Ansible自动化运维应用实战
centos7.4
|
主机名称 |
IP |
配置 |
用途 |
|
controlnode |
172.16.1.120 |
1核/1G/60G |
ansible |
|
slavenode1 |
172.16.1.121 |
1核/1G/60G |
被管理主机 |
|
slavenode2 |
172.16.1.122 |
1核/1G/60G |
被管理主机 |
第
1 章
Ansible概述
1.
IT自动化的好处
团队影响
• 节省时间,提高工作效率
• 消除重复任务
• 更少的错误风险
• 改善协作和工作满意度
企业影响
• 克服复杂性
• 更多创新资源
• 加强问责制和合规性
2.
Ansible是什么
Ansible是一种IT自动化工具。它可以配置系统,部署软件以及协调更高级的IT任务,例如持续部署,滚动更新。Ansible适用于管理企业IT基础设施,从具有少数主机的小规模到数千个实例的企业环境。Ansible也是一种简单的自动化语言,可以完美地描述IT应用程序基础结构。

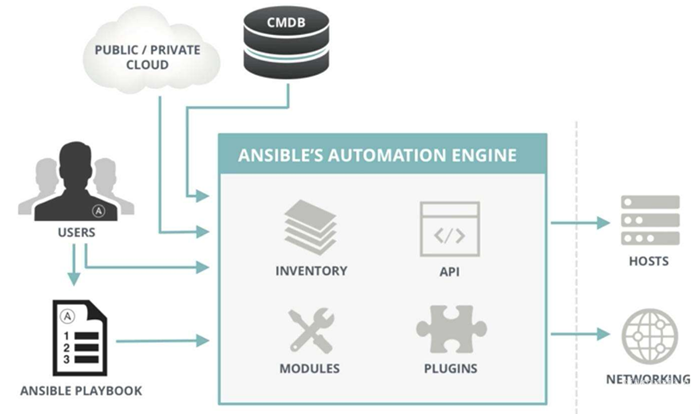
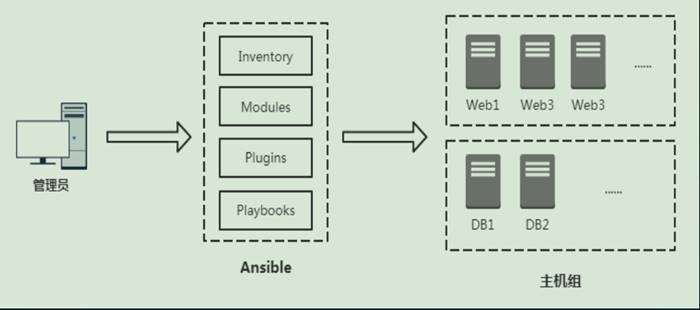
3.
Ansible架构
第 2 章
Ansible安装与配置
在172.16.1.120节点上操作
1.Ansible使用要求
服务端要求
• Python2.6/2.7/3.x
• RedHat,Debian,CentOS,OSX等。不支持Windows
被管理端要求
• OpenSSH
• Python2.6/2.7/3.x
2.安装Ansible
• yum
install ansible -y (推荐)
• pip
install ansible
• https://releases.ansible.com/ansible or
https://github.com/ansible/ansible.git
3.修改配置文件
# vi
/etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
[defaults]
#
默认配置项
inventory
= /etc/ansible/hosts
# 远程主机清单
forks =
15
# 执行并发数,默认5
sudo_user =
root
# ssh远程主机sudo 提权到的用户
remote_port = 22
# ssh远程主机的端口号
host_key_checking = False
# 禁用SSH密钥主机检查。
timeout =
30
# 执行超时时间,默认10s
log_path =
/var/log/ansible.log
# 日志路径
private_key_file = /root/.ssh/id_rsa
#
基于密钥方式连接远程主机的本地密钥路径
#
如果设置,则始终使用此私钥文件进行身份验证。
#
清单列表密钥路径
> private_key_file > 执行ansible用户的密钥路径
说明:
1)
如果未开启host_key_checking =
False选项会报如下错误


4.Inventory(主机清单)
# /etc/ansible/hosts
#
示例1:未分组的主机
green.example.com
blue.example.com
192.168.100.1
192.168.100.10
# 示例2:属于webservers组主机集合
[webservers]
alpha.example.org
beta.example.org
192.168.1.100
192.168.1.110
www[001:006].example.com
#
表示www001.example.com到www006.example.com的主机
示例3:属于dbservers组主机集合
[dbservers]
db01.intranet.mydomain.net
db02.intranet.mydomain.net
10.25.1.56
10.25.1.57
db-[99:101]-node.example.com
#
主机和主机组变量(主机变量优先级大于主机组变量)
vim /etc/ansible/hosts
[webservers]
172.16.1.121:22 ansible_ssh_user=root
ansible_ssh_pass='123456' http_port=80
172.16.1.122:22 ansible_ssh_user=root
ansible_ssh_pass='123456'
[webservers:vars]
http_port=8080
server_name=www.baidu.com
实验:
ansible
webservers -m command -a "echo {{http_port}}" -o

ansible webservers -m command -a
"echo {{server_name}}" -o

命令说明:
ansible webservers -m command -a
"echo {{http_port}}" -o
ansible:ansible命令
webservers:/etc/ansible/hosts中配置的主机组名称,指定 all (分组和未分组的主机)代表所有主机,指定172.16.1.121代表单台主机。
-m:指定使用的模块,默认是command模块(简单的shell命令),可以省略不写。
-a:指定具体使用的shell指令,比如"echo
{{http_port}}"表示在远程主机上打印http_port这个变量。
-o:对ansible的输出的结果进行压缩(即,输出的结果显示在一行)。
#
组变量分解到单个文件(文件名和inventory中配置的主机组名一致,并且以.yml结尾)
mkdir -p
/etc/ansible/group_vars/
vim
/etc/ansible/group_vars/webservers.yml
http_port:
8080
server_name: www.baidu.com
#
ansible常用命令
ansible:ansible指令
ansible-doc:ansible帮助命令,后接模块名称
ansible-playbook:ansible剧本
第 3 章
ad-hoc命令
在172.16.1.120节点上操作。
ad-hoc指在linux终端上直接使用ansible命令,执行临时命令,不会记录任何操作记录。
inventory中配置的连接远端主机的用户名、密码或密钥,优先级最高。
1.命令行工具常用选项
格式:ansible< host-pattern> [
options ]
选项:
-a MODULE_ARGS,
--args=MODULE_ARGS
#
模块参数
-C, --check
#
运行检查,不执行任何操作
-e EXTRA_VARS,
