Tensorflow加载预训练模型和保存模型(ckpt文件)以及迁移学习finetuning
转载自:https://blog.csdn.net/huachao1001/article/details/78501928
使用tensorflow过程中,训练结束后我们需要用到模型文件。有时候,我们可能也需要用到别人训练好的模型,并在这个基础上再次训练。这时候我们需要掌握如何操作这些模型数据。
1 Tensorflow模型文件
我们在checkpoint_dir目录下保存的文件结构如下:
|--checkpoint_dir
| |--checkpoint
| |--MyModel.meta
| |--MyModel.data-00000-of-00001
| |--MyModel.index
1.1 meta文件
MyModel.meta文件保存的是图结构,meta文件是pb(protocol buffer)格式文件,包含变量、op、集合等。
1.2 ckpt文件
ckpt文件是二进制文件,保存了所有的weights、biases、gradients等变量。在tensorflow 0.11之前,保存在.ckpt文件中。0.11后,通过两个文件保存,如:
MyModel.data-00000-of-00001
MyModel.index
1.3 checkpoint文件
我们还可以看,checkpoint_dir目录下还有checkpoint文件,该文件是个文本文件,里面记录了保存的最新的checkpoint文件以及其它checkpoint文件列表。在inference时,可以通过修改这个文件,指定使用哪个model
2 保存Tensorflow模型
tensorflow 提供了tf.train.Saver类来保存模型,值得注意的是,在tensorflow中,变量是存在于Session环境中,也就是说,只有在Session环境下才会存有变量值,因此,保存模型时需要传入session:
saver = tf.train.Saver()
saver.save(sess,"./checkpoint_dir/MyModel")
看一个简单例子:
import tensorflow as tf
w1 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape=[2]), name='w1')
w2 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape=[5]), name='w2')
saver = tf.train.Saver()
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
saver.save(sess, './checkpoint_dir/MyModel')
执行后,在checkpoint_dir目录下创建模型文件如下:
checkpoint
MyModel.data-00000-of-00001
MyModel.index
MyModel.meta
另外,如果想要在1000次迭代后,再保存模型,只需设置global_step参数即可
保存的模型文件名称会在后面加-1000,如下:
checkpoint
MyModel-1000.data-00000-of-00001
MyModel-1000.index
MyModel-1000.meta
在实际训练中,我们可能会在每1000次迭代中保存一次模型数据,但是由于图是不变的,没必要每次都去保存,可以通过如下方式指定不保存图:
saver.save(sess, './checkpoint_dir/MyModel',global_step=step,write_meta_graph=False)
另一种比较实用的是,如果你希望每2小时保存一次模型,并且只保存最近的5个模型文件:
tf.train.Saver(max_to_keep=5, keep_checkpoint_every_n_hours=2)
注意:tensorflow默认只会保存最近的5个模型文件,如果你希望保存更多,可以通过
max_to_keep来指定
如果我们不对tf.train.Saver指定任何参数,默认会保存所有变量。如果你不想保存所有变量,而只保存一部分变量,可以通过指定variables/collections。在创建tf.train.Saver实例时,通过将需要保存的变量构造list或者dictionary,传入到Saver中:
import tensorflow as tf
w1 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape=[2]), name='w1')
w2 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape=[5]), name='w2')
saver = tf.train.Saver([w1,w2])
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
saver.save(sess, './checkpoint_dir/MyModel',global_step=1000)
3 导入训练好的模型
在第1小节中我们介绍过,tensorflow将图和变量数据分开保存为不同的文件。因此,在导入模型时,也要分为2步:构造网络图和加载参数
3.1 构造网络图
一个比较笨的方法是,手敲代码,实现跟模型一模一样的图结构。其实,我们既然已经保存了图,那就没必要在去手写一次图结构代码。
saver=tf.train.import_meta_graph('./checkpoint_dir/MyModel-1000.meta')
上面一行代码,就把图加载进来了
3.2 加载参数
仅仅有图并没有用,更重要的是,我们需要前面训练好的模型参数(即weights、biases等),本文第2节提到过,变量值需要依赖于Session,因此在加载参数时,先要构造好Session:
import tensorflow as tf
with tf.Session() as sess:
new_saver = tf.train.import_meta_graph('./checkpoint_dir/MyModel-1000.meta')
new_saver.restore(sess, tf.train.latest_checkpoint('./checkpoint_dir'))
