list使用详解
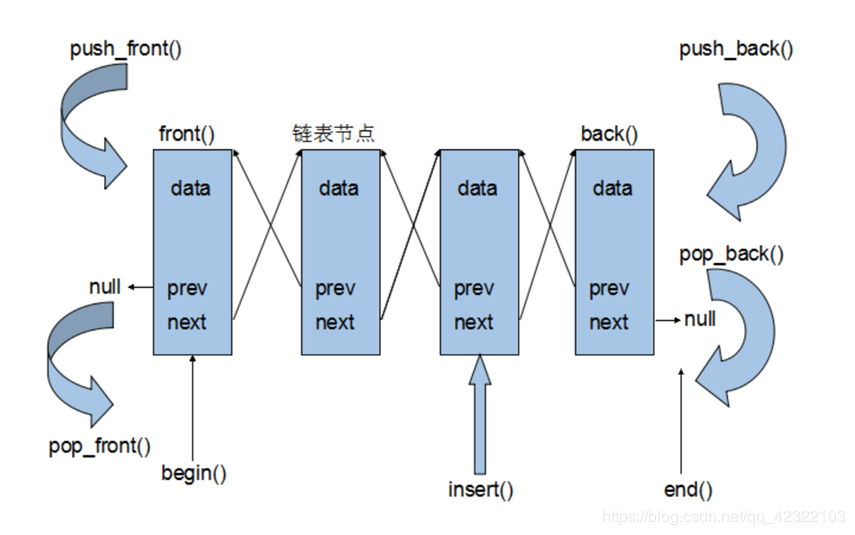
List双向链表
再谈链表
List链表的概念再度出现了,作为线性表的一员,C++的STL提供了快速进行构建的方法,为此,在前文的基础上通过STL进行直接使用,这对于程序设计中快速构建原型是相当有必要的,这里的STL链表是单链表的形式。
头文件
头文件:#include<list>
初始化
格式为:explicit list (const allocator_type& alloc = allocator_type());
我们以int类型作为参数为例进行创建,其创建方法与vector无异
定义的代码如下:
- list<int> l1; //创建一个空链表
- list<int> l2(10); //创建一个链表其有10个空元素
- list<int> l3(5,20); //创建一个链表其有5个元素内容为20
- list<int> l4(l3.begin(),l3.end()); //创建一个链表其内容为l3的内容
- list<int> l5(l4); //创建一个链表其内容为l4的内容
除此之外,还可以直接使用数组来初始化向量:
- int n[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
- list<int> a(n, n + 5); // 将数组n的前5个元素作为列表a的初值
迭代器
遍历代码举例(其方法和vector版本无异只是更加精简):
- list<int> li;
- for(list<int>::iterator it=li.begin();it!=li.end();it++){
- cout<<*it<<' ';
- }
基本操作
3.1 容量函数
- 容器大小:
lst.size(); - 容器最大容量:
lst.max_size(); - 更改容器大小:
lst.resize(); - 容器判空:
lst.empty();
- #include <iostream>
- #include <list>
- using namespace std;
- int main(int argc, char* argv[])
- {
- list<int> lst;
- for (int i = 0; i<6; i++)
- {
- lst.push_back(i);
- }
- cout << lst.size() << endl; // 输出:6
- cout << lst.max_size() << endl; // 输出:357913941
- lst.resize(0); // 更改元素大小
- cout << lst.size() << endl; // 输出:0
- if (lst.empty())
- cout << "元素为空" << endl; // 输出:元素为空
- return 0;
- }
3.2 添加函数
- 头部添加元素:
lst.push_front(const T& x); - 末尾添加元素:
lst.push_back(const T& x); - 任意位置插入一个元素:
lst.insert(iterator it, const T& x); - 任意位置插入 n 个相同元素:
lst.insert(iterator it, int n, const T& x); - 插入另一个向量的 [forst,last] 间的数据:
lst.insert(iterator it, iterator first, iterator last);
- #include <iostream>
- #include <list>
- using namespace std;
- int main(int argc, char* argv[])
- {
- list<int> lst;
- // 头部增加元素
- lst.push_front(4);
- // 末尾添加元素
- lst.push_back(5);
- // 任意位置插入一个元素
- list<int>::iterator it = lst.begin();
- lst.insert(it, 2);
- // 任意位置插入n个相同元素
- lst.insert(lst.begin(), 3, 9);
- // 插入另一个向量的[forst,last]间的数据
- list<int> lst2(5, 8);
- lst.insert(lst.begin(), lst2.begin(), ++lst2.begin());
- // 遍历显示
- for (it = lst.begin(); it != lst.end(); it++)
- cout << *it << " "; // 输出:8 9 9 9 2 4 5
- cout << endl;
- return 0;
- }
- li.insert(li.begin(),10); //在链表最前端插入数据10
- li.insert(li.begin(),5,20); //在链表最前端插入5个数据内容为20
- list<int> k(2,50); //创建一个新的链表k,其拥有2个元素内容均为50
- li.insert(li.begin(),li.begin(),li.end()); //在链表v最前端插入链表上K的全部内容
3.3 删除函数
- 头部删除元素:
lst.pop_front(); - 末尾删除元素:
lst.pop_back(); - 任意位置删除一个元素:
lst.erase(iterator it); - 删除 [first,last] 之间的元素:
lst.erase(iterator first, iterator last); - 清空所有元素:
