JavaWeb_(Spring框架)Spring中的aop事务
1、事务相关知识
a)什么是事务:把多条数据库操作捆绑到一起执行,要么都成功,要么都失败;
b)事务的原则ACID:
i.原子性:事务包含的所有操作,要么全部成功,要么全部失败回滚,成功全部应用到数据库,失败不能对数据库有任何影响;
ii.一致性:事务在执行前和执行后必须一致;例如A和B一共有100块钱,无论A、B之间如何转账,他们的钱始终相加都是100;
iii.隔离性:多用户并发访问同一张表时,数据库为每一个用户开启新的事务,该事务不能被其他事务所影响,相互有隔离;
iv.持久性:一个事务一旦提交,则对数据库中数据的改变是永久的,即便系统故障也不会丢失;
c)并发可能引起的问题:
i.脏读:一个事务读取到另一个事务未提交的数据;
ii.不可重复读:一个事务读取到另一个事务已提交(Update操作)的数据,导致前后读取不一致;
iii.幻读(虚读):一个事务中读取到别的事务插入(Insert操作)的数据,导致前后读取不一致;
d)事务的隔离级别:根据实际情况选择;
i.Serializable串行化:可避免脏读、不可重复读和幻读;
ii.Repeatable read可重复读:可避免脏读、不可重复读;(MySql默认值)
iii.Read committed读已提交:可避免脏读;
iv.Read uncommitted读未提交:任何情况都无法保证;
2、Spring-aop事务
a)事务基本操作:打开事务、提交事务、回滚事务;
b)Spring中利用接口来管理不同框架的事务操作;
i.通过实现PlatformTransactionManager接口支持不同的框架完成各自的事务处理;
ii.为不同平台提供对应的事务管理器的实现:JDBC&Mybatis:DataSourceTransactionManager;
c)Spring-aop事务通过配置事务的隔离级别、事务传播行为、是否只读来操作;
i.隔离级别:串行化、可重复读、读已提交、读未提交;
ii.是否只读:
1.true:不可改变数据库中的数据,查询操作推荐,
2.false:可以改变数据库数据;
iii.事务传播行为:事务方法嵌套调用的规则:
xService.x(); -> yService.y();
1.REQUIRED:如果当前没有事务,就创建一个新事务,如果当前存在事务,就加入该事务,该设置是最常用的设置;
2.REQUIRES_NEW:创建新事务,无论当前存不存在事务,都创建新事务;
3.SUPPORTS:支持当前事务,如果当前存在事务,就加入该事务,如果当前不存在事务,就以非事务执行;
4.NOT_SUPPORTED:以非事务方式执行操作,如果当前存在事务,就把当前事务挂起(暂停);
5.MANDATORY:支持当前事务,如果当前存在事务,就加入该事务,如果当前不存在事务,就抛出异常;
6.NEVER:以非事务方式执行,如果当前存在事务,则抛出异常;
7.NESTED:如果当前存在事务,则在嵌套事务内执行。如果当前没有事务,则执行与REQUIRED类似的操作。
3、Spring-aop事务 – 从麻烦的事务代码中走出之xml配置版aop事务;
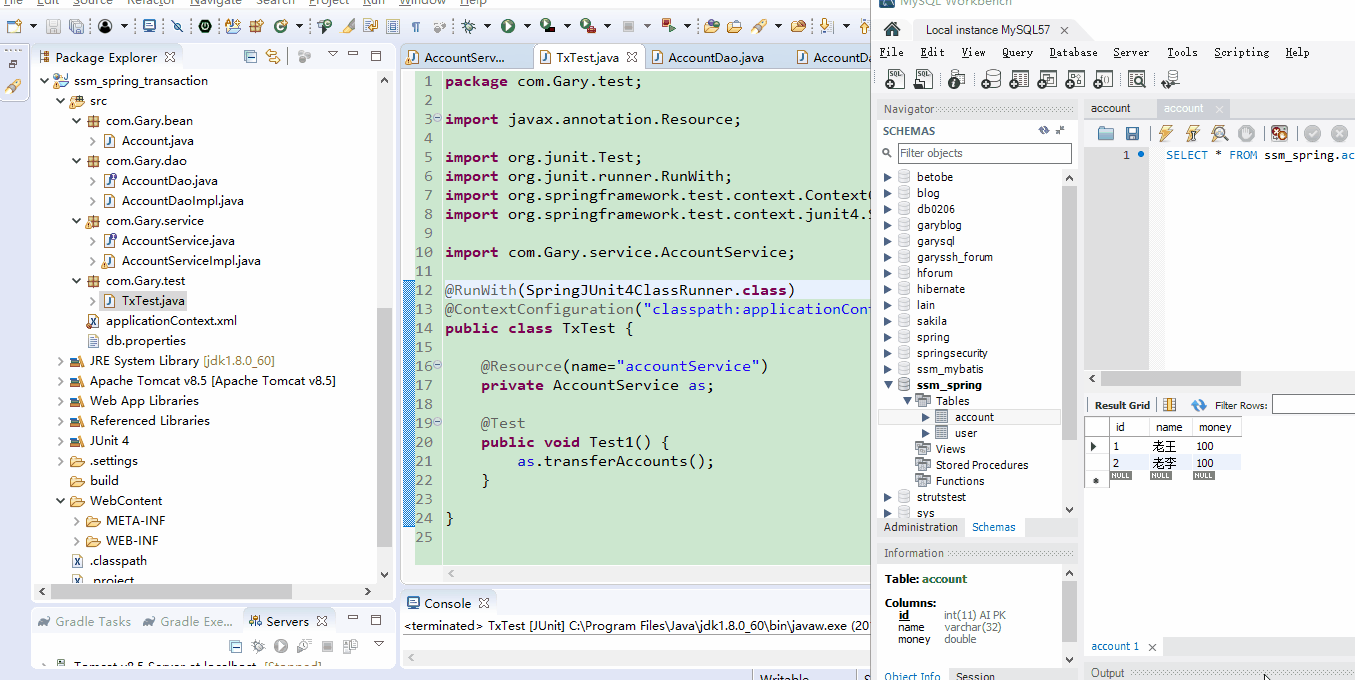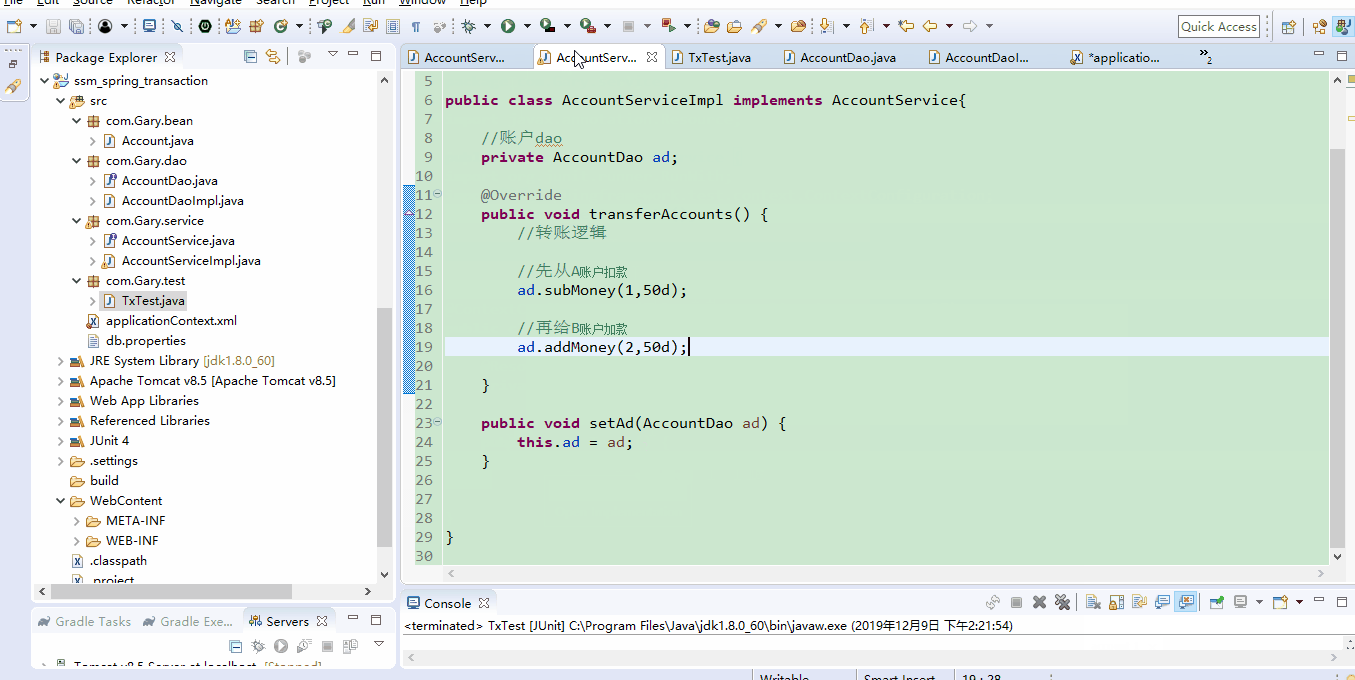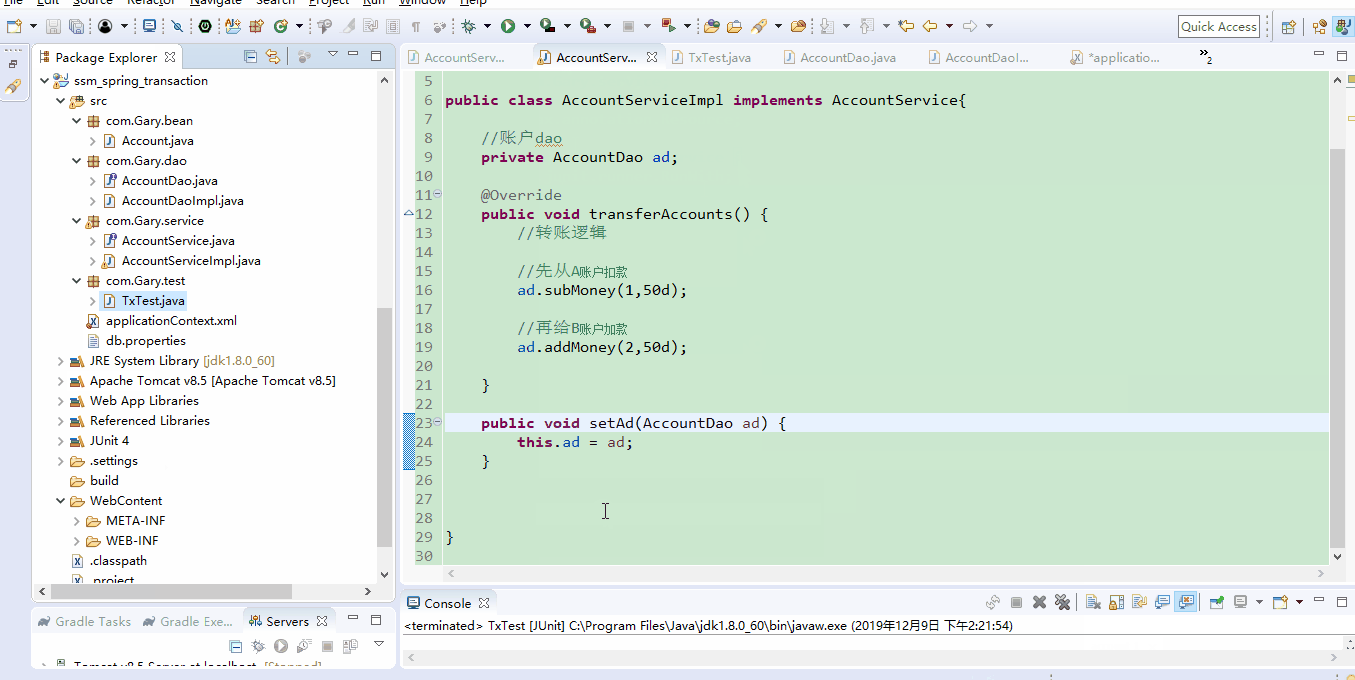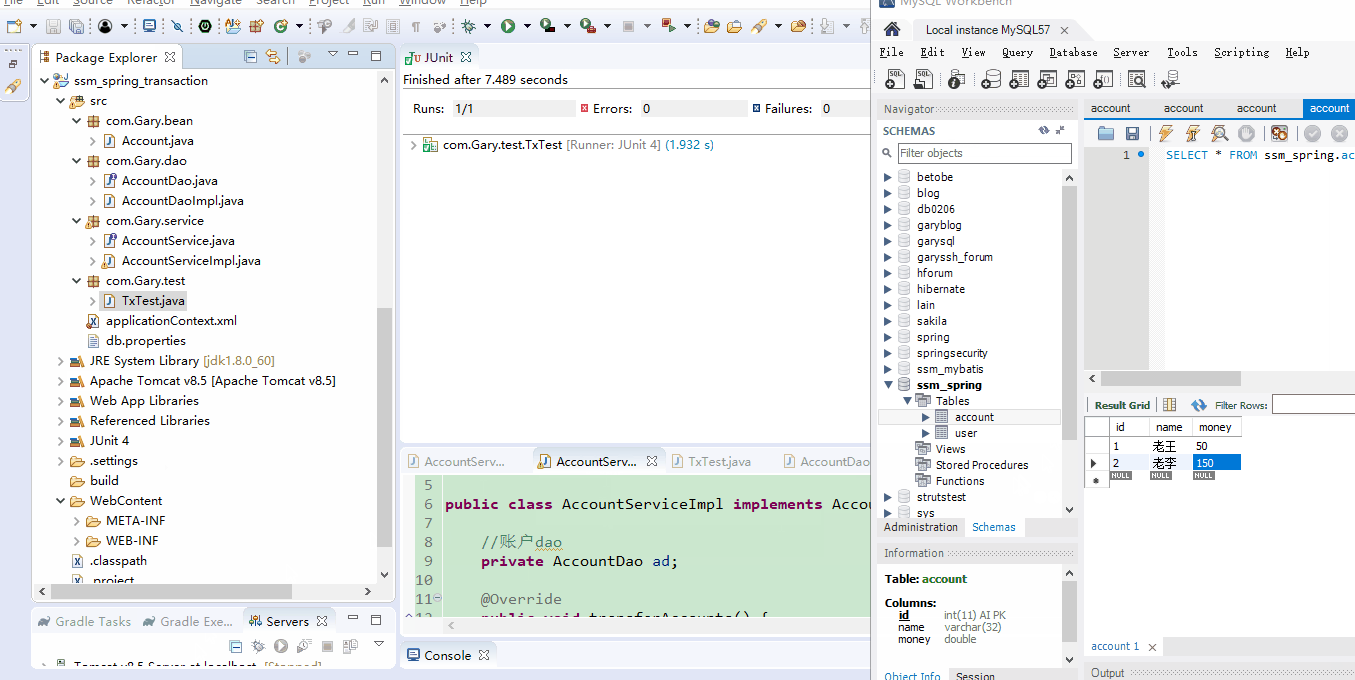
a)使用经典的转账案例进行测试,准备数据:bean、service、dao;
