【异常检测】Isolation forest 的spark 分布式实现
1.算法简介
算法的原始论文 http://cs.nju.edu.cn/zhouzh/zhouzh.files/publication/icdm08b.pdf 。python的sklearn中已经实现了相关的api,对于单机的数据已经足够使用了,链接如下 http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.ensemble.IsolationForest.html 。如果你想探究分布式下该算法怎么实现,下面细看。
按照惯例先讲一下算法的思想,对于已经了解的小伙伴来说,这段跳过。它的思路有点类似随机森林,并发训练N棵树,每棵树是没有关联的,且每棵树用到的样本和属性也是随机的,所不同的是,isolation forest (下面简称IF)是非监督的算法,通过构建二叉树,然后在构建好的树上,来预测样本的深度,如果深度太浅,则是疑似异常的样本。更加详细的论断和细节请查看论文,或者参考国内各大博客主写的个人感悟,我们把重点放在分布式实现上面。
2.分布式实现
在实现之前重点关注一点,IF算法并不需要所有的样本,甚至不能使用太多的样本,使用小样本的情况,算法效果更优。这一点在论文中有论断:
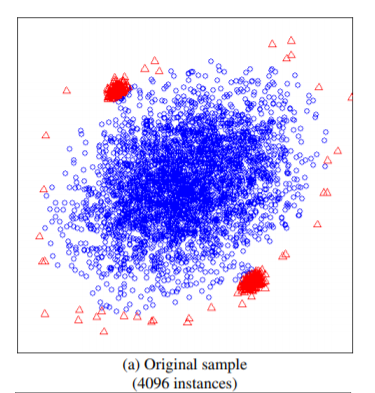
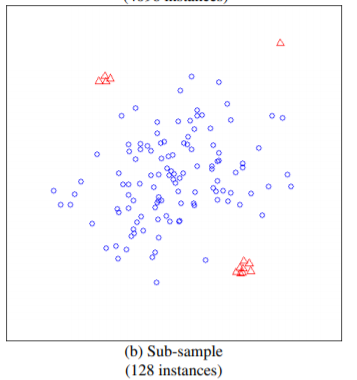
如上图所示,如果使用全部的样本作为训练集,则异常的样本,未必能识别出来,而在小样本下可以轻松识别。论文中比较了这两种方式,前者AUC达到0.67,而后者能达到0.91。
基于上面的论断,每棵树的样本大小不能太大,当然下面实现的方式既支持小样本又支持大样本,这个依赖于用户自己喜欢了
import java.util.concurrent.Executors
import org.apache.spark.SparkContext
import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD import org.apache.spark.storage.StorageLevel
import scala.concurrent.duration.Duration
import scala.concurrent.{Await, ExecutionContext, Future}
import scala.util.Random
import org.apache.hadoop.fs._ sealed trait ITree case class ITreeBranch(left: ITree, right: ITree, split_column: Int, split_value: Double) extends ITree case class ITreeLeaf(size: Long) extends ITree /** @param trees trained trees
* @param maxSamples The number of samples to train each base tree
*/
case class IForest(trees: Array[ITree], maxSamples: Int) { def predict(x: Array[Double]) = {
if (trees.forall(_ == null)) {
throw new Exception("Please train before predict!!")
} else {
val predictions = trees.map(s => pathLength(x, s, 0)).toList
math.pow(2, -(predictions.sum / predictions.size) / cost(maxSamples))
}
} @scala.annotation.tailrec
final def pathLength(x: Array[Double], tree: ITree, path_length: Int): Double = {
tree match {
case ITreeLeaf(size) =>
path_length + cost(size) case ITreeBranch(left, right, split_column, split_value) =>
val sample_value = x(split_column)
if (sample_value < split_value)
pathLength(x, left, path_length + 1)
else
pathLength(x, right, path_length + 1)
}
} private def cost(num_items: Long): Double =
if (num_items <= 1) 1.0 else 2.0 * (math.log(num_items - 1.0) + 0.577215664901532860606512090082402431) - (2.0 * (num_items - 1.0) / num_items) } object IForest { /**
* @param numTrees The number of base tree in the ensemble
* @param maxSamples The number of samples to train each base tree ,should be small!! should be small!! should be small!!
* should be small!! should be small!! should be small!!