lst.clear();
- #include <iostream>
- #include <list>
- using namespace std;
- int main(int argc, char* argv[])
- {
- list<int> lst;
- for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++)
- lst.push_back(i);
- // 头部删除元素
- lst.pop_front();
- // 末尾删除元素
- lst.pop_back();
- // 任意位置删除一个元素
- list<int>::iterator it = lst.begin();
- lst.erase(it);
- // 删除[first,last]之间的元素
- lst.erase(lst.begin(), ++lst.begin());
- // 遍历显示
- for (it = lst.begin(); it != lst.end(); it++)
- cout << *it << " "; // 输出:3 4 5 6
- cout << endl;
- // 清空所有元素
- lst.clear();
- // 判断list是否为空
- if (lst.empty())
- cout << "元素为空" << endl; // 输出:元素为空
- return 0;
- }
- li.erase(li.begin()); //删除第一个元素
- li.erase(li.begin(),li.begin()+4); //删除前4个元素
3.4 访问函数
- 访问第一个元素:
lst.front(); - 访问最后一个元素:
lst.back();
- #include <iostream>
- #include <list>
- using namespace std;
- int main(int argc, char* argv[])
- {
- list<int> lst;
- for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++)
- lst.push_back(i);
- // 访问第一个元素
- cout << lst.front() << endl; // 输出:0
- // 访问最后一个元素
- cout << lst.back() << endl; // 输出:5
- return 0;
- }
3.5 其他函数
- 多个元素赋值:
lst.assign(int nSize, const T& x); // 类似于初始化时用数组进行赋值 - 交换两个同类型容器的元素:
swap(list&, list&); 或 lst.swap(list&); - 合并两个列表的元素(默认升序排列):
lst.merge(); - 在任意位置拼接入另一个list:
lst.splice(iterator it, list&); - 删除容器中相邻的重复元素:
lst.unique();
- #include <iostream>
- #include <list>
- using namespace std;
- int main(int argc, char* argv[])
- {
- // 多个元素赋值s
- list<int> lst1;
- lst1.assign(3, 1);
- list<int> lst2;
- lst2.assign(3, 2);
- // 交换两个容器的元素
- // swap(lst1, lst2); // ok
- lst1.swap(lst2);
- // 遍历显示
- cout << "交换后的lst1: ";
- list<int>::iterator it;
- for (it = lst1.begin(); it!=lst1.end(); it++)
- cout << *it << " "; // 输出:2 2 2
- cout << endl;
- // 遍历显示
- cout << "交换后的lst2: ";
- for (it = lst2.begin(); it != lst2.end(); it++)
- cout << *it << " "; // 输出:1 1 1
- cout << endl;
- list<int> lst3;
- lst3.assign(3, 3);
- list<int> lst4;
- lst4.assign(3, 4);
- // 合并两个列表的元素
- lst4.merge(lst3); // 不是简单的拼接,而是会升序排列
- cout << "合并后的lst4: ";
- for (it = lst4.begin(); it != lst4.end(); it++)
- cout << *it << " "; // 输出:3 3 3 4 4 4
- cout << endl;
- list<int> lst5;
- lst5.assign(3, 5);
- list<int> lst6;
- lst6.assign(3, 6);
- // 在lst6的第2个元素处,拼接入lst5
- lst6.splice(++lst6.begin(), lst5);
- cout << "拼接后的lst6: ";
- for (it = lst6.begin(); it != lst6.end(); it++)
- cout << *it << " "; // 输出:6 5 5 5 6 6
- cout << endl;
- // 删除容器中相邻的重复元素
- list<int> lst7;
- lst7.push_back(1);
- lst7.push_back(1);