数据库account表中添加三个字段,并添加两条叫数据

实现老王(A)向老李(B)转账操作,AccountServiceImpl.java中实现转账操作
@Override
public void transferAccounts() {
//转账逻辑 //先从A账户扣款
ad.subMoney(1,50d); //再给B账户加款
ad.addMoney(2,50d);
}
package com.Gary.bean;
public class Account {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Double money;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Double getMoney() {
return money;
}
public void setMoney(Double money) {
this.money = money;
}
}
Account.java
package com.Gary.dao;
public interface AccountDao {
//扣款
void subMoney(Integer i, Double d);
//加款
void addMoney(Integer i, Double d);
}
AccountDao.java
package com.Gary.dao;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.support.JdbcDaoSupport;
public class AccountDaoImpl extends JdbcDaoSupport implements AccountDao {
@Override
public void subMoney(Integer id, Double money) {
String sql = "update account set money = money - ? where id = ?";
getJdbcTemplate().update(sql,money,id);
}
@Override
public void addMoney(Integer id, Double money) {
String sql = "update account set money = money + ? where id = ?";
getJdbcTemplate().update(sql,money,id);
}
}
AccountDaoImpl.java
package com.Gary.service;
public interface AccountService {
//转账接口
void transferAccounts();
}
AccountService.java
package com.Gary.service; import com.Gary.bean.Account;
import com.Gary.dao.AccountDao; public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService{ //账户dao
private AccountDao ad; @Override
public void transferAccounts() {
//转账逻辑 //先从A账户扣款
ad.subMoney(1,50d); //再给B账户加款
