Splay普及版
辣么,我要介绍我自学的\(Splay\)了,虽然跟大佬们讲得会有些重复,但是自认为把一些玄妙的东西点出来了\(qwq\)
\(0x01\) 引言
首先,我并没觉得\(Splay\)有多难……代码长的原因也就最多是因为不用指针太麻烦……就好像你链表不用指针而用数组模拟,在插入删除的时候就有你好受的了\(qnq\),更何况树形结构更为麻烦,在树上的操作也更加花样繁多。总之,麻烦。
但是\(Splay\)在我眼中却更像是一种可以放诸四海而皆可用的算法,不但可以有效替代二叉搜索树、\(AVL\)树等数据结构,也不会由于\(Treap\)的随机键值而靠脸拿分(其实大多数情况下,只要没有因为被大佬%而rp--,\(Treap\)也是不错的选择),并且时间复杂度也是很可观的。
那么无论怎样,在学习一种新的、我喜欢的东西之前,总是要送一句话勉励自己,并抨击那些认为这种高级数据结构没有什么学的必要的人:
\(\color{cyan}{A}\) \(\color{cyan}{person}\) \(\color{cyan}{who}\) \(\color{cyan}{is}\) \(\color{cyan}{regarded}\) \(\color{cyan}{as}\) \(\color{cyan}{a}\) \(\color{cyan}{loser}\) \(\color{cyan}{isn't}\) \(\color{cyan}{those}\) \(\color{cyan}{ordinarys}\) \(\color{cyan}{,but}\) \(\color{cyan}{the}\) \(\color{cyan}{satisfieds}\)
最怕你一生庸碌无为,却总是安慰自己平凡可贵
那么开始吧!
一.旋转是个什么东西???

旋转这个操作呢,在之前的数据结构中,可谓见所未见,闻所未闻(瞎扯淡\(ing\))。那么我们就先从旋转开始研究吧\(qwq\)!
由于是建立在一株二叉搜索树上的,所以当时是一条链时,旋转并不会影响树的结构\(qwqqq\)。
于是,二叉搜索树的旋转,完!
诶,骗你的啦,怎么可能完,你要知道每个节点可都是还有子节点的,如果直接旋转的话,就会出现一个节点有三个子节点的情况\(emmmmmm\)这可不是我们想看到的,因为瞬间你的一棵\(BT\)就毁灭了\(qwqqqq\)。
那么其实为了满足\(BST\)的特性,我们在上面这个图里可以看到如下内容:
根据点权来列不等式:
\(Y>X,B>X,\)如果\(Y<B,\)那么显然B不会跑到左子树去,所以得出结论:$$Y>B$$
所以我们可以发现,对于旋转时子节点的子树,我们完全可以将这个多余的子树转移到它原来的父节点上即可。
那么这个地方我们就得出一个宝贵的规律来:
我们定义一个结点与他父亲的关系是\(x\),那么在旋转时,他的父亲成为了他的\(!x\)儿子,并且那个上文中所说的“多余结点”,同时也是当前节点的\(!x\)儿子,但在旋转之后需要成为当前节点的“前”父节点的\(x\)儿子。
诶,其实这是找规律啦,但是也从另一个方面揭示了二叉搜索树的的某些本质\(qwqqq\)
\(Talk\) \(is\) \(\color{silver}{cheap}\) \(,show\) \(you\) \(the\) \(\color{silver}{code}\):
inline void update(int x){
if(x){
sub_size[x]=cnt[x];
if(sons[x][1])sub_size[x]+=sub_size[sons[x][1]];
if(sons[x][0])sub_size[x]+=sub_size[sons[x][0]];
}
return ;
}
inline bool get_which(int x){
return sons[f[x]][1]==x;
}
inline void rotate(int x){
int father=f[x],g_father=f[father];
bool which_son=get_which(x);//当前节点的关系
sons[father][which_son]=sons[x][which_son^1];
f[sons[father][which_son]]=father;
sons[x][which_son^1]=father;
f[father]=x;
f[x]=g_father;
if(g_father){
sons[g_father][get_which(father)]=x;
}
update(x);
update(father);
}
\(son\)表示每个节点的左右儿子,\(f\)表示每个节点的父亲\(sub\_size[i]\)表示以\(i\)为根的子树的大小。
诶,为什么要记录子树大小啊?