- lst7.push_back(2);
- lst7.push_back(2);
- lst7.push_back(3);
- lst7.push_back(2);
- lst7.unique();
- cout << "删除容器中相邻的重复元素后的lst7: ";
- for (it = lst7.begin(); it != lst7.end(); it++)
- cout << *it << " "; // 输出:1 2 3 2
- cout << endl;
- return 0;
- }
排序sort()
- #include<iostream>
- #include<list>
- using namespace std;s
- int cmp(const int &a,const int &b){
- //简单的自定义降序序列
- return a>b;
- }
- int main(){
- list<int> li; //创建一个空链表
- for(int i=10;i>=6;i--){
- li.push_back(i);
- }
- li.push_front(3);
- li.push_back(20);
- list<int> li2(li);
- for(list<int>::iterator it=li.begin();it!=li.end();it++){
- cout<<*it<<' ';
- }
- cout<<endl;
- //排序前3 10 9 8 7 6 20//
- li.sort();
- for(list<int>::iterator it=li.begin();it!=li.end();it++){
- cout<<*it<<' ';
- }
- cout<<endl;
- //默认排序后 3 6 7 8 9 10 20//
- li2.sort(cmp);
- for(list<int>::iterator it=li2.begin();it!=li2.end();it++){
- cout<<*it<<' ';
- }
- cout<<endl;
- //自定义排序后 20 10 9 8 7 6 3//
- return 0;
- }
迭代器与算法
1. 迭代器
- 开始迭代器指针:
lst.begin(); - 末尾迭代器指针:
lst.end();// 指向最后一个元素的下一个位置 - 指向常量的开始迭代器指针:
lst.cbegin();// 意思就是不能通过这个指针来修改所指的内容,但还是可以通过其他方式修改的,而且指针也是可以移动的。 - 指向常量的末尾迭代器指针:
lst.cend(); - 反向迭代器指针,指向最后一个元素:
lst.rbegin(); - 反向迭代器指针,指向第一个元素的前一个元素:
lst.rend();
- #include <iostream>
- #include <list>
- using namespace std;
- int main(int argc, char* argv[])
- {
- list<int> lst;
- lst.push_back(1);
- lst.push_back(2);
- lst.push_back(3);
- cout << *(lst.begin()) << endl; // 输出:1
- cout << *(--lst.end()) << endl; // 输出:3
- cout << *(lst.cbegin()) << endl; // 输出:1
- cout << *(--lst.cend()) << endl; // 输出:3
- cout << *(lst.rbegin()) << endl; // 输出:3
- cout << *(--lst.rend()) << endl; // 输出:1
- cout << endl;
- return 0;
- }
2. 算法
- 遍历元素
- list<int>::iterator it;
- for (it = lst.begin(); it != lst.end(); it++)
- cout << *it << endl;
- 元素翻转
- #include <algorithm>
- reverse(lst.begin(), lst.end());
- 元素排序
- #include <algorithm>
- sort(lst.begin(), lst.end()); // 采用的是从小到大的排序
- // 如果想从大到小排序,可以采用先排序后反转的方式,也可以采用下面方法:
- // 自定义从大到小的比较器,用来改变排序方式
- bool Comp(const int& a, const int& b)
- {
- return a > b;
- }
- sort(lst.begin(), lst.end(), Comp);
总结
可以看到,list 与 vector、deque 的用法基本一致,除了以下几处不同:
- list 为双向迭代器,故不支持
it+=i; - list 不支持下标访问和at方法访问。
list使用详解的更多相关文章
- Linq之旅:Linq入门详解(Linq to Objects)
示例代码下载:Linq之旅:Linq入门详解(Linq to Objects) 本博文详细介绍 .NET 3.5 中引入的重要功能:Language Integrated Query(LINQ,语言集 ...
- 架构设计:远程调用服务架构设计及zookeeper技术详解(下篇)
一.下篇开头的废话 终于开写下篇了,这也是我写远程调用框架的第三篇文章,前两篇都被博客园作为[编辑推荐]的文章,很兴奋哦,嘿嘿~~~~,本人是个很臭美的人,一定得要截图为证: 今天是2014年的第一天 ...