ad.addMoney(2,50d); } public void setAd(AccountDao ad) {
this.ad = ad;
} }
AccountServiceImpl.java
package com.Gary.test; import javax.annotation.Resource; import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner; import com.Gary.service.AccountService; @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext.xml")
public class TxTest { @Resource(name="accountService")
private AccountService as; @Test
public void Test1() {
as.transferAccounts();
} }
TxTest.java
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.3.xsd"> <!-- 依赖关系 dao -> -> dataSource -->
<!-- 读取配置文件 -->
<context:property-placeholder location="db.properties" /> <!-- 配置 dataSource -->
<bean name="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driverClass}" />
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.jdbcUrl}" />
<property name="user" value="${jdbc.user}" />
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" />
</bean> <!-- dao -->
<bean name="accountDao" class="com.Gary.dao.AccountDaoImpl">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
</bean> <!-- service -->
<bean name="accountService" class="com.Gary.service.AccountServiceImpl">
<property name="ad" ref="accountDao" />
</bean> </beans>
applicationContext.xml
jdbc.driverClass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.jdbcUrl=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ssm_spring
jdbc.user=root
jdbc.password=123456
db.properties
当AccountServiceImpl.java中转账操作异常时,比如1/0
@Override
public void transferAccounts() {
//转账逻辑 //先从A账户扣款
ad.subMoney(1,50d); int a = 1/0; //再给B账户加款
ad.addMoney(2,50d); }
