SaltStact自动化运维工具02
Grains基础:
• Grains是saltstack最重要的组件之一
• 存储minion端的基本信息,这些信息一般都是静态的,如CPU、内核、操作系统等
• Grains存储在minion本地
• 管理员可以在minion端进行grains值的修改,如增加、删除等
Grains基础应用
应用一: 获取minion端所有grains信息
# salt '随便一台主机名' grains.items 相当于python字典的items() 列出key value
#salt '随便一台主机名' grains.ls 只列出key
#salt '随便一台主机名' grains.get saltversion 获取某个key的value
• 通过grains.item获取minion端的fqdn信息
# salt '随便一台主机名' grains.item fqdn
- [root@linux-node1 ~]# salt 'linux-node1.localdomain' grains.items
- linux-node1.localdomain:
- ----------
- SSDs:
- biosreleasedate:
- 07/02/2015
- biosversion:
- 6.00
- cpu_flags:
- - fpu
- - vme
- - de
- - pse
- - tsc
- - msr
- - pae
- - mce
- - cx8
- - apic
- - sep
- - mtrr
- - pge
- - mca
- - cmov
- - pat
- - pse36
- - clflush
- - dts
- - mmx
- - fxsr
- - sse
- - sse2
- - ss
- - ht
- - syscall
- - nx
- - pdpe1gb
- - rdtscp
- - lm
- - constant_tsc
- - arch_perfmon
- - pebs
- - bts
- - nopl
- - xtopology
- - tsc_reliable
- - nonstop_tsc
- - aperfmperf
- - eagerfpu
- - pni
- - pclmulqdq
- - vmx
- - ssse3
- - fma
- - cx16
- - pcid
- - sse4_1
- - sse4_2
- - x2apic
- - movbe
- - popcnt
- - tsc_deadline_timer
- - aes
- - xsave
- - avx
- - f16c
- - rdrand
- - hypervisor
- - lahf_lm
- - abm
- - epb
- - tpr_shadow
- - vnmi
- - ept
- - vpid
- - fsgsbase
- - tsc_adjust
- - bmi1
- - avx2
- - smep
- - bmi2
- - invpcid
- - xsaveopt
- - dtherm
- - arat
- - pln
- - pts
- cpu_model:
- Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-4710MQ CPU @ 2.50GHz
- cpuarch:
- x86_64
- disks:
- - sda
- - sr0
- - dm-0
- - dm-1
- - dm-2
- dns:
- ----------
- domain:
- ip4_nameservers:
- - 192.168.0.1
- ip6_nameservers:
- nameservers:
- - 192.168.0.1
- options:
- search:
- - localdomain
- sortlist:
- domain:
- localdomain
- fqdn:
- localhost.localdomain
- fqdn_ip4:
- - 127.0.0.1
- fqdn_ip6:
- - ::1
- fqdns:
- gid:
- 0
- gpus:
- |_
- ----------
- model:
- SVGA II Adapter
- vendor:
- vmware
- groupname:
- root
- host:
- localhost
- hwaddr_interfaces:
- ----------
- ens33:
- 00:0c:29:fd:fa:c7
- lo:
- 00:00:00:00:00:00
- virbr0:
- 52:54:00:17:39:b3
- virbr0-nic:
- 52:54:00:17:39:b3
- id:
- linux-node1.localdomain
- init:
- systemd
- ip4_gw:
- 192.168.0.1
- ip4_interfaces:
- ----------
- ens33:
- - 192.168.0.2
- lo:
- - 127.0.0.1
- virbr0:
- - 192.168.122.1
- virbr0-nic:
- ip6_gw:
- False
- ip6_interfaces:
- ----------
- ens33:
- - fe80::cd7:c134:744a:cf30
- lo:
- - ::1
- virbr0:
- virbr0-nic:
- ip_gw:
- True
- ip_interfaces:
- ----------
- ens33:
- - 192.168.0.2
- - fe80::cd7:c134:744a:cf30
- lo:
- - 127.0.0.1
- - ::1
- virbr0:
- - 192.168.122.1
- virbr0-nic:
- ipv4:
- - 127.0.0.1
- - 192.168.0.2
- - 192.168.122.1
- ipv6:
- - ::1
- - fe80::cd7:c134:744a:cf30
- kernel:
- Linux
- kernelrelease:
- 3.10.0-957.el7.x86_64
- kernelversion:
- #1 SMP Thu Nov 8 23:39:32 UTC 2018
- locale_info:
- ----------
- defaultencoding:
- UTF-8
- defaultlanguage:
- zh_CN
- detectedencoding:
- UTF-8
- localhost:
- linux-node1.localdomain
- lsb_distrib_codename:
- CentOS Linux 7 (Core)
- lsb_distrib_id:
- CentOS Linux
- machine_id:
- 37a27c09411541ca8f072be3ccc05527
- manufacturer:
- VMware, Inc.
