tensorflow的官方强化学习库agents的相关内容及一些注意事项
源代码地址:
https://github.com/tensorflow/agents
TensorFlow给出的官方文档说明:
https://tensorflow.google.cn/agents
相关视频:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=U7g7-Jzj9qo
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tAOApRQAgpc
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=52DTXidSVWc&list=PLQY2H8rRoyvxWE6bWx8XiMvyZFgg_25Q_&index=2
-----------------------------------------------------------
框架实现的算法:
论文1:
论文3:
论文4:
论文5:
论文6:
论文7:
论文8:
论文9:
论文10:
====================================
1. gym的环境版本有要求,给出具体安装及Atari的安装:
pip install gym[atari]==0.23.0
pip install gym[accept-rom-license]
=====================================
2. 代码的逻辑bug
tf_agents/specs/array_spec.py 代码bug:
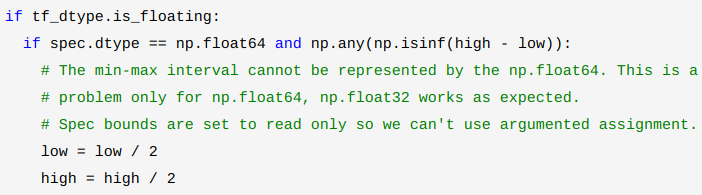
def sample_bounded_spec(spec, rng):
"""Samples the given bounded spec. Args:
spec: A BoundedSpec to sample.
rng: A numpy RandomState to use for the sampling. Returns:
An np.array sample of the requested spec.
"""
tf_dtype = tf.as_dtype(spec.dtype)
low = spec.minimum
high = spec.maximum if tf_dtype.is_floating:
if spec.dtype == np.float64 and np.any(np.isinf(high - low)):
# The min-max interval cannot be represented by the np.float64. This is a
# problem only for np.float64, np.float32 works as expected.
# Spec bounds are set to read only so we can't use argumented assignment.
low = low / 2
high = high / 2
return rng.uniform(
low,
high,
size=spec.shape,
).astype(spec.dtype) else:
if spec.dtype == np.int64 and np.any(high - low < 0):
# The min-max interval cannot be represented by the tf_dtype. This is a
# problem only for int64.
low = low / 2
high = high / 2 if np.any(high < tf_dtype.max):
high = np.where(high < tf_dtype.max, high + 1, high)
elif spec.dtype != np.int64 or spec.dtype != np.uint64:
# We can still +1 the high if we cast it to the larger dtype.
high = high.astype(np.int64) + 1 if low.size == 1 and high.size == 1:
return rng.randint(
low,
high,
size=spec.shape,
dtype=spec.dtype,
)
else:
return np.reshape(
np.array([
rng.randint(low, high, size=1, dtype=spec.dtype)
for low, high in zip(low.flatten(), high.flatten())
]), spec.shape)
这个代码的意思就是在给定区间能进行均匀抽样,但是由于区间可能过大因此导致无法使用库函数抽样,因此需要对区间进行压缩。
当抽样的数据类型为np.float64时,由代码:
np.array(np.zeros(10), dtype=np.float64)+np.finfo(np.float64).max-np.finfo(np.float64).min

np.random.uniform(size=10, low=np.finfo(np.float64).min, high=np.finfo(np.float64).max)

可以知道,当类型为np.float64时,如果抽样区间过大会(超出数值表示范围)导致无法抽样,因此进行压缩区间:
当数据类型为np.float32时,虽然也会存在超出表示范围的问题:
np.array(np.zeros(10), dtype=np.float32)+np.finfo(np.float32).max-np.finfo(np.float32).min

但是由于函数 np.random.uniform 的计算中会把np.float32转为np.float64,因此不会出现报错,如下:
np.random.uniform(size=10, low=np.finfo(np.float32).min, high=np.finfo(np.float32).max)

---------------------------------------------------
当数值类型为int时,区间访问过大的检测代码为:
np.any(high - low < 0)
原因在意np.float类型数值超出表示范围会表示为infi变量,但是int类型则会以溢出形式表现,如:

但是在使用numpy.random.randint 函数时,即使范围为最大范围也没有报错:
np.random.randint(size=10000, low=tf.as_dtype(np.int64).min, high=tf.as_dtype(np.int64).max)

np.random.randint(size=10000, low=np.iinfo(np.int64).min, high=np.iinfo(np.int64).max)

而且即使由于high值是取开区间的,我们对high值加1以后也没有报错:
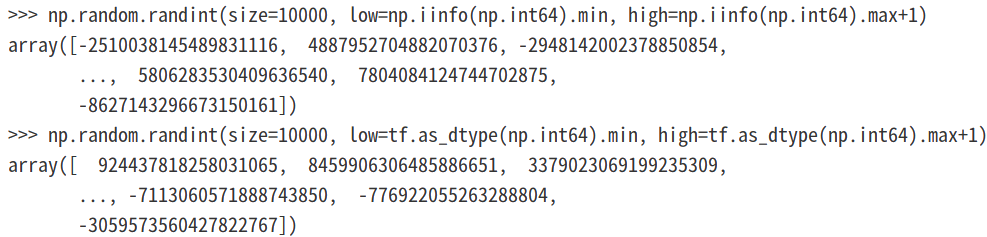
但是需要注意,此时传给np.random.randint函数中的low和high数值都为python数据类型int而不是numpy中的np.int64,下面我们看下numpy.float64类型是否会溢出:
当以数组形式传递最高high值并使其保持np.float64类型,发现使用high+1就会溢出:
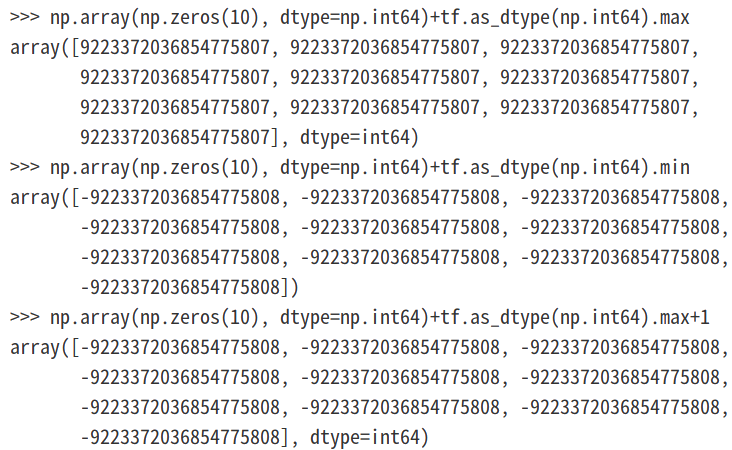
可以看到使用最大范围+1作为high值会导致报错:
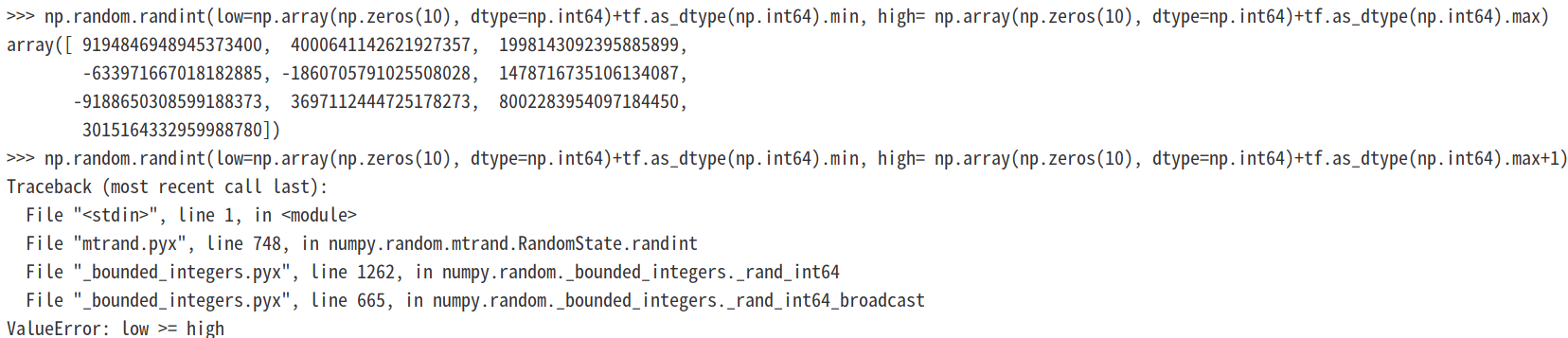
可以看到在使用numpy.random.randint时对上下限还是要注意的,虽然numpy.random.randint对上限是开区间,但是+1操作是很可能引起溢出错误的。
这也就是为什么 high+1操作之前要做判断了,如下:

不过如果数据类型不为np.int64,并且也不为np.uint64,那么我们依然可以把high值转为np.int64后在+1 ,但是上面的逻辑判断是有一定问题的,这些修正后如下:

总的修改后的代码为:
def sample_bounded_spec(spec, rng):
"""Samples the given bounded spec. Args:
spec: A BoundedSpec to sample.
