Android View post 方法
解析View.post方法。分析一下这个方法的流程。
说起post方法,我们很容易联想到Handler的post方法,都是接收一个Runnable对象。那么这两个方法有啥不同呢?
Handler的post方法
先来简单看一下Handler的post(Runnable)方法。这个方法是将一个Runnable加到消息队列中,并且会在这个handler关联的线程里执行。
下面是关联的部分源码。可以看到传入的Runnable对象,装入Message后,被添加进了queue队列中。
Handler 有关的部分源码
// android.os Handler 有关的部分源码
public final boolean post(@NonNull Runnable r) {
return sendMessageDelayed(getPostMessage(r), 0);
}
private static Message getPostMessage(Runnable r) {
Message m = Message.obtain();
m.callback = r;
return m;
}
public final boolean sendMessageDelayed(@NonNull Message msg, long delayMillis) {
if (delayMillis < 0) {
delayMillis = 0;
}
return sendMessageAtTime(msg, SystemClock.uptimeMillis() + delayMillis);
}
public boolean sendMessageAtTime(@NonNull Message msg, long uptimeMillis) {
MessageQueue queue = mQueue;
if (queue == null) {
RuntimeException e = new RuntimeException(
this + " sendMessageAtTime() called with no mQueue");
Log.w("Looper", e.getMessage(), e);
return false;
}
return enqueueMessage(queue, msg, uptimeMillis);
}
private boolean enqueueMessage(@NonNull MessageQueue queue, @NonNull Message msg,
long uptimeMillis) {
msg.target = this;
msg.workSourceUid = ThreadLocalWorkSource.getUid();
if (mAsynchronous) {
msg.setAsynchronous(true);
}
return queue.enqueueMessage(msg, uptimeMillis);
}
具体流程,可以看handler介绍
View的post方法
我们直接跟着post的源码走。
public boolean post(Runnable action) {
final AttachInfo attachInfo = mAttachInfo;
if (attachInfo != null) {
return attachInfo.mHandler.post(action);
}
// Postpone the runnable until we know on which thread it needs to run.
// Assume that the runnable will be successfully placed after attach.
getRunQueue().post(action);
return true;
}
private HandlerActionQueue getRunQueue() {
if (mRunQueue == null) {
mRunQueue = new HandlerActionQueue();
}
return mRunQueue;
}
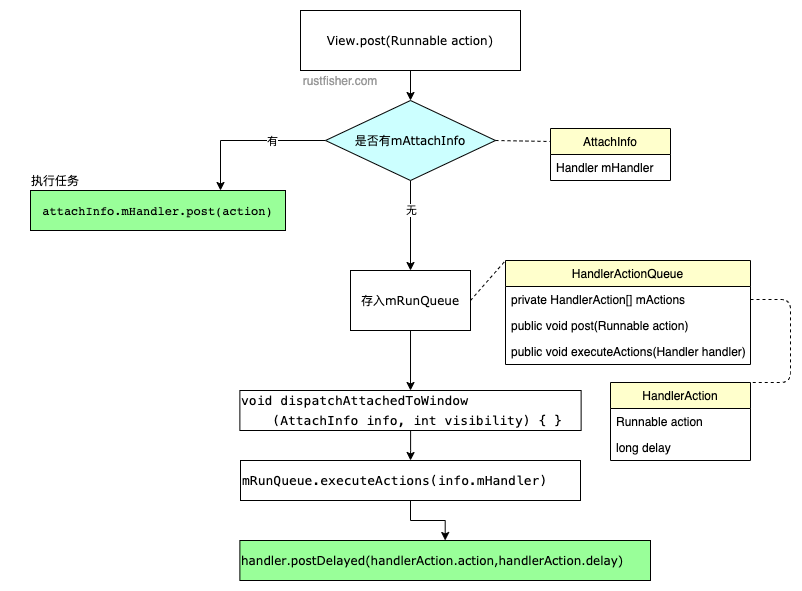
可以看到一开始就查询是否有attachInfo,如果有,则用attachInfo.mHandler来执行这个任务。
如果没有attachInfo,则添加到View自己的mRunQueue中。确定运行的线程后,再执行任务。
post(Runnable action)的返回boolean值,如果为true,表示任务被添加到消息队列中了。
如果是false,通常表示消息队列关联的looper正在退出。
那么我们需要了解AttachInfo和HandlerActionQueue。
AttachInfo
AttachInfo是View的静态内部类。View关联到父window后,用这个类来存储一些信息。
AttachInfo存储的一部分信息如下:
WindowId mWindowIdwindow的标志View mRootView最顶部的viewHandler mHandler这个handler可以用来处理任务
HandlerActionQueue
当View还没有handler的时候,拿HandlerActionQueue来缓存任务。HandlerAction是它的静态内部类,存储Runnable与延时信息。
public class HandlerActionQueue {
private HandlerAction[] mActions;
public void post(Runnable action)
public void executeActions(Handler handler)
// ...
private static class HandlerAction {
final Runnable action;
final long delay;
// ...
}
}
View的mRunQueue
将任务(runnable)排成队。当View关联上窗口并且有handler后,再执行这些任务。
/**
* Queue of pending runnables. Used to postpone calls to post() until this
* view is attached and has a handler.