\(qwqqq\)是为了方便执行之后的\(zz\)操作啊
那么接下来我们看\(Splay\)操作,其实这个操作十分地简单,不过是拼命地向上旋转至根节点而已,但在这其中还有些地方值得注意:
\(\mathcal{1.}\)如果爷爷节点、父节点与自己不共线,那么就是这样
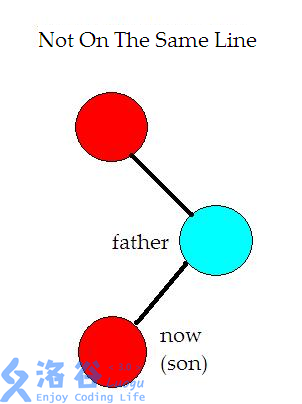
这时实际上并不会怎样……你就不断旋转就行了\(qwq\)
\(\mathcal{2.}\)如果三个节点共线的话,那么就先要旋转父节点,因为如果先旋转子节点的话,我们就会发现原来华丽的一条链的结构被破坏,接下来的一系列操作即会导致这棵树失衡,所以应该先旋转父节点,再旋转子节点\(qwq\)
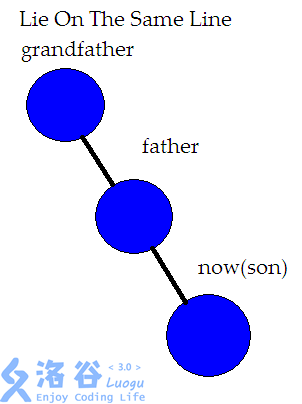
╮( ̄▽ ̄")╭虽然我不是很想做效果图,但是为了你们我忍了(逃
那么接下来是当三个点共线时的两种处理方式的不同结果:
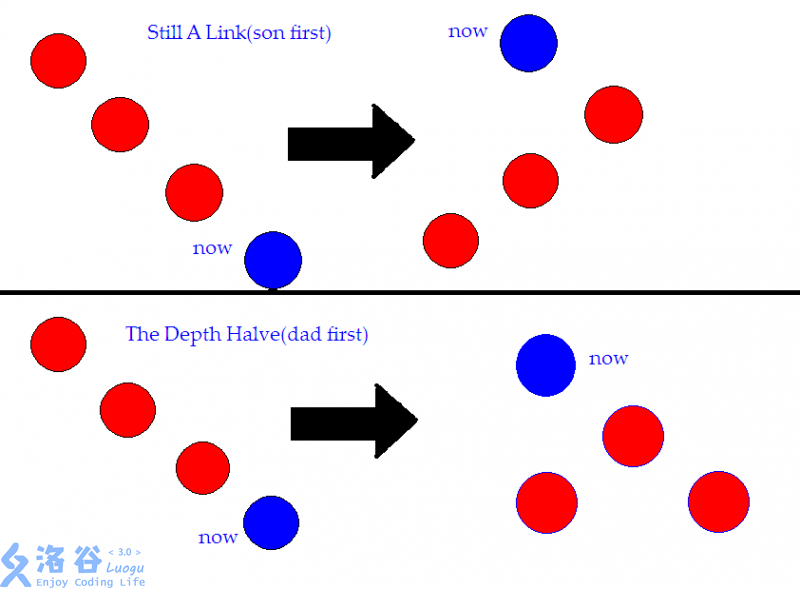
\(emmmm\)实质上就是说,我们在链很长的时候,每次执行先旋父节点再旋当前节点的操作,一次总操作之后,这条链的深度会减半。
\(Talk\) \(is\) \(\color{silver}{cheap}\) \(,show\) \(you\) \(the\) \(\color{silver}{code}\):
inline void splay(int x){
for (int fa;fa=f[x];rotate(x))
if (f[fa])
rotate((get_which(x)==get_which(fa))?fa:x);
root=x;
}
诶,上图画的好像不是很浅显,因为节点数太少了\(qnq\),但是无论如何,本蒟蒻用机房的\(XP\)画图做图很难受的\(QAQ\)
那么接下来……那些二叉搜索树的插入删除操作我就不赘述了,因为本身二叉搜索树就可以支持找前驱后继、找排名找数,所以只需要注意以下两点:
1.每次进行有关点的操作时都要\(Splay\)一次,因为要维护树的随机性
2.注意第一条中的“有关点”,比如当给出排名找数的时候,由于其实跟这个点没什么关系,所以不用\(Splay\).
