利用python绘制分析路易斯安那州巴吞鲁日市的人口密度格局
前言
数据来源于王法辉教授的GIS和数量方法,以后有空,我会利用python来实现里面的案例,这里向王法辉教授致敬。
绘制普查人口密度格局
使用属性查询提取区边界
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import geopandas as gpd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
plt.style.use('ggplot')#使用ggplot样式
%matplotlib inline#输出在线图片
plt.rcParams['font.family'] = ['sans-serif']
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']# 替换sans-serif字体为黑体
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 解决坐标轴负数的负号显示问题
regions = gpd.GeoDataFrame.from_file('../Census.gdb',layer='County')
regions
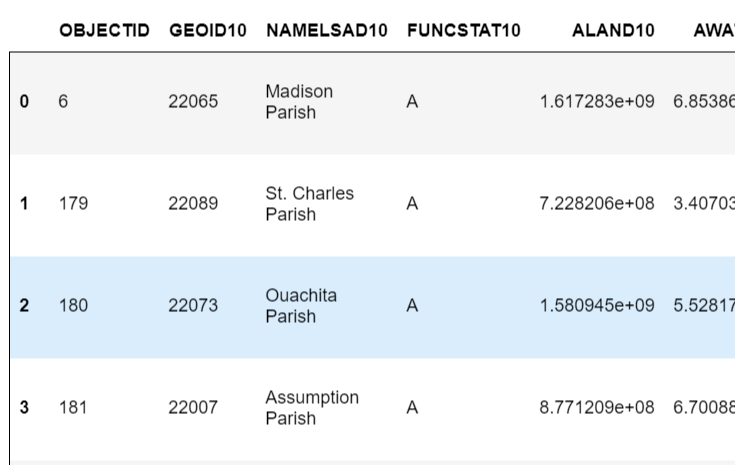
BRTrt = regions[regions.NAMELSAD10=='East Baton Rouge Parish']
投影
BRTrt = BRTrt.to_crs('EPSG:26915')
BRTrt.crs

BRTrt.to_file('BRTrt.shp')
裁剪数据
Tract = gpd.GeoDataFrame.from_file('../Census.gdb',layer='Tract')
Tract = Tract.to_crs('EPSG:26915')
TractUtm = gpd.GeoDataFrame.from_file('TractUtm.shp')
BRTrtUtm = gpd.GeoDataFrame.from_file('BRTrt.shp')
# Set workspace
env.workspace = r"MyProject"
# Set local variables
in_features = "TractUtm.shp"
clip_features = "BRTrt.shp"
out_feature_class = "BRTrtUtm.shp"
xy_tolerance = ""
# Execute Clip
arcpy.Clip_analysis(in_features, clip_features, out_feature_class, xy_tolerance)

计算面积和人口密度
BRTrtUtm = gpd.GeoDataFrame.from_file('BRTrtUtm.shp')
BRTrtUtm['area'] = BRTrtUtm.area/1000000
## 计算人口密度
BRTrtUtm['PopuDen'] = BRTrtUtm['DP0010001']/BRTrtUtm['area']
BRTrtUtm.to_file('BRTrtUtm.shp')
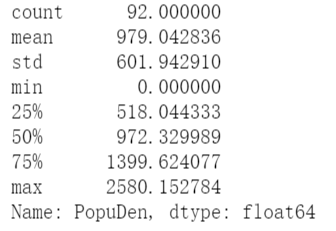
描述统计
BRTrtUtm['PopuDen'].describe()
人口密度图
