Netty学习笔记(2)ByteBuffer
1. 测试ByteBuffer
1.1 依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.netty</groupId>
<artifactId>netty-all</artifactId>
<version>4.1.48.Final</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.20</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.code.gson</groupId>
<artifactId>gson</artifactId>
<version>2.8.6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.guava</groupId>
<artifactId>guava</artifactId>
<version>20.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId>
<version>1.2.4</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
1.2 新建文本文件data.txt
15354154154aahbaj
1.3 使用 FileChannel 来读取文件内容
输入或输出流,或者RandomAccessFile获取FileChannel
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 输入或输出流获得 ,或者RandomAccessFile获取FileChannel
try (FileChannel channel = new FileInputStream("data.txt").getChannel()) {
// 准备缓冲区 缓冲区10字节
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(10);
int len = -1;
while ((len = channel.read(buffer)) != -1) {
log.debug("读取到的字节数{}", len);
// 切换buffer为读模式就可以获取数据
buffer.flip();
while (buffer.remaining() > 0) {
byte b = buffer.get();
log.debug("读取到的字符{}", (char) b);
}
// 却换为写模式
buffer.clear();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
2. ByteBuffer正确使用步骤
ByteBuffer初始是写状态
- 向 buffer 写入数据,例如调用 channel.read(buffer)
- 调用 flip() 切换至读模式
- 从 buffer 读取数据,例如调用 buffer.get()
- 调用 clear() 或 compact() 切换至写模式
- 重复 1~4 步骤
3. ByteBuffer 结构
ByteBuffer 有以下重要属性
- capacity
- position
- limit
一开始
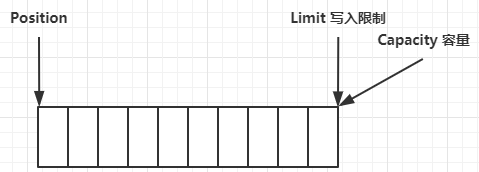
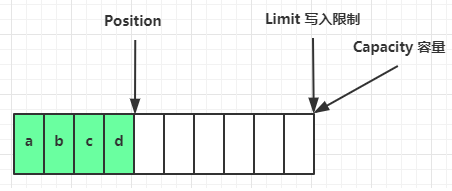
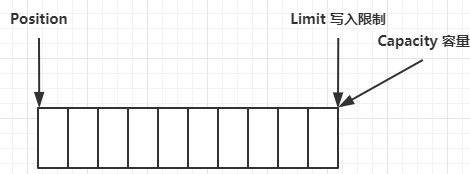
写模式下,position 是写入位置,limit 等于容量,下图表示写入了 4 个字节后的状态
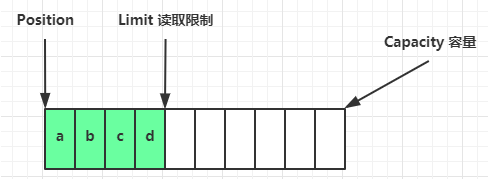
flip 动作发生后,position 切换为读取位置,limit 切换为读取限制
读取 4 个字节后,状态
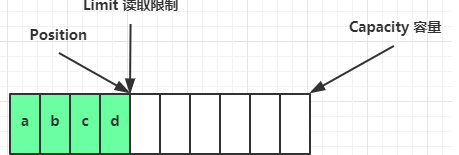
clear 动作发生后,状态
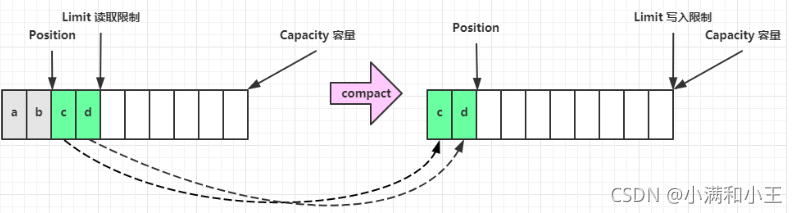
compact 方法,是把未读完的部分向前压缩,然后切换至写模式
4. ByteBuffer调试工具类
package com.wang.c1;
import io.netty.util.internal.StringUtil;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import static io.netty.util.internal.MathUtil.isOutOfBounds;
import static io.netty.util.internal.StringUtil.NEWLINE;
public class ByteBufferUtil {
private static final char[] BYTE2CHAR = new char[256];
private static final char[] HEXDUMP_TABLE = new char[256 * 4];
private static final String[] HEXPADDING = new String[16];
private static final String[] HEXDUMP_ROWPREFIXES = new String[65536 >>> 4];
private static final String[] BYTE2HEX = new String[256];
private static final String[] BYTEPADDING = new String[16];
static {
final char[] DIGITS = "0123456789abcdef".toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++) {
HEXDUMP_TABLE[i << 1] = DIGITS[i >>> 4 & 0x0F];
HEXDUMP_TABLE[(i << 1) + 1] = DIGITS[i & 0x0F];
}
int i;
// Generate the lookup table for hex dump paddings
for (i = 0; i < HEXPADDING.length; i++) {
