四则运算 Python实现(杨浩政,张兆敏)
四则运算
GitHub仓库:https://github.com/15crmor/Arithmetic
项目要求:
题目:实现一个自动生成小学四则运算题目的命令行程序说明:
说明:
自然数:0, 1, 2, …。
- 真分数:1/2, 1/3, 2/3, 1/4, 1’1/2, …。
- 运算符:+, −, ×, ÷。
- 括号:(, )。
- 等号:=。
- 分隔符:空格(用于四则运算符和等号前后)。
- 算术表达式:
e = n | e1 + e2 | e1 − e2 | e1 × e2 | e1 ÷ e2 | (e),
其中e, e1和e2为表达式,n为自然数或真分数。
- 四则运算题目:e = ,其中e为算术表达式。
需求:
1.(完成)使用 -n 参数控制生成题目的个数
2.(完成)使用 -r 参数控制题目中数值(自然数、真分数和真分数分母)的范围,该参数可以设置为1或其他自然数。
3.(完成)生成的题目中计算过程不能产生负数
4.(完成)生成的题目中如果存在形如e1 ÷ e2的子表达式,那么其结果应是真分数
5.(完成)每道题目中出现的运算符个数不超过3个。
6.(完成)程序一次运行生成的题目不能重复,即任何两道题目不能通过有限次交换+和×左右的算术表达式变换为同一道题目。生成的题目存入执行程序的当前目录下的Exercises.txt文件
7.(完成)在生成题目的同时,计算出所有题目的答案,并存入执行程序的当前目录下的Answers.txt文件
8.(完成)程序应能支持一万道题目的生成。
9.(完成)程序支持对给定的题目文件和答案文件,判定答案中的对错并进行数量统计。统计结果输出到文件Grade.txt,格式如下:
Correct: 5 (1, 3, 5, 7, 9)
Wrong: 5 (2, 4, 6, 8, 10)
设计实现过程
总体构思:
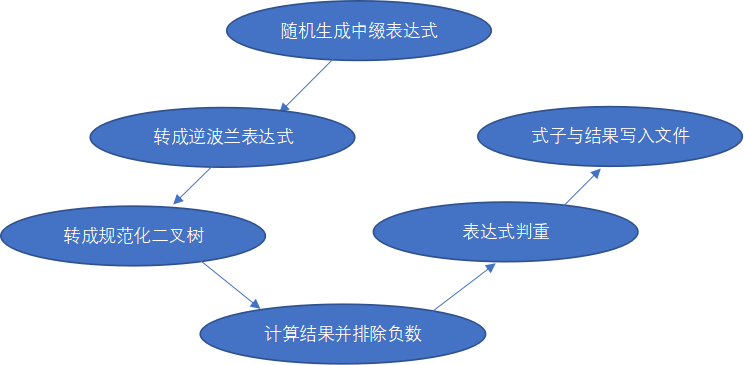
表达式:
将整数也看作分数来生成随机数,为Fraction类型,有numerator,denominator两个属性,然后根据运算符个数生成表达式,如:A+B*C/D。
再转换成逆波兰表达式,然后转化成规范化的二叉树如:随机生成表达式:2*6+5*7 à 逆波兰表达式:26*57*+ , 再转化成二叉树的同时进行规范化并计算结果存入树的value属性中:
- 二叉树的叶子节点都为数字,非叶子节点都为运算符,当规范化二叉树时,其实是遍历逆波兰式列表中的元素,然后创建一个空树,若遍历到的元素不是运算符,就将数字添加入树的属性,并将树存入列表stack中,若是运算符,则弹出列表中后两个树t2、t1,此时两个树中情况无非是
1. 2.

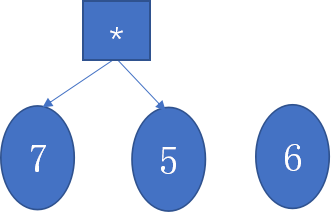
3.
