Redis实现的分布式锁和分布式限流
随着现在分布式越来越普遍,分布式锁也十分常用,我的上一篇文章解释了使用zookeeper实现分布式锁(传送门),本次咱们说一下如何用Redis实现分布式锁和分布限流。
Redis有个事务锁,就是如下的命令,这个命令的含义是将一个value设置到一个key中,如果不存在将会赋值并且设置超时时间为30秒,如何这个key已经存在了,则不进行设置。
SET key value NX PX
这个事务锁很好的解决了两个单独的命令,一个设置set key value nx,即该key不存在的话将对其进行设置,另一个是expire key seconds,设置该key的超时时间。我们可以想一下,如果这两个命令用程序单独使用会存在什么问题:
1. 如果一个set key的命令设置了key,然后程序异常了,expire时间没有设置,那么这个key会一直锁住。
2. 如果一个set key时出现了异常,但是直接执行了expire,过了一会儿之后另一个进行set key,还没怎么执行代码,结果key过期了,别的线程也进入了锁。
还有很多出问题的可能点,这里我们就不讨论了,下面咱们来看看如何实现吧。本文使用的Spring Boot 2.x + Spring data redis + Swagger +lombok + AOP + lua脚本。在实现的过程中遇到了很多问题,都一一解决实现了。依赖的POM文件如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.1.2.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.hqs</groupId>
<artifactId>distributedlock</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>distributedlock</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description> <properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties> <dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId>
<version>2.9.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId>
<version>2.9.2</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clients</groupId>
<artifactId>jedis</artifactId>
<version>2.9.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies> <build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build> </project>
使用了两个lua脚本,一个用于执行lock,另一个执行unlock。咱们简单看一下,lock脚本就是采用Redis事务执行的set nx px命令,其实还有set nx ex命令,这个ex命令是采用秒的方式进行设置过期时间,这个px是采用毫秒的方式设置过期时间。value需要使用一个唯一的值,这个值在解锁的时候需要判断是否一致,如果一致的话就进行解锁。这个也是官方推荐的方法。另外在lock的地方我设置了一个result,用于输出测试时的结果,这样就可以结合程序去进行debug了。
local expire = tonumber(ARGV[])
local ret = redis.call('set', KEYS[], ARGV[], 'NX', 'PX', expire)
local strret = tostring(ret)
--用于查看结果,我本机获取锁成功后程序返回随机结果"table: 0x7fb4b3700fe0",否则返回"false"
redis.call('set', 'result', strret)
if strret == 'false' then
return false
else
return true
end
redis.call('del', 'result')
if redis.call('get', KEYS[]) == ARGV[] then
return redis.call('del', KEYS[])
else
return
end
来看下代码,主要写了两个方法,一个是用与锁另外一个是用于结解锁。这块需要注意的是使用RedisTemplate<String, String>,这块意味着key和value一定都是String的,我在使用的过程中就出现了一些错误。首先初始化两个脚本到程序中,然后调用执行脚本。
package com.hqs.distributedlock.lock; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.script.RedisScript;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import java.util.Collections; @Slf4j
@Component
public class DistributedLock { //注意RedisTemplate用的String,String,后续所有用到的key和value都是String的
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String, String> redisTemplate; @Autowired
RedisScript<Boolean> lockScript; @Autowired
RedisScript<Long> unlockScript; public Boolean distributedLock(String key, String uuid, String secondsToLock) {
Boolean locked = false;
try {
String millSeconds = String.valueOf(Integer.parseInt(secondsToLock) * 1000);
locked =redisTemplate.execute(lockScript, Collections.singletonList(key), uuid, millSeconds);
log.info("distributedLock.key{}: - uuid:{}: - timeToLock:{} - locked:{} - millSeconds:{}",
key, uuid, secondsToLock, locked, millSeconds);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("error", e);
}
return locked;
} public void distributedUnlock(String key, String uuid) {
Long unlocked = redisTemplate.execute(unlockScript, Collections.singletonList(key),
uuid);
log.info("distributedLock.key{}: - uuid:{}: - unlocked:{}", key, uuid, unlocked); } }
还有一个就是脚本定义的地方需要注意,返回的结果集一定是Long, Boolean,List, 一个反序列化的值。这块要注意。
package com.hqs.distributedlock.config; import com.sun.org.apache.xpath.internal.operations.Bool;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.script.DefaultRedisScript;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.script.RedisScript;
import org.springframework.scripting.ScriptSource;
import org.springframework.scripting.support.ResourceScriptSource; @Configuration
@Slf4j
public class BeanConfiguration { /**
* The script resultType should be one of
* Long, Boolean, List, or a deserialized value type. It can also be null if the script returns
* a throw-away status (specifically, OK).