可以发现,老王(A)向老李(B)转账了50块钱,但因为中途发生了异常,老李没有收到,可数据库中真实扣了50块钱

package com.Gary.service; import com.Gary.bean.Account;
import com.Gary.dao.AccountDao; public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService{ //账户dao
private AccountDao ad; @Override
public void transferAccounts() {
//转账逻辑 //先从A账户扣款
ad.subMoney(1,50d); //异常
int a = 1/0; //再给B账户加款
ad.addMoney(2,50d); } public void setAd(AccountDao ad) {
this.ad = ad;
} }
AccountServiceImpl.java
b)使用事务需要额外导入tx包和tx约束;
c)配置事务核心管理器: DataSourceTransactionManager;
<!-- 配置事务核心管理器 不同平台不一样 -->
<bean name="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
d)配置事务通知 tx:Advice;
<!-- 事务通知 -->
<tx:advice id="txAdivce" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="transferAccounts" isolation="DEFAULT" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
e)配置aop;
<!-- 配置aop -->
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(* com.Gary.service.*ServiceImpl.*(..))" id="txPc"/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdivce" pointcut-ref="txPc"/>
</aop:config>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.3.xsd"> <!-- 依赖关系 dao -> -> dataSource -->
<!-- 读取配置文件 -->
<context:property-placeholder location="db.properties" /> <!-- 配置 dataSource -->
<bean name="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driverClass}" />
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.jdbcUrl}" />
<property name="user" value="${jdbc.user}" />
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" />
</bean> <!-- dao -->
<bean name="accountDao" class="com.Gary.dao.AccountDaoImpl">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