\(Show\) \(The\) \(Whole\) \(Code\):
// luogu-judger-enable-o2
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
#define MAXN 1000000
int f[MAXN],cnt[MAXN],value[MAXN],sons[MAXN][2],sub_size[MAXN],whole_size,root;
inline int qread(){
int res=0,k=1;
char c=getchar();
while(!isdigit(c)){
if(c=='-')k=-1;
c=getchar();
}
while(isdigit(c)){
res=(res<<1)+(res<<3)+c-48;
c=getchar();
}
return res*k;
}
inline void S_Clear(int x){
sons[x][0]=sons[x][1]=f[x]=sub_size[x]=cnt[x]=value[x]=0;
}
inline bool get_which(int x){
return sons[f[x]][1]==x;
}
inline void update(int x){
if (x){
sub_size[x]=cnt[x];
if (sons[x][0]) sub_size[x]+=sub_size[sons[x][0]];
if (sons[x][1]) sub_size[x]+=sub_size[sons[x][1]];
}
return ;
}
inline void rotate(int x){
int father=f[x],g_father=f[father],which_son=get_which(x);
sons[father][which_son]=sons[x][which_son^1];
f[sons[father][which_son]]=father;
sons[x][which_son^1]=father;
f[father]=x;
f[x]=g_father;
if(g_father){
sons[g_father][sons[g_father][1]==father]=x;
}
update(father);
update(x);
}
inline void splay(int x){
for (int fa;fa=f[x];rotate(x))
if (f[fa])
rotate((get_which(x)==get_which(fa))?fa:x);
root=x;
}
inline void insert(int x){
if(!root){
whole_size++;
sons[whole_size][0]=sons[whole_size][1]=f[whole_size]=0;
root=whole_size;
sub_size[whole_size]=cnt[whole_size]++;
value[whole_size]=x;
return ;
}
int now=root,fa=0;
while(1){
if(x==value[now]){
cnt[now]++;
update(now);
update(fa);
splay(now);
break;
}
fa=now;
now=sons[now][value[now]<x];
if(!now){
whole_size++;
sons[whole_size][0]=sons[whole_size][1]=0;
f[whole_size]=fa;
sub_size[whole_size]=cnt[whole_size]=1;
sons[fa][value[fa]<x]=whole_size;
value[whole_size]=x;
update(fa);
splay(whole_size);
break;
}
}
}
inline int find_num(int x){
int now=root;
while(1){
if(sons[now][0]&&x<=sub_size[sons[now][0]])
now=sons[now][0];
else {
int temp=(sons[now][0]?sub_size[sons[now][0]]:0)+cnt[now];
if(x<=temp)return value[now];
x-=temp;
now=sons[now][1];
}
}
}
inline int find_rank(int x){
int now=root,ans=0;
while(1){
if (x<value[now])
now=sons[now][0];
else{
ans+=(sons[now][0]?sub_size[sons[now][0]]:0);
if (x==value[now]){
splay(now); return ans+1;
}
ans+=cnt[now];
now=sons[now][1];
}
}
}
inline int find_pre(){
int now=sons[root][0];
while(sons[now][1])now=sons[now][1];
return now;
}
inline int find_suffix(){
int now=sons[root][1];
while(sons[now][0])now=sons[now][0];
return now;
}
inline void my_delete(int x){
int hhh=find_rank(x);
if (cnt[root]>1){
cnt[root]--;
update(root);
return;
}
if (!sons[root][0]&&!sons[root][1]) {
S_Clear(root);
root=0;
return;
}
if (!sons[root][0]){
int old_root=root;
root=sons[root][1];
f[root]=0;
S_Clear(old_root);
return;
}
else if (!sons[root][1]){
int old_root=root;
root=sons[root][0];
f[root]=0;
S_Clear(old_root);
return;
}
int left_max=find_pre(),old_root=root;
splay(left_max);
sons[root][1]=sons[old_root][1];
f[sons[old_root][1]]=root;
S_Clear(old_root);
update(root);
}
int main(){
int m,num,be_dealt;
cin>>m;
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
num=qread();
be_dealt=qread();
switch(num)
{
case 1:insert(be_dealt);break;
case 2:my_delete(be_dealt);break;
case 3:printf("%d\n",find_rank(be_dealt));break;
case 4:printf("%d\n",find_num(be_dealt));break;
case 5:insert(be_dealt);printf("%d\n",value[find_pre()]);my_delete(be_dealt);break;
case 6:insert(be_dealt);printf("%d\n",value[find_suffix()]);my_delete(be_dealt);break;
}
}
return 0;
}
\(0x02\) \(Splay\)的渐进难度:
嗯呐……我发现本蒟做这种题总会被卡……并且总是被一些奇奇怪怪的东西卡死……呃不是算法,是打代码时不细心,导致调试了好长时间\(ORZ\).