* @return
*/
@Bean
public RedisScript<Long> limitScript() {
RedisScript redisScript = null;
try {
ScriptSource scriptSource = new ResourceScriptSource(new ClassPathResource("/scripts/limit.lua"));
// log.info("script:{}", scriptSource.getScriptAsString());
redisScript = RedisScript.of(scriptSource.getScriptAsString(), Long.class);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("error", e);
}
return redisScript; } @Bean
public RedisScript<Boolean> lockScript() {
RedisScript<Boolean> redisScript = null;
try {
ScriptSource scriptSource = new ResourceScriptSource(new ClassPathResource("/scripts/lock.lua"));
redisScript = RedisScript.of(scriptSource.getScriptAsString(), Boolean.class);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("error" , e);
}
return redisScript;
} @Bean
public RedisScript<Long> unlockScript() {
RedisScript<Long> redisScript = null;
try {
ScriptSource scriptSource = new ResourceScriptSource(new ClassPathResource("/scripts/unlock.lua"));
redisScript = RedisScript.of(scriptSource.getScriptAsString(), Long.class);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("error" , e);
}
return redisScript;
} @Bean
public RedisScript<Long> limitAnother() {
DefaultRedisScript<Long> redisScript = new DefaultRedisScript<>();
redisScript.setScriptSource(new ResourceScriptSource(new ClassPathResource("/scripts/limit.lua")));
redisScript.setResultType(Long.class);
return redisScript;
} }
好了,这块就写好了,然后写好controller类准备测试。
@PostMapping("/distributedLock")
@ResponseBody
public String distributedLock(String key, String uuid, String secondsToLock, String userId) throws Exception{
// String uuid = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
Boolean locked = false;
try {
locked = lock.distributedLock(key, uuid, secondsToLock);
if(locked) {
log.info("userId:{} is locked - uuid:{}", userId, uuid);
log.info("do business logic");
TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS.sleep(3000);
} else {
