linux系统编程之文件与IO(八):文件描述符相关操作-dup,dup2,fcntl
本节目标:
1,文件共享
- 打开文件内核数据结构
- 一个进程两次打开同一个文件
- 两个进程打开同一个文件
2,复制文件描述符(dup、dup2、fcntl)
一,文件共享
1,一个进程打开两个文件内核数据结构
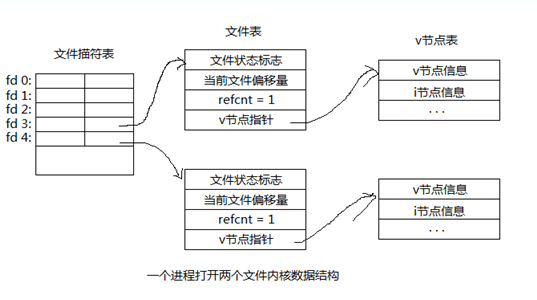
说明:
文件描述符表:每个进程都有一张,彼此独立,每个文件描述符表项都指向一个文件表,文件描述符0(STDIN_FILENO)、1(STDOUT_FILENO)、2(STDERR_FILENO),默认已经打开,分别表示:标准输入,标准输出,标准错误设备。
文件表:每打开一个文件就对应一张文件表,文件表可以共享,当多个文件描述符指向同一个文件表时,文件表中的
refcnt字段会相应变化。文件状态标识:文件的打开模式(R,W,RW,APPEND,NOBLOCK,等),当前文件偏移量,refcnt:被引用数量,
v节点指针:指向一个v节点表。
v节点表:每个文件对应一个,无论被被多少个进程打开都只有一个,它包括v节点信息(主要是stat结构体中的信息),i节点信息。
每个进程默认只能打开1024个文件描述符,当一个进程打开一个文件时,默认会从0开始查找未被使用的描述符,由于0,1,2默认被占用,所有一般从3开始使用。
2、一个进程两次打开同一个文件
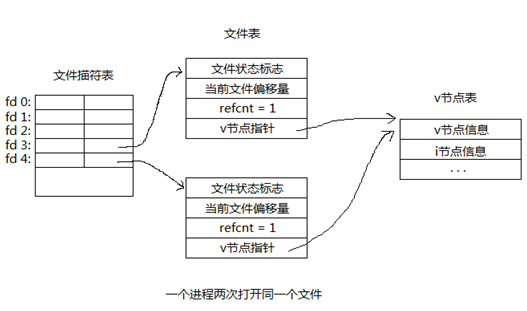
当一个进程多次打开同一个文件时,首先会在描述符表顺序查找未被使用的描述符,然后每打开一次建立一张文件表,但各文件表中的v节点指针都指向同一个v节点表。
示例程序:
- #include <unistd.h>
- #include <sys/stat.h>
- #include <sys/types.h>
- #include <sys/stat.h>
- #include <fcntl.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <errno.h>
- #include <string.h>
- #define ERR_EXIT(m) \
- do \
- { \
- perror(m); \
- exit(EXIT_FAILURE); \
- } while()
- int main(int argc, char *argv[])
- {
- int fd1;
- int fd2;
- char buf1[] = {};
- char buf2[] = {};
- fd1 = open("test.txt", O_RDONLY);
- if (fd1 == -)
- ERR_EXIT("open error");
- read(fd1, buf1, );
- printf("buf1=%s\n", buf1);
- fd2 = open("test.txt", O_RDWR);
- if (fd2 == -)
- ERR_EXIT("open error");
- read(fd2, buf2, );
- printf("buf2=%s\n", buf2);
- write(fd2, "AAAAA", );
- memset(buf1, , sizeof(buf1));
- read(fd1, buf1, );
- printf("buf1=%s\n", buf1);
- close(fd1);
- close(fd2);
- return ;