那么,这道题的题面戳这里
那么对于区间反转这种操作,我们由于原数列的顺序已经给定,所以不能按照权值排序,所以选择按照点的编号建立一棵二叉搜索树。
诶,所以啊,不用一个个\(insert\)编号,我们只需要进行一下递归建树即可\(qwq\)——建树可以仿照线段树的建树\(qwq\)
那么就类似这样:
struct Splay_tree{
int f,sub_size,cnt,value,tag;
int son[2];
}s[MAXN];
inline void update(int x){
if(x){
s[x].sub_size=s[x].cnt;
if(s[x].son[0])s[x].sub_size+=s[s[x].son[0]].sub_size;
if(s[x].son[1])s[x].sub_size+=s[s[x].son[1]].sub_size;
}
}
int build_tree(int l, int r, int fa) {
if(l > r) { return 0; }
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
int now = ++ wz;
s[now].f=fa;
s[now].son[0]=s[now].son[1]=0;
s[now].cnt++;
s[now].value=original[mid];
s[now].sub_size++;
s[now].son[0] = build_tree(l, mid - 1, now);
s[now].son[1] = build_tree(mid + 1, r, now);
update(now);
return now;
}
\(emmmm\)码风还算是中规中矩吧\(qwq\)
那么我们现在已经有一棵编号树了(并且由于递归建树,一开始是平衡的),我们要对它进行区间翻转操作。那么实际上我们可以发现,在反转区间\([l\)~\(r]\)的时候,我们可以考虑利用\(Splay\)的性质,将\(l-1\)翻转至根节点,再将\(r+1\)翻转至根节点的幼儿子,类似这样:
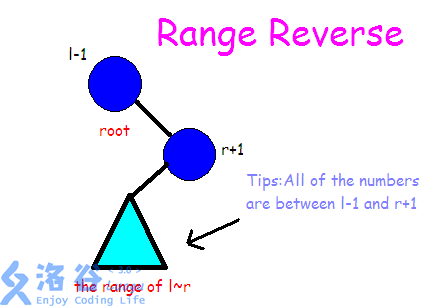
\(emmm\)本蒟蒻用英文作图只是因为会使风格更简约\(qwq\)
但在这里还是需要注意,我们为了方便,在\(1\)号节点之前和\(n\)号节点之后又加了两个节点并赋值为\(-INF\)和\(INF\),作为虚点,既满足二叉搜索树的性质,又可以让我们在翻转\(1\)~\(n\)时不会\(GG\)
那么实际上,在我们把当前区间确定下来之后,我们就要开始进行反转操作。而对于反转操作,我们可以不断替换子节点的左右子树达到此目的。
比如对于\(1\)~\(5\)这个序列,我们反转\(2~4\)这个区间,过程就是这样:
首先建树,在这里用一个可行的树来举个栗子:
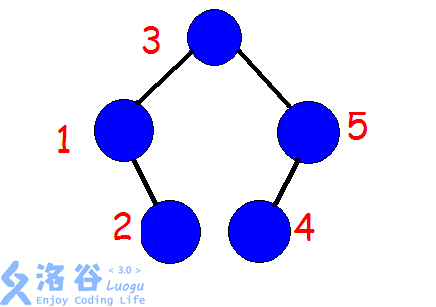
那么实际上我们如果反转\(2~4\)那么我们需要先将\(1\)和\(5\)旋转上去,类似这样:
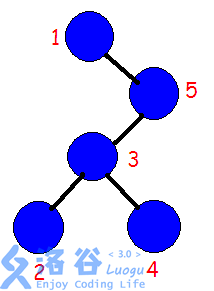
实际上我们翻转两个子树就相当于反转\(2\)~\(4\) \(qwq\)
但在这个地方我们可以考虑打个标记,标记的存在就只在于记录现在对于当前节点应不应该翻转两个子树。
\(\color{gold}{Talk}\) \(is\) \(\color{silver}{cheap}\) \(,\color{gold}{show}\) \(you\) \(the\) \(\color{silver}{code}\):
inline void pushdown(int x){
if(x&&s[x].tag){
s[s[x].son[1]].tag^=1;
s[s[x].son[0]].tag^=1;
swap(s[x].son[1],s[x].son[0]);
s[x].tag=0;
}
}
inline int find(int x){
int now=root;
while(1)
{
pushdown(now);
if(x<=s[s[now].son[0]].sub_size){
now=s[now].son[0];
}
else {
x-=s[s[now].son[0] ].sub_size + 1;
if(!x)return now;
now=s[now].son[1];
}
}
}
inline void reverse(int x,int y){
int l=x-1,r=y+1;
l=find(l),r=find(r);
splay(l,0);
splay(r,l);
int pos=s[root].son[1];
pos=s[pos].son[0];
s[pos].tag^=1;//标记最初打在操作区间的根节点上
}
然后还有些需要注意的,注释了\(qwq\)
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MAXN 1000007
#define INF 100000089