--extra-vars=EXTRA_VARS
#
设置附加变量 key=value
-f FORKS,
--forks=FORKS
#
指定并行进程数量,默认5
-i INVENTORY,
--inventory=INVENTORY
#
指定主机清单文件路径
--list-hosts
#
输出匹配的主机列表,不执行任何操作
-m MODULE_NAME,
--module-name=MODULE_NAME
#
执行的模块名,默认command
--syntax-check
#
语法检查playbook文件,不执行任何操作
-t TREE, --tree=TREE
#
将日志输出到此目录
-v,
--verbose
#
详细信息,-vvv更多, -vvvv debug
--version
#
查看程序版本
连接选项:控制谁连接主机和如何连接
-k, --ask-pass
#
请求连接密码
--private-key=PRIVATE_KEY_FILE,
--key-file=PRIVATE_KEY_FILE
#
私钥文件
-u REMOTE_USER,
--user=REMOTE_USER
#
连接用户,默认None。
-T TIMEOUT,
--timeout=TIMEOUT
#
覆盖连接超时时间,默认10秒
提权选项:控制在目标主机以什么用户身份运行
-b,
--become
#
以另一个用户身份操作
--become-method=BECOME_METHOD
#
提权方法,默认sudo
--become-user=BECOME_USER
#
提权后的用户身份,默认root
-K,
--ask-become-pass
#
提权密码
2.SSH密码认证
[webservers]
172.16.1.121:22 ansible_ssh_user=root
ansible_ssh_pass='123456'
172.16.1.122:22 ansible_ssh_user=root
ansible_ssh_pass='123456'
3.SSH秘钥对认证
ssh-keygen
#
一直回车完成密钥对的创建
ssh-copy-id root@172.16.1.122
#
发送公钥到被管理主机
vim
/etc/ansible/hosts
[webservers]
172.16.1.121:22 ansible_ssh_user=root ansible_ssh_key=/root/.ssh/id_rsa
172.16.1.122:22 ansible_ssh_user=root
#
在/etc/ansible/ansible.cfg中配置了private_key_file =
/root/.ssh/id_rsa,
#
不指定ansible_ssh_key=/root/.ssh/id_rsa也可,如果指定会覆盖配置。
# 生产环境中推荐使用ssh密钥对认证,下面的实验都是基于ssh密钥对做的。
第 4 章
Ansible常用模块
4.1 执行shell命令(shell模块与sudo使用)
1
shell模块
-m
command 模块不支持
"&&、||、>>、>"等特殊符号,只能执行一些简单的shell命令,如果想要执行一些复杂的命令需要使用 -m
shell 模块。
2
ansible 进行sudo提权
(1)
在172.16.1.120节点上操作
1)
配置主机清单
#
vim /etc/ansible/hosts
[webservers]
172.16.1.121:22
ansible_ssh_user=user ansible_ssh_key=/root/.ssh/id_rsa
172.16.1.122:22
ansible_ssh_user=user ansible_ssh_key=/root/.ssh/id_rsa
2)
发送root用户的公钥分别到172.16.1.121、172.16.1.122节点的user用户下
#
ssh-copy-id user@172.16.1.121
#
ssh-copy-id user@172.16.1.122
(2)
分别在172.16.1.121和172.16.1.122节点上进行操作
1)
创建user用户
#
useradd user
#
echo "user" | passwd --stdin user
2)
sudo提权
#
visudo
user ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:
ALL
(3)
测试
在172.16.1.120节点上进行操作
#
ansible webservers -m shell -a "ls /root/" --become
--become-user root -o

(4)
补充
如果inventory中指定远程主机的形式为<主机IP>:<ssh端口号>,且远程主机用户没有使用NOPASSWD:
ALL
那么使用如下命令可进行普通用户的提权操作。
#
ansible webservers -m shell -a "ls /root/" -u user -k --become --become-user
root -K -o

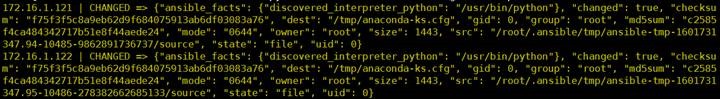
4.2 文件传输(copy、file)
1
copy
#
ansible webservers -m copy -a "src=/root/anaconda-ks.cfg dest=/tmp/"
-o
2
file
#
ansible webservers -m file -a "dest=/root/lc_dir state=directory"
-o

#
"value of state must be one of: absent, directory, file, hard, link,
touch"
4.3 管理软件包(yum)
#
ansible webservers -m yum -a "name=httpd state=present" -o
#
"value of state must be one of: absent, installed, latest, present,
removed"
4.4 用户和组(user、group)
1
user
#
ansible webservers -m user -a "name=foo password=liuchang.com state=present"
-o
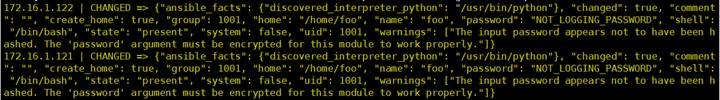
"value
of state must be one of: absent, present"
2
group
#
ansible webservers -m group -a "name=bee state=present" -o

"value
of state must be one of: absent, present"