</bean> <!-- service -->
<bean name="accountService" class="com.Gary.service.AccountServiceImpl">
<property name="ad" ref="accountDao" />
</bean> <!-- 配置事务核心管理器 不同平台不一样 -->
<bean name="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean> <!-- 事务通知 -->
<tx:advice id="txAdivce" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="transferAccounts" isolation="DEFAULT" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice> <!-- 配置aop -->
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(* com.Gary.service.*ServiceImpl.*(..))" id="txPc"/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdivce" pointcut-ref="txPc"/>
</aop:config> </beans>
applicationContext.xml
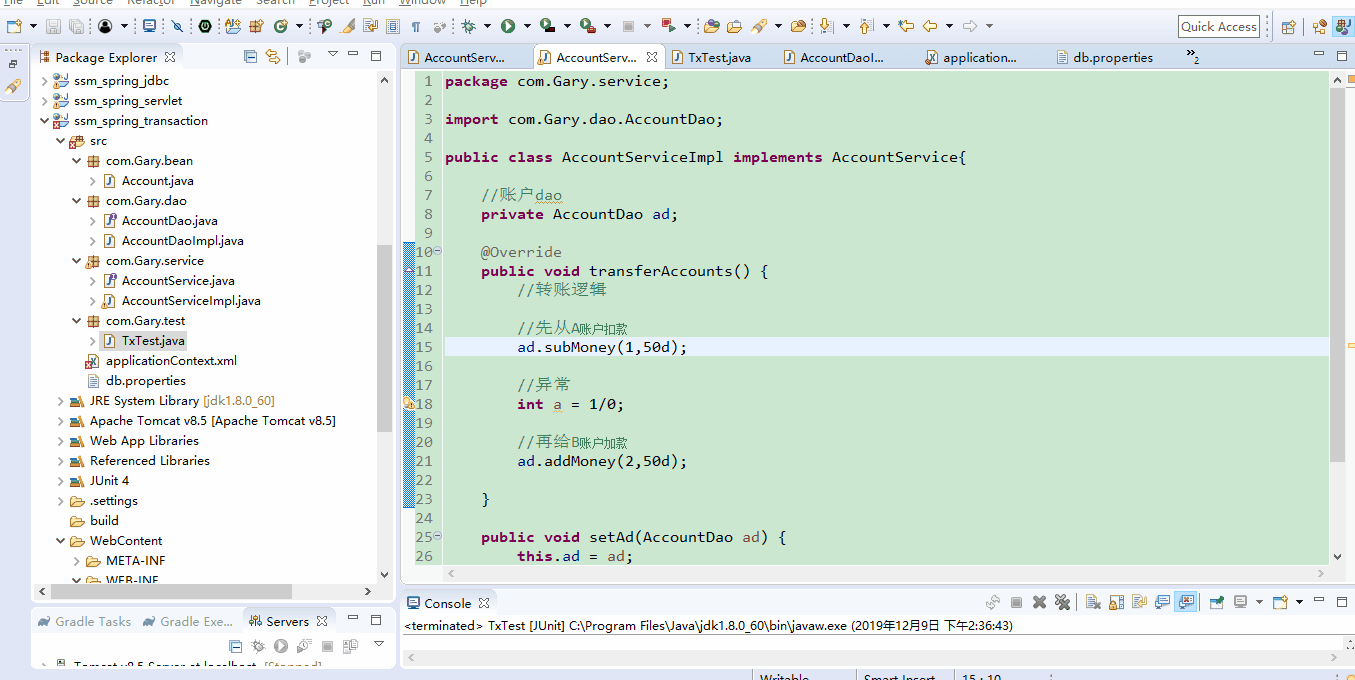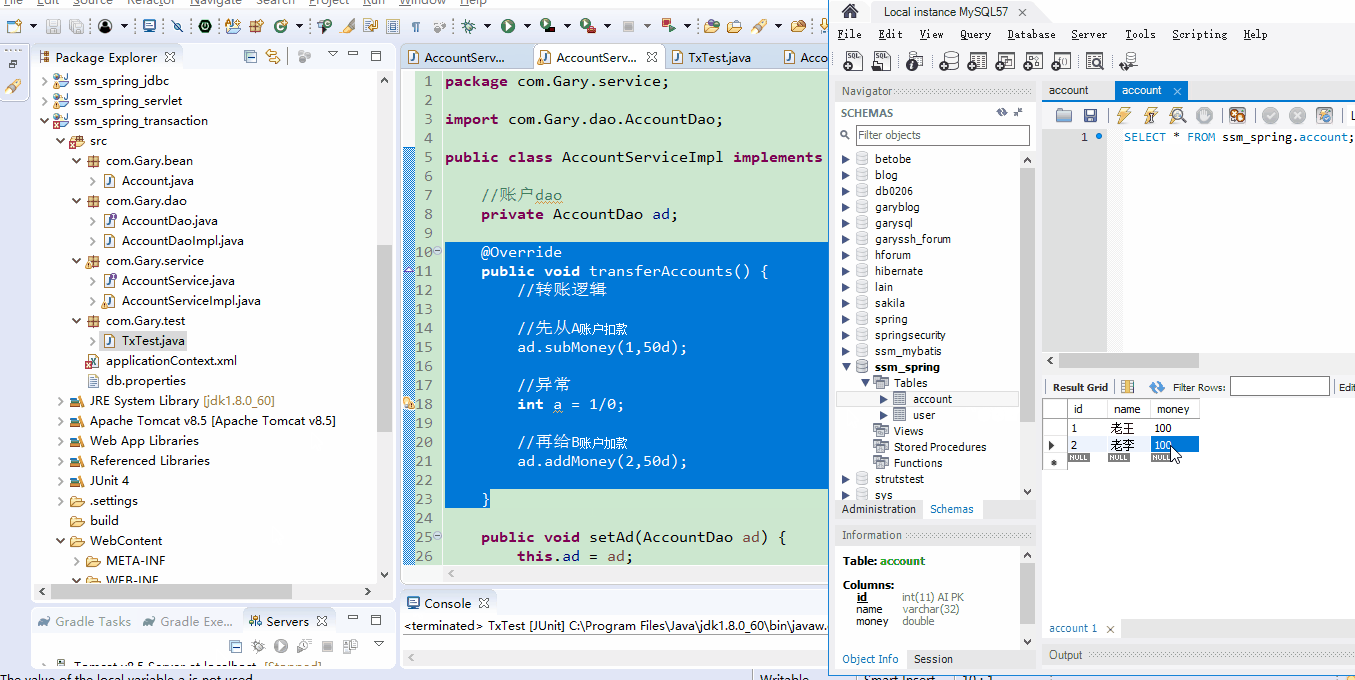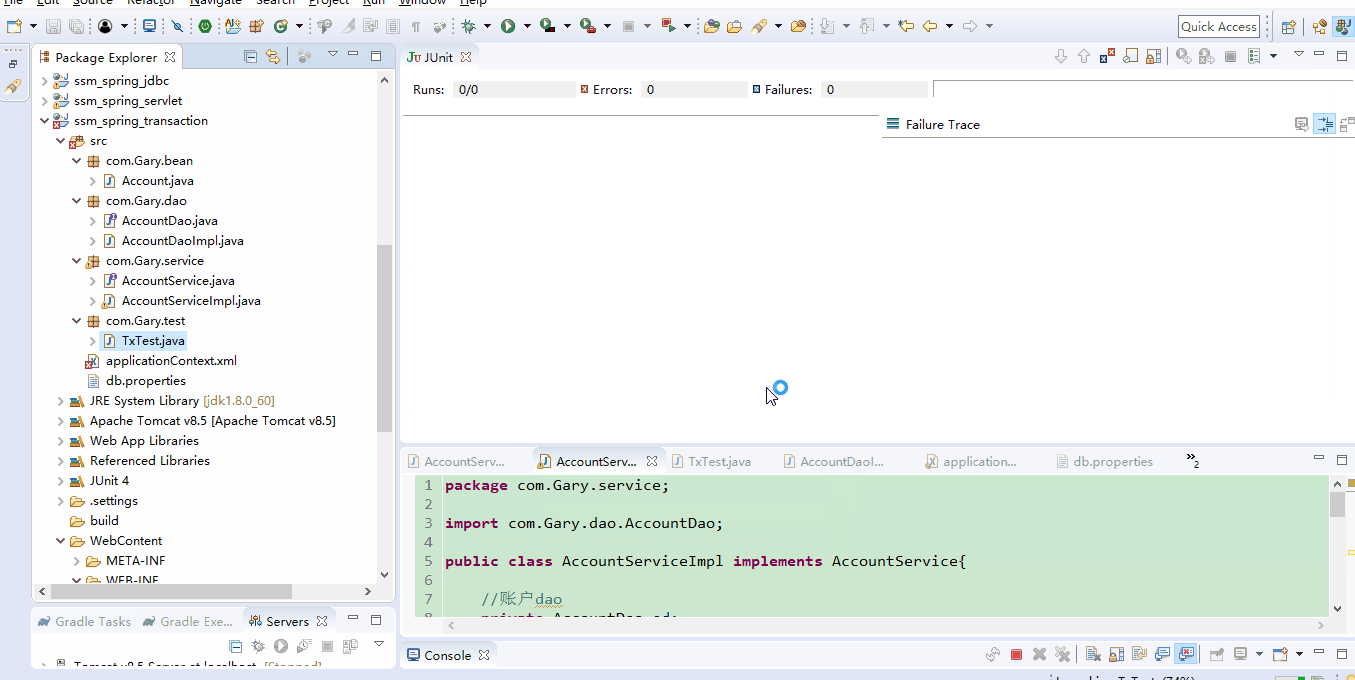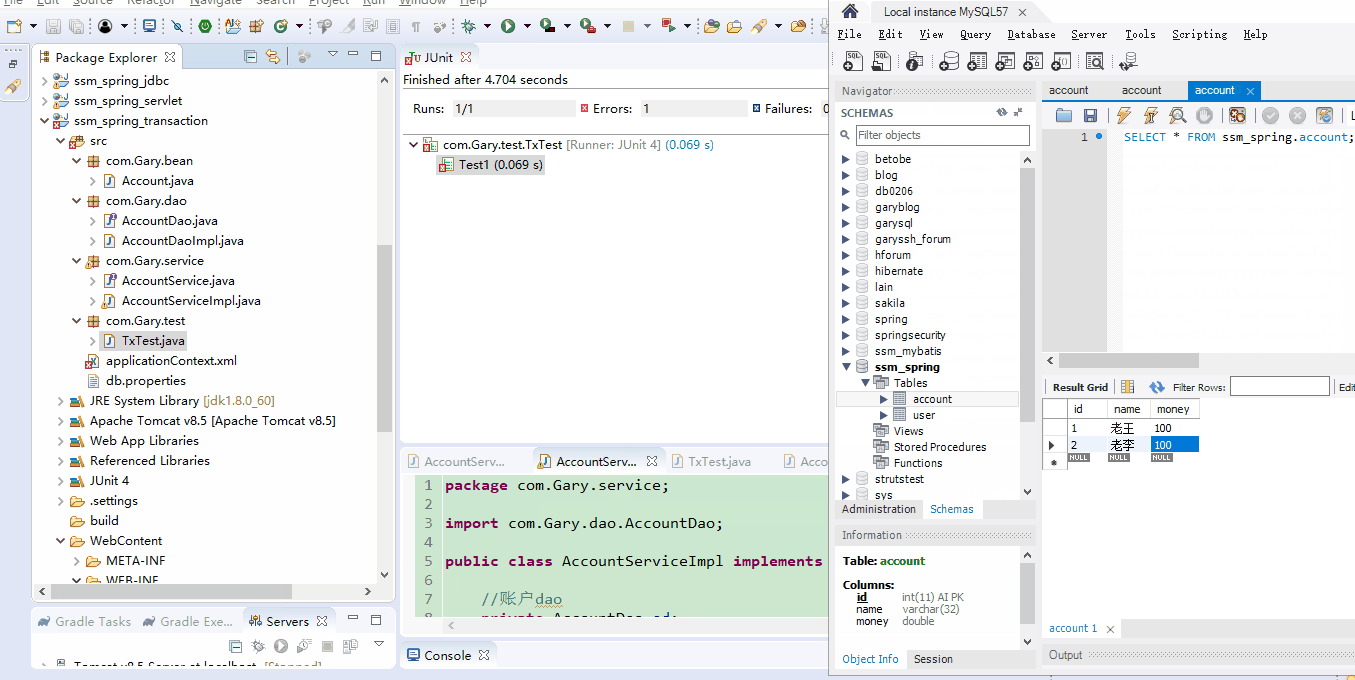
测试后发现,当A向B转账过程发生异常后,A向B转账的50块钱会进行回滚。
xml配置版事务
如果存在多个事务,可以在applicationContext.xml下进行注解配置
<!-- 事务通知 -->
<tx:advice id="txAdivce" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="transferAccounts" isolation="DEFAULT" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false"/>
<tx:method name="save*" isolation="DEFAULT" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false"/>
<tx:method name="delete*" isolation="DEFAULT" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false"/>
<tx:method name="update*" isolation="DEFAULT" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false"/>