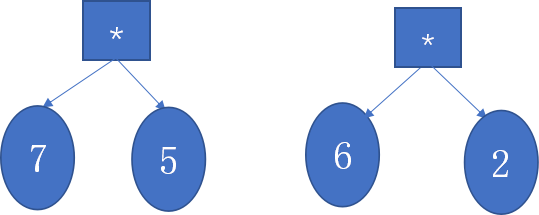
4.
- 通过计算比较value值(有运算符则为两数运算后的值,不论是什么运算符,都为t1 op t2,并非左子树 op 右子树)将vlaue较大的设为左子树并计算新的value,若value值相等,则通过判定优先级来确定左右子树。
负数与除数为0:
负数的产生是由于t1 < t2,同时若在进行减法后的值为0且做除数,则出现除数为0情况,所以通过条件判断舍弃在运算符为“-”时,t1 <= t2 的二叉树
判断表达式是否重复
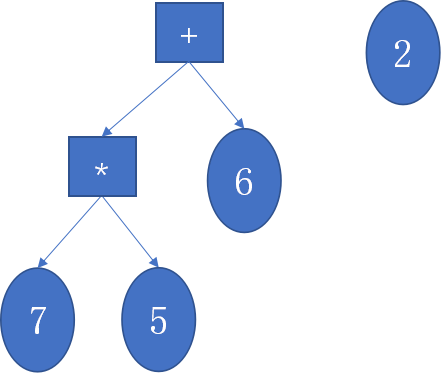
转换成规范二叉树,然后再以逆波兰格式转成字符串形式,存在一个列表里,每次生成了一个新式子后,就按上面方法生成规范化的二叉树并转成逆波兰形式字符串与列表中所有元素比较。
- 例如2*6+5*7与7*5+6*2生成的规范化二叉树都为:
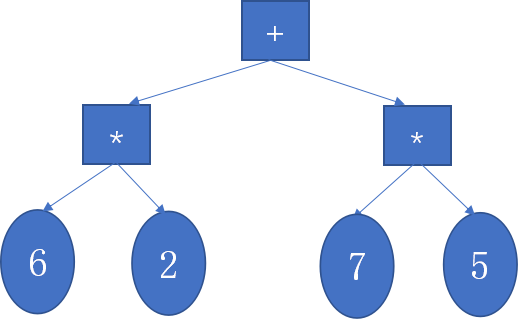
其返回的字符串逆波兰式相同,即2*6+5*7与7*5+6*2是一样的表达式。
主要的类和函数有:
class Arith(object)
- creat(self, problem_number, r) # 生成四则运算和答案在判重后写入文件
- main(self, arith, argv) # 支持命令行输入参数
class BinaryTree(object) # 二叉树
- out_put_tree(self, tree, s) # 返回二叉树逆波兰形式的字符串
class Caculation(object)
- caulate(self, op, f1, f2) # 计算f1 op f2 的值(op为运算符)
- max(self, num1, num2) # 比较两分数大小
class Check(object) # 判重
- check_tree(self, tree) # 对二叉树进行判重,若不重复返回True
class Compare(object)
- grade(self, exercise_file, answer_file) # 比较两文件答案并记录
class Create(object) # 生成四则运算表达式
- create_operator(self) # 随机生成运算符
- create_arith(self, r) # 生成范围在r以内的四则运算表达式
- proper_fraction(self, list) # 将假分数化为带分数
class Fractions(object) # 分数类
class CreateTree(object) # 生成规范二叉树
- toRPN(self, list) # 生成逆波兰表达式
- createTree(self, suffix) # 将逆波兰式转化为规范化二叉树
- priority(self, operatorout, operatorin) # 判定优先级
代码说明:
生成四则运算表达式:
def create_arith(self, r):
x = 0
list = []
operator_num = random.randint(1, 3)
e1 = Create()
e2 = Create()
if operator_num == 1:
list.append(e1.create_number(r))
list.append(e2.create_operator())
list.append(e1.create_number(r))
elif operator_num == 2:
start = random.randint(0, 2)
end = 0
if start > 0:
end = start + 1
for i in range(1, 4):
if i == start:
list.append("(")
list.append(e1.create_number(r))
if i == end:
list.append(")")
list.append(e2.create_operator())
list.pop()
elif operator_num == 3:
start = random.randint(0, 3)
end = 0
if start > 0:
end = start + 1 + random.randint(0, 1)
if end >= 4:
end = 4
for i in range(1, 5):
if i == start:
list.append("(")
list.append(e1.create_number(r))
if i == end:
list.append(")")
list.append(e2.create_operator())
list.pop()
else:
list.append(e1.create_number(r))
list.append(e2.create_operator())
list.append(e1.create_number(r))
return list
假分数化为带分数:
# 将表达式假分数转化为带分数
def proper_fraction(self, list):
num = 0
for fract in list:
if type(fract) == Fraction:
n1 = fract.numerator
n2 = fract.denominator
if n2 == 1:
num += 1
continue
elif n1 > n2:
sub = int(n1/n2)
n1 = n1 % n2
list[num] = '%d%s%d/%d' %(sub, '’', n1,n2)
num += 1
return list # 将答案假分数转化为带分数
def pop_fracte(self, re):
n1 = re.numerator
n2 = re.denominator
if n2 == 1:
return n1
elif n1 < n2:
return re
else:
sub = int(n1/n2)
n1 = n1 % n2
return '%d%s%d/%d' % (sub, '’', n1, n2)
生成逆波兰式:
def toRPN(self, list):
right = []
aStack = []
position = 0
while True:
if self.isOperator(list[position]):
if list == [] or list[position] == "(":
aStack.append(list[position])
else:
if list[position] == ")":
while True:
if aStack != [] and aStack[-1] != "(":
operator = aStack.pop()
right.append(operator)
else:
if aStack != []:
aStack.pop()
break
else:
while True:
if aStack != [] and self.priority(list[position], aStack[-1]):
operator = aStack.pop()
if operator != "(":
right.append(operator)
else:
break
aStack.append(list[position])
else:
right.append(list[position])
position = position + 1
if position >= len(list):
break
while aStack != []:
operator = aStack.pop()
if operator != "(":
right.append(operator)
return right
将逆波兰式转化成规范化的二叉树:
def createTree(self, suffix):
stacks = [] for i in range(0, len(suffix)):
tree = BinaryTree()
ob = suffix[i]
c = Caculation.Caculation()
if self.isOperator(ob):
t2 = BinaryTree()
t1 = BinaryTree()
t2 = stacks.pop()
t1 = stacks.pop()
if ob == '-' and t1.value <= t2.value:
return None
else:
if self.maxTree(t1, t2):
tree.set_date(ob)
tree.set_left(t1)
tree.set_right(t2)
tree.set_value(c.caulate(ob, t1.value, t2.value))
else:
tree.set_date(ob)
tree.set_left(t2)