- EntityFramework Core 1.1 Add、Attach、Update、Remove方法如何高效使用详解
前言 我比较喜欢安静,大概和我喜欢研究和琢磨技术原因相关吧,刚好到了元旦节,这几天可以好好学习下EF Core,同时在项目当中用到EF Core,借此机会给予比较深入的理解,这里我们只讲解和EF 6. ...
- Java 字符串格式化详解
Java 字符串格式化详解 版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载. 微博:厉圣杰 文中如有纰漏,欢迎大家留言指出. 在 Java 的 String 类中,可以使用 format() 方法 ...
- Android Notification 详解(一)——基本操作
Android Notification 详解(一)--基本操作 版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载. 微博:厉圣杰 源码:AndroidDemo/Notification 文中如有纰 ...
- Android Notification 详解——基本操作
Android Notification 详解 版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载. 前几天项目中有用到 Android 通知相关的内容,索性把 Android Notificatio ...
- Git初探--笔记整理和Git命令详解
几个重要的概念 首先先明确几个概念: WorkPlace : 工作区 Index: 暂存区 Repository: 本地仓库/版本库 Remote: 远程仓库 当在Remote(如Github)上面c ...
- Drawable实战解析:Android XML shape 标签使用详解(apk瘦身,减少内存好帮手)
Android XML shape 标签使用详解 一个android开发者肯定懂得使用 xml 定义一个 Drawable,比如定义一个 rect 或者 circle 作为一个 View 的背景. ...
- Node.js npm 详解
一.npm简介 安装npm请阅读我之前的文章Hello Node中npm安装那一部分,不过只介绍了linux平台,如果是其它平台,有前辈写了更加详细的介绍. npm的全称:Node Package M ...
- .NET应用和AEAI CAS集成详解
1 概述 数通畅联某综合SOA集成项目的统一身份认证工作,需要第三方系统配合进行单点登录的配置改造,在项目中有需要进行单点登录配置的.NET应用系统,本文专门记录.NET应用和AEAI CAS的集成过 ...
随机推荐
- 在STM32F401上移植uC/OS的一个小问题 [原创]
STM32F401xx是意法半导体新推出的Cortex-M4内核的MCU,相较于已经非常流行的STM32F407xx和STM32F427xx等相同内核的MCU而言,其特点是功耗仅为128uA/MHz, ...
- SQL 练习16
按平均成绩从高到低显示所有学生的所有课程的成绩以及平均成绩 SELECT * from SC LEFT JOIN (SELECT sid,AVG(score) 平均成绩 from SC GROUP B ...
- 在docker安装tomcat的时候,报错:Caused by: java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: The AJP Connector is configured with secretRequired="true
初识docker,试着在docker中安装tomcat(安装的tomcat8.5),并且挂载到宿主机的相关目录下,结果启动的时候报错: 12-May-2020 01:14:34.061 SEVERE ...
- 栈编程和函数控制流: 从 continuation 与 CPS 讲到 call/cc 与协程
原标题:尾递归优化 快速排序优化 CPS 变换 call/cc setjmp/longjmp coroutine 协程 栈编程和控制流 讲解 本文为部分函数式编程的扩展及最近接触编程语言控制流的学习和 ...
- DataTable 读取每一行的内容
foreach (DataRow item in dataTable.Rows) { for (int i = 0; i < dataTable.Columns.Count; i++) { Co ...
- asp.net core 声明controller的方法
1, 对类名直接添加Controller, 如TestController. 2, 继承Controller 类. 3, 对类名添加controller的属性, 如[Controller]
- 【spring 注解驱动开发】Spring AOP原理
尚学堂spring 注解驱动开发学习笔记之 - AOP原理 AOP原理: 1.AOP原理-AOP功能实现 2.AOP原理-@EnableAspectJAutoProxy 3.AOP原理-Annotat ...
- .NET 元数据概述
元数据是一种二进制信息,用以对存储在公共语言运行库可移植可执行文件 (PE) 文件或存储在内存中的程序进行描述.将您的代码编译为 PE 文件时,便会将元数据插入到该文件的一部分中,而将代码转换为 Mi ...
- QT中的对象模型――QPointer
QPointer是一个模板类,为QObject对象提供了守卫指针(Guarded Pointer).什么是守卫指针?守卫指针QPointer<T>类似于普通C++指针T *,有且仅有一点不 ...
- 关于Ubuntu18.04 linux系统使用安装JDK Mysql
平台部署 一.安装JDK step1.下载OracleJDKstep2. 解压step3. 加入环境变量 具体操作如下: lemon@ubuntu:~$ cd ~/download/ lemon@ub ...