<tx:method name="select*" isolation="DEFAULT" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="true"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
注解版事务
需要在aplicationContext.xml中开启注解事务
<!-- 开启注解事务 -->
<tx:annotation-driven/>
添加事务,只需要在方法上使用@Transactional注解
给转账事务添加注解
@Override
@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.DEFAULT,propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED,readOnly = false)
public void transferAccounts() {
//转账逻辑 //先从A账户扣款
ad.subMoney(1,50d); //异常
int a = 1/0; //再给B账户加款
ad.addMoney(2,50d); }
package com.Gary.service; import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Isolation;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Propagation;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional; import com.Gary.dao.AccountDao; public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService{ //账户dao
private AccountDao ad; @Override
@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.DEFAULT,propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED,readOnly = false)
public void transferAccounts() {
//转账逻辑 //先从A账户扣款
ad.subMoney(1,50d); //异常
int a = 1/0; //再给B账户加款
ad.addMoney(2,50d); } public void setAd(AccountDao ad) {
this.ad = ad;
} }
AccountServiceImpl.java
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.3.xsd"> <!-- 依赖关系 dao -> -> dataSource -->
<!-- 读取配置文件 -->
<context:property-placeholder location="db.properties" /> <!-- 配置 dataSource -->
<bean name="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driverClass}" />
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.jdbcUrl}" />
<property name="user" value="${jdbc.user}" />
