javascript实现数据结构: 树和二叉树,二叉树的遍历和基本操作
树型结构是一类非常重要的非线性结构。直观地,树型结构是以分支关系定义的层次结构。
树在计算机领域中也有着广泛的应用,例如在编译程序中,用树来表示源程序的语法结构;在数据库系统中,可用树来组织信息;在分析算法的行为时,可用树来描述其执行过程等等。
下面讲解的内容完整代码在这:https://github.com/LukeLin/data-structure-with-js/blob/master/Binary%20tree/BinaryTree.js
首先看看树的一些概念:
1.树(Tree)是n(n>=0)个结点的有限集。在任意一棵非空树中:
(1)有且仅有一个特定的称为根(Root)的结点;
(2)当n>1时,其余结点可分为m(m>0)个互不相交的有限集T1,T2,T3,...Tm,其中每一个集合本身又是一棵树,并且称为根的子树(Subtree)。
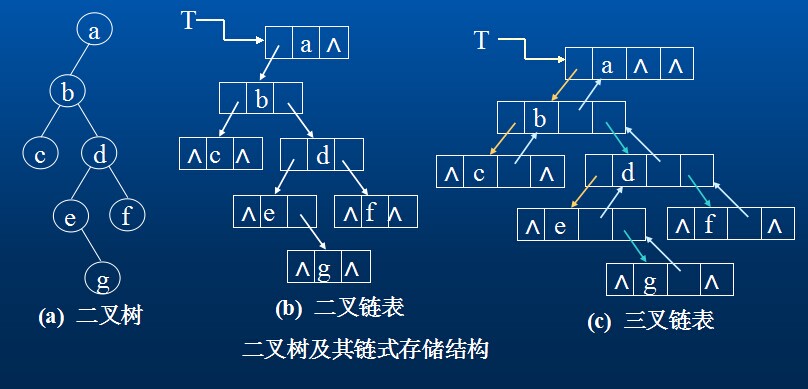
例如,(a)是只有一个根结点的树;(b)是有13个结点的树,其中A是根,其余结点分成3个互不相交的子集:T1={B,E,F,K,L},t2={D,H,I,J,M};T1,T2和T3都是根A的子树,且本身也是一棵树。
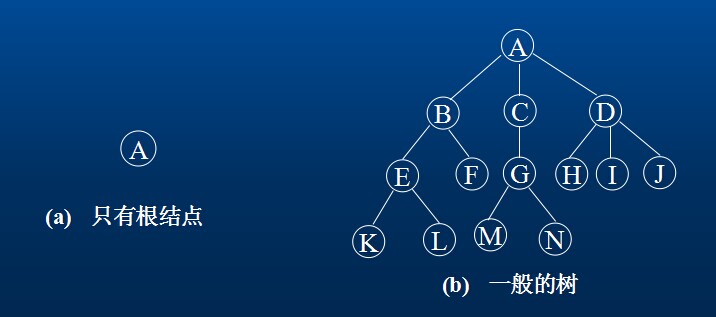
2.树的结点包含一个数据元素及若干指向其子树的分支。结点拥有的子树数称为结点的度(Degree)。例如,(b)中A的度为3,C的度为1,F的度为0.度为0的结点称为叶子(Leaf)或者终端结点。度不为0的结点称为非终端结点或分支结点。树的度是树内各结点的度的最大值。(b)的树的度为3.结点的子树的根称为该结点的孩子(Child)。相应的,该结点称为孩子的双亲(Parent)。同一个双亲的孩子之间互称兄弟(Sibling)。结点的祖先是从根到该结点所经分支上的所有结点。反之,以某结点为根的子树中的任一结点都称为该结点的子孙。