- master:
- 192.168.0.2
- mdadm:
- mem_total:
- 3771
- nodename:
- linux-node1.localdomain
- num_cpus:
- 4
- num_gpus:
- 1
- os:
- CentOS
- os_family:
- RedHat
- osarch:
- x86_64
- oscodename:
- CentOS Linux 7 (Core)
- osfinger:
- CentOS Linux-7
- osfullname:
- CentOS Linux
- osmajorrelease:
- 7
- osrelease:
- 7.6.1810
- osrelease_info:
- - 7
- - 6
- - 1810
- path:
- /usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin
- pid:
- 21258
- productname:
- VMware Virtual Platform
- ps:
- ps -efHww
- pythonexecutable:
- /usr/bin/python
- pythonpath:
- - /usr/bin
- - /usr/lib64/python27.zip
- - /usr/lib64/python2.7
- - /usr/lib64/python2.7/plat-linux2
- - /usr/lib64/python2.7/lib-tk
- - /usr/lib64/python2.7/lib-old
- - /usr/lib64/python2.7/lib-dynload
- - /usr/lib64/python2.7/site-packages
- - /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages
- pythonversion:
- - 2
- - 7
- - 5
- - final
- - 0
- saltpath:
- /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/salt
- saltversion:
- 2019.2.0
- saltversioninfo:
- - 2019
- - 2
- - 0
- - 0
- selinux:
- ----------
- enabled:
- True
- enforced:
- Enforcing
- serialnumber:
- VMware-56 4d 48 8f 93 62 a0 3f-01 fa 25 b5 f5 fd fa c7
- server_id:
- 740310944
- shell:
- /bin/sh
- swap_total:
- 3967
- systemd:
- ----------
- features:
- +PAM +AUDIT +SELINUX +IMA -APPARMOR +SMACK +SYSVINIT +UTMP +LIBCRYPTSETUP +GCRYPT +GNUTLS +ACL +XZ +LZ4 -SECCOMP +BLKID +ELFUTILS +KMOD +IDN
- version:
- 219
- uid:
- 0
- username:
- root
- uuid:
- 8f484d56-6293-3fa0-01fa-25b5f5fdfac7
- virtual:
- VMware
- zfs_feature_flags:
- False
- zfs_support:
- False
- zmqversion:
- 4.1.4
- [root@linux-node1 ~]#
应用二
root@linux-node1 ~]# vim /srv/salt/base/web/apache.sls
apache-install:
pkg.installed:
- name: httpd
apache-service:
service.running:
- name: httpd
- enable: True
[root@linux-node1 ~]# vim /srv/salt/base/top.sls
base:
'os:CentOS':
- match: grain
- web.apache
[root@linux-node1 ~]# salt '*' state.highstate
应用三 通过minion的配置文件定义grains
[root@web1 ~]# vim /etc/salt/minion
grains:
web:
apache
[root@web1 ~]# systemctl restart salt-minion.service
[root@web2 ~]# vim /etc/salt/minion
grains:
web:
nginx
[root@web2 ~]# systemctl restart salt-minion.service
[root@sm ~]# salt '*' saltutil.sync_grains
web1:
db1:
cache:
web2:
db2:
[root@sm ~]# salt -G 'web:apache' test.ping
web1:
True
[root@sm ~]# salt -G 'web:nginx' test.ping
web2:
True
[root@sm ~]# salt 'web1' grains.item web
web1:
----------
web:
apache
[root@sm ~]# salt 'web2' grains.item web
web2:
----------
web:
nginx
应用四 在minion的/etc/salt下创建一个grains文件自定义grains键值对
例子一
[root@linux-node2 ~]# vim /etc/salt/grains
haha: linux-node1
[root@linux-node2 ~]# systemctl restart salt-minion
[root@linux-node1 ~]# salt '*' grains.get haha
linux-node1.localdomain:
linux-node2.localdomain:
linux-node1
例子二
[root@linux-node2 ~]# vim /etc/salt/grains
haha: linux-node1
[root@linux-node1 ~]# salt '*' saltutil.sync_grains 不需要重启就可以获取值 相对于例子一
[root@linux-node1 ~]# salt '*' grains.get haha
linux-node1.localdomain:
linux-node2.localdomain:
linux-node1
Pillar基础 在master端设置
• Pillar也是saltstack最重要的组件之一
• 作用是定义与被控主机相关的任何数据,定义好的数据可以被其他组件使用
• 存储在master端,存放需要提供给minion的信息
• 常用于敏感信息,每个minion只能访问master分配给自己的pillar信息
• 用于经常动态变化的信息
eg