struct Splay_tree{
int f,sub_size,cnt,value,tag;
int son[2];
}s[MAXN];
int original[MAXN],root,wz;
inline bool which(int x){
return x==s[s[x].f].son[1];
}
inline void update(int x){
if(x){
s[x].sub_size=s[x].cnt;
if(s[x].son[0])s[x].sub_size+=s[s[x].son[0]].sub_size;
if(s[x].son[1])s[x].sub_size+=s[s[x].son[1]].sub_size;
}
}
inline void pushdown(int x){
if(x&&s[x].tag){
s[s[x].son[1]].tag^=1;
s[s[x].son[0]].tag^=1;
swap(s[x].son[1],s[x].son[0]);
s[x].tag=0;
}
}
inline void rotate(int x){
int fnow=s[x].f,ffnow=s[fnow].f;
pushdown(x),pushdown(fnow);
bool w=which(x);
s[fnow].son[w]=s[x].son[w^1];
s[s[fnow].son[w]].f=fnow;
s[fnow].f=x;
s[x].f=ffnow;
s[x].son[w^1]=fnow;
if(ffnow){
s[ffnow].son[s[ffnow].son[1]==fnow]=x;
}
update(fnow);
}
inline void splay(int x,int goal){
for(int qwq;(qwq=s[x].f)!=goal;rotate(x)){
if(s[qwq].f!=goal){//这个地方特别重要,原因是需要判断的是当前的父亲有没有到目标节点,而如果把“qwq”改成“x”……就会炸
rotate(which(x)==which(qwq)?qwq:x);
}
}
if(goal==0){
root=x;
}
}
int build_tree(int l, int r, int fa) {
if(l > r) { return 0; }
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
int now = ++ wz;
s[now].f=fa;
s[now].son[0]=s[now].son[1]=0;
s[now].cnt++;
s[now].value=original[mid];
s[now].sub_size++;
s[now].son[0] = build_tree(l, mid - 1, now);
s[now].son[1] = build_tree(mid + 1, r, now);
update(now);
return now;
}
inline int find(int x){
int now=root;
while(1)
{
pushdown(now);
if(x<=s[s[now].son[0]].sub_size){
now=s[now].son[0];
}
else {
x-=s[s[now].son[0] ].sub_size + 1;
if(!x)return now;
now=s[now].son[1];
}
}
}
inline void reverse(int x,int y){
int l=x-1,r=y+1;
l=find(l),r=find(r);
splay(l,0);
splay(r,l);
int pos=s[root].son[1];
pos=s[pos].son[0];
s[pos].tag^=1;
}
inline void dfs(int now){
pushdown(now);
if(s[now].son[0])dfs(s[now].son[0]);
if(s[now].value!=-INF&&s[now].value!=INF){
cout<<s[now].value<<" ";
}
if(s[now].son[1])dfs(s[now].son[1]);
}
int main(){
int n,m,x,y;
cin>>n>>m;
original[1]=-INF,original[n+2]=INF;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
original[i+1]=i;
}
root=build_tree(1,n+2,0);//有一个良好的定义变量习惯很重要……重复定义同一个变量(比如全局的和局部的同名)那么就会发生覆盖。
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
cin>>x>>y;
reverse(x+1,y+1);
}
dfs(root);
}
最后来几道例题:
戳这里
这个题算是平衡树系列的一个进阶版本了吧\(qwq\).