* @param maxFeatures The fraction of features to train each base tree value in (0.0,1.0]
* // * @param withReplacement whether sampling is done with replacement, do something in future
* @param nJobs The number of jobs to run in parallel for fit ,do something in future
*/
def buildForest(data: RDD[Array[Double]], numTrees: Int = 100, maxSamples: Int = 256, maxFeatures: Double = 1.0, nJobs: Int = 10, distribute: Boolean = false) = {
val sc = data.sparkContext
val cacheData = if (sc.getRDDStorageInfo.filter(_.id == data.id).nonEmpty) data else data.persist(StorageLevel.MEMORY_AND_DISK)
val dataCnt = data.count()
println(s"AllSmaples =>${dataCnt}") val numFeatures = cacheData.take(1)(0).size
checkData(cacheData, numFeatures)
val sampleNumSamples = Math.min(maxSamples, dataCnt).toInt
val sampleNumFeatures = (maxFeatures * numFeatures).toInt
val maxDepth = Math.ceil((math.log(math.max(sampleNumSamples, 2)) / math.log(2))).toInt val sampleRatio = Math.min(sampleNumSamples * 1.0 / dataCnt * 2, 1.0)
val trees =
if (distribute) {
implicit val xc = ExecutionContext.fromExecutorService(Executors.newFixedThreadPool(nJobs))
val tasks = (0 until numTrees).map {
i =>
val sampleData = cacheData.sample(false, sampleRatio, System.currentTimeMillis()).zipWithIndex().filter(_._2 <= sampleNumSamples).map(_._1)
parallizeGrow(sampleData, maxDepth, numFeatures, sampleNumFeatures)
}
val results = Await.result(Future.sequence(tasks), Duration.Inf)
results.toArray
}
else
(0 until numTrees).sliding(nJobs, nJobs).map {
arr =>
sc.union(
arr.map {
i =>
cacheData.sample(false, sampleRatio, System.currentTimeMillis()).zipWithIndex().filter(_._2 <= sampleNumSamples)
.map(_._1).repartition(1).mapPartitions {
iter =>
val delta = iter.toArray
val sampleFeatures = if (sampleNumFeatures < numFeatures) Random.shuffle((0 until numFeatures).toList).take(sampleNumFeatures) else (0 until numFeatures).toList
Iterator(growTree(delta, maxDepth, sampleFeatures, 0))
}
}
).collect()
}.reduce(_ ++ _) new IForest(trees, maxSamples)
} def saveModel(sc: SparkContext, iforest: IForest, path: String) = {
val hdfs=FileSystem.get(sc.hadoopConfiguration)
hdfs.delete(new Path(path), true)
sc.parallelize(Seq(iforest), 1).saveAsObjectFile(path)
} def loadModel(sc: SparkContext, path: String) = {
sc.objectFile[IForest](path).collect()(0)
} private def growTree(data: Array[Array[Double]], maxDepth: Int, sampleFeatures: Seq[Int], currentDepth: Int): ITree = {
val numSamples = data.length
if (currentDepth >= maxDepth || numSamples <= 1 || data.distinct.length == 1) {
new ITreeLeaf(numSamples)
} else {
val splitColumn = sampleFeatures(Random.nextInt(sampleFeatures.length))
val columnValue = data.map(_.apply(splitColumn))
val colMin = columnValue.min
val colMax = columnValue.max
val splitValue = colMin + Random.nextDouble() * (colMax - colMin)
val dataLeft = data.filter(_ (splitColumn) < splitValue)
val dataRight = data.filter(_ (splitColumn) >= splitValue)
new ITreeBranch(growTree(dataLeft, maxDepth, sampleFeatures, currentDepth + 1),
growTree(dataRight, maxDepth, sampleFeatures, currentDepth + 1),