log.info("userId:{} is not locked - uuid:{}", userId, uuid);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("error", e);
} finally {
if(locked) {
lock.distributedUnlock(key, uuid);
}
}
return "ok";
}
我也写了一个测试类,用于测试和输出结果, 使用100个线程,然后锁的时间设置10秒,controller里边需要休眠3秒模拟业务执行。
@Test
public void distrubtedLock() {
String url = "http://localhost:8080/distributedLock";
String uuid = "abcdefg";
// log.info("uuid:{}", uuid);
String key = "redisLock";
String secondsToLive = "10"; for(int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
final int userId = i;
new Thread(() -> {
MultiValueMap<String, String> params = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
params.add("uuid", uuid);
params.add("key", key);
params.add("secondsToLock", secondsToLive);
params.add("userId", String.valueOf(userId));
String result = testRestTemplate.postForObject(url, params, String.class);
System.out.println("-------------" + result);
}
).start();
} }
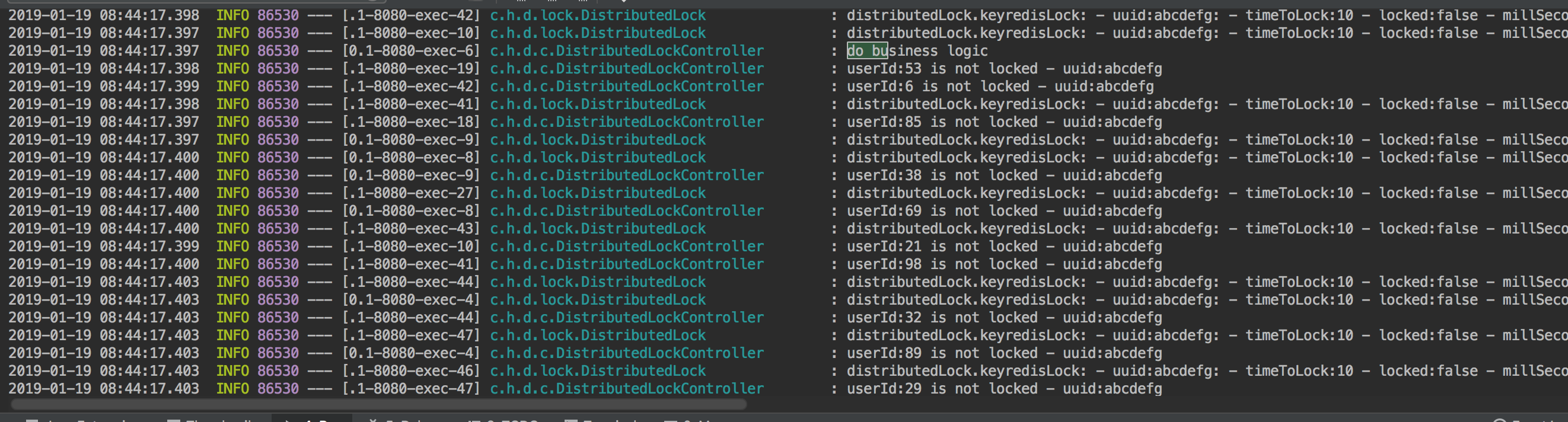
获取锁的地方就会执行do business logic, 然后会有部分线程获取到锁并执行业务,执行完业务的就会释放锁。
分布式锁就实现好了,接下来实现分布式限流。先看一下limit的lua脚本,需要给脚本传两个值,一个值是限流的key,一个值是限流的数量。获取当前key,然后判断其值是否为nil,如果为nil的话需要赋值为0,然后进行加1并且和limit进行比对,如果大于limt即返回0,说明限流了,如果小于limit则需要使用Redis的INCRBY key 1,就是将key进行加1命令。并且设置超时时间,超时时间是秒,并且如果有需要的话这个秒也是可以用参数进行设置。
--lua 下标从 1 开始
-- 限流 key
local key = KEYS[]
-- 限流大小
local limit = tonumber(ARGV[]) -- 获取当前流量大小
local curentLimit = tonumber(redis.call('get', key) or "") if curentLimit + > limit then
-- 达到限流大小 返回
return ;
else
-- 没有达到阈值 value + 1
redis.call("INCRBY", key, )
-- EXPIRE后边的单位是秒
redis.call("EXPIRE", key, )
return curentLimit +
end
执行limit的脚本和执行lock的脚本类似。
package com.hqs.distributedlock.limit; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.script.RedisScript;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import java.util.Collections; /**
* @author huangqingshi
* @Date 2019-01-17
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class DistributedLimit { //注意RedisTemplate用的String,String,后续所有用到的key和value都是String的