好吧我承认,这个题我一开始做的时候已经想出了大约\(60\)%的样子,但是最后还是偷偷地瞅了眼题解,发现似乎很有道理,然后\(A\)了\(emmmm\).
那么好像很显然,我们坑定不能一个一个地修改,区间修改由于每次都是\(1\)~\(n\),所以并没有什么很大的意义。所以我们可以考虑引入一个标记,每次\(A\)就$$delta+=num$$每次\(I\)就$$insert(num-delta)$$,询问时就$$cout<<query+delta$$,再加上几个判断是不是非法操作。
\(emmmmm\)好像海星,到这一步大约已经可以够得着\(NOIP\)的思维难度了。然而这是一道省选题,所以这么搞还是捕星,因为删除操作和询问离职人员好像很难搞。
那么,在这里我们考虑将\(-INF\)和\(INF\)在一开始就插入平衡树里。每次\(insert\)操作\(tot++\),最后只需要用$$tot-(find_rank(INF)-2)$$就可以算出离职人数。
那么只剩下最后一个问题了——我们该怎么删除呢?这里就需要用到一个二叉搜索树里很精妙的操作了——删除根的子树。我们可以在执行\(S\)操作时先\(delta-=num\),然后将\(-INF\)旋转到根节点,将\(minn-delta\)旋转到根节点的右儿子,然后删除根节点的右子树的左子树即可。
诶这个操作很熟悉啊,不也是区间翻转时的操作吗?
诶怎么旋转\(minn-delta\)啊?
我们可以很简单地插入删除,这很简单,但是为什么要以\(minn-delta\)作为所删除的单调区间的上界?这个地方你可以稍微意会一下……因为我们插入的是\(num-delta\)啊!
嗯,我还是太弱了。
\(\color{red}{Code}:\)
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
#define MAXN 1000000
#define INF 283653129
int f[MAXN],cnt[MAXN],value[MAXN],sons[MAXN][2],sub_size[MAXN],whole_size,root;
inline int qread(){
int res=0,k=1;
char c=getchar();
while(!isdigit(c)){
if(c=='-')k=-1;
c=getchar();
}
while(isdigit(c)){
res=(res<<1)+(res<<3)+c-48;
c=getchar();
}
return res*k;
}
inline void S_Clear(int x){
sons[x][0]=sons[x][1]=f[x]=sub_size[x]=cnt[x]=value[x]=0;
}
inline bool get_which(int x){
return sons[f[x]][1]==x;
}
inline void update(int x){
if (x){
sub_size[x]=cnt[x];
if (sons[x][0]) sub_size[x]+=sub_size[sons[x][0]];
if (sons[x][1]) sub_size[x]+=sub_size[sons[x][1]];
}
return ;
}
inline void rotate(int x){
int father=f[x],g_father=f[father],which_son=get_which(x);
sons[father][which_son]=sons[x][which_son^1];
f[sons[father][which_son]]=father;
sons[x][which_son^1]=father;
f[father]=x;
f[x]=g_father;
if(g_father){
sons[g_father][sons[g_father][1]==father]=x;
}
update(father);
update(x);
}
inline void splay(int x,int goal){
for(int qwq;(qwq=f[x])!=goal;rotate(x)){
if(f[qwq]!=goal){
rotate(get_which(x)==get_which(qwq)?qwq:x);
}
}
if(!goal){
root=x;
}
}
inline void insert(int x){
if(!root){
whole_size++;
sons[whole_size][0]=sons[whole_size][1]=f[whole_size]=0;
root=whole_size;
sub_size[whole_size]=cnt[whole_size]++;
value[whole_size]=x;
return ;
}
int now=root,fa=0;
while(1){
if(x==value[now]){
cnt[now]++;
update(now);
update(fa);
splay(now,0);
break;
}
fa=now;
now=sons[now][value[now]<x];
if(!now){
whole_size++;
sons[whole_size][0]=sons[whole_size][1]=0;
f[whole_size]=fa;
sub_size[whole_size]=cnt[whole_size]=1;
sons[fa][value[fa]<x]=whole_size;