splitColumn, splitValue)
}
} private def parallizeGrow(data: RDD[Array[Double]], maxDepth: Int, numFeatures: Int, sampleNumFeatures: Int)(implicit xc: ExecutionContext) = Future {
val sampleFeatures = if (sampleNumFeatures < numFeatures) Random.shuffle((0 until numFeatures).toList).take(sampleNumFeatures) else (0 until numFeatures)
growTree(data, maxDepth, sampleFeatures, 0)
} private def growTree(data: RDD[Array[Double]], maxDepth: Int, sampleFeatures: Seq[Int], currentDepth: Int): ITree = {
val sc = data.sparkContext
val cacheData = if (sc.getRDDStorageInfo.filter(_.id == data.id).length > 0) data else data.persist(StorageLevel.MEMORY_AND_DISK)
val numSamples = cacheData.count()
val ret = if (currentDepth >= maxDepth || numSamples <= 1 || cacheData.distinct.count() == 1) {
new ITreeLeaf(numSamples)
} else {
val splitColumn = sampleFeatures(Random.nextInt(sampleFeatures.length))
val columnValue = cacheData.map(_ (splitColumn))
val colMin = columnValue.min()
val colMax = columnValue.max()
val splitValue = colMin + Random.nextDouble() * (colMax - colMin)
val dataLeft = cacheData.filter(_ (splitColumn) < splitValue)
val dataRight = cacheData.filter(_ (splitColumn) >= splitValue)
new ITreeBranch(growTree(dataLeft, maxDepth, sampleFeatures, currentDepth + 1),
growTree(dataRight, maxDepth, sampleFeatures, currentDepth + 1),
splitColumn, splitValue)
} cacheData.unpersist()
ret
} private def checkData(data: RDD[Array[Double]], numFeatures: Int) = {
assert(data.filter(arr => !(arr.length == numFeatures)).isEmpty(), "data must in equal column size")
} }
代码说明:
- 代码主要参考https://github.com/hsperr/first_steps_in_scala
- 原始代码中有错误,具体在predict 函数中num_samples 参数应该是每棵树的样本数量,而不是所有的样本数量。
- 原始代码中,不是并行的,关键在于trees.map(s=>growTree(getRandomSubsample(data, subSampleSize/numSamples.toDouble, seed), maxHeight, numColumns)) 这一行,在spark的driver端进行解析中,是一个个action串行执行的。
- 原始代码中其实漏掉了一个树的停止分裂的条件,那就是如果剩余的样本都相同的话,也停止生长。另外两个的停止生长的条件是达到树的最大深度和只剩下小于等于1个样本。
- buildForest函数,参数的具体含义参照注释,基本是仿照python的参数来实现的,唯一值得解释的是distribute,默认值是false。当该参数为true时,代码会在driver端起njobs个线程,然后每个线程监控执行一个action算子去生成一棵树,具体调用的是 growTree(data: RDD[Array[Double]]...)这个函数;参数为false时,实际上每个partition里面的样本是对原始样本上的小采样,然后在小采样的样本上进行构建一个棵树,你会发现里面的实现和单机是一样的,唯一区别是在分布式的大数据上进行的采样,以及生成大批量的一堆树,具体实现参照 growTree(data: Array[Array[Double]]...) 函数。
- 每颗树的深度是样本数目取log2之后算出来的,这个和python的api保持一致。
- 至于什么样的样本才是异常的,这个根据打出来的分数,降序排列。然后可以根据百分比进行设置阈值,或者根据具体的分数进行设置阈值。唯一抓住的核心是,要看一下分数在总体样本上的一个分布,然后根据分布做决策。
3.总结
1.代码已经测试通过,直接mvn编译打包,运行环境为hadoop3.1.0和spark2.3,大家放心使用。
2.如有疑问欢迎指正,大家相互学习交流。
【异常检测】Isolation forest 的spark 分布式实现的更多相关文章
- Python机器学习笔记 异常点检测算法——Isolation Forest
Isolation,意为孤立/隔离,是名词,其动词为isolate,forest是森林,合起来就是“孤立森林”了,也有叫“独异森林”,好像并没有统一的中文叫法.可能大家都习惯用其英文的名字isolat ...
- 异常检测算法--Isolation Forest
南大周志华老师在2010年提出一个异常检测算法Isolation Forest,在工业界很实用,算法效果好,时间效率高,能有效处理高维数据和海量数据,这里对这个算法进行简要总结. iTree 提到森林 ...
- 异常检测算法:Isolation Forest
iForest (Isolation Forest)是由Liu et al. [1] 提出来的基于二叉树的ensemble异常检测算法,具有效果好.训练快(线性复杂度)等特点. 1. 前言 iFore ...
- 【异常检测】孤立森林(Isolation Forest)算法简介
简介 工作的过程中经常会遇到这样一个问题,在构建模型训练数据时,我们很难保证训练数据的纯净度,数据中往往会参杂很多被错误标记噪声数据,而数据的质量决定了最终模型性能的好坏.如果进行人工二次标记,成本会 ...