tree.set_right(t1)
tree.set_value(c.caulate(ob, t1.value, t2.value))
stacks.append(tree)
else:
tree.set_value(ob)
tree.set_date(ob)
stacks.append(tree)
return tree
对二叉树判重:
# 对二叉树进行判重
def check_tree(self, tree):
if self.check == []:
self.check.append(tree)
return True
else:
for i in range(len(self.check)):
if self.check[i] == tree:
return False
self.check.append(tree)
return True
二叉树类:
class BinaryTree(object):
def __init__(self):
self.date = None
self.left = None
self.right = None
self.value = None def tree(self, date, left, right, value):
self.date = date
self.left = left
self.right = right
self.value = value def set_date(self, date):
self.date = date def set_left(self, left):
self.left = left def set_right(self, right):
self.right = right def set_value(self, value):
self.value = value def to_string(self, tree):
s = ""
s = self.out_put_tree(tree, s)
return s def out_put_tree(self, tree, s):
if tree != None:
s1 = self.out_put_tree(tree.left, s)
s2 = self.out_put_tree(tree.right, s)
if type(tree.date) == Fractions.Fractions:
return str(s1) + str(s2) + str(tree.date.to_string())
else:
return str(s1) + str(s2) + str(tree.date)
return s
分数类:
class Fractions(object):
def __init__(self):
self.numerator = None
self.denominator = None def setNumerator(self,numerator):
self.numerator = numerator def setDenominator(self,denominator):
self.denominator = denominator def toString(self):
a = self.numerator
b = self.denominator
return str(Fraction(a, b))
计算参数值:
def caulate(self, op, f1, f2):
result = Fractions.Fractions()
n1 = int(f1.numerator)
d1 = int(f1.denominator)
n2 = int(f2.numerator)
d2 = int(f2.denominator)
list = []
if op == '+':
re = Fraction(n1, d1) + Fraction(n2, d2) elif op == '-':
re = Fraction(n1, d1) - Fraction(n2, d2) elif op == '×':
re = Fraction(n1, d1) * Fraction(n2, d2) else:
re = Fraction(n1, d1) / Fraction(n2, d2) return re
文件比较,判断错误答案并记录:
# 对两个文件中的答案进行比较并记录
def grade(self, exercise_file, answer_file):
correct = []