int padding = HEXPADDING.length - i;
StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder(padding * 3);
for (int j = 0; j < padding; j++) {
buf.append(" ");
}
HEXPADDING[i] = buf.toString();
}
// Generate the lookup table for the start-offset header in each row (up to 64KiB).
for (i = 0; i < HEXDUMP_ROWPREFIXES.length; i++) {
StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder(12);
buf.append(NEWLINE);
buf.append(Long.toHexString(i << 4 & 0xFFFFFFFFL | 0x100000000L));
buf.setCharAt(buf.length() - 9, '|');
buf.append('|');
HEXDUMP_ROWPREFIXES[i] = buf.toString();
}
// Generate the lookup table for byte-to-hex-dump conversion
for (i = 0; i < BYTE2HEX.length; i++) {
BYTE2HEX[i] = ' ' + StringUtil.byteToHexStringPadded(i);
}
// Generate the lookup table for byte dump paddings
for (i = 0; i < BYTEPADDING.length; i++) {
int padding = BYTEPADDING.length - i;
StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder(padding);
for (int j = 0; j < padding; j++) {
buf.append(' ');
}
BYTEPADDING[i] = buf.toString();
}
// Generate the lookup table for byte-to-char conversion
for (i = 0; i < BYTE2CHAR.length; i++) {
if (i <= 0x1f || i >= 0x7f) {
BYTE2CHAR[i] = '.';
} else {
BYTE2CHAR[i] = (char) i;
}
}
}
/**
* 打印所有内容
* @param buffer
*/
public static void debugAll(ByteBuffer buffer) {
int oldlimit = buffer.limit();
buffer.limit(buffer.capacity());
StringBuilder origin = new StringBuilder(256);
appendPrettyHexDump(origin, buffer, 0, buffer.capacity());
System.out.println("+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+");
System.out.printf("position: [%d], limit: [%d]\n", buffer.position(), oldlimit);
System.out.println(origin);
buffer.limit(oldlimit);
}
/**
* 打印可读取内容
* @param buffer
*/
public static void debugRead(ByteBuffer buffer) {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(256);
appendPrettyHexDump(builder, buffer, buffer.position(), buffer.limit() - buffer.position());
System.out.println("+--------+-------------------- read -----------------------+----------------+");
System.out.printf("position: [%d], limit: [%d]\n", buffer.position(), buffer.limit());
System.out.println(builder);
}
private static void appendPrettyHexDump(StringBuilder dump, ByteBuffer buf, int offset, int length) {
if (isOutOfBounds(offset, length, buf.capacity())) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(
"expected: " + "0 <= offset(" + offset + ") <= offset + length(" + length
+ ") <= " + "buf.capacity(" + buf.capacity() + ')');
}
if (length == 0) {
return;
}
dump.append(
" +-------------------------------------------------+" +
NEWLINE + " | 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |" +
NEWLINE + "+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+");
final int startIndex = offset;
final int fullRows = length >>> 4;
final int remainder = length & 0xF;
// Dump the rows which have 16 bytes.