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String, String> redisTemplate; @Autowired
RedisScript<Long> limitScript; public Boolean distributedLimit(String key, String limit) {
Long id = 0L; try {
id = redisTemplate.execute(limitScript, Collections.singletonList(key),
limit);
log.info("id:{}", id);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("error", e);
} if(id == 0L) {
return false;
} else {
return true;
}
} }
接下来咱们写一个限流注解,并且设置注解的key和限流的大小:
package com.hqs.distributedlock.annotation; import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target; /**
* 自定义limit注解
* @author huangqingshi
* @Date 2019-01-17
*/
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface DistriLimitAnno {
public String limitKey() default "limit";
public int limit() default 1;
}
然后对注解进行切面,在切面中判断是否超过limit,如果超过limit的时候就需要抛出异常exceeded limit,否则正常执行。
package com.hqs.distributedlock.aspect; import com.hqs.distributedlock.annotation.DistriLimitAnno;
import com.hqs.distributedlock.limit.DistributedLimit;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import java.lang.reflect.Method; /**
* @author huangqingshi
* @Date 2019-01-17
*/
@Slf4j
@Aspect
@Component
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy(proxyTargetClass = true)
public class LimitAspect { @Autowired
DistributedLimit distributedLimit; @Pointcut("@annotation(com.hqs.distributedlock.annotation.DistriLimitAnno)")
public void limit() {}; @Before("limit()")
public void beforeLimit(JoinPoint joinPoint) throws Exception {
MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();
Method method = signature.getMethod();
DistriLimitAnno distriLimitAnno = method.getAnnotation(DistriLimitAnno.class);
String key = distriLimitAnno.limitKey();
int limit = distriLimitAnno.limit();
Boolean exceededLimit = distributedLimit.distributedLimit(key, String.valueOf(limit));
if(!exceededLimit) {