4.5 从源代码管理系统部署(git)
1
安装git软件包
#
ansible webservers -m yum -a "name=git state=present" -o
2
拉去源代码到本地
#
ansible webservers -m git -a "repo=https://github.com/ansible/ansible.git
dest=/tmp/ansible/" -o

说明:目标目录必须是一个空目录,如果不存在会自动创建。
4.6 管理服务(service)
#
ansible webservers -m service -a "name=httpd state=started"
-o
#
"value of state must be one of: reloaded, restarted, started,
stopped"
#
ansible webservers -m service -a "name=httpd enabled=true" -o
#
"Valid
booleans include: 0, 'on', 'f', 'false', 1, 'no', 'n', '1', '0', 't', 'y',
'off', 'yes', 'true'"
4.7 收集目标主机信息(setup)
#
ansible webservers -m setup -a "filter=ansible_nodename"

常用过滤选项:
ansible_nodename #
主机名
ansible_os_family #
操作系统
ansible_pkg_mgr # 包管理软件名称
ansible_processor # 处理器信息
ansible_processor_cores #
处理器的核数
第 5 章
Playbook基本使用
在172.16.1.120节点上进行操作
1.使用Playbook的好处
特点
• 易读的编排语言
• 适合配置管理和应用部署
• 非常适合部署复杂的工作
2.先来认识一下Playbook
2.1 自动部署Nginx
#
cat /root/nginx.yml
---
-
hosts: webservers
vars:
hello:
Ansible
tasks:
-
name: Add repo
yum_repository:
name: nginx
description: nginx repo
baseurl:
http://nginx.org/packages/centos/7/$basearch/
gpgcheck: no
enabled: 1
-
name: Install nginx
yum:
name: nginx
state: latest
-
name: Copy nginx configuration file
copy:
src: ./site.conf
dest: /etc/nginx/conf.d/site.conf
-
name: Start nginx
service:
name: nginx
state: restarted
-
name: Create wwwroot directory
file:
dest: /var/www/html
state: directory
-
name: Create test page index.html
shell:
echo "hello {{hello}}" > /var/www/html/index.html
2.2 检测语法
#
ansible-playbook nginx.yml --syntax-check
2.3 nginx站点配置
#
cat /root/site.conf
server
{
listen
80;
server_name
www.liuchang.com;
location
/ {
root /var/www/html;
index index.html;
}
}
2.4
ansible-playbook执行及测试访问
1
执行ansible-playbook
#
ansible-playbook nginx.yml
2
访问测试网站
#
curl 172.16.1.121 -H "Host:www.liuchang.com"
hello
Ansible
3.YAML语法
• 缩进表示层级关系
• 不支持制表符“tab”缩进,使用空格缩进
• 通常开头缩进 2 个空格
• 字符后缩进 1 个空格,如冒号、逗号等
• “---” 表示YAML格式,一个文件的开始
• “#”注释
4.Playbook文件结构
---
-
name: play1
hosts: webservers
gather_facts: no
remote_user: root
vars:
var_name:
value
tasks:
-
name: echo
shell: "echo {{var_name}}"
-
name: play2
hosts: webservers
gather_facts: no
remote_user: root
vars:
var_name:
value
tasks:
-
name: echo
shell: "echo {{var_name}}"
---
- hosts: webservers
gather_facts:
no
remote_user:
root
vars:
var_name:
value
tasks:
- name:
echo
shell:
"echo {{var_name}}"
5.在变更时执行操作(handlers)
notify:在任务结束时触发
handlers:由特定条件触发Tasks,handlers:
与 tasks:
对齐
#
cat nginx_handler.yml
---
-
hosts: webservers
gather_facts: no
-
name: Copy nginx configuration file
copy:
src: ./site.conf
dest: /etc/nginx/conf.d/site.conf
notify:
- restart nginx
-
name: restart nginx
service:
name=nginx state=reloaded
6.任务控制(tags)
1
playbook文件
#
cat redis_tags.yml
---
-
hosts: webservers
gather_facts: no
tasks:
-
name: Install redis
yum: name=redis state=present
tags: install
-
name: Copy redis configuration file
copy: src=redis.conf
dest=/etc/redis/redis.conf
tags: configuration
-
name: Restart redis
service: name=redis state=restarted
