【SpringMVC】@RequestMapping注解
@RequestMapping注解的源码
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Mapping
public @interface RequestMapping {
String name() default "";
@AliasFor("path")
String[] value() default {};
@AliasFor("value")
String[] path() default {};
RequestMethod[] method() default {};
String[] params() default {};
String[] headers() default {};
String[] consumes() default {};
String[] produces() default {};
}
@RequestMapping注解的功能
@RequestMapping注解的作用就是将请求和处理请求的控制器方法关联起来,建立映射关系。
SpringMVC 接收到指定的请求,就会来找到在映射关系中对应的控制器方法来处理这个请求。
该注解可以标识在类和方法上。
@RequestMapping注解的位置
@RequestMapping标识一个类:设置映射请求的请求路径的初始信息
@RequestMapping标识一个方法:设置映射请求请求路径的具体信息
如果有请求路径的初始信息,则先设置请求路径的初始信息才能设置请求路径的具体信息。
比如,想从index的超链接跳转到welcome页面:
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>首页</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>首页</h1>
<a th:href="@{/testRequestMapping}">访问welcome页面 </a>
</body>
</html>
index的超链接跳转的路径是/testRequestMapping
welcome.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>welcome</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to My Blog</h1>
</body>
</html>
在welcome的控制器的类和方法上都加上RequestMapping注解
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public class RequestMappingController {
@RequestMapping("/testRequestMapping")
public String welcome(){
return "welcome";
}
}
结果就是跳转失败
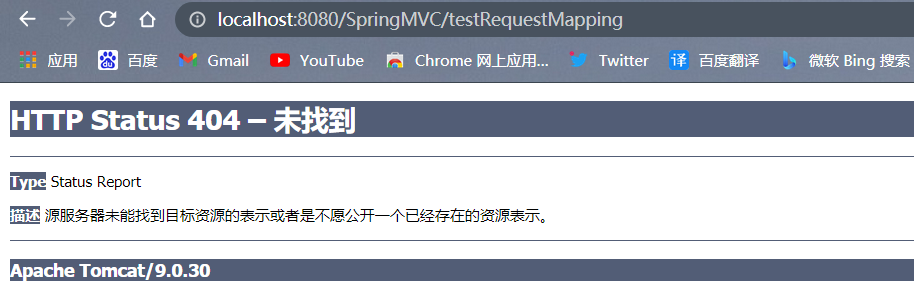
如果修改跳转路径为/hello/testRequestMapping,即可成功
<a th:href="@{/hello/testRequestMapping}">访问welcome页面 </a>
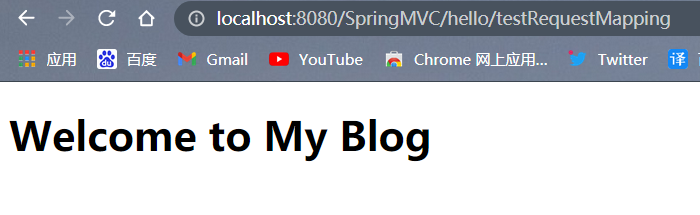
@RequestMapping注解的value属性
@RequestMapping注解的value属性通过请求的请求地址匹配请求映射
@RequestMapping注解的value属性是一个字符串类型的数组,表示该请求映射能够匹配多个请求地址所对应的请求
@RequestMapping注解的value属性必须设置,至少通过请求地址匹配请求映射
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>首页</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>首页</h1>
<a th:href="@{/testRequestMapping}">通过/testRequestMapping访问welcome页面 </a>
<br>
<a th:href="@{/test}">通过/test访问welcome页面 </a>
</body>
</html>
@Controller
public class RequestMappingController {
@RequestMapping(value = {"/testRequestMapping","/test"})
public String welcome(){