for (int row = 0; row < fullRows; row++) {
int rowStartIndex = (row << 4) + startIndex;
// Per-row prefix.
appendHexDumpRowPrefix(dump, row, rowStartIndex);
// Hex dump
int rowEndIndex = rowStartIndex + 16;
for (int j = rowStartIndex; j < rowEndIndex; j++) {
dump.append(BYTE2HEX[getUnsignedByte(buf, j)]);
}
dump.append(" |");
// ASCII dump
for (int j = rowStartIndex; j < rowEndIndex; j++) {
dump.append(BYTE2CHAR[getUnsignedByte(buf, j)]);
}
dump.append('|');
}
// Dump the last row which has less than 16 bytes.
if (remainder != 0) {
int rowStartIndex = (fullRows << 4) + startIndex;
appendHexDumpRowPrefix(dump, fullRows, rowStartIndex);
// Hex dump
int rowEndIndex = rowStartIndex + remainder;
for (int j = rowStartIndex; j < rowEndIndex; j++) {
dump.append(BYTE2HEX[getUnsignedByte(buf, j)]);
}
dump.append(HEXPADDING[remainder]);
dump.append(" |");
// Ascii dump
for (int j = rowStartIndex; j < rowEndIndex; j++) {
dump.append(BYTE2CHAR[getUnsignedByte(buf, j)]);
}
dump.append(BYTEPADDING[remainder]);
dump.append('|');
}
dump.append(NEWLINE +
"+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+");
}
private static void appendHexDumpRowPrefix(StringBuilder dump, int row, int rowStartIndex) {
if (row < HEXDUMP_ROWPREFIXES.length) {
dump.append(HEXDUMP_ROWPREFIXES[row]);
} else {
dump.append(NEWLINE);
dump.append(Long.toHexString(rowStartIndex & 0xFFFFFFFFL | 0x100000000L));
dump.setCharAt(dump.length() - 9, '|');
dump.append('|');
}
}
public static short getUnsignedByte(ByteBuffer buffer, int index) {
return (short) (buffer.get(index) & 0xFF);
}
}
5. ByteBuffer 常见方法
5.1 分配空间
- allocate()
- allocateDirect()
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(ByteBuffer.allocate(16).getClass());
System.out.println(ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(16).getClass());
/**
* class java.nio.HeapByteBuffer 使用堆内存 , 读写效率低, 受到gc影响
* class java.nio.DirectByteBuffer 使用直接内存: 读写效率高, 不受到gc影响, 分配的效率低, 可能造成内存泄漏
*/
}
5.2 向buffer中写入数据
- 调用 channel 的 read 方法
int readBytes = channel.read(buf);
- 调用 buffer 自己的 put 方法
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(10);
byteBuffer.put(new byte[] {'a', 'b', 'c', 'd'});
5.3 从 buffer 读取数据
byteBuffer.flip();
// 从头开始读
byteBuffer.get(new byte[4]);
5.4 改变position 指针位置
5.4.1 rewind()
get 方法会让 position 读指针向后走,如果想重复读取数据
- 可以调用 rewind 方法将 position 重新置为 0
- 或者调用 get(int i) 方法获取索引 i 的内容,它不会移动读指针
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(10);
byteBuffer.put(new byte[] {'a', 'b', 'c', 'd'});
byteBuffer.flip();
// 从头开始读
byteBuffer.get(new byte[4]);
ByteBufferUtil.debugAll(byteBuffer);
// 把position 改为零, 又可以重头读
byteBuffer.rewind();
ByteBufferUtil.debugAll(byteBuffer);
5.4.2 mark 和 reset