3.结点的层次(Level)从根开始定义起,根为第一层,跟的孩子为第二层。若某结点在第l层,则其子树的根就在第l+1层。其双亲在同一层的结点互为堂兄弟。例如,结点G与E,F,H,I,J互为堂兄弟。树中结点的最大层次称为树的深度(Depth)或高度。(b)的树的深度为4。
4.如果将树中结点的各子树看成从左至右是有次序的(即不能交换),则称该树为有序树,否则称为无序树。在有序树中最左边的子树的根称为第一个孩子,最右边的称为最后一个孩子。
5.森林(Forest)是m(m>=0)棵互不相交的树的集合。对树中每个结点而言,其子树的集合即为森林。
接下来看看二叉树相关的概念:
二叉树(Binary Tree)是另一种树型结构,它的特点是每个结点至多只有两棵子树(即二叉树中不存在度大于2的结点),并且,二叉树的子树有左右之分(其次序不能任意颠倒。)
二叉树的性质:
1.在二叉树的第i层上至多有2的i-1次方个结点(i>=1)。
2.深度为k的二叉树至多有2的k次方-1个结点,(k>=1)。
3.对任何一棵二叉树T,如果其终端结点数为n0,度为2的结点数为n2,则n0 = n2 + 1;
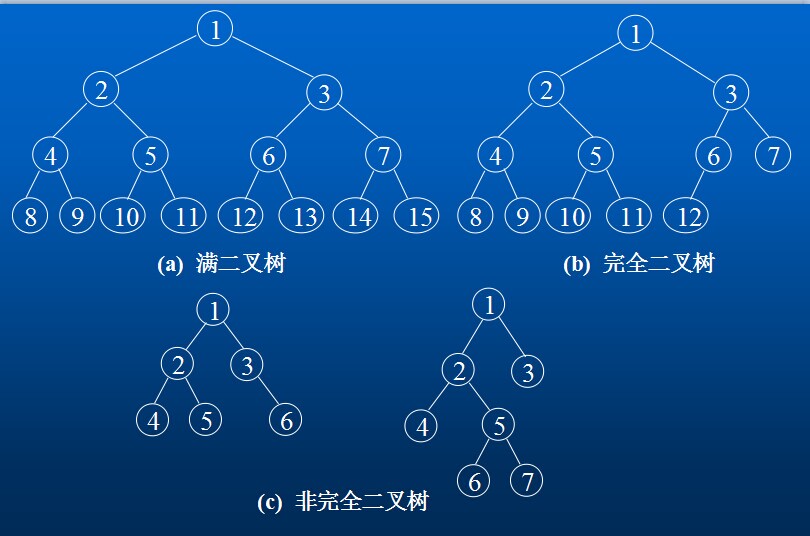
一棵深度为k且有2的k次方-1个结点的二叉树称为满二叉树。
深度为k的,有n个结点的二叉树,当且仅当其每一个结点都与深度为k的满二叉树中编号从1至n的结点一一对应时,称之为完全二叉树。
下面是完全二叉树的两个特性:
4.具有n个结点的完全二叉树的深度为Math.floor(log 2 n) + 1
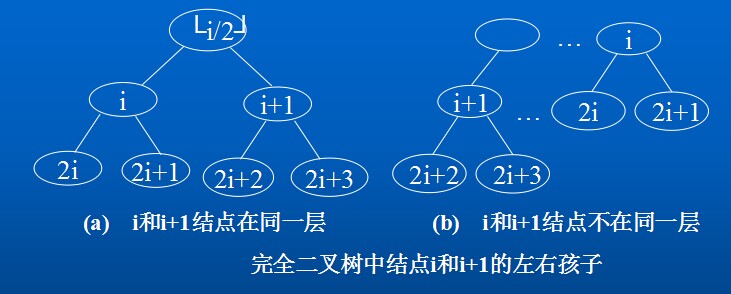
5.如果对一棵有n个结点的完全二叉树(其深度为Math.floor(log 2 n) + 1)的结点按层序编号(从第1层到第Math.floor(2 n) + 1,每层从左到右),则对任一结点(1<=i<=n)有:
(1)如果i=1,则结点i、是二叉树的根,无双亲;如果i>1,则其双亲parent(i)是结点Math.floor(i/2)。
(2)如果2i > n,则结点i无左孩子(结点i为叶子结点);否则其左孩子LChild(i)是结点2i.