- }
运行结果:
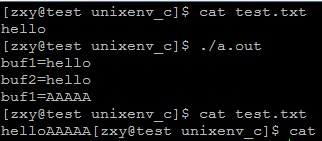
说明:先创建test.txt文件写入hello,再同一个进程两次打开该文件,可见每打开一次文件就参数一张文件表,不共享偏移量,都开始位置读取,之后利用第二个文件描述符写入AAAAA,在利用第一个描述符可以读取出,表明都指向同一个v节点表,操作同一个文件。
3,两个不同进程打开同一个文件
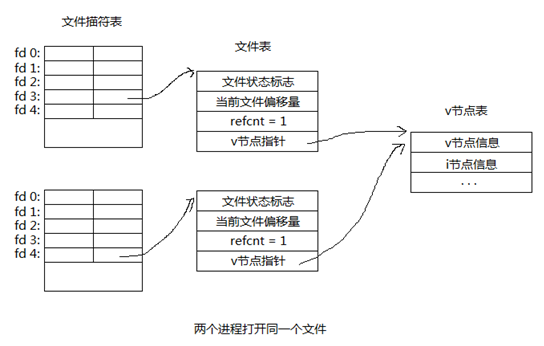
当不同进程打开同一个文件时,每个进程首先在它们各自的文件描述符表中顺序查找未被使用的描述符,最终获得的文件描述符可能相同也可能不同,每个fd指向各自的文件表,但同样,每个文件表中的v节点指针都指向同一个v节点表。
二、复制文件描述符
复制前:
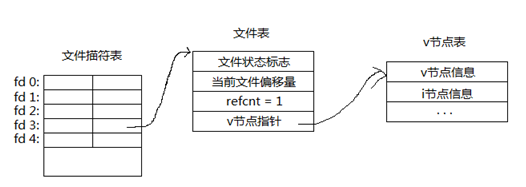
复制后:
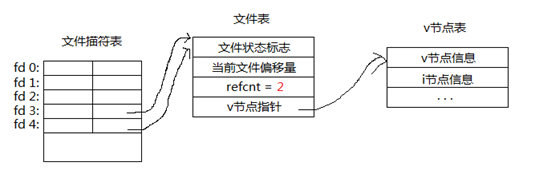
复制后,两个文件描述符都指向了同一个文件表,refcnt=2。
复制文件描述符有三种方法:
1,dup
2,dup2
#include <unistd.h>
int dup(int oldfd);
int dup2(int oldfd, int newfd);
DESCRIPTION
These system calls create a copy of the file descriptor oldfd.
dup() uses the lowest-numbered unused descriptor for the new descriptor.
dup2() makes newfd be the copy of oldfd, closing newfd first if necessary, but note
the following:
* If oldfd is not a valid file descriptor, then the call fails, and newfd is not closed.
* If oldfd is a valid file descriptor, and newfd has the same value as
oldfd, then dup2() does nothing, and returns newfd.
After a successful return from one of these system calls, the old and new file descriptors may be used interchangeably. They refer to the same open file description (see open(2)) and thus share file offset and file status flags; for example, if the file offset is modified by using lseek(2) on one of the descriptors, the offset is also changed for the other.
RETURN VALUE
On success, these system calls return the new descriptor. On error, -1 is returned, and errno is set appropriately.