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" />
</bean> <!-- dao -->
<bean name="accountDao" class="com.Gary.dao.AccountDaoImpl">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
</bean> <!-- service -->
<bean name="accountService" class="com.Gary.service.AccountServiceImpl">
<property name="ad" ref="accountDao" />
</bean> <!-- 配置事务核心管理器 不同平台不一样 -->
<bean name="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean> <!-- 事务通知 -->
<tx:advice id="txAdivce" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="transferAccounts" isolation="DEFAULT" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false"/>
<tx:method name="save*" isolation="DEFAULT" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false"/>
<tx:method name="delete*" isolation="DEFAULT" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false"/>
<tx:method name="update*" isolation="DEFAULT" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false"/>
<tx:method name="select*" isolation="DEFAULT" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="true"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice> <!-- 配置aop -->
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(* com.Gary.service.*ServiceImpl.*(..))" id="txPc"/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdivce" pointcut-ref="txPc"/>
</aop:config> <!-- 开启注解事务 -->
<tx:annotation-driven/> </beans>
applicationContext.xml
JavaWeb_(Spring框架)Spring中的aop事务的更多相关文章
- Spring框架IOC容器和AOP解析 非常 有用
Spring框架IOC容器和AOP解析 主要分析点: 一.Spring开源框架的简介 二.Spring下IOC容器和DI(依赖注入Dependency injection) 三.Spring下面 ...