wrong = []
co = 0
wr = 0
with open(answer_file, 'r') as f1, open(exercise_file, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f2:
answers = f2.readlines()
line = 0
for r_answers in f1.readlines():
if answers[line] == r_answers:
co += 1
correct.append(line+1)
else:
wr += 1
wrong.append(line+1)
line += 1
with open('gread.txt', 'w') as f3:
f3.write(f"Correct: {str(co)} ({', '.join(str(s) for s in correct if s not in [None])})" + '\n')
f3.write(f"Correct: {str(wr)} ({', '.join(str(s) for s in wrong if s not in [None])})" + '\n')
print("文件比较完成")
生成表达式判重后写入文件:
# 生成问题和答案在判重后写入文件
def creat(self, problem_number, r):
creat_pro = CreatProblem.Create()
t = BinaryTree.BinaryTree()
c = Check.Check()
with open("Exercises.txt", "w") as file1, open("Answer.txt", "w") as file2:
num = 0
while num < problem_number:
arith = creat_pro.create_arith(r) # 生成四则运算列表
Ju = CreateTree.Judge()
al = Ju.toRPN(arith) # 将列表转换成逆波兰式
print(al)
string = creat_pro.to_string(creat_pro.proper_fraction(arith))
ta = Ju.createTree(al) # 将逆波兰式生成规范二叉树
print(t.to_string(ta))
if ta:
val = str(creat_pro.pop_fracte(ta.value))
if c.check_tree(t.to_string(ta)): # 进行判重
file1.write("%d. " % (num+1) + string + '\n')
file2.write("%d. " % (num+1) + val + '\n')
num +=1
print("四则运算题目生成完毕,数量为%d个" % problem_number)
命令行程序入口:
# 支持命令行键入参数
def main(self, arith, argv):
problem_number = None
num_range = None
exercise_file = None
answer_file = None
try:
opts, args = getopt.getopt(argv, "n:r:e:a:")
except getopt.GetoptError:
print('Error: arith.py -n <problem_number> -r <num_range>')
print(' or: test_arg.py -e -e <exercisefile>.txt -a <answerfile>.txt')
sys.exit(2) for opt, arg in opts:
if opt in("-n"):
problem_number = int(arg)
elif opt in ("-r"):
num_range = int(arg)
elif opt in("-e"):
exercise_file = arg
elif opt in("-a"):
answer_file = arg
if problem_number and num_range:
arith.creat(problem_number, num_range)
elif exercise_file and answer_file:
compare = Compare.Compare()