mark 是在读取时,做一个标记,即使 position 改变,只要调用 reset 就能回到 mark 的位置
rewind 和 flip 都会清除 mark 位置
ByteBuffer byteBuffer2 = ByteBuffer.allocate(10);
byteBuffer2.put(new byte[] {'a', 'b', 'c', 'd'});
byteBuffer2.flip();
ByteBufferUtil.debugAll(byteBuffer2);
byteBuffer2.get();
// 下标为1位置标记
byteBuffer2.mark();
byteBuffer2.get();
byteBuffer2.get();
ByteBufferUtil.debugAll(byteBuffer2);
byteBuffer2.reset();
ByteBufferUtil.debugAll(byteBuffer2);

5.5 字符串与 ByteBuffer 互转
5.5.1 字符串转为ByteBuffer
5.5.1.1 put
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(10);
String str = "hello";
byteBuffer.put(str.getBytes());
ByteBufferUtil.debugAll(byteBuffer);
5.5.1.2 CharSet
CharSet , 自动切换到读模式
ByteBuffer byteBuffer1 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.encode(str);
ByteBufferUtil.debugAll(byteBuffer1);
5.5.1.3 wrap
wrap, 自动切换到读模式
ByteBuffer byteBuffer2 = ByteBuffer.wrap(str.getBytes());
ByteBufferUtil.debugAll(byteBuffer2);
5.5.2 ByteBuffer转化为字符串
String s = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.decode(byteBuffer1).toString();
6. 分散读取和集中写入
6.1 分散读取
有一个文本文件 3parts.txt
onetwothree
使用如下方式读取,可以将数据填充至多个 buffer
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (FileChannel channel = new RandomAccessFile("3parts.txt","r").getChannel()) {
ByteBuffer b1 = ByteBuffer.allocate(3);
ByteBuffer b2 = ByteBuffer.allocate(3);
ByteBuffer b3 = ByteBuffer.allocate(5);
channel.read(new ByteBuffer[] {b1, b2, b3});
ByteBufferUtil.debugAll(b1);
ByteBufferUtil.debugAll(b2);
ByteBufferUtil.debugAll(b3);
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}

6.2 集中写
public static void main(String[] args) {
ByteBuffer b1 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.encode("hello");
ByteBuffer b2 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.encode("java");
ByteBuffer b3 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.encode("!");
try (FileChannel channel = new RandomAccessFile("words.txt", "rw").getChannel()) {
channel.write(new ByteBuffer[] {b1, b2, b3});
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
Netty学习笔记(2)ByteBuffer的更多相关文章
- Netty学习笔记-入门版
目录 Netty学习笔记 前言 什么是Netty IO基础 概念说明 IO简单介绍 用户空间与内核空间 进程(Process) 线程(thread) 程序和进程 进程切换 进程阻塞 文件描述符 文件句 ...
- Netty学习笔记(二) 实现服务端和客户端
在Netty学习笔记(一) 实现DISCARD服务中,我们使用Netty和Python实现了简单的丢弃DISCARD服务,这篇,我们使用Netty实现服务端和客户端交互的需求. 前置工作 开发环境 J ...
- Netty 学习笔记(1)通信原理
前言 本文主要从 select 和 epoll 系统调用入手,来打开 Netty 的大门,从认识 Netty 的基础原理 —— I/O 多路复用模型开始. Netty 的通信原理 Netty 底层 ...
- Netty学习笔记(二)——netty组件及其用法
1.Netty是 一个异步事件驱动的网络应用程序框架,用于快速开发可维护的高性能协议服务器和客户端. 原生NIO存在的问题 1) NIO的类库和API繁杂,使用麻烦:需要熟练掌握Selector.Se ...
- Netty学习笔记(六) 简单的聊天室功能之WebSocket客户端开发实例
在之前的Netty相关学习笔记中,学习了如何去实现聊天室的服务段,这里我们来实现聊天室的客户端,聊天室的客户端使用的是Html5和WebSocket实现,下面我们继续学习. 创建客户端 接着第五个笔记 ...