此时,W1和W2加载进了图,并且可以被访问:
import tensorflow as tf
with tf.Session() as sess:
saver = tf.train.import_meta_graph('./checkpoint_dir/MyModel-1000.meta')
saver.restore(sess,tf.train.latest_checkpoint('./checkpoint_dir'))
print(sess.run('w1:0'))
##Model has been restored. Above statement will print the saved value
执行后,打印如下:
[ 0.51480412 -0.56989086]
或者:
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np with tf.Session() as sess:
# restore graph
saver = tf.train.import_meta_graph('my_net/save_net.ckpt.meta') #restore ckpt
saver.restore(sess, "my_net/save_net.ckpt") # check variable W and b, like weight or bias
print("weights:", sess.run('weights:0'))
print("biases:", sess.run('biases:0'))
4 使用恢复的模型
前面我们理解了如何保存和恢复模型,很多时候,我们希望使用一些已经训练好的模型,如prediction、fine-tuning以及进一步训练等。这时候,我们可能需要获取训练好的模型中的一些中间结果值,可以通过graph.get_tensor_by_name('w1:0')来获取,注意w1:0是tensor的name。
假设我们有一个简单的网络模型,代码如下:
import tensorflow as tf
w1 = tf.placeholder("float", name="w1")
w2 = tf.placeholder("float", name="w2")
b1= tf.Variable(2.0,name="bias")
#定义一个op,用于后面恢复
w3 = tf.add(w1,w2)
w4 = tf.multiply(w3,b1,name="op_to_restore")
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
#创建一个Saver对象,用于保存所有变量
saver = tf.train.Saver()
#通过传入数据,执行op
print(sess.run(w4,feed_dict ={w1:4,w2:8}))
#打印 24.0 ==>(w1+w2)*b1
#现在保存模型
saver.save(sess, './checkpoint_dir/MyModel',global_step=1000)
接下来我们使用graph.get_tensor_by_name()方法来操纵这个保存的模型。
import tensorflow as tf
sess=tf.Session()
#先加载图和参数变量
saver = tf.train.import_meta_graph('./checkpoint_dir/MyModel-1000.meta')
saver.restore(sess, tf.train.latest_checkpoint('./checkpoint_dir'))
# 访问placeholders变量,并且创建feed-dict来作为placeholders的新值
graph = tf.get_default_graph()
w1 = graph.get_tensor_by_name("w1:0")
w2 = graph.get_tensor_by_name("w2:0")
feed_dict ={w1:13.0,w2:17.0}
#接下来,访问你想要执行的op
op_to_restore = graph.get_tensor_by_name("op_to_restore:0")
print(sess.run(op_to_restore,feed_dict))
#打印结果为60.0==>(13+17)*2
注意:保存模型时,只会保存变量的值,placeholder里面的值不会被保存
如果你不仅仅是用训练好的模型,还要加入一些op,或者说加入一些layers并训练新的模型,可以通过一个简单例子来看如何操作:
import tensorflow as tf
sess = tf.Session()
# 先加载图和变量
saver = tf.train.import_meta_graph('my_test_model-1000.meta')
saver.restore(sess, tf.train.latest_checkpoint('./'))
# 访问placeholders变量,并且创建feed-dict来作为placeholders的新值
graph = tf.get_default_graph()
w1 = graph.get_tensor_by_name("w1:0")
w2 = graph.get_tensor_by_name("w2:0")
feed_dict = {w1: 13.0, w2: 17.0}
#接下来,访问你想要执行的op
op_to_restore = graph.get_tensor_by_name("op_to_restore:0")
# 在当前图中能够加入op
add_on_op = tf.multiply(op_to_restore, 2)
print (sess.run(add_on_op, feed_dict))
# 打印120.0==>(13+17)*2*2
如果只想恢复图的一部分,并且再加入其它的op用于fine-tuning。只需通过graph.get_tensor_by_name()方法获取需要的op,并且在此基础上建立图,看一个简单例子,假设我们需要在训练好的VGG网络使用图,并且修改最后一层,将输出改为2,用于fine-tuning新数据:
- ......
- ......