value[whole_size]=x;
update(fa);
splay(whole_size,0);
break;
}
}
}
inline int find_num(int x){
int now=root;
while(1){
if(sons[now][0]&&x<=sub_size[sons[now][0]])
now=sons[now][0];
else {
int temp=(sons[now][0]?sub_size[sons[now][0]]:0)+cnt[now];
if(x<=temp)return value[now];
x-=temp;
now=sons[now][1];
}
}
}
inline int find_ID(int x){
int now=root;
while(1){
if(x==value[now]){
return now;
}
else now=sons[now][value[now]<x];
}
}
inline int find_rank(int x){
int now=root,ans=0;
while(1){
if (x<value[now])
now=sons[now][0];
else{
ans+=(sons[now][0]?sub_size[sons[now][0]]:0);
if (x==value[now]){
splay(now,0); return ans+1;
}
ans+=cnt[now];
now=sons[now][1];
}
}
}
inline int find_pre(){
int now=sons[root][0];
while(sons[now][1])now=sons[now][1];
return now;
}
inline int find_suffix(){
int now=sons[root][1];
while(sons[now][0])now=sons[now][0];
return now;
}
inline void my_delete(int x){
int hhh=find_rank(x);
if (cnt[root]>1){
cnt[root]--;
update(root);
return;
}
if (!sons[root][0]&&!sons[root][1]) {
S_Clear(root);
root=0;
return;
}
if (!sons[root][0]){
int old_root=root;
root=sons[root][1];
f[root]=0;
S_Clear(old_root);
return;
}
else if (!sons[root][1]){
int old_root=root;
root=sons[root][0];
f[root]=0;
S_Clear(old_root);
return;
}
int left_max=find_pre(),old_root=root;
splay(left_max,0);
sons[root][1]=sons[old_root][1];
f[sons[old_root][1]]=root;
S_Clear(old_root);
update(root);
}
int main(){
int m,num,minn;
char a;
cin>>m>>minn;
insert(-INF);
insert(INF);
int delta=0,sumtot=0;
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
cin>>a>>num;
switch(a){
case 'I' :{
if(num<minn)break;
insert(num-delta);
sumtot++;
break;
}
case 'A':{
delta+=num;
break;
}
case 'S':{
delta-=num;
insert(minn-delta);
int a=find_ID(-INF),b=find_ID(minn-delta);
splay(a,0);
splay(b,a);
sons[sons[root][1]][0]=0;
my_delete(minn-delta);
break;
}
case 'F':{
int sumnow=find_rank(INF)-2;
if(sumnow<num){
cout<<-1<<endl;
break;
}
int res=find_num(sumnow+2-num);
cout<<res+delta<<endl;
break;
}
}
}
int sumnow=find_rank(INF)-2;
cout<<sumtot-sumnow;
return 0;
}
代码好长啊……足足写了5.04K
Splay普及版的更多相关文章
- 课程分享 企业普及版贝斯OA与工作流系统
企业普及版贝斯OA与工作流系统 基于J2EE+JBPM3.x/JBPM4.3+Flex流程设计器+Jquery+授权认证企业普及版贝斯OA与工作流系统 假设对这个课程有兴趣的.能够和我联系.QQ205 ...
- [您有新的未分配科技点]可,可,可持久化!?------0-1Trie和可持久化Trie普及版讲解
这一次,我们来了解普通Trie树的变种:0-1Trie以及在其基础上产生的可持久化Trie(其实,普通的Trie也可以可持久化,只是不太常见) 先简单介绍一下0-1Trie:一个0-1Trie节点只有 ...
- BZOJ 1500 splay终结版...