(3)如果2i + 1 > n,则结点i无右孩子;否则其右孩子RChild(i)是结点2i + 1;
二叉树的存储结构
1.顺序存储结构
用一组连续的存储单元依次自上而下,自左至右存储完全二叉树上的结点元素,即将二叉树上编号为i的结点元素存储在加上定义的一维数组中下标为i-1的分量中。“0”表示不存在此结点。这种顺序存储结构仅适用于完全二叉树。
因为,在最坏情况下,一个深度为k且只有k个结点的单支树(树中不存在度为2的结点)却需要长度为2的n次方-1的一维数组。
2.链式存储结构
二叉树的结点由一个数据元素和分别指向其左右子树的两个分支构成,则表示二叉树的链表中的结点至少包含三个域:数据域和左右指针域。有时,为了便于找到结点的双亲,则还可在结点结构中增加一个指向其双亲结点的指针域。利用这两种结构所得的二叉树的存储结构分别称之为二叉链表和三叉链表。
在含有n个结点的二叉链表中有n+1个空链域,我们可以利用这些空链域存储其他有用信息,从而得到另一种链式存储结构---线索链表。
二叉树的遍历主要分三种:
先(根)序遍历:根左右
中(根)序遍历:左根右
后(根)序遍历:左右根
二叉树的顺序存储结构:
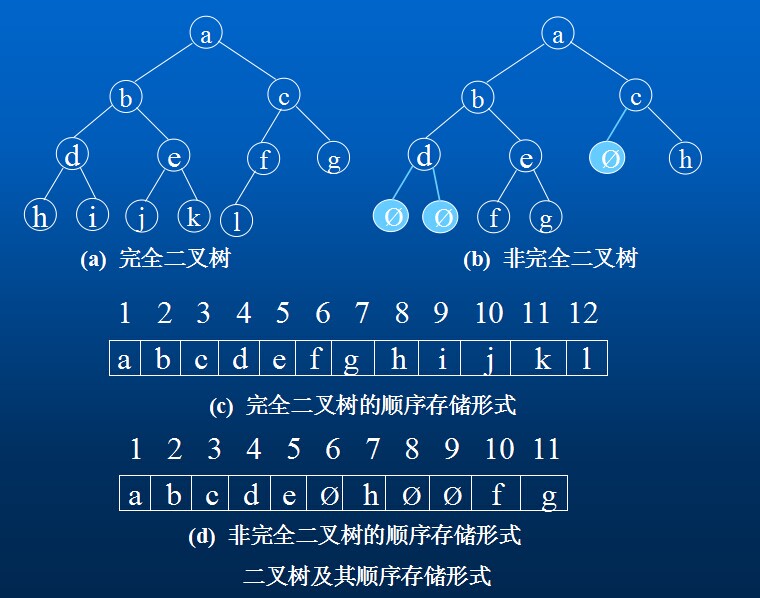
二叉树的链式存储形式:
// 顺序存储结构
var tree = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, , 6, , , 7]; // 链式存储结构
function BinaryTree(data, leftChild, rightChild) {
this.data = data || null;
// 左右孩子结点
this.leftChild = leftChild || null;
this.rightChild = rightChild || null;
}
遍历二叉树(Traversing Binary Tree):是指按指定的规律对二叉树中的每个结点访问一次且仅访问一次。
1.先序遍历二叉树
1)算法的递归定义是:
若二叉树为空,则遍历结束;否则
⑴ 访问根结点;
⑵ 先序遍历左子树(递归调用本算法);
⑶ 先序遍历右子树(递归调用本算法)。
算法实现:
// 顺序存储结构的递归先序遍历
var tree = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, , 6, , , 7]; console.log('preOrder:');
void function preOrderTraverse(x, visit) {
visit(tree[x]);
if (tree[2 * x + 1]) preOrderTraverse(2 * x + 1, visit);
if (tree[2 * x + 2]) preOrderTraverse(2 * x + 2, visit);
}(0, function (value) {
console.log(value);
}); // 链式存储结构的递归先序遍历
BinaryTree.prototype.preOrderTraverse = function preOrderTraverse(visit) {
visit(this.data);
if (this.leftChild) preOrderTraverse.call(this.leftChild, visit);
if (this.rightChild) preOrderTraverse.call(this.rightChild, visit);
};
2)非递归算法:
设T是指向二叉树根结点的变量,非递归算法是: 若二叉树为空,则返回;否则,令p=T;
(1) p为根结点;
(2) 若p不为空或者栈不为空;
(3) 若p不为空,访问p所指向的结点, p进栈, p = p.leftChild,访问左子树;
(4) 否则;退栈到p,然后p = p.rightChild, 访问右子树
(5) 转(2),直到栈空为止。
代码实现:
// 链式存储的非递归先序遍历
// 方法1
BinaryTree.prototype.preOrder_stack = function (visit) {
var stack = new Stack();
stack.push(this);
while (stack.top) {
var p;
// 向左走到尽头
while ((p = stack.peek())) {
p.data && visit(p.data);
stack.push(p.leftChild);
}
stack.pop();
if (stack.top) {
p = stack.pop();
stack.push(p.rightChild);
}
}
};
// 方法2
BinaryTree.prototype.preOrder_stack2 = function (visit) {
var stack = new Stack();
var p = this;
while (p || stack.top) {
if (p) {
stack.push(p);
p.data && visit(p.data);
p = p.leftChild;
} else {
p = stack.pop();
p = p.rightChild;
}
}
};
2.中序遍历二叉树:
1)算法的递归定义是:
若二叉树为空,则遍历结束;否则
⑴ 中序遍历左子树(递归调用本算法);
⑵ 访问根结点;
⑶ 中序遍历右子树(递归调用本算法)。
// 顺序存储结构的递归中序遍历
var tree = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, , 6, , , 7]; console.log('inOrder:');
void function inOrderTraverse(x, visit) {
if (tree[2 * x + 1]) inOrderTraverse(2 * x + 1, visit);
visit(tree[x]);
if (tree[2 * x + 2]) inOrderTraverse(2 * x + 2, visit);
}(0, function (value) {
console.log(value);
}); // 链式存储的递归中序遍历
BinaryTree.prototype.inPrderTraverse = function inPrderTraverse(visit) {
if (this.leftChild) inPrderTraverse.call(this.leftChild, visit);
visit(this.data);
if (this.rightChild) inPrderTraverse.call(this.rightChild, visit);
};
2) 非递归算法
T是指向二叉树根结点的变量,非递归算法是: 若二叉树为空,则返回;否则,令p=T
⑴ 若p不为空,p进栈, p=p.leftChild ;
⑵ 否则(即p为空),退栈到p,访问p所指向的结点,p=p.rightChild ;
⑶ 转(1);
直到栈空为止。