- saver = tf.train.import_meta_graph('vgg.meta')
- # 访问图
- graph = tf.get_default_graph()
- #访问用于fine-tuning的output
- fc7= graph.get_tensor_by_name('fc7:0')
- #如果你想修改最后一层梯度,需要如下
- fc7 = tf.stop_gradient(fc7) # It's an identity function
- fc7_shape= fc7.get_shape().as_list()
- new_outputs=2
- weights = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([fc7_shape[3], num_outputs], stddev=0.05))
- biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.05, shape=[num_outputs]))
- output = tf.matmul(fc7, weights) + biases
- pred = tf.nn.softmax(output)
- # Now, you run this with fine-tuning data in sess.run()
五、查看模型的所有层的输入输出的tensor name
- import os
- import re
- import tensorflow as tf
- from tensorflow.python import pywrap_tensorflow
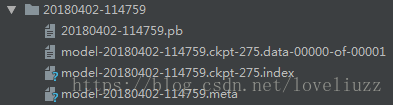
- model_exp = "20180402-114759"
- def get_model_filenames(model_dir):
- files = os.listdir(model_dir)
- meta_files = [s for s in files if s.endswith('.meta')]
- if len(meta_files)==0:
- raise load_modelValueError('No meta file found in the model directory (%s)' % model_dir)
- elif len(meta_files)>1:
- raise ValueError('There should not be more than one meta file in the model directory (%s)' % model_dir)
- meta_file = meta_files[0]
- ckpt = tf.train.get_checkpoint_state(model_dir) # 通过checkpoint文件找到模型文件名
- if ckpt and ckpt.model_checkpoint_path:
- # ckpt.model_checkpoint_path表示模型存储的位置,不需要提供模型的名字,它回去查看checkpoint文件
- ckpt_file = os.path.basename(ckpt.model_checkpoint_path)
- return meta_file, ckpt_file
- meta_files = [s for s in files if '.ckpt' in s]
- max_step = -1
- for f in files:
- step_str = re.match(r'(^model-[\w\- ]+.ckpt-(\d+))', f)
- if step_str is not None and len(step_str.groups())>=2:
- step = int(step_str.groups()[1])
- if step > max_step:
- max_step = step
- ckpt_file = step_str.groups()[0]
- return meta_file, ckpt_file
- meta_file, ckpt_file = get_model_filenames(model_exp)
- print('Metagraph file: %s' % meta_file)
- print('Checkpoint file: %s' % ckpt_file)
- reader = pywrap_tensorflow.NewCheckpointReader(os.path.join(model_exp, ckpt_file))
- var_to_shape_map = reader.get_variable_to_shape_map()
- for key in var_to_shape_map:
- print("tensor_name: ", key)
- # print(reader.get_tensor(key))
- with tf.Session() as sess:
- saver = tf.train.import_meta_graph(os.path.join(model_exp, meta_file))
- saver.restore(tf.get_default_session(),
- os.path.join(model_exp, ckpt_file))
- print(tf.get_default_graph().get_tensor_by_name("Logits/weights:0"))
六、tensorflow从已经训练好的模型中,恢复指定权重(构建新变量、网络)并继续训练(finetuning)
该部分转载自:https://blog.csdn.net/ying86615791/article/details/76215363
假如要保存或者恢复指定tensor,并且把保存的graph恢复(插入)到当前的graph中呢?
总的来说,目前我会的是两种方法,命名都是很关键!
两种方式保存模型,
1.保存所有tensor,即整张图的所有变量,
2.只保存指定scope的变量
两种方式恢复模型,
1.导入模型的graph,用该graph的saver来restore变量
2.在新的代码段中写好同样的模型(变量名称及scope的name要对应),用默认的graph的saver来restore指定scope的变量
两种保存方式:
1.保存整张图,所有变量
- ...
- init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
- saver = tf.train.Saver()
- config = tf.ConfigProto()
- config.gpu_options.allow_growth=True
- with tf.Session(config=config) as sess:
- sess.run(init)
- ...
- writer.add_graph(sess.graph)
- ...
- saved_path = saver.save(sess,saver_path)
- ...
2.保存图中的部分变量
- ...
- init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
- vgg_ref_vars = tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES, scope='vgg_feat_fc')#获取指定scope的tensor
- saver = tf.train.Saver(vgg_ref_vars)#初始化saver时,传入一个var_list的参数
- config = tf.ConfigProto()
- config.gpu_options.allow_growth=True
- with tf.Session(config=config) as sess:
- sess.run(init)
- ...