示例程序:
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <unistd.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- #include <fcntl.h>
- int main(void)
- {
- int fd;
- fd = open("test.txt",O_WRONLY);
- if( fd == -){
- perror("open error");
- exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
- }
- int fd2;
- fd2 = dup(fd);
- if(fd2 == -){
- perror("dup error");
- exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
- }
- printf("oldfd = %d\n",fd);
- printf("newfd = %d\n",fd2);
- int fd3;
- close(); //或者close(STDIN_FILENO)
- fd3 = dup(fd);
- if(fd3 == -){
- perror("dup error");
- exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
- }
- printf("after close stdin,the newfd = %d\n",fd3);
- exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
- }
运行结果:
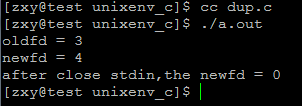
用dup进行文件描述符的复制时,顺序查找即从0开始查找可以文件描述符
示例2:
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <unistd.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- #include <fcntl.h>
- int main(void)
- {
- int fd;
- fd = open("test.txt",O_WRONLY);
- if( fd == -){
- perror("open error");
- exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
- }
- int fd2;
- fd2 = dup2(fd,);
- if(fd2 == -){
- perror("dup error");
- exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
- }
- printf("oldfd = %d\n",fd);
- printf("newfd = %d\n",fd2);
- exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
- }
运行结果:
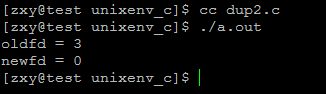
用dup2进行文件描述符复制时,指定需要复制的新的描述符,如果该描述符已经被占用,则先关闭它在重新复制,类似于先调用close再dup
3,fcntl
功能:操纵文件描述符,改变已打开的文件的属性
#include <fcntl.h>
int fcntl(int fd, int cmd, ... /* arg */ );
DESCRIPTION
fcntl() performs one of the operations described below on the open file
descriptor fd. The operation is determined by cmd.
fcntl() can take an optional third argument. Whether or not this argu-
ment is required is determined by cmd. The required argument type is
indicated in parentheses after each cmd name (in most cases, the
required type is long, and we identify the argument using the name
arg), or void is specified if the argument is not required.
由第二个参数指定操作类型,后面点的可变参数指定该命令所需的参数
这里我们进行文件描述符复制,可将cmd 设为: F_DUPFD (long),该命令表示:
Find the lowest numbered available file descriptor greater than
or equal to arg and make it be a copy of fd. This is different
from dup2(2), which uses exactly the descriptor specified.
On success, the new descriptor is returned.
示例程序:
- #include <unistd.h>
- #include <sys/stat.h>
- #include <sys/types.h>
- #include <sys/stat.h>
- #include <fcntl.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <errno.h>
- #include <string.h>
- #define ERR_EXIT(m) \
- do \
- { \
- perror(m); \
- exit(EXIT_FAILURE); \
- } while()
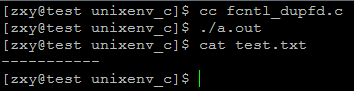
- int main(int argc, char *argv[])
- {
- int fd;
- fd = open("test.txt", O_WRONLY);
- if (fd == -)
- ERR_EXIT("open error");
- close();
- if (fcntl(fd, F_DUPFD, ) < )
- ERR_EXIT("dup fd error");
- printf("-----------\n");//进行重定向,将不会显示在标准输出,
- return ;
- }
运行结果:
linux系统编程之文件与IO(八):文件描述符相关操作-dup,dup2,fcntl的更多相关文章
- linux系统编程之文件与io(一)
经过了漫长的学习,C语言相关的的基础知识算是告一段落了,这也是尝试用写博客的形式来学习c语言,回过头来看,虽说可能写的内容有些比较简单,但是个人感觉是有史起来学习最踏实的一次,因为里面的每个实验都是自 ...
- linux系统编程之文件与io(五)
上一节中已经学习了文件描述符的复制,复制方法有三种,其中最后一种fcntl还并未使用到,关于这个函数,不光只有复制文件描述符的功能,还有其它一些用法,本节就对其进行一一剖析: fcntl常用操作: 这 ...
- linux系统编程之文件与io(四)
今天继续学习文件与io,主要是学习文件共享及文件.复制文件描述符,有点抽象,主要是概念上的理解,但是很重要,下面一一来分解: 文件共享: 回顾一下,在linux系统调用中,是通过文件描述符来访问文件的 ...
- Linux C 程序 文件操作(Linux系统编程)(14)
文件操作(Linux系统编程) 创建一个目录时,系统会自动创建两个目录.和.. C语言实现权限控制函数 #include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> ...
