/7450948.html
- deque双端队列容器
//deque双端队列容器 //deque双端队列容器与vector一样,采用线性表顺序存储结构,但与vector不同的是, //deque采用的分块线性存储结构来存储数据,每块的大小一般为512字节 ...
- deque双端队列笔记
clear()clear()clear():清空队列 pushpushpush_back()back()back():从尾部插入一个元素. pushpushpush_front()front()fro ...
- STL容器:deque双端队列学习
所谓deque,是"double-ended queue"的缩写; 它是一种动态数组形式,可以向两端发展,在尾部和头部插入元素非常迅速; 在中间插入元素比较费时,因为需要移动其它元 ...
- Java 集合深入理解(10):Deque 双端队列
点击查看 Java 集合框架深入理解 系列, - ( ゜- ゜)つロ 乾杯~ 什么是 Deque Deque 是 Double ended queue (双端队列) 的缩写,读音和 deck 一样,蛋 ...
- c++ deque 双端队列
双端队列: 函数 描述 c.assign(beg,end)c.assign(n,elem) 将[beg; end)区间中的数据赋值给c.将n个elem的拷贝赋值给c. c.at(idx) 传回索引 ...
- 算法-deque双端队列
Python的deque模块,它是collections库的一部分.deque实现了双端队列,意味着你可以从队列的两端加入和删除元素 1.基本介绍 # 实例化一个deque对象d = deque()d ...
- deque双端队列(常用方法总结)
/*关于C++ STL中deque的学习*/ #include<cstdio> #include<iostream> #include<deque> using n ...
- [STL] deque 双端队列
随机推荐
- Android欢迎页短暂白屏
在style中application theme下添加以下代码: <item name="android:windowIsTranslucent" >true</ ...
- CSIC_716_20191113【装饰器进阶以及迭代器】
装饰器的进阶主要包含叠加装饰器和有参装饰器 叠加装饰器:在一个被装饰的对象中,添加多个装饰器. 为什么要用叠加装饰器的原因: -每一个新的功能都应该写一个新的装饰器,否则会导致,代码冗余,结构不 ...
- mysql 监控及优化——转载自http://www.cnblogs.com/suansuan/
1.Mysql连接数 Mysql默认最大连接数为100. 设置Mysql的最大连接数,在Mysql的配置文件中增加: max_connections = 1000 #Mysql的最大连接数,默认如 ...
- Java 多线程 - Future
Java中Future的使用场景和解析 https://blog.csdn.net/hongtaolong/article/details/83349705 (细看!!!)
- day11 grep正则匹配
ps aus | trep nginx # 查看所有正在运行的nginx任务 别名路径: alias test_cmd='ls -l' PATH路径: 临时修改: PATH=$PATH:/usr/lo ...
- 牛客多校第四场 J Free 最短路
题意: 求最短路,但是你有k次机会可以把路径中某条边的长度变为0. 题解: 跑k+1次迪杰斯特拉,设想有k+1组dis数组和优先队列,第k组就意味着删去k条边的情况,每次松弛操作,松弛的两点i,j和距 ...
- FHS 文件层次标准
FHS:文件层次标准 操作系统自身运行使用的 /bin: 存放可执行的二进制程序,管理员和普通用户都可以使用 /sbin:管理员才能执行的命令 运行正常功能的程序存放位置 /usr/bin /usr/ ...
- Date、DateFormat、Calendar、System、Math类总结
java.util.Date: 构造方法 public Date() 空参构造,返回当前时间 public Date(long 毫秒值) 指定毫秒值的时间 普通方法 long getTime() 获取 ...
- 面试系列26 如何基于dubbo进行服务治理、服务降级、失败重试以及超时重试
(1)服务治理 1)调用链路自动生成 一个大型的分布式系统,或者说是用现在流行的微服务架构来说吧,分布式系统由大量的服务组成.那么这些服务之间互相是如何调用的?调用链路是啥?说实话,几乎到后面没人搞的 ...
- wpf Rectangle
<Rectagle Width="100" Height="100" Stroke="Black" Fill="Blue&q ...