rng: A numpy RandomState to use for the sampling. Returns:
An np.array sample of the requested spec.
"""
tf_dtype = tf.as_dtype(spec.dtype)
low = spec.minimum
high = spec.maximum if tf_dtype.is_floating:
if spec.dtype == np.float64 and np.any(np.isinf(high - low)):
# The min-max interval cannot be represented by the np.float64. This is a
# problem only for np.float64, np.float32 works as expected.
# Spec bounds are set to read only so we can't use argumented assignment.
low = low / 2
high = high / 2
return rng.uniform(
low,
high,
size=spec.shape,
).astype(spec.dtype) else:
if spec.dtype == np.int64 and np.any(high - low < 0):
# The min-max interval cannot be represented by the tf_dtype. This is a
# problem only for int64.
low = low / 2
high = high / 2 if np.any(high < tf_dtype.max):
high = np.where(high < tf_dtype.max, high + 1, high)
elif spec.dtype != np.int64 and spec.dtype != np.uint64:
# We can still +1 the high if we cast it to the larger dtype.
high = high.astype(np.int64) + 1 if low.size == 1 and high.size == 1:
return rng.randint(
low,
high,
size=spec.shape,
dtype=spec.dtype,
)
else:
return np.reshape(
np.array([
rng.randint(low, high, size=1, dtype=spec.dtype)
for low, high in zip(low.flatten(), high.flatten())
]), spec.shape)
加入对np.uint64类型的判断:
def sample_bounded_spec(spec, rng):
"""Samples the given bounded spec. Args:
spec: A BoundedSpec to sample.
rng: A numpy RandomState to use for the sampling. Returns:
An np.array sample of the requested spec.
"""
tf_dtype = tf.as_dtype(spec.dtype)
low = spec.minimum
high = spec.maximum if tf_dtype.is_floating:
if spec.dtype == np.float64 and np.any(np.isinf(high - low)):
# The min-max interval cannot be represented by the np.float64. This is a
# problem only for np.float64, np.float32 works as expected.
# Spec bounds are set to read only so we can't use argumented assignment.
low = low / 2
high = high / 2
return rng.uniform(
low,
high,
size=spec.shape,
).astype(spec.dtype) else:
if spec.dtype == np.int64 and np.any(high - low < 0):
# The min-max interval cannot be represented by the tf_dtype. This is a
# problem only for int64.
low = low / 2
high = high / 2 if spec.dtype == np.uint64 and np.any(high >= np.iinfo(np.int64).max):
low = low / 2
high = high / 2 if np.any(high < tf_dtype.max):
high = np.where(high < tf_dtype.max, high + 1, high)
elif spec.dtype != np.int64 and spec.dtype != np.uint64:
# We can still +1 the high if we cast it to the larger dtype.
high = high.astype(np.int64) + 1 if low.size == 1 and high.size == 1:
return rng.randint(
low,
high,
size=spec.shape,
dtype=spec.dtype,
)
else:
return np.reshape(
np.array([
rng.randint(low, high, size=1, dtype=spec.dtype)
for low, high in zip(low.flatten(), high.flatten())
]), spec.shape)
===========================================
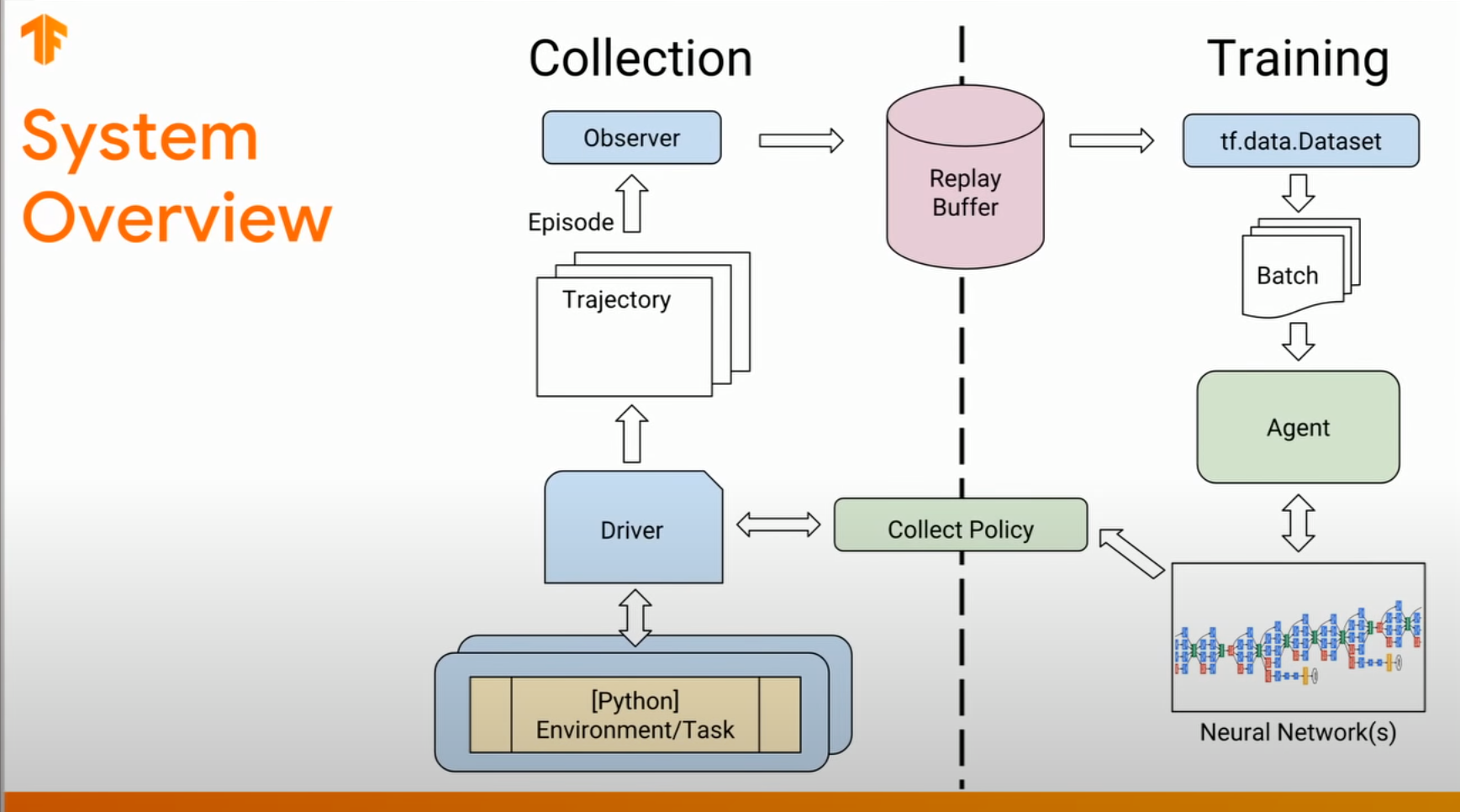
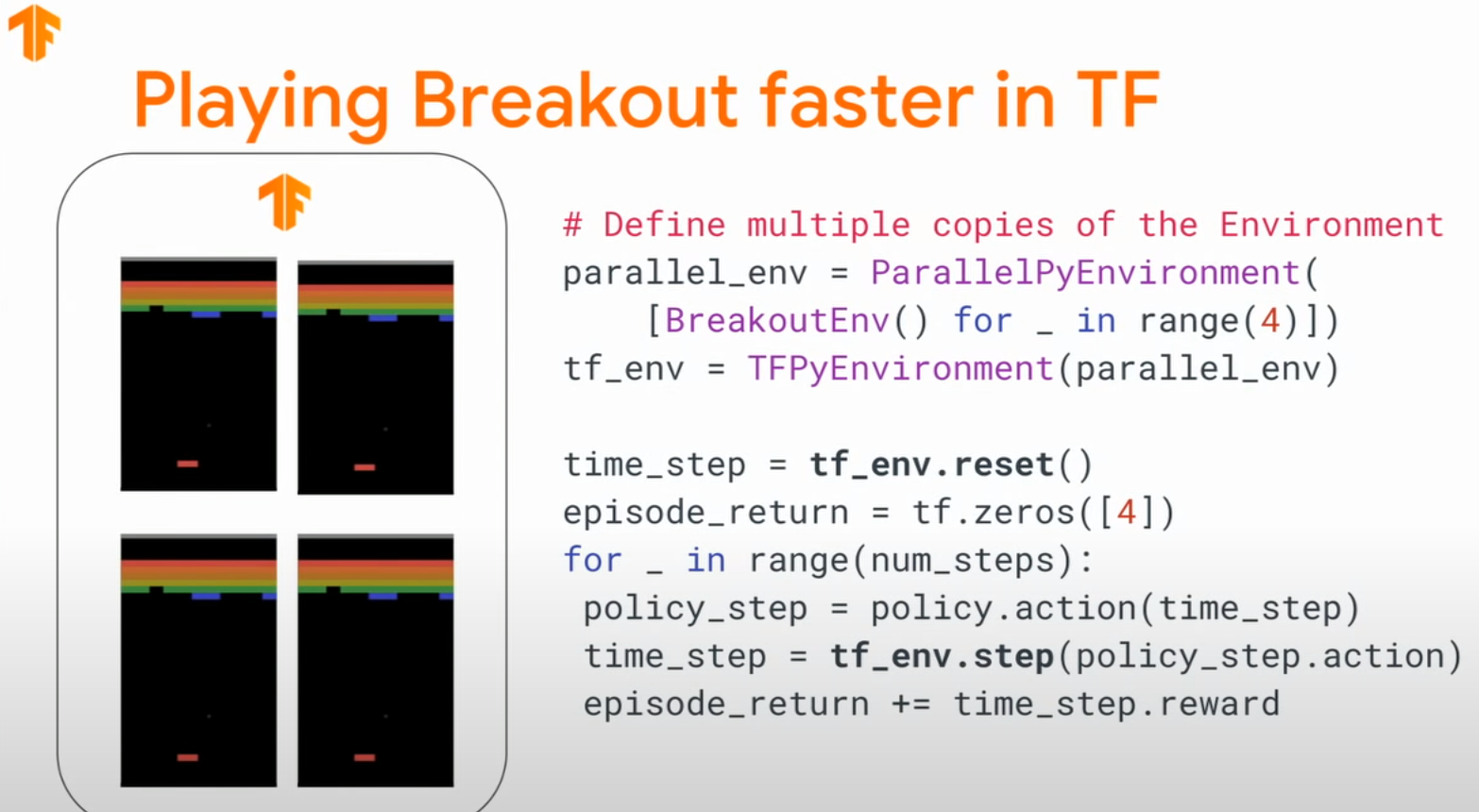
tf-agents框架的交互逻辑代码:
===========================================





tensorflow的官方强化学习库agents的相关内容及一些注意事项的更多相关文章
- 学习笔记之html5相关内容
写一下昨天学习的html5的相关内容,首先谈下初次接触html5的感受.以前总是听说html5是如何的强大,如何的将要改变世界.总是充满了神秘感.首先来谈一下我接触的第一个属性是 input的里面的 ...
- 强化学习之四:基于策略的Agents (Policy-based Agents)
本文是对Arthur Juliani在Medium平台发布的强化学习系列教程的个人中文翻译,该翻译是基于个人分享知识的目的进行的,欢迎交流!(This article is my personal t ...
- 强化学习之三:双臂赌博机(Two-armed Bandit)
本文是对Arthur Juliani在Medium平台发布的强化学习系列教程的个人中文翻译,该翻译是基于个人分享知识的目的进行的,欢迎交流!(This article is my personal t ...
- DQN 强化学习
pytorch比tenserflow简单. 所以我们模仿用tensorflow写的强化学习. 学习资料: 本节的全部代码 Tensorflow 的 100行 DQN 代码 我制作的 DQN 动画简介 ...
- 强化学习之七:Visualizing an Agent’s Thoughts and Actions
本文是对Arthur Juliani在Medium平台发布的强化学习系列教程的个人中文翻译,该翻译是基于个人分享知识的目的进行的,欢迎交流!(This article is my personal t ...