compare.grade('ReAnswer.txt', 'Answer.txt')
else:
print('Error: arith.py -n <problem_number> -r <num_range>')
print(' or: test_arg.py -e -e <exercisefile>.txt -a <answerfile>.txt')
测试运行
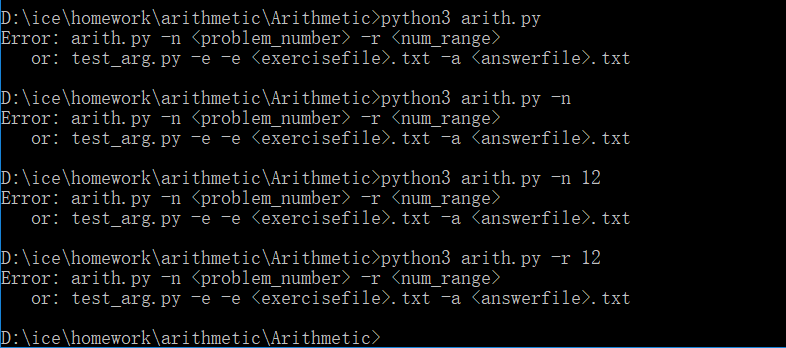
参数错误提示
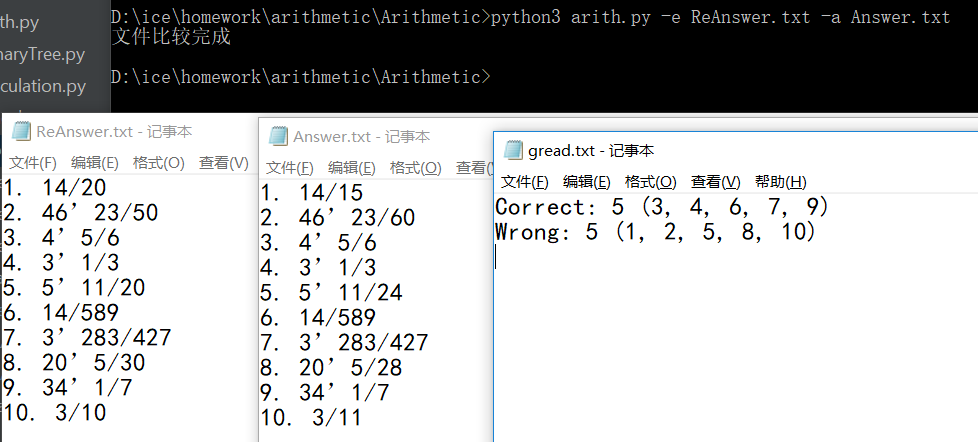
生成10道题的题目与答案

文件答案比较
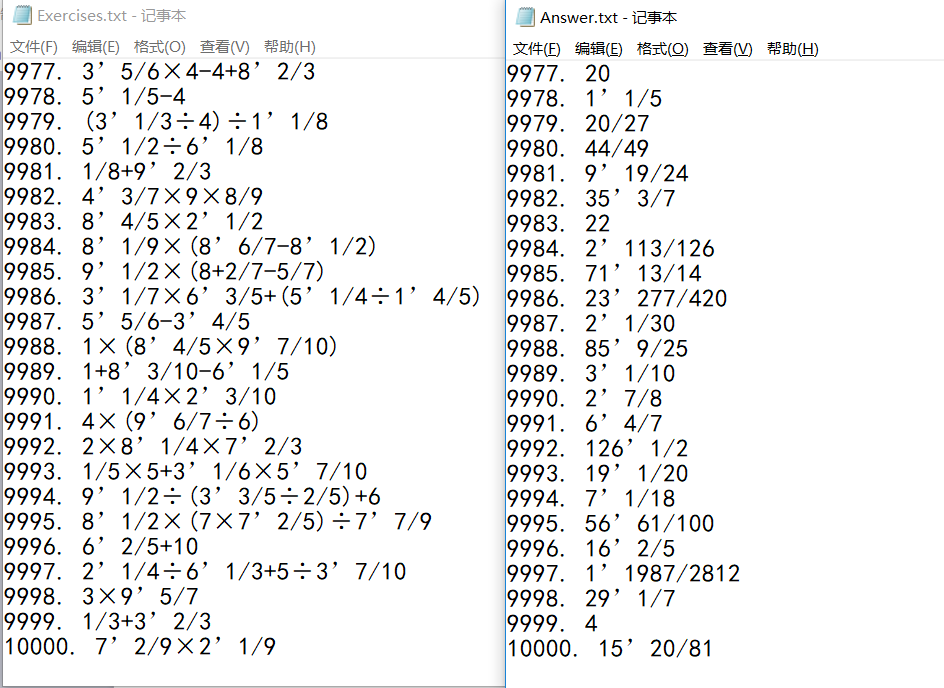
生成一万道题目
以下为一万到题目和答案的链接
PSP
|
PSP2.1 |
Personal Software Process Stages |
预估耗时(分钟) |
实际耗时(分钟) |
|
Planning |
计划 |
60 |
80 |
|
· Estimate |
· 估计这个任务需要多少时间 |
50 |
50 |
|
Development |
开发 |
900 |
800 |
|
· Analysis |
· 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) |
40 |
80 |
|
· Design Spec |
· 生成设计文档 |
60 |
60 |
|
· Design Review |
· 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) |
20 |
30 |
|
· Coding Standard |
· 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) |
30 |
30 |
|
· Design |
· 具体设计 |
60 |
180 |
|
· Coding |
· 具体编码 |
500 |
800 |
|
· Code Review |
· 代码复审 |
100 |
120 |
|
· Test |
· 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) |
120 |
150 |
|
Reporting |
报告 |
60 |
90 |
|
· Test Report |
· 测试报告 |
30 |
30 |
|
· Size Measurement |
· 计算工作量 |
20 |
30 |
|
· Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan |
· 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 |
20 |
20 |
|
合计 |
2070 |
2550 |
项目小结:
在本次结点编程四则运算项目中,与杨浩政同学一起组队讨论写代码。首先呢,我们一起讨论如何实现这个项目,共同讨论书写设计文档。在写设计文档的过程中,我们很多想法都不一样,由于我的编程水平比较低,缺乏经验,一般来说,都是以杨浩政同学的想法为主,我的想法为辅。在交流设计思路的过程中,我们两人的思维也会碰撞出更好的解决思路。在双方都认为自己的想法比较好时,会各自说出自己想法的优点,然后再共同思考哪个实现途径更优。最大的感触是:多听听不同的想法,会使自己的思维更开阔。(来自张兆敏同学的小结)
本次结对编程我主要负责代码实现,这次编程对我的帮助很大,让我明白了只有思路足够清晰才能更快更好地实现功能,在拿到项目后一定要多思考如何实现更简洁方便,而不是边写边想,到最后不停修改。与队友的讨论也启发了我一些思路,只要思路上能找到合适的方法,那么实现起来就会容易快速很多。(来自杨浩政的小结)
四则运算 Python实现(杨浩政,张兆敏)的更多相关文章
- 利用python打印杨辉三角
用python打印杨辉三角 介绍 杨辉三角,是初高中时候的一个数列,其核心思想就是说生成一个数列,该数列中的每一个元素,都是之前一个数列中,同样位置的元素和前一个元素的和. 正好在python中,也就 ...
- (双人项目)四则运算 组员:杨钰宁 闫浩楠 开发语言:Python。
需求分析:1.适用人群:小学生. 2.能进行“+,—,*,/” 的四则运算.难度可以随时修改. 3.提交试卷后可以显示所得分数并显示错题个数. 4.可以显示答对的题及其打错的题的序号. 代码如下: i ...
