Self-Taught Learning to Deep Networks
In this section, we describe how you can fine-tune and further improve the learned features using labeled data. When you have a large amount of labeled training data, this can significantly improve your classifier's performance.
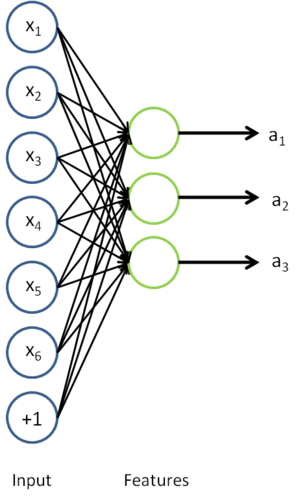
In self-taught learning, we first trained a sparse autoencoder on the unlabeled data. Then, given a new example
, we used the hidden layer to extract features
. This is illustrated in the following diagram:
We are interested in solving a classification task, where our goal is to predict labels
. We have a labeled training set
of
labeled examples. We showed previously that we can replace the original features
with features
computed by the sparse autoencoder (the "replacement" representation). This gives us a training set
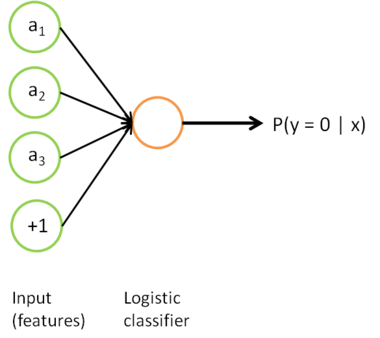
. Finally, we train a logistic classifier to map from the features
to the classification label
.
we can draw our logistic regression unit (shown in orange) as follows:
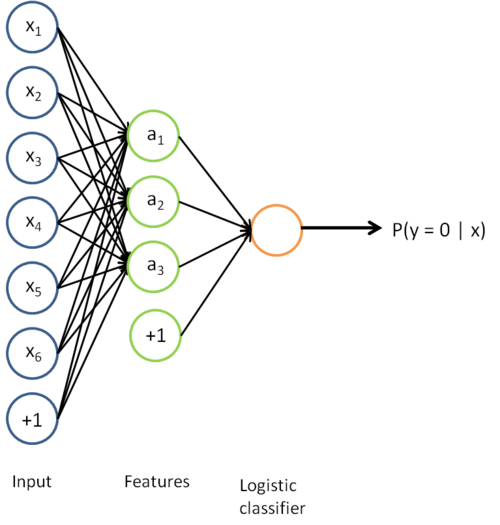
Now, consider the overall classifier (i.e., the input-output mapping) that we have learned using this method. In particular, let us examine the function that our classifier uses to map from from a new test example
to a new prediction p(y = 1 | x). We can draw a representation of this function by putting together the two pictures from above. In particular, the final classifier looks like this:
The parameters of this model were trained in two stages: The first layer of weights 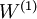 mapping from the input
mapping from the input 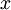 to the hidden unit activations
to the hidden unit activations 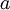 were trained as part of the sparse autoencoder training process. The second layer of weights
were trained as part of the sparse autoencoder training process. The second layer of weights 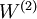 mapping from the activations
mapping from the activations 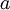 to the output
to the output 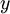 was trained using logistic regression (or softmax regression).
was trained using logistic regression (or softmax regression).
But the form of our overall/final classifier is clearly just a whole big neural network. So, having trained up an initial set of parameters for our model (training the first layer using an autoencoder, and the second layer via logistic/softmax regression), we can further modify all the parameters in our model to try to further reduce the training error. In particular, we can fine-tune the parameters, meaning perform gradient descent (or use L-BFGS) from the current setting of the parameters to try to reduce the training error on our labeled training set 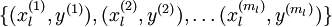 .
.
When fine-tuning is used, sometimes the original unsupervised feature learning steps (i.e., training the autoencoder and the logistic classifier) are called pre-training. The effect of fine-tuning is that the labeled data can be used to modify the weights W(1) as well, so that adjustments can be made to the features a extracted by the layer of hidden units.
if we are using fine-tuning usually we will do so with a network built using the replacement representation. (If you are not using fine-tuning however, then sometimes the concatenation representation can give much better performance.)
When should we use fine-tuning? It is typically used only if you have a large labeled training set; in this setting, fine-tuning can significantly improve the performance of your classifier. However, if you have a large unlabeled dataset (for unsupervised feature learning/pre-training) and only a relatively small labeled training set, then fine-tuning is significantly less likely to help.