tags: restart
2
执行指定的tags
#
ansible-playbook redis_tags.yml --tags "install,restart"
3
跳过指定的tags
#
ansible-playbook redis_tags.yml --skip-tags "configuration"
7.Playbook文件调试debug
1
语法检查:ansible-playbook
main.yml --syntax-check
debug:
只能存在一个单独的任务中,该任务中无其它的命令。
2
打印语句
#
cat ansible_debug.yml
---
-
hosts: webservers
gather_facts: yes
vars:
server_name:
www.liuchang.com
tasks:
-
name: test1
debug:
msg="{{server_name}}"
-
name: test2
debug:
msg:
- "{{inventory_hostname}}"
-
"{{ansible_hostname}}"
8.案例:自动部署Tomcat
#
cat tomcat.yml
---
-
hosts: webservers
gather_facts: no
vars:
tomcat_version:
8.5.58
tomcat_install_dir:
/usr/local
tasks:
-
name: Install jdk1.8
yum: name=java-1.8.0-openjdk
state=present
-
name: Download tomcat
get_url:
url=http://mirrors.hust.edu.cn/apache/tomcat/tomcat-8/v{{ tomcat_version
}}/bin/apache-tomcat-{{ tomcat_version }}.tar.gz dest=/tmp
-
name: Unarchive tomcat-{{ tomcat_version }}.tar.gz
unarchive:
src: /tmp/apache-tomcat-{{
tomcat_version }}.tar.gz
dest: "{{ tomcat_install_dir
}}"
copy: no
-
name: Start tomcat
shell: cd {{ tomcat_install_dir }}
&&
mv apache-tomcat-{{ tomcat_version
}} tomcat8 &&
cd tomcat8/bin&& nohup
./startup.sh &
第 6 章
Playbook定义变量与使用
1.命令行
2.在Inventory中定义也可以在/etc/ansible/group_vars/中创建
3.在Playbook中定义变量
playbook变量使用的优先级:
命令行变量( -e )>
playbook变量 > inventory主机变量 >
inventory组变量
1
playbook 文件
#
cat var.yml
---
-
hosts: webservers
gather_facts: no
vars:
var_name1:
value1
var_name2:
value2
tasks:
-
name: line_var
debug: msg="{{server_names}}"
-
name: playbook_var
shell: echo {{var_name1}}&&
echo
{{var_name2}}
2
测试
#
ansible-playbook var.yml -e server_names=www.souhu.com
4.在Role中定义
5.注册变量(register)
将一个任务运行后返回的值写入到变量中,方便下一个任务使用。
#
cat register.yml
-
hosts: webservers
gather_facts: no
tasks:
-
name: Get date
command: date +"%F_%T"
register: datetime
-
name: Echo datetime
file: dest=/tmp/{{datetime.stdout}}
state=touch
-
name: Echo datetime Debug
debug: msg="{{datetime.stdout}}"
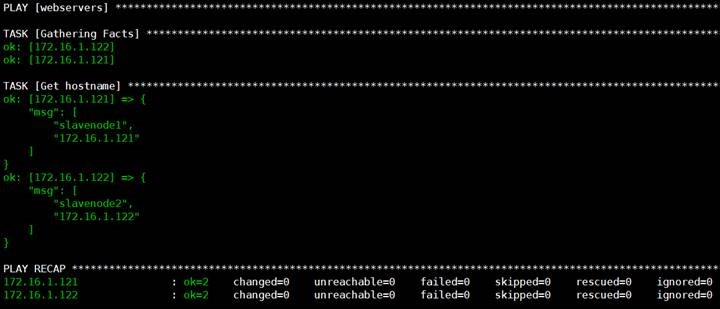
6.系统信息变量(facts)
1
playbook文件
#
cat system_info.yml
---
-
hosts: webservers
gather_facts: yes
tasks:
-
name: Get hostname
debug:
msg:
-
"{{ansible_hostname}}"
-
"{{inventory_hostname}}"
2
查看执行结果
#
ansible-playbook system_info.yml
第 7 章
Playbook文件复用
1.include
& import区别
include*(动态):在运行时导入
• --list-tags,--list-tasks不会显示到输出
• 不能使用notify触发来自include*内处理程序名称(handlers)
import*(静态):在Playbook解析时预先导入
• 不能与循环一起使用
• 将变量用于目标文件或角色名称时,不能使用inventory(主机/主机组等)中的变量
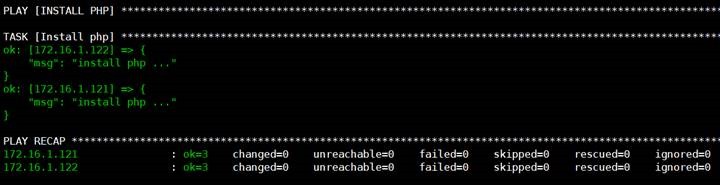
2.import_playbook
1
# cat lnmp.yml
---
-
import_playbook: nginx.yml
-
import_playbook: mysql.yml
-
import_playbook: php.yml
2
# cat nginx.yml
---
-
name: INSTALL NGINX
hosts: webservers
gather_facts: no
tasks:
-
name: Install nginx
debug: msg="install nginx ..."
3
# cat mysql.yml
---
-
name: INSTALL MYSQL
hosts: webservers
gather_facts: no
tasks:
-
name: Install mysql
debug: msg="install mysql ..."
4
# cat php.yml
---
-
name: INSTALL PHP
hosts: webservers
gather_facts: no
tasks:
-
name: Install php
debug: msg="install php ..."