- [Spring框架]Spring AOP基础入门总结二:Spring基于AspectJ的AOP的开发.
前言: 在上一篇中: [Spring框架]Spring AOP基础入门总结一. 中 我们已经知道了一个Spring AOP程序是如何开发的, 在这里呢我们将基于AspectJ来进行AOP 的总结和学习 ...
- 跟着刚哥学习Spring框架--Spring容器(二)
Spring容器 启动Spring容器(实例化容器) -- IOC容器读取Bean配置创建Bean实例之前,必须对它进行实例化(加载启动),这样才可以从容器中获取Bean的实例并使用. Bean是S ...
- Spring框架 - Spring和Spring框架组成
Spring框架 - Spring和Spring框架组成 Spring是什么?它是怎么诞生的?有哪些主要的组件和核心功能呢? 本文通过这几个问题帮助你构筑Spring和Spring Framework ...
- JavaWeb_(Struts2框架)Action中struts-default下result的各种转发类型
此系列博文基于同一个项目已上传至github 传送门 JavaWeb_(Struts2框架)Struts创建Action的三种方式 传送门 JavaWeb_(Struts2框架)struts.xml核 ...
- JavaWeb_(Spring框架)Spring中IoC与DI概念入门
Spring是于2003 年兴起的一个轻量级的Java 开源框架,它由Rod Johnson创建.传统J2EE应用的开发效率低,Spring作为开源的中间件,提供J2EE应用的各层的解决方案,Spri ...
- JavaWeb_(Spring框架)Spring整合Hibernate
Dao层类要继承HibernateDaoSupport.java父类 原先使用Hibernate框架hibernate.cfg.xml配置数据库 <hibernate-configuration ...
- Spring框架IOC容器和AOP解析
主要分析点: 一.Spring开源框架的简介 二.Spring下IOC容器和DI(依赖注入Dependency injection) 三.Spring下面向切面编程(AOP)和事务管理配置 一.S ...
- spring框架学习笔记7:事务管理及案例
Spring提供了一套管理项目中的事务的机制 以前写过一篇简单的介绍事务的随笔:http://www.cnblogs.com/xuyiqing/p/8430214.html 还有一篇Hibernate ...
随机推荐
- DRF框架中链表数据通过ModelSerializer深度查询方法汇总
DRF框架中链表数据通过ModelSerializer深度查询方法汇总 一.准备测试和理解准备 创建类 class Test1(models.Model): id = models.IntegerFi ...
- Python实现定时执行任务的三种方式简单示例
本文实例讲述了Python实现定时执行任务的三种方式.分享给大家供大家参考,具体如下: 1.定时任务代码 import time,os,sched schedule = sched.scheduler ...
- 3.Redis数据类型
Redis的五大数据类型: 1.string(字符串) string是redis最基本的类型,你可以理解成与Memcached一模一样的类型,一个key对应一个value. string类型是二进制安 ...
- 【hadoop】细读MapReduce的工作原理
前言:中秋节有事外加休息了一天,今天晚上重新拾起Hadoop,但感觉自己有点烦躁,不知后续怎么选择学习Hadoop的方法. 干脆打开电脑,决定: 1.先将Hadoop的MapReduce和Yarn基本 ...
- Flutter——Expanded组件("可伸缩"组件)
Expanded组件可以结合Row和Column布局组件使用. Expanded组件的常用属性 属性 说明 flex 元素占整个父Row/Column的比例 child 子元素 import 'pac ...
- SPI、I2C、I2S
1. SPI总线 1.1 基础概念: 技术性能 SPI接口是Motorola 首先提出的全双工三线同步串行外围接口,采用主从模式(Master Slave)架构:支持多slave模式应用,一般仅支持单 ...
- Spark(二)算子详解
目录 Spark(二)算子讲解 一.wordcountcount 二.编程模型 三.RDD数据集和算子的使用 Spark(二)算子讲解 @ 一.wordcountcount 基于上次的wordcoun ...
- less避免编译
less里面有一个避免编译,有时候我们需要输出一些不正确的css语法或者使用less不认识的专有语法.要输出这样的值我们可以在字符串前加上一个~ /*避免编译*/ .test_03{ width: 3 ...
- n诺挑战赛5题解
Drinking 题意:就是给你n瓶酒的初始伤害值,第几天喝这瓶酒伤害值就是这瓶酒的初始伤害值第几倍,而且他每天喝的瓶数不超过m.要你输出所有的情况,就是他喝(1~n)瓶的伤害值的最小, 思路:就是这 ...
- 【python】使用plotly生成图表数据
安装 在 ubuntu 环境下,安装 plotly 很简单 python 版本2.7+ pip install plotly 绘图 在 plotly 网站注册后,可以直接将生成的图片保存到网站上,便于 ...
