TensorFlow简易学习[3]:实现神经网络
TensorFlow本身是分布式机器学习框架,所以是基于深度学习的,前一篇TensorFlow简易学习[2]:实现线性回归对只一般算法的举例只是为说明TensorFlow的广泛性。本文将通过示例TensorFlow如何创建、训练一个神经网络。
主要包括以下内容:
神经网络基础
基本激励函数
创建神经网络
神经网络简介
关于神经网络资源很多,这里推荐吴恩达的一个Tutorial。
基本激励函数
关于激励函数的作用,常有解释:不使用激励函数的话,神经网络的每层都只是做线性变换,多层输入叠加后也还是线性变换。因为线性模型的表达能力不够,激励函数可以引入非线性因素(ref1)。 关于如何选择激励函数,激励函数的优缺点等可参考已标识ref1, ref2。
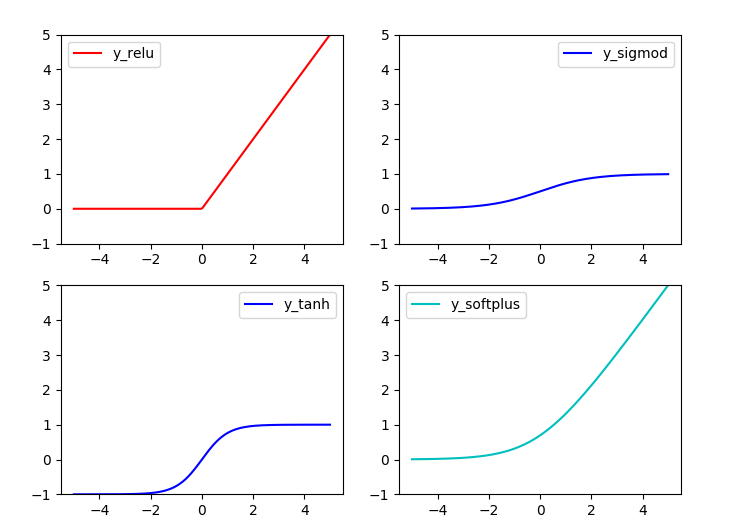
常用激励函数有(ref2): tanh, relu, sigmod, softplus
激励函数在TensorFlow代码实现:
#!/usr/bin/python '''
Show the most used activation functions in Network
''' import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt x = np.linspace(-5, 5, 200) #1. struct
#following are popular activation functions
y_relu = tf.nn.relu(x)
y_sigmod = tf.nn.sigmoid(x)
y_tanh = tf.nn.tanh(x)
y_softplus = tf.nn.softplus(x) #2. session
sess = tf.Session()
y_relu, y_sigmod, y_tanh, y_softplus =sess.run([y_relu, y_sigmod, y_tanh, y_softplus]) # plot these activation functions
plt.figure(1, figsize=(8,6)) plt.subplot(221)
plt.plot(x, y_relu, c ='red', label = 'y_relu')
plt.ylim((-1, 5))
plt.legend(loc = 'best') plt.subplot(222)
plt.plot(x, y_sigmod, c ='b', label = 'y_sigmod')
plt.ylim((-1, 5))
plt.legend(loc = 'best') plt.subplot(223)
plt.plot(x, y_tanh, c ='b', label = 'y_tanh')
plt.ylim((-1, 5))
plt.legend(loc = 'best') plt.subplot(224)
plt.plot(x, y_softplus, c ='c', label = 'y_softplus')
plt.ylim((-1, 5))
plt.legend(loc = 'best') plt.show()
结果:
创建神经网络
创建层
定义函数用于创建隐藏层/输出层:
#add a layer and return outputs of the layer
def add_layer(inputs, in_size, out_size, activation_function=None):
#1. initial weights[in_size, out_size]
Weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([in_size,out_size]))
#2. bias: (+0.1)
biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1,out_size]) + 0.1)
#3. input*Weight + bias
Wx_plus_b = tf.matmul(inputs, Weights) + biases
#4. activation
if activation_function is None:
outputs = Wx_plus_b
else:
outputs = activation_function(Wx_plus_b)
return outputs
定义网络结构
此处定义一个三层网络,即:输入-单层隐藏层-输出层。可通过以上函数添加层数。网络为全连接网络。
# add hidden layer
l1 = add_layer(xs, 1, 10, activation_function=tf.nn.relu)
# add output layer
prediction = add_layer(l1, 10, 1, activation_function=None)
训练
利用梯度下降,训练1000次。
loss function: suqare error
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(ys - prediction), reduction_indices=[1]))
GD = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.1)
train_step = GD.minimize(loss)
完整代码
#!/usr/bin/python '''
Build a simple network
''' import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np #1. add_layer
def add_layer(inputs, in_size, out_size, activation_function=None):