5
查看执行结果
#
ansible-playbook lnmp.yml

6
补充
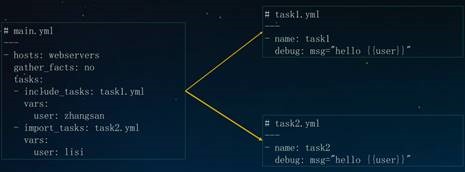
3.include tasks& import
tasks
1
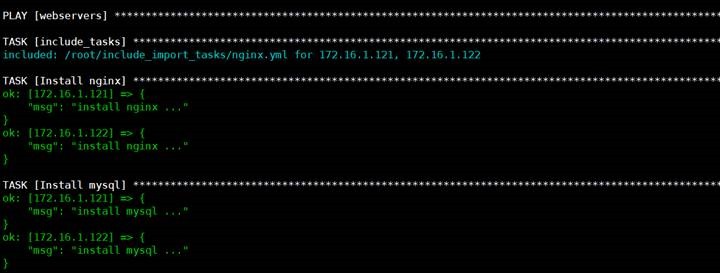
# cat lnmp.yml
---
-
hosts: webservers
gather_facts: no
tasks:
-
include_tasks: nginx.yml
vars:
name: nginx
-
import_tasks: mysql.yml
vars:
name: mysql
-
import_tasks: php.yml
vars:
name: php
2
# cat nginx.yml
---
-
name: Install nginx
debug: msg="install {{name}} ..."
3
# cat mysql.yml
---
-
name: Install mysql
debug: msg="install {{name}} ..."
4
# cat php.yml
---
-
name: Install php
debug: msg="install {{name}} ..."
5
查看执行结果
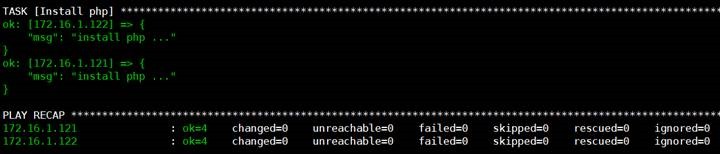
6
补充
第 8 章
Playbook流程控制
1.条件
1
playbook文件
#
cat condition.yml
---
-
hosts: webservers
gather_facts: yes
tasks:
-
name: Host 172.16.1.121 run this task
debug:
msg="{{ansible_default_ipv4.address}}"
when: ansible_default_ipv4.address ==
'10.0.0.121'
-
name: Update apache version - yum
yum: name=httpd state=present
when: ansible_pkg_mgr == 'yum'
notify: restart httpd
-
name: Update apache version - apt
apt: name=apache2 state=present
update_cache=yes
when: ansible_pkg_mgr == 'apt'
notify: restart apache2
-
name: shut down CentOS 7 and Debian 7 systems
command: echo "hello"
when: (ansible_distribution == "CentOS" and
ansible_distribution_major_version == "7") or
(ansible_distribution == "Debian"
and ansible_distribution_major_version == "7")
-
name: shut down CentOS 7 systems
command: echo "hello"
when:
- ansible_distribution ==
"CentOS"
- ansible_distribution_major_version
== "7"
handlers:
-
name: restart httpd
service: name=httpd state=restared
-
name: restart apache2
service: name=apache2 state=restared
2
查看运行结果
#
ansible-playbook condition.yml
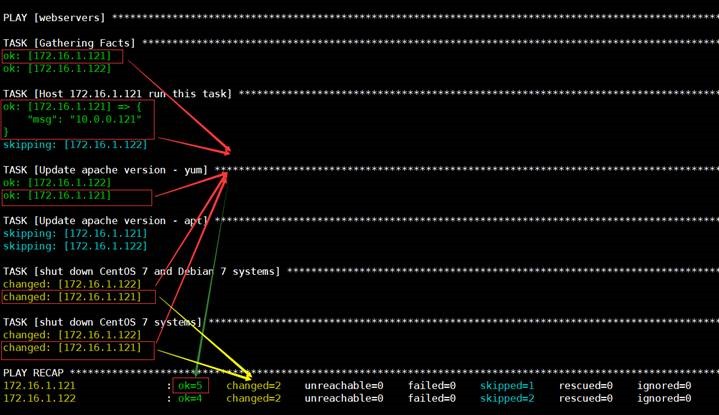
2.循环
1
playbook文件
#
cat cycle.yml
---
-
hosts: webservers
gather_facts: no
tasks:
-
name: with_list
debug: msg="{{item}}"
with_list:
- one
- two
-
name: with_list -> loop
user: name={{item}} state=present
loop:
- wangwu
- zhaoliu
-
name: with_items
user: name={{item.name}} group={{item.groups}}
state=present
with_items:
- {name: 'zhangsan', groups:
'nginx'}
- {name: 'lisi', groups:
'nginx'}
2
查看运行结果
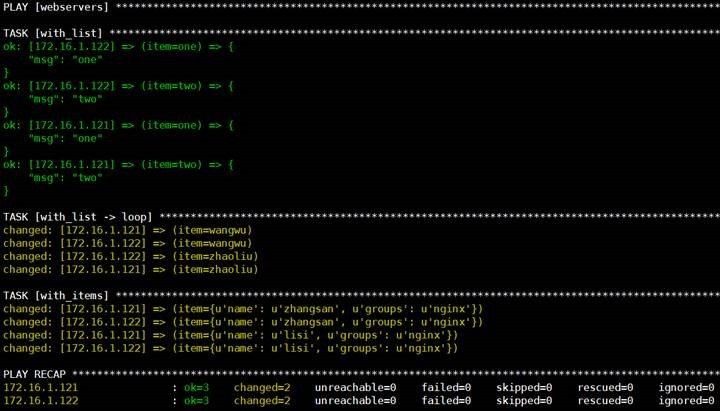
第 9 章
Playbook模板(jinja2)
1.条件和循环
1
playbool文件
#
cat jinja2.yml
-
hosts: webservers
gather_facts: no
vars:
hello: Ansible
tasks:
-
template: src=f.j2 dest=/tmp/f.j2
2模板文件
#
cat f.j2
#########List_Loop#########
{%
set list=['one', 'two', 'three'] %}
{%
for i in list %}
{% if
i == 'two' %}
->
two
{%
elif loop.index == 1 %}