throw new RuntimeException("exceeded limit");
}
} }
因为有抛出异常,这里我弄了一个统一的controller错误处理,如果controller出现Exception的时候都需要走这块异常。如果是正常的RunTimeException的时候获取一下,否则将异常获取一下并且输出。
package com.hqs.distributedlock.util; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.NativeWebRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map; /**
* @author huangqingshi
* @Date 2019-01-17
* 统一的controller错误处理
*/
@Slf4j
@ControllerAdvice
public class UnifiedErrorHandler {
private static Map<String, String> res = new HashMap<>(2); @ExceptionHandler(value = Exception.class)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.OK)
@ResponseBody
public Object processException(HttpServletRequest req, Exception e) {
res.put("url", req.getRequestURL().toString()); if(e instanceof RuntimeException) {
res.put("mess", e.getMessage());
} else {
res.put("mess", "sorry error happens");
}
return res;
} }
好了,接下来将注解写到自定义的controller上,limit的大小为10,也就是10秒钟内限制10次访问。
@PostMapping("/distributedLimit")
@ResponseBody
@DistriLimitAnno(limitKey="limit", limit = 10)
public String distributedLimit(String userId) {
log.info(userId);
return "ok";
}
也是来一段Test方法来跑,老方式100个线程开始跑,只有10次,其他的都是limit。没有问题。
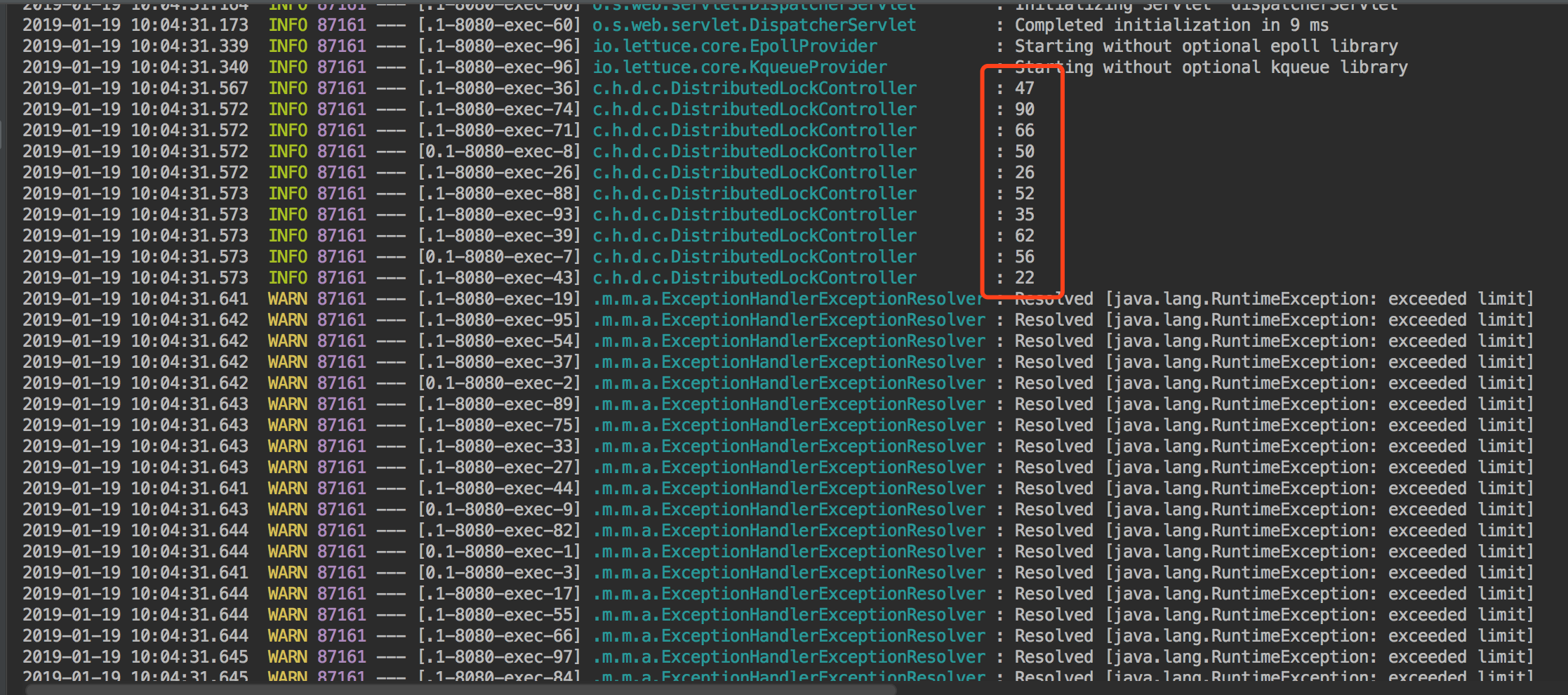
总结一下,这次实现采用了使用lua脚本和Redis实现了锁和限流,但是真实使用的时候还需要多测试,另外如果此次Redis也是采用的单机实现方法,使用集群的时候可能需要改造一下。关于锁这块其实Reids他们自己也实现了RedLock, java实现的版本Redission。也有很多公司使用了,功能非常强大。各种场景下都用到了。
如有问题,欢迎拍砖~
Redis实现的分布式锁和分布式限流的更多相关文章
- zookeeper之分布式锁以及分布式计数器(通过curator框架实现)
有人可能会问zookeeper我知道,但是curator是什么呢? 其实curator是apachede针对zookeeper开发的一个api框架是apache的顶级项目 他与zookeeper原生a ...
- Redis的n种妙用,分布式锁,分布式唯一id,消息队列,抽奖……
介绍 redis是键值对的数据库,常用的五种数据类型为字符串类型(string),散列类型(hash),列表类型(list),集合类型(set),有序集合类型(zset) Redis用作缓存,主要两个 ...
- Redis系列(二)--分布式锁、分布式ID简单实现及思路
分布式锁: Redis可以实现分布式锁,只是讨论Redis的实现思路,而真的实现分布式锁,Zookeeper更加可靠 为什么使用分布式锁: 单机环境下只存在多线程,通过同步操作就可以实现对并发环境的安 ...
- redis 加锁与释放锁(分布式锁1)
使用Redis的 SETNX 命令可以实现分布式锁 SETNX key value 返回值 返回整数,具体为 - 1,当 key 的值被设置 - 0,当 key 的值没被设置 分布式锁使用 impor ...