// 方法1
inOrder_stack1: function (visit) {
var stack = new Stack();
stack.push(this); while (stack.top) {
var p;
// 向左走到尽头
while ((p = stack.peek())) {
stack.push(p.leftChild);
} stack.pop(); if (stack.top) {
p = stack.pop();
p.data && visit(p.data);
stack.push(p.rightChild);
}
}
},
// 方法2
inOrder_stack2: function (visit) {
var stack = new Stack();
var p = this; while (p || stack.top) {
if (p) {
stack.push(p);
p = p.leftChild;
} else {
p = stack.pop();
p.data && visit(p.data);
p = p.rightChild;
}
}
},
3.后序遍历二叉树:
1)递归算法
若二叉树为空,则遍历结束;否则
⑴ 后序遍历左子树(递归调用本算法);
⑵ 后序遍历右子树(递归调用本算法) ;
⑶ 访问根结点 。
// 顺序存储结构的递归后序遍历
var tree = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, , 6, , , 7]; console.log('postOrder:');
void function postOrderTraverse(x, visit) {
if (tree[2 * x + 1]) postOrderTraverse(2 * x + 1, visit);
if (tree[2 * x + 2]) postOrderTraverse(2 * x + 2, visit);
visit(tree[x]);
}(0, function (value) {
console.log(value);
}); // 链式存储的递归后序遍历
BinaryTree.prototype.postOrderTraverse = function postOrderTraverse(visit) {
if (this.leftChild) postOrderTraverse.call(this.leftChild, visit);
if (this.rightChild) postOrderTraverse.call(this.rightChild, visit);
visit(this.data);
};
2) 非递归算法
在后序遍历中,根结点是最后被访问的。因此,在遍历过程中,当搜索指针指向某一根结点时,不能立即访问,而要先遍历其左子树,此时根结点进栈。当其左子树遍历完后再搜索到该根结点时,还是不能访问,还需遍历其右子树。所以,此根结点还需再次进栈,当其右子树遍历完后再退栈到到该根结点时,才能被访问。 因此,设立一个状态标志变量mark:
mark=0表示刚刚访问此结点,mark=1表示左子树处理结束返回,
mark=2表示右子树处理结束返回。每次根据栈顶的mark域决定做何动作
算法实现思路:
(1) 根结点入栈,且mark = 0;
(2) 若栈不为空,出栈到node;
(3) 若node的mark = 0,修改当前node的mark为1,左子树入栈;
(4) 若node的mark = 1,修改当前node的mark为2,右子树入栈;
(5) 若node的mark = 2,访问当前node结点的值;
(6) 直到栈为空结束。
postOrder_stack: function (visit) {
var stack = new Stack();
stack.push([this, 0]);
while (stack.top) {
var a = stack.pop();
var node = a[0];
switch (a[1]) {
case 0:
stack.push([node, 1]); // 修改mark域
if (node.leftChild) stack.push([node.leftChild, 0]); // 访问左子树
break;
case 1:
stack.push([node, 2]);
if (node.rightChild) stack.push([node.rightChild, 0]);
break;
case 2:
node.data && visit(node.data);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
下面是完整代码,其中包括二叉树的遍历和基本操作:
// 顺序存储结构
(function () {
// 顺序存储结构的遍历
var tree = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, , 6, , , 7]; console.log('preOrder:');
void function preOrderTraverse(x, visit) {
visit(tree[x]);
if (tree[2 * x + 1]) preOrderTraverse(2 * x + 1, visit);
if (tree[2 * x + 2]) preOrderTraverse(2 * x + 2, visit);
}(0, function (value) {
console.log(value);
}); console.log('inOrder:');
void function inOrderTraverse(x, visit) {
if (tree[2 * x + 1]) inOrderTraverse(2 * x + 1, visit);
visit(tree[x]);
if (tree[2 * x + 2]) inOrderTraverse(2 * x + 2, visit);
}(0, function (value) {
console.log(value);
}); console.log('postOrder:');
void function postOrderTraverse(x, visit) {
if (tree[2 * x + 1]) postOrderTraverse(2 * x + 1, visit);
if (tree[2 * x + 2]) postOrderTraverse(2 * x + 2, visit);
visit(tree[x]);
}(0, function (value) {
console.log(value);
});
}()); var Stack = require('../Stack/stack');
var Queue = require('../Queue/Queue').Queue; // 链式存储结构
function BinaryTree(data, leftChild, rightChild) {
this.data = data || null;