->
one
{%
else %}
{{i}}
{%
endif %}
{%
endfor %}
######Group_Vars###########
{{
http_port }}
{{
server_name }}
########Dict_Loop##########
{%
set dict={'zhangsan': '26', 'lisi': '25'} %}
{%
for key, value in dict.iteritems() %}
{{key}} -> {{value}}
{%
endfor %}
2.案例:管理Nginx配置文件
1
playbool文件
[root@controlnode
~]# cat /root/ansible_yml/jinja2_nginx/main.yml
---
-
hosts: webservers
gather_facts: no
vars:
http_port:
80
server_name:
www.changliu.com
tasks:
-
name: Copy nginx configuration file
template: src=site.conf.j2
dest=/etc/nginx/conf.d/site.conf
notify: reload nginx
handlers:
-
name: reload nginx
service: name=nginx state=reloaded
2
模板文件
[root@controlnode
~]# cat /root/ansible_yml/jinja2_nginx/site.conf.j2
{%
set list=[10, 11, 12, 13, 14] %}
upstream
{{ server_name }} {
{%
for i in list %}
server 172.16.1.{{ i
}}:8080;
{%
endfor %}
}
server
{
listen {{
http_port }};
server_name {{ server_name }};
location
/ {
proxy_pass http://{{ server_name
}};
}
}
3
查看执行结果
[root@controlnode ~]#
ansible-playbook /root/ansible_yml/jinja2_nginx/main.yml
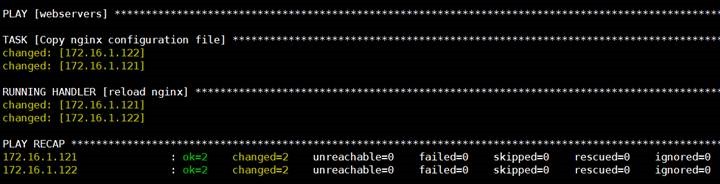
4
在被管理主机上查看结果
[root@slavenode1
~]# cat /etc/nginx/conf.d/site.conf
upstream
www.changliu.com {
server
172.16.1.10:8080;
server
172.16.1.11:8080;
server
172.16.1.12:8080;
server
172.16.1.13:8080;
server
172.16.1.14:8080;
}
server
{
listen 80;
server_name www.changliu.com;
location
/ {
proxy_pass
http://www.changliu.com;
}
}
第 10 章 角色(roles)
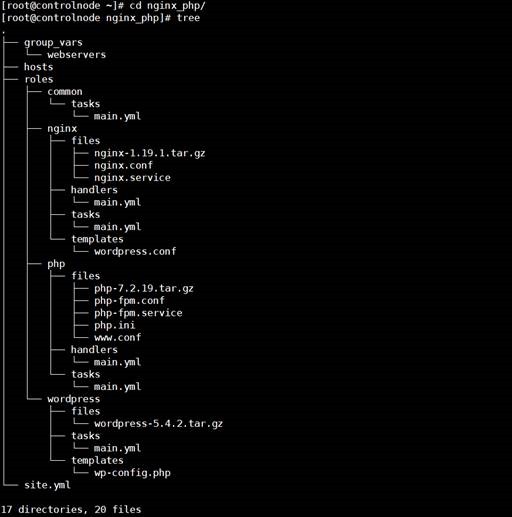
1.Roles目录结构
site.yml # role 执行的入口,是一个playbook文件,定义了要执行的roles所在的目录
hosts # 远程主机组
group_vars/ # 主机组变量
roles/
common/ #
存放公共角色的目录
tasks/
handlers/
files/
templates/
vars/
defaults/
meta/
webservers/#
存放指定角色目录
tasks/
defaults/
meta/
tasks # 包含角色要执行的主要任务列表,必须包含一个main.yml文件。
handlers # 包含角色使用的处理程序,必须包含一个main.yml文件。
defaults # 角色默认的变量
vars # 角色其他的变量
files # 角色部署时用到的文件
templates # 角色部署时用到的模板(jinja2)
meta # 角色定义的一些元数据
2.Roles基本使用
示例一:
---
-
hosts: webservers
roles:
-
common
-
nginx
-
php
示例二:
---
-
hosts: webservers
roles:
-
common
-
role: nginx
vars:
dir: '/opt/a'
app_port: 5000
-
role: php
vars:
dir: '/opt/b'
app_port: 5001
示例三:
---
-
hosts: webservers
roles:
-
role: common
tags: ["common"]
-
role: nginx
tags: ["nginx"]
-
role: php
tags: ["php"]
3 使用roles部署nginx_php_wordpress环境
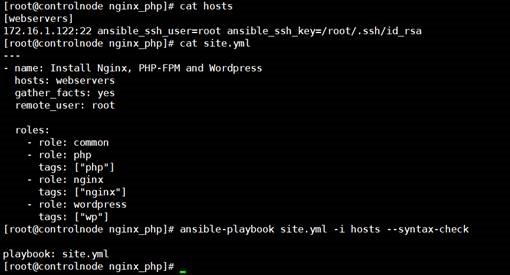
(1)
roles 目录结构
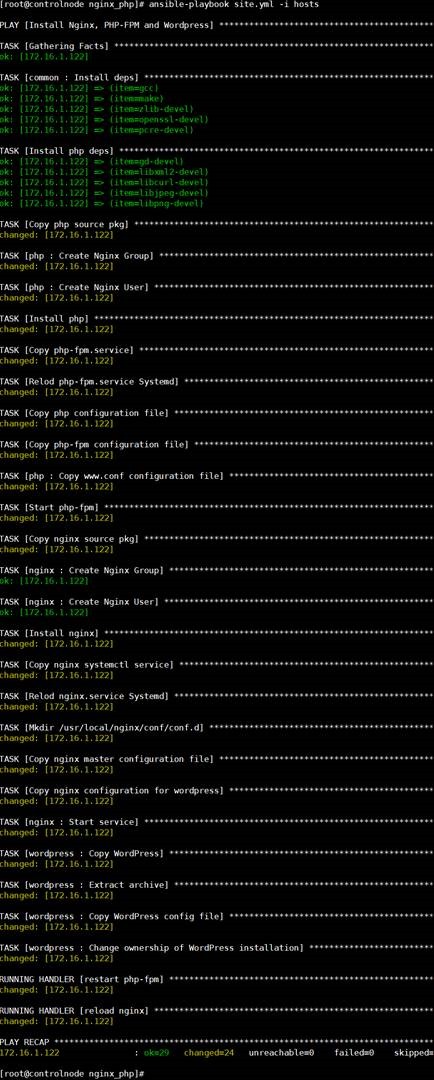
(1)
执行roles
(2)
第二次执行roles
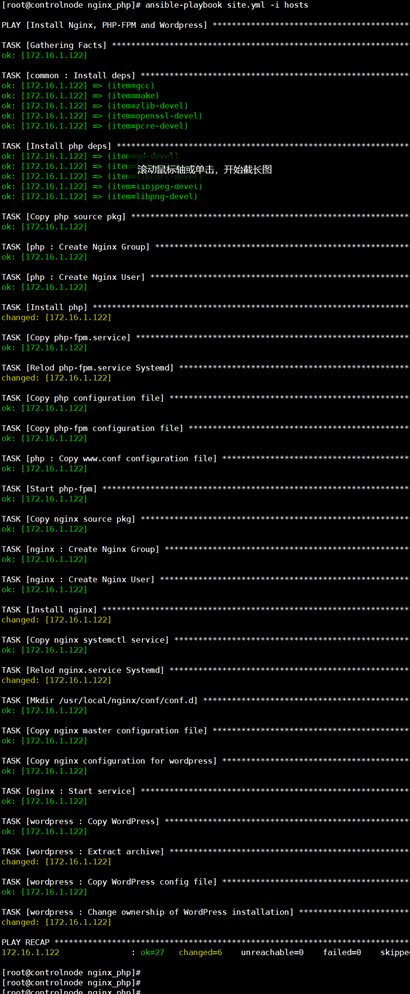
最佳实践:https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/userguide/playbooksbest_practices.html