Self-Taught Learning to Deep Networks的更多相关文章
- 【论文考古】联邦学习开山之作 Communication-Efficient Learning of Deep Networks from Decentralized Data
B. McMahan, E. Moore, D. Ramage, S. Hampson, and B. A. y Arcas, "Communication-Efficient Learni ...
- Communication-Efficient Learning of Deep Networks from Decentralized Data
郑重声明:原文参见标题,如有侵权,请联系作者,将会撤销发布! Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Artificial Intell ...
- Deep Learning 8_深度学习UFLDL教程:Stacked Autocoders and Implement deep networks for digit classification_Exercise(斯坦福大学深度学习教程)
前言 1.理论知识:UFLDL教程.Deep learning:十六(deep networks) 2.实验环境:win7, matlab2015b,16G内存,2T硬盘 3.实验内容:Exercis ...
- (转)Understanding, generalisation, and transfer learning in deep neural networks
Understanding, generalisation, and transfer learning in deep neural networks FEBRUARY 27, 2017 Thi ...
- 论文笔记之:UNSUPERVISED REPRESENTATION LEARNING WITH DEEP CONVOLUTIONAL GENERATIVE ADVERSARIAL NETWORKS
UNSUPERVISED REPRESENTATION LEARNING WITH DEEP CONVOLUTIONAL GENERATIVE ADVERSARIAL NETWORKS ICLR 2 ...
- 深度学习材料:从感知机到深度网络A Deep Learning Tutorial: From Perceptrons to Deep Networks
In recent years, there’s been a resurgence in the field of Artificial Intelligence. It’s spread beyo ...
- This instability is a fundamental problem for gradient-based learning in deep neural networks. vanishing exploding gradient problem
The unstable gradient problem: The fundamental problem here isn't so much the vanishing gradient pro ...
- [译]深度神经网络的多任务学习概览(An Overview of Multi-task Learning in Deep Neural Networks)
译自:http://sebastianruder.com/multi-task/ 1. 前言 在机器学习中,我们通常关心优化某一特定指标,不管这个指标是一个标准值,还是企业KPI.为了达到这个目标,我 ...
- Learning Combinatorial Embedding Networks for Deep Graph Matching(基于图嵌入的深度图匹配)
1. 文献信息 题目: Learning Combinatorial Embedding Networks for Deep Graph Matching(基于图嵌入的深度图匹配) 作者:上海交通大学 ...
随机推荐
- SQL流程控制语句
1 GoTo语句 IF 12>9GOTO print1ELSE GOTO print2 print1:PRINT '执行了流程1'--GOTO theEndprint2:PRINT '执行了流程 ...
- 编译报错一列----aclocal找不到
编译源码包报错: 说aclocal这个命令找不到 解决: 使用 yum install -y automake问题解决
- POJ2299 树状数组求逆序对
裸题,不多解释. #include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<algorithm> #include<cstri ...
- [ZJOI2012]旅游(树的直径)
[ZJOI2012]旅游 题目描述 到了难得的暑假,为了庆祝小白在数学考试中取得的优异成绩,小蓝决定带小白出去旅游~~ 经过一番抉择,两人决定将T国作为他们的目的地.T国的国土可以用一个凸N边形来表示 ...
- 题解 CF1037D 【Valid BFS?】
不管怎么说,这都不是道紫题吧... 这里采用的思想有点类似轻重链剖分. 我们按照每个节点在序列里面出现的顺序,把每一个节点连出去的边都排一个序. 这样(如果序列没错)肯定会按照序列的方式遍历完全图. ...
- 【Henu ACM Round#20 B】Contest
[链接] 我是链接,点我呀:) [题意] 在这里输入题意 [题解] 根据时间和原分数. 算出对应的分数就可以了. [代码] #include <bits/stdc++.h> using n ...
- berkeley db储存URL队列的简单实现增、删、查
Berkeley DB(BDB)是一个高效的嵌入式数据库编程库,C语言.C++.Java.Perl.Python.Tcl以及其它非常多语言都有其相应的API. Berkeley DB能够保存随意 ...
- 使用 gradle 在编译时动态设置 Android resValue / BuildConfig / Manifes中<meta-data>变量的值
转载请标明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/xx326664162/article/details/49247815 文章出自:薛瑄的博客 你也能够查看我的其它同类文章.也会让你有一定的 ...
- 彻底解决lazarus安装组件后烦人的编译时单元找不到的问题!
以安装indy为例 1/下载组件包, http://www.indyproject.org/Sockets/fpc/indy-10.2.0.3.zip 2/爆开放于C:\lazarus\compone ...
- js如何生成[n,m]的随机数(整理总结)
js如何生成[n,m]的随机数(整理总结) 一.总结 一句话总结: // max - 期望的最大值 // min - 期望的最小值 parseInt(Math.random()*(max-min+1) ...