// 左右孩子结点
this.leftChild = leftChild || null;
this.rightChild = rightChild || null;
}
exports.BinaryTree = BinaryTree;
BinaryTree.prototype = {
constructor: BinaryTree,
// 判断两棵树是否相似
isSimilar: function isSimilar(tree) {
return tree &&
this.leftChild && isSimilar.call(this.leftChild, tree.leftChild) &&
this.rightChild && isSimilar.call(this.rightChild, tree.rightChild);
},
createBinaryTree: function (tree) {
void function preOrderTraverse(node, x, visit) {
visit(node, tree[x]); if (tree[2 * x + 1]) preOrderTraverse(node.leftChild = new BinaryTree(), 2 * x + 1, visit);
if (tree[2 * x + 2]) preOrderTraverse(node.rightChild = new BinaryTree(), 2 * x + 2, visit);
}(this, 0, function (node, value) {
node.data = value;
});
}, // 先序遍历二叉树的非递归算法
preOrder_stack: function (visit) {
var stack = new Stack();
stack.push(this); while (stack.top) {
var p;
// 向左走到尽头
while ((p = stack.peek())) {
p.data && visit(p.data);
stack.push(p.leftChild);
} stack.pop(); if (stack.top) {
p = stack.pop();
stack.push(p.rightChild);
}
}
},
preOrder_stack2: function (visit) {
var stack = new Stack();
var p = this; while (p || stack.top) {
if (p) {
stack.push(p);
p.data && visit(p.data);
p = p.leftChild;
} else {
p = stack.pop();
p = p.rightChild;
}
}
},
inOrder_stack1: function (visit) {
var stack = new Stack();
stack.push(this); while (stack.top) {
var p;
// 向左走到尽头
while ((p = stack.peek())) {
stack.push(p.leftChild);
} stack.pop(); if (stack.top) {
p = stack.pop();
p.data && visit(p.data);
stack.push(p.rightChild);
}
}
},
inOrder_stack2: function (visit) {
var stack = new Stack();
var p = this; while (p || stack.top) {
if (p) {
stack.push(p);
p = p.leftChild;
} else {
p = stack.pop();
p.data && visit(p.data);
p = p.rightChild;
}
}
},
// 为了区分两次过栈的不同处理方式,在堆栈中增加一个mark域,
// mark=0表示刚刚访问此结点,mark=1表示左子树处理结束返回,
// mark=2表示右子树处理结束返回。每次根据栈顶的mark域决定做何动作
postOrder_stack: function (visit) {
var stack = new Stack();
stack.push([this, 0]); while (stack.top) {
var a = stack.pop();
var node = a[0]; switch (a[1]) {
case 0:
stack.push([node, 1]); // 修改mark域
if (node.leftChild) stack.push([node.leftChild, 0]); // 访问左子树
break;
case 1:
stack.push([node, 2]);
if (node.rightChild) stack.push([node.rightChild, 0]);
break;
case 2:
node.data && visit(node.data);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}, preOrderTraverse: function preOrderTraverse(visit) {
visit(this.data);
if (this.leftChild) preOrderTraverse.call(this.leftChild, visit);
if (this.rightChild) preOrderTraverse.call(this.rightChild, visit);
},
inPrderTraverse: function inPrderTraverse(visit) {
if (this.leftChild) inPrderTraverse.call(this.leftChild, visit);
visit(this.data);
if (this.rightChild) inPrderTraverse.call(this.rightChild, visit);
},
postOrderTraverse: function postOrderTraverse(visit) {
if (this.leftChild) postOrderTraverse.call(this.leftChild, visit);
if (this.rightChild) postOrderTraverse.call(this.rightChild, visit);
visit(this.data);
}, levelOrderTraverse: function (visit) {
var queue = new Queue();
queue.enQueue(this); while (queue.rear) {
var p = queue.deQueue();
p.data && visit(p.data);
p.leftChild && queue.enQueue(p.leftChild);