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12,12)) #设置画布大小
ax = plt.gca()
ax.set_title("巴吞鲁日市2010年人口密度模式",fontsize=24,loc='center')
BRTrtUtm.plot(ax=ax,column='PopuDen',linewidth=0.5,cmap='Reds'
,edgecolor='k',legend=True,)
# plt.savefig('巴吞鲁日市2010年人口密度模式.jpg',dpi=300)
plt.show()

分析同心环区的人口密度格式
生成同心环
## 两种方法生成多重缓冲区的阈值
dis = list(np.arange(2000,26001,2000))
dis
dis = list(range(2000,26001,2000))
dis
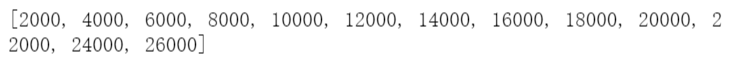
## 真的特别神奇distances只有这样写列表才可以运行
# Set local variables
inFeatures = "BRCenter"
outFeatureClass = "rings.shp"
distances = [2000, 4000, 6000, 8000, 10000,
12000, 14000, 16000, 18000,
20000, 22000, 24000, 26000]
bufferUnit = "meters"
# Execute MultipleRingBuffer
arcpy.MultipleRingBuffer_analysis(inFeatures, outFeatureClass, distances, bufferUnit, "", "ALL")
相交
try:
# Set the workspace (to avoid having to type in the full path to the data every time)
arcpy.env.workspace = "MyProject"
# Process: Find all stream crossings (points)
inFeatures = ["rings", "BRTrtUtm"]
intersectOutput = "TrtRings.shp"
arcpy.Intersect_analysis(inFeatures, intersectOutput,)
except Exception as err:
print(err.args[0])
TrtRings = gpd.GeoDataFrame.from_file('TrtRings.shp')
TrtRings['area'] = TrtRings.area/1000000
TrtRings['EstPopu'] = TrtRings['PopuDen'] * TrtRings['POLY_AREA']
融合
arcpy.env.workspace = "C:/data/Portland.gdb/Taxlots"
# Set local variables
inFeatures = "TrtRings"
outFeatureClass = "DissRings.shp"
dissolveFields = ["distance"]
statistics_fields = [["POLY_AREA","SUM"], ["PopuDen","SUM"]]