示例参考:https://github.com/ansible/ansible-examples
3.补充
(1)
ansiable使用roles的作用
1)
一键部署所需要的项目;
2)
可以将配置打包分享给其他人使用,被分享的人也可以做到一键部署;
3)
roles的目录是已经约定好的,很容易维护和管理。
(2)
ansible软件输出颜色说明
1)
绿色信息: 查看主机信息/对主机未做改动
2)
黄色信息: 对主机数据信息做了修改
3)
红色信息: 命令执行出错了
4)
粉色信息: 忠告信息
5)
蓝色信息: 显示ansible命令执行的过程
第11章批量部署zabbix-aget
1 playbook脚本
#
cat zabbix_agent.yml
---
-
hosts: webservers
gather_facts: yes
vars:
zabbix_server:
10.0.0.120
tasks:
-
name: Copy zabbix agent - CentOS6
# yum:
name=https://repo.zabbix.com/zabbix/4.0/rhel/6/x86_64/zabbix-agent-4.0.0-2.el6.x86_64.rpm
state=present
copy: src=zabbix-agent-4.0.23-1.el6.x86_64.rpm
dest=/tmp
when: ansible_distribution == "CentOS" and
ansible_distribution_major_version == "6"
-
name: Copy zabbix agent - CentOS7
# yum:
name=https://repo.zabbix.com/zabbix/4.0/rhel/7/x86_64/zabbix-agent-4.0.0-2.el7.x86_64.rpm
state=present
copy: src=zabbix-agent-4.0.23-1.el7.x86_64.rpm
dest=/tmp
when: ansible_distribution == "CentOS" and
ansible_distribution_major_version == "7"
-
name: Install zabbix agent - CentOS6
yum:
name=/tmp/zabbix-agent-4.0.23-1.el6.x86_64.rpm state=present
when: ansible_distribution == "CentOS" and
ansible_distribution_major_version == "6"
-
name: Install zabbix agent - CentOS7
yum: name=/tmp/zabbix-agent-4.0.23-1.el7.x86_64.rpm
state=present
when: ansible_distribution == "CentOS" and
ansible_distribution_major_version == "7"
-
name: Copy zabbix agent configuration file
template: src=zabbix_agentd.conf.j2
dest=/etc/zabbix/zabbix_agentd.conf
notify:
- restart
zabbix-agent
-
name: Start zabbix agent
service: name=zabbix-agent state=started
enabled=true
handlers:
-
name: restart zabbix-agent
service: name=zabbix-agent
state=restarted
2 jinja2文件
#
cat zabbix_agentd.conf.j2
PidFile=/var/run/zabbix/zabbix_agentd.pid
LogFile=/var/log/zabbix/zabbix_agentd.log
LogFileSize=0
DebugLevel=3
EnableRemoteCommands=0
Server={{
zabbix_server }}
ListenPort=10050
ListenIP={{
ansible_default_ipv4.address }}
StartAgents=3
ServerActive={{
zabbix_server }}
Hostname={{
ansible_default_ipv4.address }}
HostnameItem=system.hostname
HostMetadata=linux
HostMetadataItem=system.uname
RefreshActiveChecks=120
BufferSend=5
BufferSize=100
MaxLinesPerSecond=20
Timeout=30
AllowRoot=0
User=zabbix
Include=/etc/zabbix/zabbix_agentd.d/*.conf
Ansible自动化运维应用实战的更多相关文章
- Python+Django+ansible playbook自动化运维项目实战☝☝☝
Python+Django+ansible playbook自动化运维项目实战☝☝☝ 一.入门引导 DevOPSDevOps(英文Development和Operations的组合)是一组过程.方法 ...