p.rightChild && queue.enQueue(p.rightChild);
}
},
// 求先序序列为k的结点的值
getPreSequence: function (k) {
var count = 0; void function recurse(node) {
if (node) {
if (++count === k) {
console.log('Value is: ' + node.data);
} else {
recurse(node.leftChild);
recurse(node.rightChild);
}
}
}(this);
},
// 求二叉树中叶子结点的数目
countLeaves: function () {
return function recurse(node) {
if (!node) return 0;
else if (!node.leftChild && !node.rightChild) return 1;
else return recurse(node.leftChild) + recurse(node.rightChild);
}(this);
},
// 交换所有结点的左右子树
revoluteBinaryTree: function revoluteBinaryTree() {
var temp = this.leftChild;
this.leftChild = this.rightChild;
this.rightChild = temp; if (this.leftChild) revoluteBinaryTree.call(this.leftChild);
if (this.rightChild) revoluteBinaryTree.call(this.rightChild);
},
// 求二叉树中以值为x的结点为根的子树深度
getSubDepth: function getSubDepth(x) {
if (this.data === x) {
console.log('subDepth: ' + this.getDepth());
} else {
if (this.leftChild) getSubDepth.call(this.leftChild, x);
if (this.rightChild) getSubDepth.call(this.rightChild, x);
}
},
getDepth: function getDepth() {
if (this === global) return 0;
else {
var m = getDepth.call(this.leftChild);
var n = getDepth.call(this.rightChild);
return (m > n ? m : n) + 1;
}
},
// 删除所有以元素x为根的子树
delSubX: function delSubX(x) {
if (this.data === x) {
this.leftChild = null;
this.rightChild = null;
} else {
if (this.leftChild) delSubX.call(this.leftChild);
if (this.rightChild) delSubX.call(this.rightChild);
}
},
// 非递归复制二叉树
copyBinaryTree_stack: function () {
// 用来存放本体结点的栈
var stack1 = new Stack();
// 用来存放新二叉树结点的栈
var stack2 = new Stack();
stack1.push(this);
var newTree = new BinaryTree();
var q = newTree;
stack2.push(newTree);
var p; while (stack1.top) {
// 向左走到尽头
while ((p = stack1.peek())) {
if (p.leftChild) q.leftChild = new BinaryTree();
q = q.leftChild;
stack1.push(p.leftChild);
stack2.push(q);
} p = stack1.pop();
q = stack2.pop(); if (stack1.top) {
p = stack1.pop();
q = stack2.pop();
if (p.rightChild) q.rightChild = new BinaryTree();
q.data = p.data;
q = q.rightChild;
stack1.push(p.rightChild); // 向右一步
stack2.push(q);
}
} return newTree;
},
// 求二叉树中结点p和q的最近祖先
findNearAncient: function (pNode, qNode) {
var pathP = [];
var pathQ = [];
findPath(this, pNode, pathP, 0);
findPath(this, qNode, pathQ, 0); for (var i = 0; pathP[i] == pathQ[i] && pathP[i]; i++);
return pathP[--i];
},
toString: function () {
},
// 求一棵二叉树的繁茂度
lushDegree: function () {
var countArr = [];
var queue = new Queue();
queue.enQueue({
node: this,
layer: 0
});
// 利用层序遍历来统计各层的结点数
var r;
while (queue.rear) {
r = queue.deQueue();
countArr[r.layer] = (countArr[r.layer] || 0) + 1; if (r.node.leftChild)
queue.enQueue({
node: r.node.leftChild,
layer: r.layer + 1
});
if (r.node.rightChild)
queue.enQueue({
node: r.node.rightChild,
layer: r.layer + 1
});
} // 最后一个队列元素所在层就是树的高度
var height = r.layer;
for (var max = countArr[0], i = 1; countArr[i]; i++)
// 求层最大结点数
if (countArr[i] > max) max = countArr[i]; return height * max;
},
// 求深度等于书的高度减一的最靠左的结点
printPath_maxDepthS1: function () {
var maxh = this.getDepth();
var path = []; if (maxh < 2) return false;
