Android布局解析,图文(转)
LinearLayout:相当于Java GUI中的FlowLayout(流式布局),就是说一个组件后边跟一个,挨着靠,一个组件把一行占满了,就靠到下一行。
linearlayoutdemo.xml

<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/L1"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".MainActivity"> <TextView
android:id="@+id/tv"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:layout_weight="3"
android:background="#ffffb859"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="@string/ll"
android:textSize="20sp" /> <LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/L21"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:orientation="horizontal"> <TextView
android:id="@+id/tv2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="#ff3fb200" /> <TextView
android:id="@+id/tv3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:layout_weight="2"
android:background="#ff3436b2" /> <TextView
android:id="@+id/tv5"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:layout_weight="3"
android:background="#ff7a75b2" /> <LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/L27"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:layout_weight="6"
android:orientation="vertical"> <LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/L37"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:layout_weight="2"
android:background="#ff44ff16"
android:orientation="horizontal"> </LinearLayout> <LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/L32"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="#ff382aff"
android:gravity="center"
android:orientation="horizontal"> </LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout> </LinearLayout>

效果:
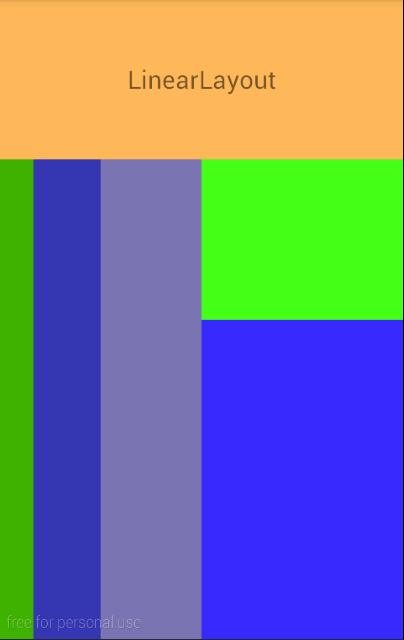
AbsolutelyLayout:绝对布局,相当于Java GUI中的空布局,就是啥也没有。组件的位置需要用坐标来显示。但是在android2.3之后已经弃用了,这种布局不能适应多种屏幕尺寸,局限性太大,但是对于独立开发者,单人单机来讲,用用也无妨。
absolutelayoutdemo.xml

<AbsoluteLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#00ffff"> <Button
android:id="@+id/er"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_x="50dp"
android:layout_y="50dp"
android:background="#ff00ff"
android:text="@string/al" />
</AbsoluteLayout>

效果:

FrameLayout:这种布局是一层叠着一层,游戏类应用常会使用,涉及到NPC的构建视图等。
framelayoutdemo.xml

<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#000000"> <TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/fl"
android:textColor="#ffff2f25"
android:textSize="40sp" /> <TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/fl"
android:textColor="#ff7e66ff"
android:textSize="70sp" /> <TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/fl"
android:textColor="#ff5eff4f"
android:textSize="50sp" />
</FrameLayout>

效果:

RelativeLayout:关系布局,顾名思义,就是靠关系,谁在谁的左边谁在谁的上边,谁前边和谁对其等等。属性这里就不赘述了,需要时查API即可。
relativelayoutdemo.xml

<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"> <TextView
android:id="@+id/t1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:background="#009922"
android:text="@string/rl"
android:textSize="40sp" /> <TextView
android:id="@+id/t2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@+id/t1"
android:background="#ff8800"
android:text="@string/rl"
android:textSize="40sp" />
</RelativeLayout>

效果:

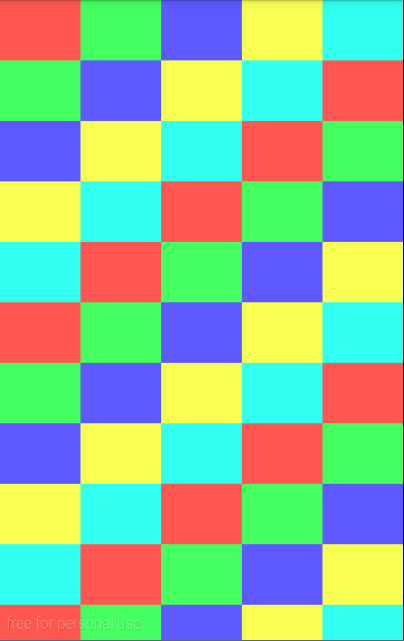
GridLayout:网格布局,自定义N x N,可拓展到屏幕外围,猜想:当某些游戏应用的地图大于手机屏幕时,可以使用此种布局,一张图片太大,可以用多张图片进行拼接,内嵌FrameLayout实现NPC在地图上。
gridlayoutdemo.xml

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<GridLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:columnCount="6"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:rowCount="10">
<Button android:background="#ffff5651" /> <Button android:background="#ff45ff61" /> <Button android:background="#ff5d59ff" /> <Button android:background="#fff9ff52" /> <Button android:background="#ff31fff0" /> <Button android:background="#ffff5651" /> <Button android:background="#ff45ff61" /> <Button android:background="#ff5d59ff" /> <Button android:background="#fff9ff52" /> <Button android:background="#ff31fff0" /> <Button android:background="#ffff5651" /> <Button android:background="#ff45ff61" /> <Button android:background="#ff5d59ff" /> <Button android:background="#fff9ff52" /> <Button android:background="#ff31fff0" /> <Button android:background="#ffff5651" /> <Button android:background="#ff45ff61" /> <Button android:background="#ff5d59ff" /> <Button android:background="#fff9ff52" /> <Button android:background="#ff31fff0" /> <Button android:background="#ffff5651" /> <Button android:background="#ff45ff61" /> <Button android:background="#ff5d59ff" /> <Button android:background="#fff9ff52" /> <Button android:background="#ff31fff0" /> <Button android:background="#ffff5651" /> <Button android:background="#ff45ff61" /> <Button android:background="#ff5d59ff" /> <Button android:background="#fff9ff52" /> <Button android:background="#ff31fff0" /> <Button android:background="#ffff5651" /> <Button android:background="#ff45ff61" /> <Button android:background="#ff5d59ff" /> <Button android:background="#fff9ff52" /> <Button android:background="#ff31fff0" /> <Button android:background="#ffff5651" /> <Button android:background="#ff45ff61" /> <Button android:background="#ff5d59ff" /> <Button android:background="#fff9ff52" /> <Button android:background="#ff31fff0" /> <Button android:background="#ffff5651" /> <Button android:background="#ff45ff61" /> <Button android:background="#ff5d59ff" /> <Button android:background="#fff9ff52" /> <Button android:background="#ff31fff0" /> <Button android:background="#ffff5651" /> <Button android:background="#ff45ff61" /> <Button android:background="#ff5d59ff" /> <Button android:background="#fff9ff52" /> <Button android:background="#ff31fff0" /> <Button android:background="#ffff5651" /> <Button android:background="#ff45ff61" /> <Button android:background="#ff5d59ff" /> <Button android:background="#fff9ff52" /> <Button android:background="#ff31fff0" /> <Button android:background="#ffff5651" /> <Button android:background="#ff45ff61" /> <Button android:background="#ff5d59ff" /> <Button android:background="#fff9ff52" /> <Button android:background="#ff31fff0" /> <Button android:background="#ffff5651" /> <Button android:background="#ff45ff61" /> <Button android:background="#ff5d59ff" /> <Button android:background="#fff9ff52" /> <Button android:background="#ff31fff0" /> <Button android:background="#ffff5651" /> <Button android:background="#ff45ff61" /> <Button android:background="#ff5d59ff" /> <Button android:background="#fff9ff52" /> <Button android:background="#ff31fff0" />
</GridLayout>