[root@linux-node1 ~]# vim /etc/salt/master
#pillar_opts: False 改成True去掉注释
[root@linux-node1 ~]# salt '*' pillar.items 查看所有隐藏的pillar数据
[root@linux-node1 ~]# vim /etc/salt/master
pillar_roots:
base:
- /srv/pillar/base
prod:
- /srv/pillar/prod
[root@linux-node1 ~]#mkdir -p /srv/pillar/{base,prod}
[root@linux-node1 ~]#systemctl restart salt-master
#######################################################################
[root@linux-node1 ~]# vim /srv/pillar/base/apache.sls 自定义隐藏数据
{% if grains['os'] == 'CentOS' %}
apache: httpd
{% elif grains['os'] == 'Debian' %}
apache: apache2
{% endif %}
[root@linux-node1 ~]# vim /srv/pillar/base/top.sls
base:
'*':
- apache
[root@linux-node1 ~]# salt '*' pillar.items 不用重启服务pillar自动加载
linux-node2.localdomain:
----------
apache:
httpd
linux-node1.localdomain:
----------
apache:
httpd
[root@linux-node1 ~]# vim /srv/salt/base/web/apache.sls
apache-install:
pkg.installed:
- name: {{ pillar['apache'] }} #调用pillar定义的值
apache-service:
service.running:
- name: {{ pillar['apache'] }}
- enable: True
[root@linux-node1 base]# vim /srv/salt/base/top.sls
base:
'os:CentOS':
- match: grain
- web.apache
salt '*' state.highstate 第一步执行/srv/salt/base/top.sls 然后执行/srv/salt/base/web/apache.sls
- 配置pillar
- • Pillar需要一个pillar_roots来维护pillar的配置
- • 默认pillar_roots为/srv/pillar
- • pillar_roots在Master配置文件中定义
- [root@sm ~]# vim /etc/salt/master
- pillar_roots:
- base:
- - /srv/pillar
- [root@sm ~]# mkdir /srv/pillar
- [root@sm ~]# systemctl restart salt-master
- Pillar数据文件
- • Pillar执行时需要一个名为top.sls的入口文件
- • 通过top.sls文件作为入口,组织其它的pillar文件
- • sls文件采用YAML格式
- [root@sm ~]# cd /srv/pillar
- [root@sm pillar]# vim top.sls
- base: # 与pillar_roots定义一致
- 'L@web1,web2': # 过滤目标
- - appweb # 用于包含 appweb
- 'E@db\d':
- - appdb
- - user
- 'cache':
- - user
- [root@sm pillar]# vim appweb.sls
- appname: web
- software:
- - apache
- - nginx
- [root@sm pillar]# vim appdb.sls
- appname: mysql
- [root@sm pillar]# vim user.sls
- users:
- zhang3: 1000
- li4: 1001
- // 获取pillar全部数据
- [root@sm pillar]# salt '*' pillar.items
- web1:
- ----------
- appname:
- web
- software:
- - apache
- - nginx
- cache:
- ----------
- users:
- ----------
- li4:
- 1001
- zhang3:
- 1000
- web2:
- ----------
- appname:
- web
- software:
- - apache
- - nginx
- db2:
- ----------
- appname:
- mysql
- users:
- ----------
- li4:
- 1001
- zhang3:
- 1000
- db1:
- ----------
- appname:
- mysql
- users:
- ----------
- li4:
- 1001
- zhang3:
- 1000
- // 将pillar数据同步至minion
- [root@sm pillar]# salt '*' saltutil.refresh_pillar
- db2:
- True
- db1:
- True
- web2:
- True
- cache:
- True
- web1:
- True
- // 根据pillar值匹配minion
- [root@sm pillar]# salt 'web1' pillar.item software
- web1:
- ----------
- software:
- - apache
- - nginx
pillar应用
salt-ssh介绍
[root@linux-node1 ~]# yum -y install salt-ssh
[root@linux-node1 ~]# vim /etc/salt/roster
linux-node1:
host: 192.168.0.2
user: root
passwd: 123123
port: 22
linux-node2:
host: 192.168.0.3
user: root
passwd: 123123
port: 22
[root@linux-node1 ~]# salt-ssh '*' test.ping #不支持交互
- linux-node1:
- ----------
- retcode:
- 254
- stderr:
- stdout:
- The host key needs to be accepted, to auto accept run salt-ssh with the -i flag:
- The authenticity of host '192.168.0.2 (192.168.0.2)' can't be established.
- ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:2hjLlAn/WOJ6Cx4Q8B70J4X1ObWstIsSvW7zcmGNL3E.
- ECDSA key fingerprint is MD5:57:81:6b:a6:62:7e:25:a3:18:04:eb:26:e0:b5:1b:68.
- Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)?
- linux-node2:
- ----------
- retcode:
- 254
- stderr:
- stdout:
- The host key needs to be accepted, to auto accept run salt-ssh with the -i flag:
- The authenticity of host '192.168.0.3 (192.168.0.3)' can't be established.
- ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:O9SmNfSYPTyD9lvCospsGqNg53nqcHtOUfaVG/poh6c.
- ECDSA key fingerprint is MD5:f1:8d:7f:5e:50:b5:27:14:ca:aa:d8:6d:47:0a:5a:04.
- Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)?
结果
[root@linux-node1 ~]# salt-ssh '*' test.ping -i #加-i 默认yes 不要交互 或者:
[root@linux-node1 ~]# salt-ssh '*' -r 'ifconfig' 等价于[root@linux-node1 ~]# salt '*' cmd.run 'ifconfig'
[root@linux-node1 ~]# vim .ssh/config #执行任何命令不用交互
StrictHostKeyChecking no
常用的远程执行模块
[root@linux-node1 ~]# salt 'linux-node1.localdomain' service.status sshd #service(模块名称).status(方法) sshd(参数)
linux-node1.localdomain:
True
[root@linux-node1 ~]#
[root@linux-node1 ~]# salt 'linux-node1.localdomain' service.available sshd
linux-node1.localdomain:
True
[root@linux-node1 ~]# salt 'linux-node1.localdomain' service.get_all #列出运行的所有服务
[root@linux-node1 ~]# salt '*' network.active_tcp #返回所有TCP连接
- linux-node1.localdomain:
- ----------
- 0:
- ----------
- local_addr:
- 192.168.0.2
- local_port:
- 4505
- remote_addr:
- 192.168.0.2
- remote_port:
- 56454
- 1:
- ----------
- local_addr:
- 192.168.0.2
- local_port:
- 56454
- remote_addr:
- 192.168.0.2
- remote_port:
- 4505
- 2:
- ----------
- local_addr:
- 192.168.0.2
- local_port:
- 4505
- remote_addr:
- 192.168.0.3
- remote_port:
- 41612
- 3:
- ----------
- local_addr:
- 192.168.0.2
- local_port:
- 22
- remote_addr:
- 192.168.0.101
- remote_port:
- 50821
- linux-node2.localdomain:
- ----------
- 0:
- ----------
- local_addr:
- 192.168.0.3
- local_port:
- 22
- remote_addr:
- 192.168.0.101
- remote_port:
- 51528
- 1:
- ----------
- local_addr:
- 192.168.0.3
- local_port:
- 41612
- remote_addr:
- 192.168.0.2
- remote_port:
- 4505
结果
[root@linux-node1 ~]# salt '*' network.connect baidu.com 80
linux-node2.localdomain:
----------
comment:
Successfully connected to baidu.com (123.125.115.110) on tcp port 80
result:
True
linux-node1.localdomain:
----------
comment:
Successfully connected to baidu.com (123.125.115.110) on tcp port 80
result:
True
[root@linux-node1 ~]# salt 'linux-node1.localdomain' state.show_top 查看top.sls里面对minion定义数据
linux-node1.localdomain:
----------
prod:
- lamp
[root@linux-node1 ~]# salt-cp 'linux-node1.localdomain' /etc/passwd /tmp/hehe #cp功能
linux-node1.localdomain:
----------
/tmp/hehe:
True
######################
远程执行返回
[root@linux-node1 ~]# salt '*' cmd.run 'yum -y install MySQL-python' 或者[root@linux-node1 ~]# salt '*' pkg.install MySQL-python
[root@linux-node1 ~]#要安装数据库 MariaDB-server