find_h(this, 1); function find_h(tree, h) {
path[h] = tree; if (h == maxh - 1) {
var s = ' ';
for (var i = 1; path[i]; i++) s += path[i].data + (path[i + 1] ? ' -> ' : '');
console.log(s);
return;
} else {
if (tree.leftChild) find_h(tree.leftChild, h + 1);
if (tree.rightChild) find_h(tree.rightChild, h + 1);
} path[h] = null;
}
},
// 求树结点的子孙总数填入descNum域中,并返回
descNum: function () {
return function recurse(node) {
var d;
if (!node) return -1;
else d = recurse(node.leftChild) + recurse(node.rightChild) + 2; node.descNum = d; return d;
}(this);
}
}; // 判断二叉树是否完全二叉树
BinaryTree.isFullBinaryTree = function (tree) {
var queue = new Queue();
var flag = 0;
queue.enQueue(tree); while (queue.rear) {
var p = queue.deQueue(); if (!p) flag = 1;
else if (flag) return false;
else {
queue.enQueue(p.leftChild);
queue.enQueue(p.rightChild);
}
} return true;
}; // 求从tree到node结点路径的递归算法
function findPath(tree, node, path, i) {
var found = false; void function recurse(tree, i) {
if (tree == node) {
found = true;
return;
} path[i] = tree;
if (tree.leftChild) recurse(tree.leftChild, i + 1);
if (tree.rightChild && !found) recurse(tree.rightChild, i + 1);
if (!found) path[i] = null;
}(tree, i);
} var global = Function('return this;')(); void function test() {
var tree = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, , 6, , , 7];
var test = new BinaryTree;
test.createBinaryTree(tree);
test.preOrderTraverse(function (value) {
console.log('preOrder: ' + value);
});
test.inPrderTraverse(function (value) {
console.log('inOrder: ' + value);
});
test.postOrderTraverse(function (value) {
console.log('postOrder: ' + value);
});
test.preOrder_stack(function (data) {
console.log('preOrderNonRecusive: ' + data);
});
test.preOrder_stack2(function (data) {
console.log('preOrder_stack2: ' + data);
});
test.inOrder_stack1(function (value) {
console.log('inOrder_stack1: ' + value);
});
test.inOrder_stack2(function (value) {
console.log('inOrder_stack2: ' + value);
});
test.postOrder_stack(function (value) {
console.log('postOrder_stack: ' + value);
});
test.getPreSequence(5);
console.log(test.countLeaves());
test.getSubDepth(6); //
test.getSubDepth(2); //
test.levelOrderTraverse(function (value) {
console.log('levelOrderTraverse: ' + value);
}); var newTree = test.copyBinaryTree_stack(); var node1 = test.leftChild.leftChild; //
var node2 = test.leftChild.rightChild.leftChild; //
var ancient = test.findNearAncient(node1, node2);
console.log(ancient); console.log('expect false: ' + BinaryTree.isFullBinaryTree(test));
newTree.rightChild.leftChild = new BinaryTree(7);
newTree.leftChild.rightChild.leftChild = null;
console.log('expect true: ' + BinaryTree.isFullBinaryTree(newTree));
console.log('lush degree: ' + test.lushDegree()); test.printPath_maxDepthS1();
console.log(test.descNum());
}();
javascript实现数据结构: 树和二叉树,二叉树的遍历和基本操作的更多相关文章
- Python入门篇-数据结构树(tree)的遍历
Python入门篇-数据结构树(tree)的遍历 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 一.遍历 迭代所有元素一遍. 二.树的遍历 对树中所有元素不重复地访问一遍,也称作扫 ...
- 数据结构-树以及深度、广度优先遍历(递归和非递归,python实现)
前面我们介绍了队列.堆栈.链表,你亲自动手实践了吗?今天我们来到了树的部分,树在数据结构中是非常重要的一部分,树的应用有很多很多,树的种类也有很多很多,今天我们就先来创建一个普通的树.其他各种各样的树 ...