- 2018/1/19 Netty学习笔记(一)
这段时间学了好多好多东西,不过更多是细节和思想上的,比如分布式事物,二次提交,改善代码质量,还有一些看了一些源码什么的; 记录一下真正的技术学习,关于Netty的学习过程; 首先说Netty之前先说一 ...
- Netty学习笔记(一)
学习圣思园Netty笔记,个人理解 2.netty宏观理解-本节内容: 1.阶段性事件驱动,一个请求分为若干阶段处理,每个阶段根据情况合理分配线程去处理,各阶段间通信采用异步事件驱动方式. 2.net ...
- Netty学习笔记
一些类与方法说明 1)ByteBuf ByteBuf的API说明: Creation of a buffer It is recommended to create a new buffer usin ...
- Netty学习笔记(一):接收nodejs模拟表单上传的文件
好久不写博客了,也好久不写代码了,这两天临时遇上一个事情,觉得不难,加上觉得手有些生,就动手做了一下,结果遇上了不少坑,有新坑,有老坑,痛苦无比,现在总算差不多了,赶紧记录下来,希望以后不再重复这种痛 ...
随机推荐
- WEB漏洞——XXE
XXE漏洞又称XML外部实体注入(XML External Entity) 介绍XXE漏洞前先说一下什么是XML XML语言 XML用于标记电子文件使其具有结构性的标记语言,可以用来标记数据定义数据类 ...
- 【Python从入门到精通】(二十五)Python多进程的使用
您好,我是码农飞哥,感谢您阅读本文,欢迎一键三连哦. 本篇重点介绍Python多进程的使用,读者朋友们可以将多进程和多线程两者做一个对比学习. 干货满满,建议收藏,需要用到时常看看. 小伙伴们如有问题 ...
- python关键字--yield
彻底理解Python中的yield
- uni-app仿抖音APP短视频+直播+聊天实例|uniapp全屏滑动小视频+直播
基于uniapp+uView-ui跨端H5+小程序+APP短视频|直播项目uni-ttLive. uni-ttLive一款全新基于uni-app技术开发的仿制抖音/快手短视频直播项目.支持全屏丝滑般上 ...
- PHP的Mhash扩展函数的学习
这次我们要学习的又是一个 Hash 加密扩展.不过这个扩展 Mhash 已经集成在了 Hash 扩展中.同时也需要注意的是,这个扩展已经不推荐使用了,我们应该直接使用 Hash 扩展中的函数来进行 H ...
- docker network 参数
一. 格式 docker network COMMAND 二.COMMAND 讲解 2.1 .docker network connect 格式 docker network connect [OPT ...
- Redis之品鉴之旅(一)
Redis之品鉴之旅(一) 好知识就如好酒,需要我们坐下来,静静的慢慢的去品鉴.Redis作为主流nosql数据库,在提升性能的方面是不可或缺的.下面就拿好小板凳,我们慢慢的来一一品鉴. 1)redi ...
- 轻松集成腾讯云短信服务实现短信发送(Java实现)
不论是阿里云还是腾讯云,要想在网站上实现短信发送功能,首先得保证你的网站域名是通过备案的,因为短信签名是需要用到备案过的域名截图,所以域名通过了,申请很快就会审批成功了. (说点题外话,备案的话,需要 ...
- Python标准库模块之heapq – 堆构造
Python标准库模块之heapq – 堆构造 读前福利:几百本经典书籍https://www.johngo689.com/2158/ 原文链接:https://www.johngo689.com/2 ...
- JVM学习笔记——堆
堆 Heap 一个 JVM 只有一个堆,堆也是 Java 内存管理的核心区域.在 JVM 启动时堆被创建,同时大小在启动时已设定好,堆是 JVM 管理最大的一块内存空间,其大小可以调节. 堆的内存空间 ...