Use the following mysql database schema:
CREATE DATABASE `salt`
DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8
DEFAULT COLLATE utf8_general_ci;
USE `salt`;
--
-- Table structure for table `jids`
--
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `jids`;
CREATE TABLE `jids` (
`jid` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
`load` mediumtext NOT NULL,
UNIQUE KEY `jid` (`jid`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
CREATE INDEX jid ON jids(jid) USING BTREE;
--
-- Table structure for table `salt_returns`
--
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `salt_returns`;
CREATE TABLE `salt_returns` (
`fun` varchar(50) NOT NULL,
`jid` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
`return` mediumtext NOT NULL,
`id` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
`success` varchar(10) NOT NULL,
`full_ret` mediumtext NOT NULL,
`alter_time` TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
KEY `id` (`id`),
KEY `jid` (`jid`),
KEY `fun` (`fun`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
--
-- Table structure for table `salt_events`
--
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `salt_events`;
CREATE TABLE `salt_events` (
`id` BIGINT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`tag` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
`data` mediumtext NOT NULL,
`alter_time` TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
`master_id` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `tag` (`tag`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
MariaDB [salt]> grant all on salt.* to salt@'%' identified by 'salt';
配置minion
[root@linux-node2 ~]# vim /etc/salt/minion
#return: mysql
#
mysql.host: '192.168.0.2'
mysql.user: 'salt'
mysql.pass: 'salt'
mysql.db: 'salt'
mysql.port: 3306
[root@linux-node2 ~]# systemctl restart salt-minion
[root@linux-node1 ~]# salt 'linux-node2.localdomain' test.ping --return mysql
linux-node2.localdomain:
True
查看数据库
MariaDB [salt]> select * from salt_returns\G;
*************************** 1. row ***************************
fun: test.ping
jid: 20190316185439085889
return: true
id: linux-node2.localdomain
success: 1
full_ret: {"fun_args": [], "jid": "20190316185439085889", "return": true, "retcode": 0, "success": true, "fun": "test.ping", "id": "linux-node2.localdomain"}
alter_time: 2019-03-16 18:54:39
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
ERROR: No query specified
MariaDB [salt]>
[root@linux-node1 ~]# vim /etc/salt/master
maser_jod_cache: mysql #加一行 [root@linux-node1 ~]# salt 'linux-node2.localdomain' test.ping #就不用加--return mysql
mysql.host: '192.168.0.2'
mysql.user: 'salt'
mysql.pass: 'salt'
mysql.db: 'salt'
mysql.port: 3306
[root@linux-node1 ~]# systemctl restart salt-master
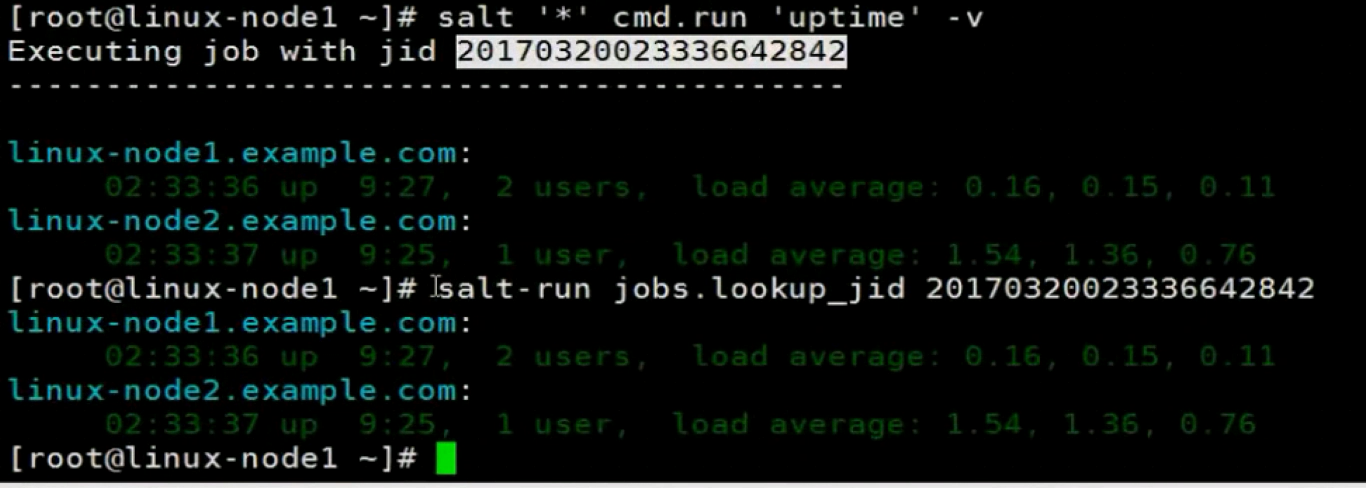
SaltStact自动化运维工具02的更多相关文章
- SaltStact自动化运维工具01
什么是saltstackSaltstack是基于python开发的一套C/S架构配置管理工具使用SSL证书签方的方式进行认证管理底层使用ZeroMQ消息队列pub/sub方式通信 – 号称世界 ...