- writer.add_graph(sess.graph)
- ...
- saved_path = saver.save(sess,saver_path)
- ...
两种恢复方式:
1.导入graph来恢复
- ...
- vgg_meta_path = params['vgg_meta_path'] # 后缀是'.ckpt.meta'的文件
- vgg_graph_weight = params['vgg_graph_weight'] # 后缀是'.ckpt'的文件,里面是各个tensor的值
- saver_vgg = tf.train.import_meta_graph(vgg_meta_path) # 导入graph到当前的默认graph中,返回导入graph的saver
- x_vgg_feat = tf.get_collection('inputs_vgg')[0] #placeholder, [None, 4096],获取输入的placeholder
- feat_decode = tf.get_collection('feat_encode')[0] #[None, 1024],获取要使用的tensor
- """
- 以上两个获取tensor的方式也可以为:
- graph = tf.get_default_graph()
- centers = graph.get_tensor_by_name('loss/intra/center_loss/centers:0')
- 当然,前提是有tensor的名字
- """
- ...
- init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
- saver = tf.train.Saver() # 这个是当前新图的saver
- config = tf.ConfigProto()
- config.gpu_options.allow_growth=True
- with tf.Session(config=config) as sess:
- sess.run(init)
- ...
- saver_vgg.restore(sess, vgg_graph_weight)#使用导入图的saver来恢复
- ...
2.重写一样的graph,然后恢复指定scope的变量
- def re_build():#重建保存的那个graph
- with tf.variable_scope('vgg_feat_fc'): #没错,这个scope要和需要恢复模型中的scope对应
- ...
- return ...
- ...
- vgg_ref_vars = tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES, scope='vgg_feat_fc') # 既然有这个scope,其实第1个方法中,导入graph后,可以不用返回的vgg_saver,再新建一个指定var_list的vgg_saver就好了,恩,需要传入一个var_list的参数
- ...
- init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
- saver_vgg = tf.train.Saver(vgg_ref_vars) # 这个是要恢复部分的saver
- saver = tf.train.Saver() # 这个是当前新图的saver
- config = tf.ConfigProto()
- config.gpu_options.allow_growth=True
- with tf.Session(config=config) as sess:
- sess.run(init)
- ...
- saver_vgg.restore(sess, vgg_graph_weight)#使用导入图的saver来恢复
- ...
总结一下,这里的要点就是,在restore的时候,saver要和模型对应,如果直接用当前graph的saver = tf.train.Saver(),来恢复保存模型的权重saver.restore(vgg_graph_weight),就会报错,提示key/tensor ... not found之类的错误;
写graph的时候,一定要注意写好scope和tensor的name,合理插入variable_scope;
最方便的方式还是,用第1种方式来保存模型,这样就不用重写代码段了,然后第1种方式恢复,不过为了稳妥,最好还是通过获取var_list,指定saver的var_list,妥妥的!
最新发现,用第1种方式恢复时,要记得当前的graph和保存的模型中没有重名的tensor,否则当前graph的tensor name可能不是那个name,可能在后面加了"_1"....-_-||
在恢复图基础上构建新的网络(变量)并训练(finetuning)
恢复模型graph和weights在上面已经说了,这里的关键点是怎样只恢复原图的权重 ,并且使optimizer只更新新构造变量(指定层、变量)。
(以下code与上面没联系)
- """1.Get input, output , saver and graph"""#从导入图中获取需要的东西
- meta_path_restore = model_dir + '/model_'+model_version+'.ckpt.meta'
- model_path_restore = model_dir + '/model_'+model_version+'.ckpt'
- saver_restore = tf.train.import_meta_graph(meta_path_restore) #获取导入图的saver,便于后面恢复
- graph_restore = tf.get_default_graph() #此时默认图就是导入的图
- #从导入图中获取需要的tensor
- #1. 用collection来获取
- input_x = tf.get_collection('inputs')[0]
- input_is_training = tf.get_collection('is_training')[0]
- output_feat_fused = tf.get_collection('feat_fused')[0]
- #2. 用tensor的name来获取
- input_y = graph_restore.get_tensor_by_name('label_exp:0')
- print('Get tensors...')