return "welcome";
}
}
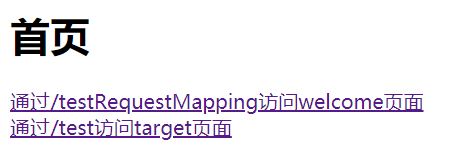
两个超连接都可访问成功
@RequestMapping注解的method属性
@RequestMapping注解的method属性通过请求的请求方式(get或post)匹配请求映射
@RequestMapping注解的method属性是一个RequestMethod类型的数组,表示该请求映射能够匹配多种请求方式的请求
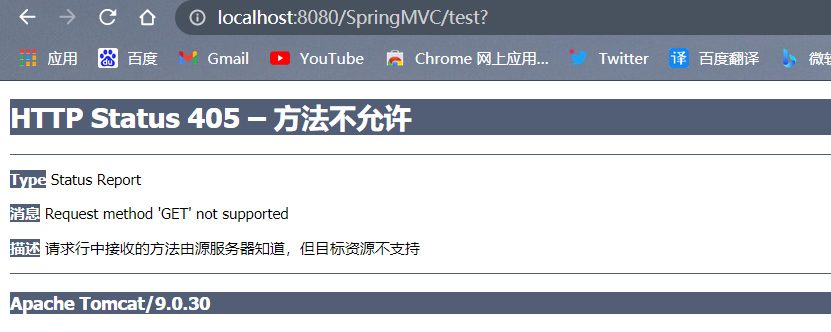
若当前请求的请求地址满足请求映射的value属性,但是请求方式不满足method属性,则浏览器报错405:Request method 'POST' not supported
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>首页</title>
</head>
<body>
<form th:action="@{/test}" method="post">
<input type="submit" value="以post方式提交">
</form>
<br>
<form th:action="@{/test}" method="get">
<input type="submit" value="以get方式提交">
</form>
</body>
</html>
welcome.html的控制器
@RequestMapping(value = "/test",
method = {RequestMethod.GET})
public String welcome(){
return "welcome";
}
如果不设置控制器的method,则index的post和get两种方式都可以访问welcome.html
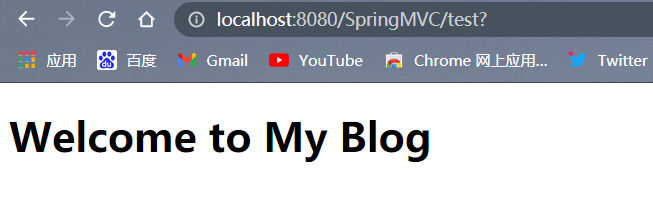
如果设置控制器的method为RequestMethod.GET,则只能用get方式访问
以post方式访问:
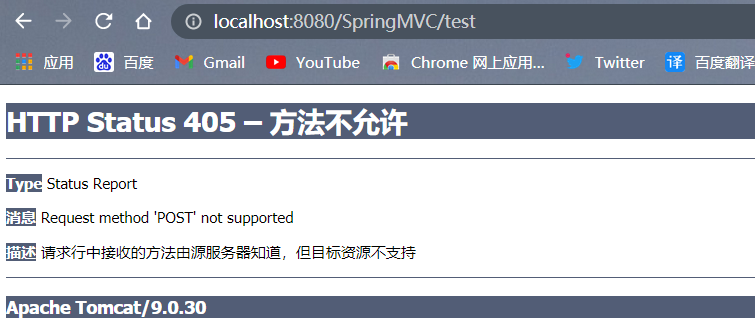
以get方式访问:
对于处理指定请求方式的控制器方法,SpringMVC中提供了@RequestMapping的派生注解
处理get请求的映射-->@GetMapping
处理post请求的映射-->@PostMapping
处理put请求的映射-->@PutMapping
处理delete请求的映射-->@DeleteMapping
免去了设置method的麻烦,只写映射路径即可
@GetMapping("/test")
public String welcome(){
return "welcome";
}
常用的请求方式有get,post,put,delete
但是目前浏览器只支持get和post,若在form表单提交时,为method设置了其他请求方式的字符串(put或delete),则按照默认的请求方式get处理
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>首页</title>
</head>
<body>
<form th:action="@{/test}" method="put">
<input type="submit" value="以put方式提交">
</form>
<br>
</body>
</html>
@PostMapping("/test")
public String welcome(){
return "welcome";
}
@RequestMapping注解的params属性
@RequestMapping注解的params属性通过请求的请求参数匹配请求映射
@RequestMapping注解的params属性是一个字符串类型的数组,可以通过四种表达式设置请求参数和请求映射的匹配关系
"param":要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须携带param请求参数
"!param":要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须不能携带param请求参数
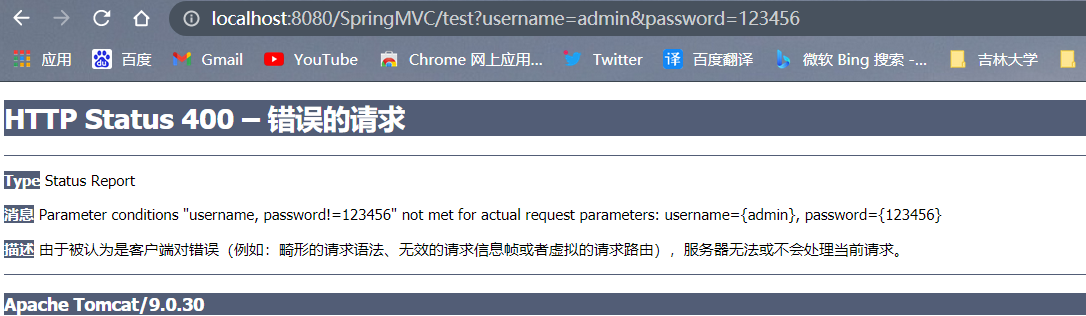
"param=value":要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须携带param请求参数且param=value
"param!=value":要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须携带param请求参数但是param!=value