- SaltStact自动化运维工具03
存储位置 类型 采集方式 场景Grains minion 静态 minion启动时,可以刷新 1.获取信息 2.匹配pil ...
- 企业级自动化运维工具应用实战-ansible
背景 公司计划在年底做一次大型市场促销活动,全面冲刺下交易额,为明年的上市做准备.公司要求各业务组对年底大促做准备,运维部要求所有业务容量进行三倍的扩容,并搭建出多套环境可以共开发和测试人员做测试,运 ...
- Ansible自动化运维工具使用
概述本文描述自动化运维工具 Ansible 的安装及基础使用方法,包含: Centos 下的安装主机配置Ad-Hoc command(命令行执行)Playbook (任务剧本)Ansible 和 Sa ...
- Ansible自动化运维工具
ansible软件介绍 python语言是运维人员必会的语言! ansible是一个基于Python开发的自动化运维工具!(saltstack) 其功能实现基于SSH远程连接服务! ans ...
- 自动化运维工具-Ansible基础
目录 自动化运维工具-Ansible基础 什么是Ansible 同类型软件对比 Ansible的功能及优点 Ansible的架构 Ansible的执行流程 安装Ansible ansible配置文件 ...
- 自动化运维工具之Puppet基础入门
一.简介 puppet是什么?它能做什么? puppet是一个IT基础设施自动化运维工具,它能够帮助系统管理员管理基础设施的整个生命周期:比如,安装服务,提供配置文件,启动服务等等一系列操作:基于pu ...
- 自动化运维工具-Ansible之2-ad-hoc
自动化运维工具-Ansible之2-ad-hoc 目录 自动化运维工具-Ansible之2-ad-hoc Ansible ad-hoc Ansible命令模块 Ansible软件管理模块 Ansibl ...
- Ansible自动化运维工具及其常用模块
Ansible自动化运维工具及其常用模块 目录 Ansible自动化运维工具及其常用模块 一.Ansible简介 1. Ansible概述 2. Ansible作用 3. Ansible的工作模块 4 ...
随机推荐
- 继续聊WPF——Expander控件(2)
<Window x:Class="Expander_Sample2.Window1" xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/win ...
- ThinkPhp5.0 引入全局自定义函数global
可以直接调用:相当于global.class.php 全局文件 ==================================================================== ...
- mysql中使用order 出现错误
- 洛谷 P2634 BZOJ 2152 【模板】点分治(聪聪可可)
题目描述 聪聪和可可是兄弟俩,他们俩经常为了一些琐事打起来,例如家中只剩下最后一根冰棍而两人都想吃.两个人都想玩儿电脑(可是他们家只有一台电脑)……遇到这种问题,一般情况下石头剪刀布就好了,可是他们已 ...
- HDU - 3040 - Happy Girls
先上题目: Happy Girls Time Limit: 6000/3000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others ...
- CGLib与JDK的动态代理
一.CGLib 简单介绍 CGLib (Code Generation Library) 是一个强大的,高性能,高质量的Code生成类库. 它能够在执行期扩展Java类与实现Java接口. Hiber ...
- 原型设计模式prototype-构造js自己定义对象
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title> ...
- 公告:CSDN博客积分系统升级(暂行版)
各位亲爱的用户: CSDN博客频道将于2014年10月22日23点至10月23日8点进行积分系统的升级,升级期间会影响大家的正常訪问和操作.给大家带来不便.敬请广大用户谅解.很多其它详情见>&g ...
- 数据结构之---C语言实现共享栈
所谓共享栈是两个栈在一个顺序的存储空间中.两个栈的栈底各自是存储空间的首尾地址. 如图我们能够将两个栈构造成一个: 如图: 从这里也就能够分析出来,栈1为空时,就是top1等于-1时.而当top2等于 ...
- 报错configure:error: no acceptable C compiler found in $PATH。。
报错configure:error: no acceptable C compiler found in $PATH.. 查看日志: 出错原因:新安装的linux系统,没有gcc库 解决方案:使用yu ...