- print('inputs shape: {}'.format(input_x.get_shape().as_list()))
- print('input_is_training shape: {}'.format(input_is_training.get_shape().as_list()))
- print('output_feat_fused shape: {}'.format(output_feat_fused.get_shape().as_list()))
- """2.Build new variable for fine tuning"""#构造新的variables用于后面的finetuning
- graph_restore.clear_collection('feat_fused') #删除以前的集合,假如finetuning后用新的代替原来的
- graph_restore.clear_collection('prob')
- #添加新的东西
- if F_scale is not None and F_scale!=0:
- print('F_scale is not None, value={}'.format(F_scale))
- feat_fused = Net_normlize_scale(output_feat_fused, F_scale)
- tf.add_to_collection('feat_fused',feat_fused)#重新添加到新集合
- logits_fused = last_logits(feat_fused,input_is_training,7) # scope name是"final_logits"
- """3.Get acc and loss"""#构造损失
- with tf.variable_scope('accuracy'):
- accuracy,prediction = ...
- with tf.variable_scope('loss'):
- loss = ...
- """4.Build op for fine tuning"""
- global_step = tf.Variable(0, trainable=False,name='global_step')
- learning_rate = tf.train.exponential_decay(initial_lr,
- global_step=global_step,
- decay_steps=decay_steps,
- staircase=True,
- decay_rate=0.1)
- update_ops = tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.UPDATE_OPS)
- with tf.control_dependencies(update_ops):
- var_list = tf.contrib.framework.get_variables('final_logits')#关键!获取指定scope下的变量
- train_op = tf.train.MomentumOptimizer(learning_rate=learning_rate,momentum=0.9).minimize(loss,global_step=global_step,var_list=var_list) #只更新指定的variables
- """5.Begin training"""
- init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
- saver = tf.train.Saver()
- config = tf.ConfigProto()
- config.gpu_options.allow_growth=True
- with tf.Session(config=config) as sess:
- sess.run(init)
- saver_restore.restore(sess, model_path_restore) #这里saver_restore对应导入图的saver, 如果用上面新的saver的话会报错 因为多出了一些新的变量 在保存的模型中是没有那些权值的
- sess.run(train_op, feed_dict)
- .......
再说明下两个关键点:
1. 如何在新图的基础上 只恢复 导入图的权重 ?
用导入图的saver: saver_restore
2. 如何只更新指定参数?
用var_list = tf.contrib.framework.get_variables(scope_name)获取指定scope_name下的变量,
然后optimizer.minimize()时传入指定var_list
附:如何知道tensor名字以及获取指定变量?
1.获取某个操作之后的输出
用graph.get_operations()获取所有op
比如<tf.Operation 'common_conv_xxx_net/common_conv_net/flatten/Reshape' type=Reshape>,
那么output_pool_flatten =
graph_restore.get_tensor_by_name('common_conv_xxx_net/common_conv_net/flatten/Reshape:0')就是那个位置经过flatten后的输出了
2.获取指定的var的值
用GraphKeys获取变量
tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES)返回指定集合的变量
比如 <tf.Variable 'common_conv_xxx_net/final_logits/logits/biases:0' shape=(7,) dtype=float32_ref>
那么var_logits_biases = graph_restore.get_tensor_by_name('common_conv_xxx_net/final_logits/logits/biases:0')就是那个位置的biases了
3.获取指定scope的collection
tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.REGULARIZATION_LOSSES,scope='common_conv_xxx_net.final_logits')
注意后面的scope是xxx.xxx不是xxx/xxx
Tensorflow加载预训练模型和保存模型(ckpt文件)以及迁移学习finetuning的更多相关文章
- Tensorflow加载预训练模型和保存模型
转载自:https://blog.csdn.net/huachao1001/article/details/78501928 使用tensorflow过程中,训练结束后我们需要用到模型文件.有时候,我 ...
- pytorch中修改后的模型如何加载预训练模型
问题描述 简单来说,比如你要加载一个vgg16模型,但是你自己需要的网络结构并不是原本的vgg16网络,可能你删掉某些层,可能你改掉某些层,这时你去加载预训练模型,就会报错,错误原因就是你的模型和原本 ...
- [Pytorch]Pytorch加载预训练模型(转)
转自:https://blog.csdn.net/Vivianyzw/article/details/81061765 东风的地方 1. 直接加载预训练模型 在训练的时候可能需要中断一下,然后继续训练 ...