- 强化学习之六:Deep Q-Network and Beyond
本文是对Arthur Juliani在Medium平台发布的强化学习系列教程的个人中文翻译,该翻译是基于个人分享知识的目的进行的,欢迎交流!(This article is my personal t ...
- 强化学习之五:基于模型的强化学习(Model-based RL)
本文是对Arthur Juliani在Medium平台发布的强化学习系列教程的个人中文翻译,该翻译是基于个人分享知识的目的进行的,欢迎交流!(This article is my personal t ...
- 强化学习之三点五:上下文赌博机(Contextual Bandits)
本文是对Arthur Juliani在Medium平台发布的强化学习系列教程的个人中文翻译,该翻译是基于个人分享知识的目的进行的,欢迎交流!(This article is my personal t ...
- 强化学习之二:Q-Learning原理及表与神经网络的实现(Q-Learning with Tables and Neural Networks)
本文是对Arthur Juliani在Medium平台发布的强化学习系列教程的个人中文翻译.(This article is my personal translation for the tutor ...
- 深度强化学习(DRL)专栏(一)
目录: 1. 引言 专栏知识结构 从AlphaGo看深度强化学习 2. 强化学习基础知识 强化学习问题 马尔科夫决策过程 最优价值函数和贝尔曼方程 3. 有模型的强化学习方法 价值迭代 策略迭代 4. ...
随机推荐
- Vue学习:13.生命周期综合
0基础如何进入IT行业? 简介:对于没有任何相关背景知识的人来说,如何才能成功进入IT行业?是否有一些特定的方法或技巧可以帮助他们实现这一目标? 方向一:学习路径 明确兴趣和目标:首先确定你对IT领域 ...
- OAuth + Security - 4 - 客户端信息存储数据库
PS:此文章为系列文章,建议从第一篇开始阅读. 在之前的所有配置中,我们的客户端信息和授权码模式下的授权码任然还是存储在数据库中的,这样就不利于我们后期的扩展,所以在正式的生成环境中,我们一般将其存储 ...
- nordic的nrf52系列——ADC在使用时如何校准增益误差(基于SDK)
简介:ADC在实际使用的时候都要进行误差校准,那Nordic的nrf52系列如何进行校准,如果不校准又有什么影响尼,接下来我将通过实验进行测试,验证不校准和校准的影响(本测试的基础是,默认输入阻抗和采 ...
- rabbitMq实现系统内的短信发送设计&动态获取BEAN
rabbitMq实现系统内的短信发送设计&动态获取BEAN 1.短信非系统的重要节点操作,可以在任务完成之后,比如下单成功,发送下单成功的mq消息,短信服务接收到mq消息,动态的判断该短信的c ...
- 《Objective-C Direct Methods》学习笔记
原文通过对Objective-C发展史.Objective-C中Runtime的动态派发,C语言的直接派发进行铺垫介绍,引出了direct methods这个"新特性"(文章写于2 ...
- Windows记录登录日志
有的时候,我们希望系统记录登录的日志,以便查看有无他人动过自己的电脑. 步骤 1.在windows中搜索并打开"组策略". 2.点击计算机配置-->Windows设置--&g ...
- 仓颉语言HelloWorld内测【仅需三步】
2024年6月21日,华为仓颉正式公开发布.还记的19年和王学智的团队做过接触,他们反馈说16年我出版的<自己动手构造编译系统>一书对他们的研发很有帮助,身为作者听到这个消息还是很开心的. ...
- supervisor 安装和基本使用
安装 yum install supervisor touch /var/run/supervisor/supervisor.sock chmod 777 /var/run/supervisor/su ...
- 【AppStore】一文让你学会IOS应用上架Appstore
前言 咱们国内现在手机分为两类,Android手机与苹果手机,现在用的各类APP,为了手机的使用安全,避免下载到病毒软件,官方都极力推荐使用手机自带的应用商城进行下载,但是国内Android手机品类众 ...
- Peaks:每周至少要进行一次用户访谈?
名字:Peaks 开发者 / 团队:Vogelhaus Apps GmbH 平台:iOS.watchOS 请简要介绍下这款产品 每个人生活的节奏都有一个内置的生理时钟,这就是所谓的昼夜节律.它不仅控制 ...