- [转]Python机器学习笔记 异常点检测算法——Isolation Forest
Isolation,意为孤立/隔离,是名词,其动词为isolate,forest是森林,合起来就是“孤立森林”了,也有叫“独异森林”,好像并没有统一的中文叫法.可能大家都习惯用其英文的名字isolat ...
- isolation forest进行异常点检测
一.简介 孤立森林(Isolation Forest)是另外一种高效的异常检测算法,它和随机森林类似,但每次选择划分属性和划分点(值)时都是随机的,而不是根据信息增益或者基尼指数来选择.在建树过程中, ...
- (转)isolation forest进行异常点检测
原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/gczr/p/9156971.html 一.简介 孤立森林(Isolation Forest)是另外一种高效的异常检测算法,它和随机森林类似, ...
- Spark实战4:异常检测算法Scala语言
异常检测原理是根据训练数据的高斯分布,计算均值和方差,若测试数据样本点带入高斯公式计算的概率低于某个阈值(0.1),判定为异常点. 1 创建数据集转化工具类,把csv数据集转化为RDD数据结构 imp ...
- 思科安全:加密流量威胁检测、加密流量威胁和恶意软件检测、识别无线干扰或威胁、Talos 情报源可加强对已知和新型威胁的防御、分布式安全异常检测
思科DNA竞品比较工具 您的网络能够驱动数字化转型吗? 根据IDC调查,45%的受调研公司计划在未来两年内做好网络数字化的准备.查看数字化网络带来的结果和商业价值. 下载报告 思科 HPE 华为 Ar ...
随机推荐
- bitMap算法实现以及ckHash函数类,将字符串映射成数字,同时可以将数字映射成字符串
ckHash函数类,将字符串映射成数字,同时可以将数字映射成字符串 说明 1.所谓的BitMap就是用一个bit位来标记某个元素所对应的value,而key即是该元素,由于BitMap使用了bit位来 ...
- 集合之Stack
在Java中Stack类表示后进先出(LIFO)的对象堆栈.栈是一种非常常见的数据结构,它采用典型的先进后出的操作方式完成的.每一个栈都包含一个栈顶,每次出栈是将栈顶的数据取出,如下: Stack通过 ...
- Spring源码分析(四)容器的基础XmlBeanFactory
摘要:本文结合<Spring源码深度解析>来分析Spring 5.0.6版本的源代码.若有描述错误之处,欢迎指正. 经过Spring源码分析(二)容器基本用法和Spring源码分析(三)容 ...
- 命令行编译执行java
命令行编译运行java程序 使用命令 javac进行编译 和 java进行执行. javac 后面跟着的是java文件的文件名,例如 HelloWorld.java. 该命令用于将 java 源文件编 ...
- Mybatis的使用与流程解析
1. 什么是MyBatis MyBatis的前身是Apache的一个开源项目ibatis,后来迁移到Google code就改名为MyBatis. 官方解释: MyBatis是一款优秀的持久层框架,它 ...
- Linux学习笔记(第九章)
压缩概念: gzip和zcat: 先进版bzip2,bzcat bzip -d 已压缩文档名 bzip -z 需压缩文档名 bzcat 解压文档打印到屏幕 tar:打包指令 注意:压缩最好拿掉根目录 ...
- 浏览器与go语言的websocket通信
简介WebSocket是HTML5一种新的协议.顾名思义,它在服务器和浏览器之间建立了全双工通信. 需求背景区块链测试系统web前端平台需要动态接收后端发送的状态信息改变一次测试session过程的状 ...
- 在vivado中自定义编辑器
在 Tools - Options - Text Editor 中选择 Custom Editor 这里我用的gvim,在Editor文本框中输入: C:/Vim/vim80/gvim.exe --r ...
- 【转载】WCF 客户端识别认证之UserName认证
原文地址: http://blog.csdn.net/zxz414644665/article/details/9308055 过程:用户调用service,服务端验证用户传来的用户名和密码(传输过程 ...
- 20155338《网络对抗技术》 Exp1 PC平台逆向破解
20155338<网络对抗技术> Exp1 PC平台逆向破解 实践目标 1.实践的对象是一个名为pwn1的linux可执行文件. 2.该程序正常执行流程是:main调用foo函数,foo函 ...