- redis 加锁与释放锁(分布式锁)
使用Redis的 SETNX 命令可以实现分布式锁 SETNX key value 返回值 返回整数,具体为 - 1,当 key 的值被设置 - 0,当 key 的值没被设置
- 高并发之 API 接口,分布式,防刷限流,如何做?
在开发分布式高并发系统时有三把利器用来保护系统:缓存.降级.限流 缓存 缓存的目的是提升系统访问速度和增大系统处理容量 降级 降级是当服务出现问题或者影响到核心流程时,需要暂时屏蔽掉,待高峰或者问题解 ...
- 基于redis实现的四种常见的限流策略
引言 在web开发中功能是基石,除了功能以外运维和防护就是重头菜了.因为在网站运行期间可能会因为突然的访问量导致业务异常.也有可能遭受别人恶意攻击 所以我们的接口需要对流量进行限制.俗称的QPS也是对 ...
- Redis解读(4):Redis中HyperLongLog、布隆过滤器、限流、Geo、及Scan等进阶应用
Redis中的HyperLogLog 一般我们评估一个网站的访问量,有几个主要的参数: pv,Page View,网页的浏览量 uv,User View,访问的用户 一般来说,pv 或者 uv 的统计 ...
- 如何用 redis 造一把分布式锁
基本概念 锁 wiki:In computer science, a lock or mutex (from mutual exclusion) is a synchronization mechan ...
随机推荐
- vue pc端网站项目开发坑点与难度记录
背景 在一pc端的web项目里,由于某些特性需要由动态语言处理,所以只在有需要使用vue来处理数据的页面,直接引入vue.js来处理.由于刚开始并没有打算使用前端来渲染数据和处理交互,所以使用了一些非 ...
- 重新看halcon模板匹配
工业中模板匹配有很多需求. 代码如下: read_image (Image, 'J:/测试图片/test1/1.bmp') get_image_size (Image, Width, Height) ...
- vsftpd控制用户禁止访问上级目录 只能访问自己目录
涉及文件: vsftpd.conf chroot_list_file=/etc/vsftpd.chroot_list 如果设置为 chroot_local_user=YES chroot_list_e ...
- igmp组播测试环境搭建
2.4G无线组播测试环境搭建: (1)组播源: VLC 或者 pixstream (2)无线: 2.4G AP (3)客户端PC: VLC播放器 有线直连 无线2.4G PC(组播源pixstream ...
- zabbix系列(十)zabbix添加对zookeeper集群的监控
1.应用场景描述 在目前公司的业务中,有部分ESB架构用ZooKeeper作为协同服务的场景,做好ZooKeeper的监控很重要. 2.ZooKeeper监控要点 系统监控 内存使用量 ZooK ...
- Android:注册登录
注册登录的实现 先在layout里新建一个xml文件: //login.xml <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"? ...
- sklearn聚类模型:基于密度的DBSCAN;基于混合高斯模型的GMM
1 sklearn聚类方法详解 2 对比不同聚类算法在不同数据集上的表现 3 用scikit-learn学习K-Means聚类 4 用scikit-learn学习DBSCAN聚类 (基于密度的聚类) ...
- PYTHON-模块time&datetime+ 目录规范
1.目录规范 ***** (1)文件夹的规范写法 bin 可执行文件 conf 配置文件 core 主要业务逻辑 db 数据文件 lib 库 (公共代码 第三方模块) log 日志文件 readme ...
- Android学习笔记————利用JDBC连接服务器数据库
/******************************************************************************************** * auth ...
- Oracle数据库常用Sql语句大全
一,数据控制语句 (DML) 部分 1.INSERT (往数据表里插入记录的语句) INSERT INTO 表名(字段名1, 字段名2, ……) VALUES ( 值1, 值2, ……); INSE ...