- python数据结构之树和二叉树(先序遍历、中序遍历和后序遍历)
python数据结构之树和二叉树(先序遍历.中序遍历和后序遍历) 树 树是\(n\)(\(n\ge 0\))个结点的有限集.在任意一棵非空树中,有且只有一个根结点. 二叉树是有限个元素的集合,该集合或 ...
- 数据结构(一)二叉树 & avl树 & 红黑树 & B-树 & B+树 & B*树 & R树
参考文档: avl树:http://lib.csdn.net/article/datastructure/9204 avl树:http://blog.csdn.net/javazejian/artic ...
- [数据结构 - 第6章] 树之链式二叉树(C语言实现)
一.什么是二叉树? 1.1 定义 二叉树,是度为二的树,二叉树的每一个节点最多只有二个子节点,且两个子节点有序. 1.2 二叉树的重要特性 (1)二叉树的第 i 层上节点数最多为 2n-1: (2)高 ...
- 常见基本数据结构——树,二叉树,二叉查找树,AVL树
常见数据结构——树 处理大量的数据时,链表的线性时间太慢了,不宜使用.在树的数据结构中,其大部分的运行时间平均为O(logN).并且通过对树结构的修改,我们能够保证它的最坏情形下上述的时间界. 树的定 ...
- JavaScript数据结构——树的实现
在计算机科学中,树是一种十分重要的数据结构.树被描述为一种分层数据抽象模型,常用来描述数据间的层级关系和组织结构.树也是一种非顺序的数据结构.下图展示了树的定义: 在介绍如何用JavaScript实现 ...
- JavaScript数据结构-树
我认为这社会上,也不差钱好多人,可能好多人也不差权力.可是我认为能得到这样的满足的也不多. –郭小平<临汾红丝带学校校长> 树是计算机科学中经经常使用到的一种数据结构. 树是一种非线性 ...
- JS数据结构第六篇 --- 二叉树力扣练习题
1.第226题:翻转二叉树 递归+迭代两种实现方式: /** 反转二叉树 * Definition for a binary tree node. * function TreeNode(val) { ...
随机推荐
- Servlet完全教程
Servlet 是一些遵从Java Servlet API的Java类,这些Java类可以响应请求.尽管Servlet可以响应任意类型的请求,但是它们使用最广泛的是响应web方面的请求. Servle ...
- 将utc时间格式化的代码
/** * 对Date的扩展,将 Date 转化为指定格式的String * 月(M).日(d).12小时(h).24小时(H).分(m).秒(s).周(E).季度(q) 可以用 1-2 个占位符 * ...
- Hibernate学习笔记(一)—— Hibernate概述及入门
一.Hibernatea概述 1.1 什么是Hibernate? 在介绍什么是Hibernate之前,我们先讨论一下什么是框架?框架是用来提高开发效率的,框架封装好了一些功能,我们需要使用这些功能时, ...
- python大作业-图书管理系统
#缺少循环执行和错误处理 #add()函数 添加了循环执行 #错误处理:regist()函数 登录和退出选择的时候添加了错误处理 import sys import importlib importl ...
- rest-assured的日志使用介绍
在许多测试用例当中,为了帮助我们创建正确的断言和发送正确的请求,打印出详细的响应和请求数据是非常有用的.为此我们可以使用rest-assured提供的预定义过滤器或者使用其中的一些快捷方法. 一.请求 ...
- SPOJ - COT2 离线路径统计
题意:求\(u\)到\(v\)的最短路径的不同权值种类个数 树上莫队试水题,这一篇是上篇的弱化部分,但可测试以下结论的正确性 设\(S(u,v)\):\(u-v\)最短路径所覆盖的点集 \(S(u,v ...
- springboot(一):入门
什么是springboot Spring Boot是由Pivotal团队提供的全新框架,其设计目的是用来简化新Spring应用的初始搭建以及开发过程.该框架使用了特定的方式来进行配置,从而使开发人员不 ...
- Q205 同构字符串
给定两个字符串 s 和 t,判断它们是否是同构的. 如果 s 中的字符可以被替换得到 t ,那么这两个字符串是同构的. 所有出现的字符都必须用另一个字符替换,同时保留字符的顺序.两个字符不能映射到同一 ...
- 【研究】Weblogic XMLDecoder反序列化漏洞(CVE-2017-10271)
影响范围: Oracle WebLogic Server 10.3.6.0.0版本 Oracle WebLogic Server 12.1.3.0.0版本 Oracle WebLogic Server ...
- vue搭建后台管理页面(点击左侧导航,切换右侧内容)
home.vue页面 <template> <div style="background-color: #EBEBEB;min-height:900px"> ...