# Execute Dissolve using LANDUSE and TAXCODE as Dissolve Fields
arcpy.Dissolve_management(inFeatures, outFeatureClass, dissolveFields, statistics_fields,)
DissRings = gpd.GeoDataFrame.from_file('DissRings.shp')
DissRings
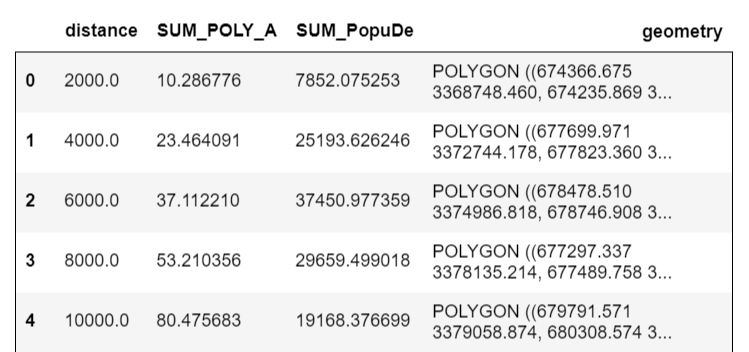
DissRings['PopuDen'] = DissRings['SUM_PopuDe'] / DissRings['SUM_POLY_A']
DissRings.set_index('distance',inplace=True)
DissRings['PopuDen'].plot(kind='bar',x='distance',
xlabel='',figsize=(8,6))
plt.savefig('同心环人口密度图.jpg',dpi=300)
plt.show()

要素转点
# Set environment settings
env.workspace = "BR.gdb"
# Set local variables
inFeatures = "BRBlkUtm"
outFeatureClass = "BRBlkPt.shp"
# Use FeatureToPoint function to find a point inside each park
arcpy.FeatureToPoint_management(inFeatures, outFeatureClass, "INSIDE")
标识
env.workspace = "MyProject"
# Set local parameters
inFeatures = "BRBlkPt"
idFeatures = "DissRings"
outFeatures = "BRBlkPt_Identity.shp"
# Process: Use the Identity function
arcpy.Identity_analysis(inFeatures, idFeatures, outFeatures)
数据筛选
BRBlkPt_Identity = gpd.GeoDataFrame.from_file('BRBlkPt_Identity.shp')
BRBlkPt_Identity.shape
BRBlkPt_Identity.tail()
## 选取数据
BRBlkPt_Identity = BRBlkPt_Identity[~(BRBlkPt_Identity['distance']==0.0)]
数据分组
rigs_data = pd.DataFrame(BRBlkPt_Identity.groupby(by=['distance'])['POP10'].sum(),columns=['POP10'])
rigs_data.reset_index(inplace=True)
rigs_data
数据连接
EstPopu = BRBlkPt_Identity[['distance','SUM_POLY_A','SUM_PopuDe']]
PopuDen = pd.merge(rigs_data,EstPopu,how='inner',left_on='distance',right_on='distance')
## 删除重复值,按理来说,应该没有重复值了,可以试试外连接
PopuDen.drop_duplicates(inplace = True)