- python实现杨辉三角
刚刚学python,原来用c++,Java很轻松实现的杨辉三角,现在用python实现,代码是少了,理解起来却不容易啊. 这里主要用到的Python的生成器. 我们都知道Python有列表解析功能,根 ...
- python 实现杨辉三角(依旧遗留问题)
1 #! usr/bin/env python3 #-*- coding :utf-8 -*- print('杨辉三角的generator') def triangles(): N=[1] while ...
- Python之杨辉三角算法实现
学习了廖雪峰的官方网站的python一些基础,里面有个题目,就是让写出杨辉三角的实现,然后我就花了时间实现了一把.思路也很简单,就是收尾插入0,然后逐层按照杨辉三角的算法去求和实现杨辉三角. 附属代码 ...
- python—networkx:在一张图中画出多个子图
通过plt.subplot能够在一张图中画出多个子图 #coding: utf-8 #!/usr/bin/env python """ Draw a graph with ...
- python输出杨辉三角
使用python列表,展示杨辉三角 # !/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- # Author:Hiuhung Wan yanghui = [] fo ...
- 这个七夕节,用Python为女友绘制一张爱心照片墙吧!【华为云技术分享】
欢迎添加华为云小助手微信(微信号:HWCloud002 或 HWCloud003),输入关键字“加群”,加入华为云线上技术讨论群:输入关键字“最新活动”,获取华为云最新特惠促销.华为云诸多技术大咖.特 ...
- 如何用Python实现杨辉三角和心
1. 如何实现杨辉三角 import copy list=[] newlist=[] def Fibonacci(list,n): newlist.append(0) if n ==1: return ...
随机推荐
- Mysql一些记忆
mysql修改密码报错是yum 安装mysql5.7 是 出现无法登陆问题以及mysql error You must reset your password using ALTER USER sta ...
- Web标准:六、html列表
Web标准:六.html列表 知识点: 1.ul无序和ol有序列表 2.改变项目符号样式或用图片定义项目符号 3.横向图文列表 4.浮动后父容器高度自适应 5.IE6的双倍边距bug 1)ul无序 ...
- SQL Server 2016/2014/2012/2008/2005/2000简体中文企业版下载地址
为什么只提供企业版下载呢?因为不管你是学生还是工作研究人员,企业版都是功能最为齐全的一个版本,比如企业版都集成了SQL Server Management Studio管理界面(俗称企业管理器的可视化 ...
- html图片链接不显示图片
html图片链接不显示图片,如下示: <a href="index.jsp"><img src="/img/index.png"/>&l ...
- 43. Multiply Strings (String)
Given two numbers represented as strings, return multiplication of the numbers as a string. Note: Th ...
- 【英宝通Unity4.0公开课学习 】(四)GUI到物理引擎
今天老妈打电话来说和老爸吵架了... 真的是家家都有本难念的经啊.前后帮她分析了个半小时才帮她解开心结...现在想想老爸还是蛮可怜的,连分享的人都木有 讲的GUI都看睡着了...因为想着可以用NGUI ...
- 神龟快跑,2016做的一款UWP游戏
神龟快跑,2016做的一款UWP游戏, 实际是H5页面, 用LAYA转AS3得到的 安装地址 https://www.microsoft.com/zh-cn/store/p/神龟快跑/9nblggh4 ...
- python 安装scikit!!!
首先,吐槽一下,真的是折腾好几天,一会更新这个,一会更新那个,总是各种奇葩问题诸如此类: cannot import check-build pip有新版本,需要更新(黄字) 其中scipy出错最多, ...
- mysql中GROUP_CONCAT的使用
现在有三个表,结构如下: cate表 CREATE TABLE `cate` ( `id` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT 'id', ...
- C# Socket网络编程精华篇
我们在讲解Socket编程前,先看几个和Socket编程紧密相关的概念: TCP/IP层次模型 当然这里我们只讨论重要的四层 01,应用层(Application):应用层是个很广泛的概念,有一些基本 ...