#1. initial weights[in_size, out_size]
Weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([in_size,out_size]))
#2. bias: (+0.1)
biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1,out_size]) + 0.1)
#3. input*Weight + bias
Wx_plus_b = tf.matmul(inputs, Weights) + biases
#4. activation
## when activation_function is None then outlayer
if activation_function is None:
outputs = Wx_plus_b
else:
outputs = activation_function(Wx_plus_b)
return outputs ##begin build network struct##
##network: 1 * 10 * 1
#2. create data
x_data = np.linspace(-1, 1, 300)[:, np.newaxis]
noise = np.random.normal(0, 0.05, x_data.shape)
y_data = np.square(x_data) - 0.5 + noise #3. placehoder: waiting for the training data
xs = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1])
ys = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1]) #4. add hidden layer
h1 = add_layer(xs, 1, 10, activation_function=tf.nn.relu)
h2 = add_layer(h1, 10, 10, activation_function=tf.nn.relu)
#5. add output layer
prediction = add_layer(h2, 10, 1, activation_function=None) #6. loss function: suqare error
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(ys - prediction), reduction_indices=[1]))
GD = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.1)
train_step = GD.minimize(loss)
## End build network struct ### ## Initial the variables
if int((tf.__version__).split('.')[1]) < 12 and int((tf.__version__).split('.')[0]) < 1:
init = tf.initialize_all_variables()
else:
init = tf.global_variables_initializer() ## Session
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(init) # called in the visual ## Traing
for step in range(1000):
#当运算要用到placeholder时,就需要feed_dict这个字典来指定输入
sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={xs:x_data, ys:y_data})
if i % 50 == 0:
# to visualize the result and improvement
try:
ax.lines.remove(lines[0])
except Exception:
pass
prediction_value = sess.run(prediction, feed_dict={xs: x_data})
# plot the prediction
lines = ax.plot(x_data, prediction_value, 'r-', lw=5)
plt.pause(1) sess.close()
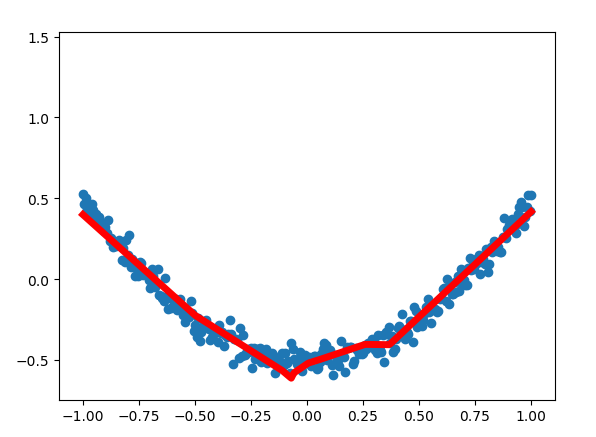
结果:
至此TensorFlow简易学习完结。
--------------------------------------
说明:本列为前期学习时记录,为基本概念和操作,不涉及深入部分。文字部分参考在文中注明,代码参考莫凡
TensorFlow简易学习[3]:实现神经网络的更多相关文章
- TensorFlow 深度学习笔记 卷积神经网络
Convolutional Networks 转载请注明作者:梦里风林 Github工程地址:https://github.com/ahangchen/GDLnotes 欢迎star,有问题可以到Is ...
- TensorFlow深度学习!构建神经网络预测股票价格!⛵
作者:韩信子@ShowMeAI 深度学习实战系列:https://www.showmeai.tech/tutorials/42 TensorFlow 实战系列:https://www.showmeai ...
- TensorFlow深度学习笔记 循环神经网络实践
转载请注明作者:梦里风林 Github工程地址:https://github.com/ahangchen/GDLnotes 欢迎star,有问题可以到Issue区讨论 官方教程地址 视频/字幕下载 加 ...