- Linux系统编程(1)——文件与I/O之C标准I/O函数与系统调用I/O
Linux系统的I/O也就是一般所说的低级I/O--操作系统提供的基本IO服务,与os绑定,特定于Linux平台.而标准I/O是ANSI C建立的一个标准I/O模型,是一个标准函数包和stdio.h头 ...
- Linux系统编程、网络编程-文件I/O
第一章:文件io 1. 文件io讲些什么 文件io这一章讲的是,如何调用Linux OS所提供的相关的OS API,实现文件的读写. 1.1 如何理解“文件IO”这个词 IO就是input outpu ...
- Linux系统编程温故知新系列 --- 01
1.大端法与小端法 大端法:按照从最高有效字节到最低有效字节的顺序存储,称为大端法 小端法:按照从最低有效字节到最高有效字节的顺序存储,称为小端法 网际协议使用大端字节序来传送TCP分节中的多字节整数 ...
- 读书笔记之Linux系统编程与深入理解Linux内核
前言 本人再看深入理解Linux内核的时候发现比较难懂,看了Linux系统编程一说后,觉得Linux系统编程还是简单易懂些,并且两本书都是讲Linux比较底层的东西,只不过侧重点不同,本文就以Linu ...
- linux系统编程:cp的另外一种实现方式
之前,这篇文章:linux系统编程:自己动手写一个cp命令 已经实现过一个版本. 这里再来一个版本,涉及知识点: linux系统编程:open常用参数详解 Linux系统编程:简单文件IO操作 /*= ...
随机推荐
- mysql 导出sql结果成csv文件
mysql -uroot -p -e "use database;sql语句:" > a.csv 举例: mysql -uroot -p -e "use main; ...
- sql server 数据库学习
http://m.blog.csdn.net/anxpp/article/details/51295020
- Linux Shell 文本处理工具集锦(转载)
内容目录: find 文件查找 grep 文本搜索 xargs 命令行参数转换 sort 排序 uniq 消除重复行 用tr进行转换 cut 按列切分文本 paste 按列拼接文本 wc 统计行和字符 ...
- preset
preset - 必应词典 美[.pri'set]英[.priː'set] v.预置:事先安排:预调:给…预定时间 网络预设:预先装置:预置位
- html节点操作与事件
<div id='a' style="width: 500px;height: 500px;background-color: grey;"> </div> ...
- IDEA 工具下导出文件及文件的目录结构插件
idea导出增量补丁插件 有时候需要导出IDEA的文件目录结构,即导出 指定修改后的JAVA文件编译后的CLASS .或者是修改过的jsp.配置文件等, 装载此插件,即可以完成导出文件 及文件的目 ...
- dede5.7 GBK 在php5.4环境下 后台编辑器无法显示文章内容
问题的原因是:是htmlspecialchars,PHP 5.4后GBK编码下默认不支持中文,转换后内容为空,UTF-8编码没有任何问题. 解决方法如下: 在\include\ckeditor\c ...
- 如何利用jQuery post传递含特殊字符的数据【转】
在jQuery中,我们通常利用$.ajax或$.post进行数据传递处理,但这里通常不能传递特殊字符,如:“<”.本文就介绍如何传递这种含特殊字符的数据. 1.准备页面和控制端代码 页面代码如下 ...
- Halcon对文件的创建、读取、写入、删除等操作总结
Halcon可以操作普通文本文件,也可以操作二进制文件.如下图所示,只需要设置“FileType”参数的取值即可明确是操作文本文件还是二进制文件: 下面的程序是操作一个.txt文本文件的完整代码: * ...
- socket编程介绍
Python 提供了两个基本的 socket 模块. 第一个是 Socket,它提供了标准的 BSD Sockets API. 第二个是 SocketServer, 它提供了服务器中心类,可以简化网络 ...