GSS系列有一丝丝像- 只不过那个是线段树 这个是splay 翻转 插入 删除啥的就是普通的splay 合在一起了而已 //By SiriusRen #include <cstdio> # ...
- 免费了 -- EXCEL插件 智表ZCELL 普及版V1.0 发布了!!!
智表(zcell)是一款浏览器仿excel表格jquery插件.智表可以为你提供excel般的智能体验,支持双击编辑.设置公式.设置显示小数精度.下拉框.自定义单元格.复制粘贴.不连续选定.合并单元格 ...
- 【BBST 之伸展树 (Splay Tree)】
最近“hiho一下”出了平衡树专题,这周的Splay一直出现RE,应该删除操作指针没处理好,还没找出原因. 不过其他操作运行正常,尝试用它写了一道之前用set做的平衡树的题http://codefor ...
- 刷题总结——二逼平衡树(bzoj3224线段树套splay)
题目: Description 您需要写一种数据结构(可参考题目标题),来维护一个有序数列,其中需要提供以下操作:1.查询k在区间内的排名2.查询区间内排名为k的值3.修改某一位值上的数值4.查询k在 ...
- 修改AssemblyInfo.cs自动生成版本号
一. 版本号自动生成方法 1.把 AssemblyInfo.cs文件中的[assembly:AssemblyVersion("1.0.0.0")]改成[assembly:Assem ...
- 统计网站访问量,以GD2库图像形式输出
index.php页面<?php session_start(); if($_SESSION[temp]==""){ //判断$_SESSION[temp]=="& ...
- paper 77:[转载]ENDNOTE使用方法,常用!
一.简介 EndNote是一款用于海量文献管理和批量参考文献管理的工具软件,自问世起就成为科研界的必备武器.在前EndNote时代,文献复习阶段从各大数据库中搜集到的文献往往千头万绪.或重复或遗漏, ...
随机推荐
- BZOJ3832: [Poi2014]Rally(拓扑排序 堆)
题意 题目链接 Sol 最直观的思路是求出删除每个点后的最长路,我们考虑这玩意儿怎么求 设\(f[i]\)表示以\(i\)结尾的最长路长度,\(g[i]\)表示以\(i\)开始的最长路长度 根据DAG ...
- drupal7 模糊查询接口
$query->condition('card_no', db_like($batch_no).'%', 'LIKE');
- JQuer.HoverDir的基本使用方法
首先引入JQ和HoverDir库 HTML部分: <ul id="da-thumbs" class="da-thumbs"> <li> ...
- CentOS7.4 + Ambari 2.6.1.5 + HDP 2.6.4.0 安装部署
1. 参考说明 参考文档: https://docs.hortonworks.com/HDPDocuments/Ambari-2.6.1.5/bk_ambari-installation/conten ...
- CentOS7系列--2.2CentOS7中配置SSH服务
CentOS7配置SSH服务 1. SSH配置 1.1. 使用SSH服务更加安全 [root@centos7 ~]# vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config 设置如下 PermitRootLo ...
- 一:JavaWeb和Tomcat的安装
1.Java Web 是java技术用来解决相关web互联网领域的技术总和. 2.Servlet是Java Servlet的简称,称为小服务程序或服务器连接器,用Java编写的服务器端程序 3.JSP ...
- redis 事务、Jedis事务处理流程
127.0.0.1:6379> multiOK127.0.0.1:6379> sadd myset a b cQUEUED ——>并没有执行,排队等待127.0.0.1:6379& ...
- Java中的Number和Math类简单介绍
Java Number类 一般地,当需要使用数字的时候,我们通常使用内置数据类型,如:byte.int.long.double 等. 实例: int a = 5000; float b = 13.65 ...
- elipse安装php
在用eclipse作为PHP的开发IDE工具时,如果下载的Eclipse不带有PHP功能,则需要我们自己来给Eclipse升级.不过也可以下载eclipseForPHP 在Eclipse的help菜单 ...
- Leetcode题解之Container With Most Water
1.题目描述 2.题目分析 首先,这个题可以使用暴力解法,时间复杂度是O(n^2),这个显然是最容易的做法,但是效率不够高,题目提供了一种解法,使用两个指针,一个从头向尾部,另外一个从尾部向头部,每一 ...