<a th:href="@{/test(username='admin',password=123456)}">测试@RequestMapping的params属性-->/test</a><br>
@RequestMapping(
value = {"/testRequestMapping", "/test"}
,method = {RequestMethod.GET, RequestMethod.POST}
,params = {"username","password!=123456"}
)
public String testRequestMapping(){
return "welcome";
}
@RequestMapping注解的headers属性
@RequestMapping注解的headers属性通过请求的请求头信息匹配请求映射
@RequestMapping注解的headers属性是一个字符串类型的数组,可以通过四种表达式设置请求头信息和请求映射的匹配关系
"header":要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须携带header请求头信息
"!header":要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须不能携带header请求头信息
"header=value":要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须携带header请求头信息且header=value
"header!=value":要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须携带header请求头信息且header!=value
若当前请求满足@RequestMapping注解的value和method属性,但是不满足headers属性,此时页面显示404错误,即资源未找到
SpringMVC路径的模糊匹配
?:表示任意的单个字符
@RequestMapping(value = "/a?a/test")
public String welcome(){
return "welcome";
}
*:表示任意的0个或多个字符
@RequestMapping(value = "/a*a/test")
public String welcome(){
return "welcome";
}
/**:表示任意的一层或多层目录
@RequestMapping(value = "/**/test")
public String welcome(){
return "welcome";
}
- 注意:
在使用
/**时,只能使用/**/xxx的方式?和*不可以用。/?来占位
SpringMVC支持路径中的占位符(重点)
原始方式:/deleteUser?id=1
rest方式:/deleteUser/1
SpringMVC路径中的占位符常用于RESTful风格中,当请求路径中将某些数据通过路径的方式传输到服务器中,就可以在相应的@RequestMapping注解的value属性中通过占位符{xxx}表示传输的数据,在通过@PathVariable注解,将占位符所表示的数据赋值给控制器方法的形参
<a th:href="@{/testRest/1/admin}">测试路径中的占位符-->/testRest</a><br>
@RequestMapping("/testRest/{id}/{username}")
public String testRest(@PathVariable("id") String id, @PathVariable("username") String username){
System.out.println("id:"+id+",username:"+username);
return "success";
}
//最终输出的内容为-->id:1,username:admin
【SpringMVC】@RequestMapping注解的更多相关文章
- SpringMVC RequestMapping注解
1.@RequestMapping 除了修饰方法,还可以修饰类 2.类定义处:提供初步的请求映射信息.相对于WEB应用的根目录 方法处:提供进一步细分映射信息 相对于类定义处的URL.若类定义处未 ...
- SpringMVC @RequestMapping注解详解
@RequestMapping 参数说明 value:定义处理方法的请求的 URL 地址.(重点) method:定义处理方法的 http method 类型,如 GET.POST 等.(重点) pa ...