效果:
Android布局解析,图文(转)的更多相关文章
- Android成长日记-Android布局优化
Android常用布局 1. LinearLayout(线性布局) 2. RelativeLayout(相对布局) 3. TableLayout(表格布局) 4. AbsoluteLayou(绝对布局 ...
- 【转】Android布局优化之ViewStub
ViewStub是Android布局优化中一个很不错的标签/控件,直接继承自View.虽然Android开发人员基本上都听说过,但是真正用的可能不多. ViewStub可以理解成一个非常轻量级的Vie ...
- android 中解析XML的方法(转)
在XML解析和使用原始XML资源中都涉及过对XML的解析,之前使用的是 DOM4J和 XmlResourceParser 来解析的.本文中将使用XmlPullParser来解析,分别解析不同复杂度的t ...
- xml布局解析报错的可能原因
xml布局解析报如下的错11-15 16:55:21.425 17633-17633/com.hongfans.mobileconnect I/LogUtils_info: [CrashHandler ...
- 从LayoutInflater分析XML布局解析成View的树形结构的过程
上一篇博客分析了XML布局怎么载入到Activity上.不了解的能够參考 从setContentView方法分析Android载入布局流程 上一篇博客仅仅是分析了怎么讲XML布局加入到 Activit ...
- Android中解析XML格式数据的方法
XML介绍:Extensible Markup Language,即可扩展标记语言 一.概述 Android中解析XML格式数据大致有三种方法: SAX DOM PULL 二.详解 2.1 SAX S ...
- Android全面解析之Context机制
前言 很高兴遇见你~ 欢迎阅读我的文章. 在文章Android全面解析之由浅及深Handler消息机制中讨论到,Handler可以: 避免我们自己去手动写 死循环和输入阻塞 来不断获取用户的输入以及避 ...
- 【转】在Android布局中使用include和merge标签
内容转自:http://fengweipeng1208.blog.163.com/blog/static/21277318020138229754135/ 在我们开发android布局时,经常会有很多 ...
- Android 布局之LinearLayout
Android 布局之LinearLayout 1 LinearLayout简介 LinearLayout是线程布局.它包括2个方向(android:orientation):“水平”(horizon ...
随机推荐
- hdu2544(自己实现优先队列)
hdu2544 dij水题,用来测试自己实现优先队列对不对 #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <stdli ...
- jQuery Ajax: $.post请求示例
jQuery Ajax: $.post请求示例 leyangjun.html页面 <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content ...
- cocos2d-x3.0 相对布局(一)
2dx相对布局和Android非常类似.假设前完成Android它应该是easy入门. Size widgetSize = Director::getInstance()->getWinSize ...
- Unreal Engine 4 创建Destructible Mesh(可破坏网格)
Unreal Engine 4的物理引擎用的是PhysX. 支持网格破坏.布料.物理粒子等,非常强大.曾经须要编码才干完毕的工作,在Unreal Engine 4 中仅仅须要拖拖拽拽就完毕了,非常方便 ...
- python网络爬虫学习笔记
python网络爬虫学习笔记 By 钟桓 9月 4 2014 更新日期:9月 4 2014 文章文件夹 1. 介绍: 2. 从简单语句中開始: 3. 传送数据给server 4. HTTP头-描写叙述 ...
- jQuery整理笔记2----jQuery选择整理
一个.基本的选择 1.ID选择器 JavaScript提供了原生方法实如今DOM中选择指定ID值得元素. 使用方法例如以下: var element=document.getElementById(& ...
- 使用HTML5 Canvas做些什么
百分比圆环进度条 // ----------------------------------------------------------- 柱状排行榜统计图 // ------------ ...
- [LeetCode92]Reverse Linked List II
题目: Reverse a linked list from position m to n. Do it in-place and in one-pass. For example:Given 1- ...
- 玩转Web之easyui(一)-----easy ui datagird 分页
easy ui 中数据表格的分页其实是很简单的,分页是在数据表格可以正常显示数据的基础上进行的,在这里给出servlet的代码,其中selectAll()方法是从数据库中提取所有数据, 分页的一种思路 ...
- UVA11294-Wedding(2-SAT)
option=com_onlinejudge&Itemid=8&page=show_problem&problem=2269">题目链接 题意:有n对夫妻參加一 ...