- Python+Django+ansible playbook自动化运维项目实战✍✍✍
Python+Django+ansible playbook自动化运维项目实战 整个课程都看完了,这个课程的分享可以往下看,下面有链接,之前做java开发也做了一些年头,也分享下自己看这个视频的感受 ...
- Python+Django+Ansible Playbook自动化运维项目实战
Python+Django+AnsiblePlaybook自动化运维项目实战 整个课程都看完了,这个课程的分享可以往下看,下面有链接,之前做java开发也做了一些年头,也分享下自己看这个视频的感受,单 ...
- Ansible自动化运维工具-上
[Ansible特点] 1)Ansible与saltstack均是基于Python语言开发的 2)安装使用简单,基于不同插件和模块实现各种软件,平台,版本的管理以及支持虚拟容器多层级的部署 3)不需要 ...
- ansible 自动化运维
Ansible 自动化运维 ansible安装epel #yum list all *ansible*#yum install *ansible*#yum info ansible#rpm -ql a ...
- Ansible 自动化运维工具
Ansible 自动化运维工具 Ansible是什么? Ansible是一个"配置管理工具"也是一个"自动化运维工具" Ansible 作用: Ansible是 ...
- ansible自动化运维03
ansible自动化运维常用模块 常用模块实现的功能:安装软件包:修改配置文件:创建程序用户组:创建目录,并修改所属和权限:挂载:启动服务:测试. command模块: shell模块: 注意:com ...
- 简单聊一聊Ansible自动化运维
一.Ansible概述 Ansible是今年来越来越火的一款开源运维自动化工具,通过Ansible可以实现运维自动化,提高运维工程师的工作效率,减少人为失误.Ansible通过本身集成的非常丰富的模块 ...
- Ansible自动化运维工具的使用
Ansible自动化运维工具的使用 host lnventory 管理主机 ip root账号密码 ssh端口 core mod ...
随机推荐
- mysql有关配置
mysql有关配置 mysql安装 mysql安装方式有三种 源代码:编译安装 二进制格式的程序包:展开至特定路径,并经过简单配置后即可使用 程序包管理器管理的程序包: rpm:有两种 OS Vend ...
- H5开发基础之像素、分辨率、DPI、PPI
H5开发基础之像素.分辨率.DPI.PPI html5 阅读约 4 分钟 2016-09-03于坝上草原 背景知识: 目前绝大部分显示器都是基于点阵的,通过一系列的小点排成一个大矩形,通过每个小 ...
- 怎么样在同一个word文件中删除不同节数的页眉
1.双击页眉,进入页眉编辑状态2.选择准备删除页眉的节,直接额删除即可.注意:为不至于因该节的改动影响其他节的页眉,需要在页眉设置上,每节都要取消链接到前一节页眉 把那张的前面和后面都插入分隔符,在页 ...
- 运维常用shell脚本一(系统指标巡检、自动创建用户、跳板机)
一.系统指标巡检脚本 #!/bin/bash menu(){ cat <<EOF +---------------------------------------------+ | 日常巡 ...
- linux服务之NFS服务篇
一.概念 NFS(Network File Server) 网络文件系统(映射).网络文件系统是FreeBSD支持的文件系统中的一种,也被称为NFS: NFS允许一个系统在网络上与他人共享目录和文件. ...
- 危险!水很深,让叔来 —— 谈谈命令查询权责分离模式(CQRS)
多年以前,那时我正年轻,做技术如鱼得水,甚至一度希望自己能当一辈子的一线程序员. 但是我又有两个小愿望想要达成:一个是想多挣点钱:另一个就是对项目的技术栈和架构选型能多有点主动权. 多挣点钱是因为当时 ...
- [论文阅读笔记] Unsupervised Attributed Network Embedding via Cross Fusion
[论文阅读笔记] Unsupervised Attributed Network Embedding via Cross Fusion 本文结构 解决问题 主要贡献 算法原理 实验结果 参考文献 (1 ...
- Go基础结构与类型04---基本数据类型
package main import "fmt" func main() { //整型 var a byte = 123 var b rune = 123 var c int = ...
- 3D Cube计算引擎加速运算
3D Cube计算引擎加速运算 华为达芬奇架构的AI芯片Ascend910,同时与之配套的新一代AI开源计算框架MindSpore. 为什么要做达芬奇架构? AI将作为一项通用技术极大地提高生产力,改 ...
- OFRecord 图片文件制数据集
OFRecord 图片文件制数据集 在 OFRecord 数据格式 和 加载与准备 OFRecord 数据集 中,分别学习了 OFRecord 数据格式,以及如何将其它数据集转为 OFRecord 数 ...