*/
private HandlerActionQueue mRunQueue;
这个mRunQueue里存储的任务啥时候被执行?我们关注dispatchAttachedToWindow方法。
void dispatchAttachedToWindow(AttachInfo info, int visibility) {
// ...
// Transfer all pending runnables.
if (mRunQueue != null) {
mRunQueue.executeActions(info.mHandler);
mRunQueue = null;
}
// ...
}
这个方法里调用了mRunQueue.executeActions。
executeActions(Handler handler)方法实际上是用传入的handler处理队列中的任务。
而这个dispatchAttachedToWindow会被ViewGroup中被调用。
或者是ViewRootImpl中调用
host.dispatchAttachedToWindow(mAttachInfo, 0);
小结
View的post方法,实际上是使用了AttachInfo的handler。
如果View当前还没有AttachInfo,则把任务添加到了View自己的HandlerActionQueue队列中,然后在dispatchAttachedToWindow中把任务交给传入的AttachInfo的handler。也可以这样认为,View.post用的就是handler.post。
我们在获取View的宽高时,会利用View的post方法,就是等View真的关联到window再拿宽高信息。
流程图归纳如下
更多请参见Android合集的最近更新
Android View post 方法的更多相关文章
- [转]Android View.onMeasure方法的理解
转自:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_61fbf8d10100zzoy.html Android View.onMeasure方法的理解 View在屏幕上显示出来要先经过 ...
- Android View.onMeasure方法的理解
View在屏幕上显示出来要先经过measure(计算)和layout(布局).1.什么时候调用onMeasure方法? 当控件的父元素正要放置该控件时调用.父元素会问子控件一个问题,“你想要用多大地方 ...
- [转载]Android View.onMeasure方法的理解
2013-12-18 10:56:28 转载自http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_61fbf8d10100zzoy.html View在屏幕上显示出来要先经过measure( ...
- Android View.onMeasure方法的理解(转载)
一下内容转载自http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_61fbf8d10100zzoy.html View在屏幕上显示出来要先经过measure(计算)和layout(布局).1 ...
- Android View各种尺寸位置相关的方法探究
Android View各种尺寸位置相关的方法探究 本来想做一个View间的碰撞检测之类的. 动手做了才发现不是想象的那么简单. 首先,写好了碰撞检测的工具类如下: package com.mengd ...
- Android View中的控件和监听方法...
PS:居然三天没写博客了...今天补上...东西虽多,但是都是一些基础...代码多了一些,有人可能会这样问,粘这么多代码有毛用..其实对于一个Android的初学者来说,一个完整的代码是最容易帮助理解 ...
- Android view中的requestLayout和invalidate方法
Android view中的requestLayout和invalidate方法 requestLayout:当view确定自身已经不再适合现有的区域时,该view本身调用这个方法要求parent v ...
- android view的setVisibility方法值的意思
android view的setVisibility方法值的意思 有三个值 visibility One of VISIBLE, INVISIBLE, or GONE. 常量值为0,意思是可见的 常 ...
- Android编程动态创建视图View的方法
在Android开 发中,在Activity中关联视图View是一般使用setContentView方法,该方法一种参数是使用XML资源直接创 建:setContentView (int layout ...
随机推荐
- Spring的@PropertySource注解使用
@PropertySource注解是Spring用于加载配置文件,默认支持.properties与.xml两种配置文件.@PropertySource属性如下: name:默认为空,不指定Spring ...
- 007 PCI总线的桥与配置(二)
一.PCI桥与PCI设备的配置空间 PCI设备都有独立的配置空间,HOST主桥通过配置读写总线事务访问这段空间.PCI总线规定了三种类型的PCI配置空间,分别是PCI Agent设备使用的配置空间,P ...
- noip模拟45[真是啥也不会]
noip模拟45 solutions 真是一个题都不会了,然而考完试之后我在10min之内切掉了最后一个题 话说这是为什么呢, 因为最后一个是回滚莫队的大板子,然而我忘记了,不不不,是没有记起来过 T ...
- spring cloud alibaba版本选择
https://github.com/alibaba/spring-cloud-alibaba/wiki/版本说明 Spring Cloud Version Spring Cloud Version ...
- maven打jar包,导入本地jar
本地jar包存放目录 项目目录/lib/*.jar 导入jar包配置 <resources> <!--扫描到的配置yml--> <resource> <dir ...
- Qt Model/View(模型/视图)结构(无师自通)
Model/View(模型/视图)结构是 Qt 中用界面组件显示与编辑数据的一种结构,视图(View)是显示和编辑数据的界面组件,模型(Model)是视图与原始数据之间的接口. GUI 应用程序的一个 ...
- C# 利用反射进行深拷贝
- 【springcloud】服务熔断与降级(Hystrix)
转自:https://blog.csdn.net/pengjunlee/article/details/86688858 服务熔断 服务熔断的作用类似于我们家用的保险丝,当某服务出现不可用或响应超时的 ...
- springboot&&springcloud知识点
spring cloud 常见面试题: A.https://blog.csdn.net/panhaigang123/article/details/79587612 B.https://blog.cs ...
- 详述 MySQL 中的行级锁、表级锁和页级锁
转自:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_35246620/article/details/69943011 refer:cnblogs.com/f-ck-need-u/p/899547 ...