- 超详细 SpringMVC @RequestMapping 注解使用技巧
@RequestMapping 是 Spring Web 应用程序中最常被用到的注解之一.这个注解会将 HTTP 请求映射到 MVC 和 REST 控制器的处理方法上. 在这篇文章中,你将会看到 @R ...
- SpringMVC源码解读 - RequestMapping注解实现解读 - RequestMappingInfo
使用@RequestMapping注解时,配置的信息最后都设置到了RequestMappingInfo中. RequestMappingInfo封装了PatternsRequestCondition, ...
- SpringMVC源码解读 - RequestMapping注解实现解读 - RequestCondition体系
一般我们开发时,使用最多的还是@RequestMapping注解方式. @RequestMapping(value = "/", param = "role=guest& ...
- SpringMVC使用注解@RequestMapping映射请求
pringMVC通过使用@RequestMapping注解,实现指定控制器可以处理哪些URL请求. 控制器的类定义及方法定义处都可以标注@RequestMapping: 类定义处:提供初步的请求映射信 ...
- (转)SpringMVC学习(六)——SpringMVC高级参数绑定与@RequestMapping注解
http://blog.csdn.net/yerenyuan_pku/article/details/72511749 高级参数绑定 现在进入SpringMVC高级参数绑定的学习,本文所有案例代码的编 ...
- SpringMVC详解一、@RequestMapping注解与Controller接收参数
SpringMVC详解一.@RequestMapping注解与Controller接收参数 https://blog.csdn.net/mxcsdn/article/details/80719258 ...
- SpringMVC源码解读 - RequestMapping注解实现解读
SpringMVC源码解读 - RequestMapping注解实现解读 - RequestCondition体系 https://www.cnblogs.com/leftthen/p/520840 ...
随机推荐
- vuejs知识总结
1.Vue.js是当下很火的一个JavaScript MVVM库,它是以数据驱动和组件化的思想构建的.ViewModel是Vue.js的核心,它是一个Vue实例. <!DOCTYPE html& ...
- NIO 输入输出
NIO 是java14 API 提供的一种新输入输出流,一套用于标准IO的文件读写,一套用于网络编程. 1. NIO 与IO 的区别 IO流以字节流输入输出,一次以一个字节进行数据操作,效率慢: NI ...
- C语言:赋值
#include <stdio.h> //=赋值运算符 //具有方向性,只能将赋值号右边的表达式的值给左边的变量 //赋值语句具有计算功能,赋值号右边可以是常量,变量或表达式都可以 //赋 ...
- C语言变量 类型判断
变量三要素: 一个变量有三个基本的要素,变量的名称,变量的类型,变量的值.所以int a = 10; 变量名为a,变量的存储类型为int型,变量的值为10. 变量还有一些属性如作用范围和存储类型. 变 ...
- 两人团队项目-石家庄地铁查询系统(web版)
大二上学期做过只有两号线的地铁查询系统,但是只能在控制台操作.这一次将线路加到了六条,并且要求web实现,下面简述一下设计思路和具体代码实现: 1.数据库建表 于我自己习惯而言,我写javaweb项目 ...
- Collection集合工具类
Ⅷ.Collections 工具类 java.util.Collections Collections 集合工具类,用来对集合进行操作,部分重要方法如下: 1.public static <T& ...
- Spark—编译Spark源码
Spark版本:Spark-2.1.0 Hadoop版本:hadooop-2.6.0-cdh5.7.0 官方文档:http://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/buildin ...
- React构建组件的方式
一.是什么 组件就是把图形.非图形的各种逻辑均抽象为一个统一的概念(组件)来实现开发的模式 在React中,一个类.一个函数都可以视为一个组件 在Vue系列中,我们了解到组件所存在的优势: 降低整个系 ...
- Skywalking-02:如何写一个Skywalking trace插件
如何写一个Skywalking trace插件 javaagent 原理 美团技术团队-Java 动态调试技术原理及实践 类图 实现 ConsumeMessageConcurrentlyInstrum ...
- springmvc学习指南 之---第27篇 spring如何实现servlet3.0无web.xml 配置servlet对象的
writedby 张艳涛 基于web.xml配置,有人说麻烦,tomcat给按照servlet3.0,实现了基于注解@WebServlet,有人说springmvc的springmvc.xml配置麻烦 ...