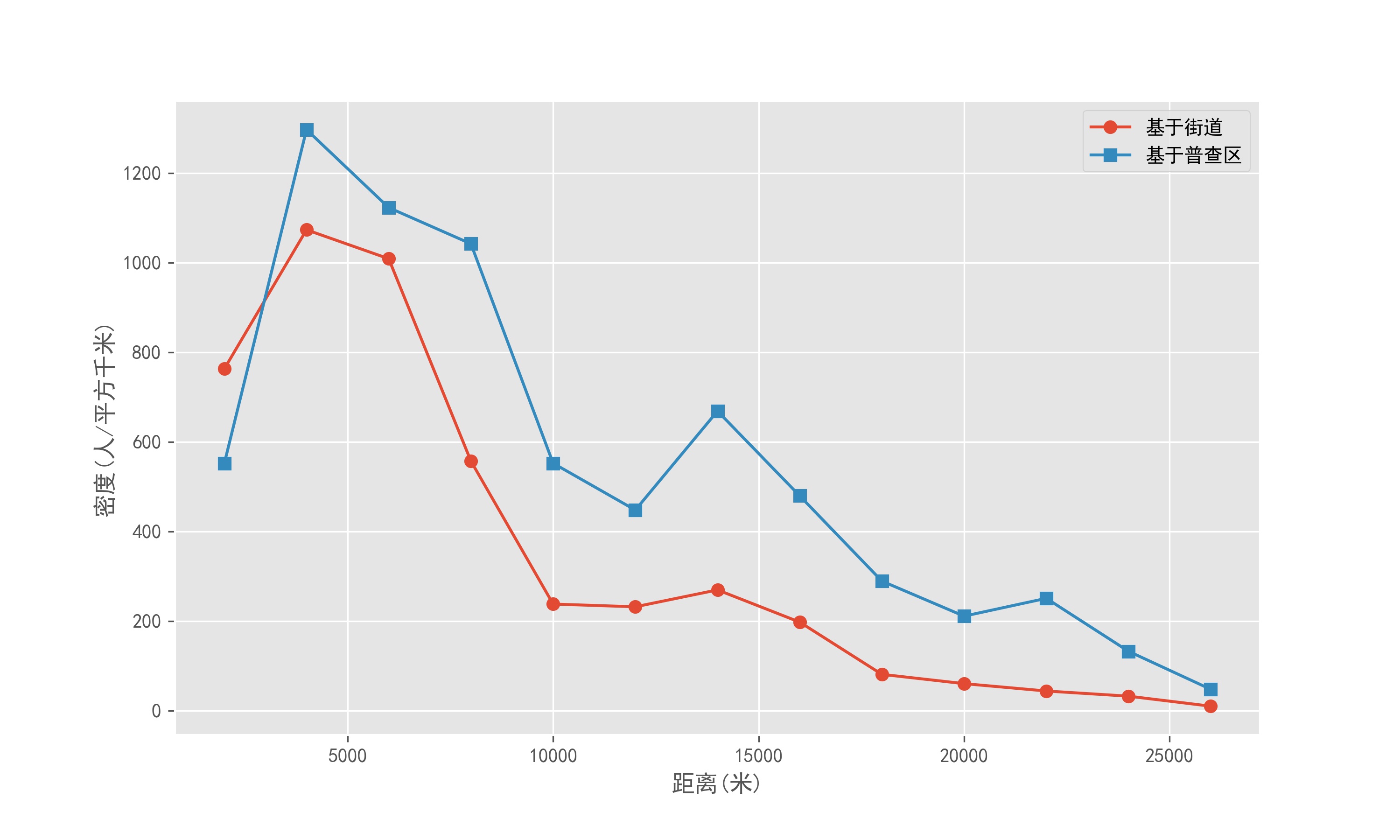
分析和比较环形区人口和密度估值
PopuDen.set_index('distance',inplace=True)
PopuDen['EstPopu'] = PopuDen['SUM_PopuDe'] / PopuDen['SUM_POLY_A']
PopuDen['PopuDen1'] = PopuDen['POP10'] / PopuDen['SUM_POLY_A']
PopuDen['EstPopu'].plot(figsize=(10,6),marker='o',xlabel='距离(米)',ylabel='密度(人/平方千米)')
PopuDen['PopuDen1'].plot(marker='s',xlabel='距离(米)',ylabel='密度(人/平方千米)')
plt.legend(['基于街道','基于普查区'])
plt.savefig('基于普查区和街区数据的人口密度模式对比.jpg',dpi=300)
plt.show()
总结
2022年的第一次写笔记,写的不是很好,而且发现许多问题,比如就是geopandas里面的area和arcpy里面的area不一样,可能是算法不一样,面积要使用投影坐标系,我相信这个应该没有人不知道了吧,要对ArcGIS Pro里面的arcpy大赞。最近感谢也比较多,比如疫情,已经有点常态化,很影响我们的生活了。心怀感恩,希望我们都有美好的未来。春燕归,巢于林木。接下来一段时间,我要忙我的毕业论文,可能会比较忙,需要数据的可以联系我。
利用python绘制分析路易斯安那州巴吞鲁日市的人口密度格局的更多相关文章
- Louis Armstrong【路易斯·阿姆斯特朗】
Louis Armstrong Louis Armstrong had two famous nicknames. 路易斯·阿姆斯特朗有两个著名的绰号. Some people called him ...
- 利用Python绘制一个正方形螺旋线
1 安装turtle Python2安装命令: pip install turtule Python3安装命令: pip3 install turtle 因为turtle库主要是在Python2中使用 ...
- 如何利用Python绘制一个爱心
刚学习Python几周,闲来无事,突然想尝试画一个爱心,步骤如下: 打开界面 打开Python shell界面,具体是Python语言的IDLE软件脚本. 2.建立脚本 单击左上角’File’,再单击 ...
- Python 学习记录----利用Python绘制奥运五环
import turtle #导入turtle模块 turtle.color("blue") #定义颜色 turtle.penup() #penup和pendown()设置画笔抬起 ...
- 利用Python进行数据分析 第4章 IPython的安装与使用简述
本篇开始,结合前面所学的Python基础,开始进行实战学习.学习书目为<利用Python进行数据分析>韦斯-麦金尼 著. 之前跳过本书的前述基础部分(因为跟之前所学的<Python基 ...
- 【Python 16】分形树绘制4.0(利用递归函数绘制分形树fractal tree)
1.案例描述 树干为80,分叉角度为20,树枝长度小于5则停止.树枝长小于30,可以当作树叶了,树叶部分为绿色,其余为树干部分设为棕色. 2.案例分析 由于分形树具有对称性,自相似性,所以我们可以用 ...