- TensorFlow简易学习[1]:基本概念和操作示例
简介 TensorFlow是一个实现机器学习算法的接口,也是执行机器学习算法的框架.使用数据流式图规划计算流程,可以将计算映射到不同的硬件和操作系统平台. 主要概念 TensorFlow的计算可以表示 ...
- TensorFlow简易学习[2]:实现线性回归
上篇介绍了TensorFlow基本概念和基本操作,本文将利用TensorFlow举例实现线性回归模型过程. 线性回归算法 线性回归算法是机器学习中典型监督学习算法,不同于分类算法,线性回归的输出是整个 ...
- TensorFlow深度学习实战---循环神经网络
循环神经网络(recurrent neural network,RNN)-------------------------重要结构(长短时记忆网络( long short-term memory,LS ...
- TensorFlow学习笔记——深层神经网络的整理
维基百科对深度学习的精确定义为“一类通过多层非线性变换对高复杂性数据建模算法的合集”.因为深层神经网络是实现“多层非线性变换”最常用的一种方法,所以在实际中可以认为深度学习就是深度神经网络的代名词.从 ...
- 深度学习之卷积神经网络CNN及tensorflow代码实例
深度学习之卷积神经网络CNN及tensorflow代码实例 什么是卷积? 卷积的定义 从数学上讲,卷积就是一种运算,是我们学习高等数学之后,新接触的一种运算,因为涉及到积分.级数,所以看起来觉得很复杂 ...
- 深度学习之卷积神经网络CNN及tensorflow代码实现示例
深度学习之卷积神经网络CNN及tensorflow代码实现示例 2017年05月01日 13:28:21 cxmscb 阅读数 151413更多 分类专栏: 机器学习 深度学习 机器学习 版权声明 ...
随机推荐
- 慢SQL汇总
select count(*) as aggregate from `yqz_feed_praise` where `uid` = '580242' and `praise_uid` <> ...
- 2017年十大奇葩画风的H5页面案例,原来脑洞可以这样大
每个人都是视觉动物,画面精美.体验奇特的H5,用户在内心一般都会满分打出,毫不吝啬,同时也毫不犹豫分享,因为此时的分享不掉价儿~ 今天给大家准备了十支H5,画风超级奇特,非常值得一看所有案例均可在19 ...
- 窗口迅速关闭的解决办法/scanf/if/for/break
break if的格式 if(a>b) { printf("max=%d\n",a); } else printf("max=%d\n",b); scan ...
- git镜像仓库
有时候我们会把一些仓库放到本地,当他更新的时候,可以使用简单命名更新他. 不是所有时间我们都有网,所以把远程的仓库作为镜像,可以方便我们查看 普通的git clone不能下载所有分支,想要简单的git ...
- 原生javascript跨浏览器常用事件处理
var eventUntil = { getEvent: function (event) {//获取事件 return event ? eve ...
- HTML笔记<note2>
文本标记 我是正常的文本段落 我是用b标记的加粗文本 我是用strong定义的强调文本 i标记的倾斜文本 em强调文本 del标记的删除线 del标记的下划线文本 特殊字符标记 显示 说明 空格&am ...
- (转)UML实践详细经典教程----用例图、顺序图、状态图、类图、包图、协作图
原文链接:http://dn.codegear.com/article/31863 面向对象的问题的处理的关键是建模问题.建模可以把在复杂世界的许多重要的细节给抽象出.许多建模工具封装了UML(也就是 ...
- HDFS 简介
hadoop分别从3个角度将主机划分为2种角色 最基本的是Master 和 从HDFS角度,将主机划分为namenode和datanode,在分布式文件系统中,目录管理很重要,管理目录相当于主人 从m ...
- SimpleDateFormat 常规用法
public class SimpleDateFormat extends DateFormat SimpleDateFormat 是一个以国别敏感的方式格式化和分析数据的具体类. 它允许格式化 (d ...
- c++连接数据库 在vc6.0
配置相关环境 我的mysql安装路径为E:\mysql-5.5.28-win32所以要在VC中设置include路径和lib的路径. 添加MySql的include目录到VC工作台中Project-& ...