- 使用Huggingface在矩池云快速加载预训练模型和数据集
作为NLP领域的著名框架,Huggingface(HF)为社区提供了众多好用的预训练模型和数据集.本文介绍了如何在矩池云使用Huggingface快速加载预训练模型和数据集. 1.环境 HF支持Pyt ...
- Java 加载、编辑和保存WPS表格文件(.et/.ett)
WPS表格文件是金山开发的专门用于处理表格数据的Office工具,属于WPS Office中WPS文字.WPS表格和WPS演示三大功能模块之一.通常以.et和.ett作为文件后缀.我们在通过后端来操作 ...
- 关于Tensorflow 加载和使用多个模型的方式
在Tensorflow中,所有操作对象都包装到相应的Session中的,所以想要使用不同的模型就需要将这些模型加载到不同的Session中并在使用的时候申明是哪个Session,从而避免由于Sessi ...
- pytorch加载预训练模型参数的方式
1.直接使用默认程序里的下载方式,往往比较慢: 2.通过修改源代码,使得模型加载已经下载好的参数,修改地方如下: 通过查找自己代码里所调用网络的类,使用pycharm自带的函数查找功能(ctrl+鼠标 ...
- 开园第一篇---有关tensorflow加载不同模型的问题
写在前面 今天刚刚开通博客,主要想法跟之前某位博主说的一样,希望通过博客园把每天努力的点滴记录下来,也算一种坚持的动力.我是小白一枚,有啥问题欢迎各位大神指教,鞠躬~~ 换了新工作,目前手头是OCR项 ...
- 用MVVM模式开发中遇到的零散问题总结(5)——将动态加载的可视元素保存为图片的控件,Binding刷新的时机
原文:用MVVM模式开发中遇到的零散问题总结(5)--将动态加载的可视元素保存为图片的控件,Binding刷新的时机 在项目开发中经常会遇到这样一种情况,就是需要将用户填写的信息排版到一张表单中,供打 ...
随机推荐
- Java流程控制之顺序结构
概述 在一个程序执行的过程中,各条语句的执行顺序对程序的结果是有直接影响的.也就是说,程序的流程对运行结果有直接的影响.所以,我们必须清楚每条语句的执行流程.而且,很多时候我们要通过控制语句的执行顺序 ...
- 第05组 Alpha冲刺(2/4)
第05组 Alpha冲刺(2/4) 队名:天码行空 组长博客连接 作业博客连接 团队燃尽图(共享): GitHub当日代码/文档签入记录展示(共享): 组员情况: 组员1:卢欢(组长) 过去两天完成了 ...
- python zip压缩文件并设置密码
zip -P "123" -r app.zip app压缩文件 密码 压缩后名称 压缩对象名称 def zipDir(dirpath, outFullNa ...
- Java连载46-Java中的多态
一.多态的语法 1.关于多态中涉及到几个概念 (1)向上转型(upcasting) 子类型转换为父类型,又被称为自动类型转换 (2)向下转型(downcasting) 父类型转换为子类型,又被称为强制 ...
- js input radio点击事件
html代码: <input type="radio" name="myname" value="1" />1 <inpu ...
- 详解JAVA8Stream API {全}
1: 概述 1.1 优势 1.2 与传统迭代器的区分 1.3 流的操作类型分为两种: 2:流的构造与转换 2:1 常见构造 2.2: 三大包装类型的构造 2.3 并行流的规则输出 2.4 流的转换 3 ...
- 常用的app包名和类名
应用 包名 启动类 QQ com.tencent.mobileqq com.tencent.mobileqq.activity.HomeActivity 微信 com.tencent.mm com.t ...
- MYSQL 高级语法
1.高级建表和插入 使用creat 和select 进行建表操作,中间采用AS 标识符: CREATE TABLE new_table AS SELECT * FROM exist_table LIM ...
- 码云git常用命令
Git常用操作命令: 1) 远程仓库相关命令 检出仓库:$ git clone git://github.com/jquery/jquery.git 查看远程仓库:$ git remote -v 添加 ...
- python基础—条件语句
一.Python基础 1.第一句python print('hello,world') Q: 后缀名可以任意? A: 导入模块时,如果不是.py后缀,会出错. 2.两种执行的方式: -python解 ...