- Python股票分析系列——数据整理和绘制.p2
该系列视频已经搬运至bilibili: 点击查看 欢迎来到Python for Finance教程系列的第2部分. 在本教程中,我们将利用我们的股票数据进一步分解一些基本的数据操作和可视化. 我们将要 ...
- 利用Python进行异常值分析实例代码
利用Python进行异常值分析实例代码 异常值是指样本中的个别值,也称为离群点,其数值明显偏离其余的观测值.常用检测方法3σ原则和箱型图.其中,3σ原则只适用服从正态分布的数据.在3σ原则下,异常值被 ...
- 利用Python分析GP服务运行结果的输出路径 & 实现服务输出路径的本地化 分类: Python ArcGIS for desktop ArcGIS for server 2015-08-06 19:49 3人阅读 评论(0) 收藏
最近,一直纠结一个问题:做好的GP模型或者脚本在本地运行,一切正常:发布为GP服务以后时而可以运行成功,而更多的是运行失败,甚至不能知晓运行成功后的结果输出在哪里. 铺天盖地的文档告诉我,如下信息: ...
随机推荐
- Linux——配置主从数据库服务
主从数据库 Linux中,数据库服务有三种:互为主主,互为主从,一主一从(主从数据库) 互为主主:数据库时时更新 互为主从:数据库达到一定的的容量再更新 一主一从:在主数据库上面创建的,可以同步到从数 ...
- HCNP Routing&Switching之组播技术-组播协议IGMP
前文我们了解了组播地址相关话题,回顾请参考https://www.cnblogs.com/qiuhom-1874/p/15616740.html:今天我们来聊一聊组播协议中IGMP协议相关话题: 组播 ...
- 2021 中国.NET开发者峰会 今日开幕
01 大会介绍 .NET Conf China 2021 是面向开发人员的社区峰会,基于 .NET Conf 2021的活动,庆祝 .NET 6 的发布和回顾过去一年来 .NET 在中国的发展成果展示 ...
- 资源分配情况(Project)
<Project2016 企业项目管理实践>张会斌 董方好 编著 资源的分配情况,无非就是未分配.已分配和过度分配三种,这些都可以通过各种视图查看,比如[资源]>[工作组规划器]视图 ...
- 【论文笔记】Leveraging Post-click Feedback for Content Recommendations
Leveraging Post-click Feedback for Content Recommendations Authors: Hongyi Wen, Longqi Yang, Deborah ...
- echarts map 地图在react项目中的使用
需求 展示海南省地图,点击市高亮展示,并在右侧展示对应市的相关数据. 准备工作 Echarts 海南地图json 效果图 代码 index.tsx import React, { useRef, us ...
- Vim使用简介
Vim操作 Vim真的很酷:D 编辑模式 正常模式:在文件中四处移动光标进行修改 插入模式:插入文本 替换模式:替换文本 可视化(一般,行,块)模式:选中文本块 命令模式:用于执行命令 在不同的操作模 ...
- 【LeetCode】145. Binary Tree Postorder Traversal 解题报告 (C++&Python)
作者: 负雪明烛 id: fuxuemingzhu 个人博客:http://fuxuemingzhu.cn/ 目录 题目描述 题目大意 解题方法 递归 迭代 日期 题目地址:https://leetc ...
- E. Congruence Equation
E. Congruence Equation 思路: 中国剩余定理 \(a^n(modp) = a^{nmod(p-1)}(modp)\),那么枚举在\([0,n-2]\)枚举指数 求\(a^i\)关 ...
- 【剑指Offer】和为S的两个数字 解题报告(Python)
[剑指Offer]和为S的两个数字 解题报告(Python) 标签(空格分隔): 剑指Offer 题目地址:https://www.nowcoder.com/ta/coding-interviews ...
