python-BeautifulSoup库详解

快速使用
通过下面的一个例子,对bs4有个简单的了解,以及看一下它的强大之处:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup html = '''
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p> <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
'''
soup = BeautifulSoup(html,'lxml')
print(soup.prettify()) #补全HTML
print('-------------------------')
print(soup.title)
print('-------------------------')
print(soup.title.name)
print('-------------------------')
print(soup.title.string) #得到标签里面的内容
print('-------------------------')
print(soup.title.parent.name)
print('-------------------------')
print(soup.p)
print('-------------------------')
print(soup.p["class"])
print('-------------------------')
print(soup.a)
print('-------------------------')
print(soup.find_all('a'))
print('-------------------------')
print(soup.find(id='link3'))
print('-------------------------')
结果如下:
<html>
<head>
<title>
The Dormouse's story
</title>
</head>
<body>
<p class="title">
<b>
The Dormouse's story
</b>
</p>
<p class="story">
Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">
Elsie
</a>
,
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">
Lacie
</a>
and
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">
Tillie
</a>
;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.
</p>
<p class="story">
...
</p>
</body>
</html>
-------------------------
<title>The Dormouse's story</title>
-------------------------
title
-------------------------
The Dormouse's story
-------------------------
head
-------------------------
<p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
-------------------------
['title']
-------------------------
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">Elsie</a>
-------------------------
[<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">Elsie</a>, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>]
-------------------------
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>
-------------------------
基本使用
标签选择器
在快速使用中我们添加如下代码:
print(soup.title)
print(type(soup.title))
print(soup.head)
print(soup.p)
通过这种soup.标签名 我们就可以获得这个标签的内容
这里有个问题需要注意,通过这种方式获取标签,如果文档中有多个这样的标签,返回的结果是第一个标签的内容,如上面我们通过soup.p获取p标签,而文档中有多个p标签,但是只返回了第一个p标签内容
获取名称
当我们通过soup.title.name的时候就可以获得该title标签的名称,即title
获取属性
print(soup.p.attrs['name'])
print(soup.p['name'])
上面两种方式都可以获取p标签的name属性值
获取内容
print(soup.p.string)
结果就可以获取第一个p标签的内容:
The Dormouse's story
嵌套选择
我们直接可以通过下面嵌套的方式获取
print(soup.head.title.string)
标签选择器
选择元素
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup html = '''
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p> <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
'''
soup = BeautifulSoup(html,'lxml')
print(soup.title)
print('-------------------------')
print(type(soup.title))
print('-------------------------')
print(soup.head)
print('-------------------------')
print(soup.p)
结果:
<title>The Dormouse's story</title>
-------------------------
<class 'bs4.element.Tag'>
-------------------------
<head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
-------------------------
<p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
HTML中有多个 p 标签,但是最终 值输出一个,可以得出当有多个是只返回第一个结果
获取名称
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup html = '''
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p> <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
'''
soup = BeautifulSoup(html,'lxml')
print(soup.title.name)
结果:
title
title.name 获取最外层的标题
获取属性
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup html = '''
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p> <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
'''
soup = BeautifulSoup(html,'lxml')
print(soup.p.attrs['name'])
print(soup.p['name'])
结果:
dromouse
dromouse
获取内容
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup html = '''
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p> <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
'''
soup = BeautifulSoup(html,'lxml')
print(soup.p.string)
结果:
The Dormouse's story
嵌套选择
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup html = '''
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p> <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
'''
soup = BeautifulSoup(html,'lxml')
print(soup.head.title.string)
结果:
The Dormouse's story
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup html = '''
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p> <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
'''
soup = BeautifulSoup(html,'lxml')
print(soup.p.b.string)
结果:
The Dormouse's story
使用BeautifulSoup解析这段代码,能够得到一个 BeautifulSoup 的对象,并能按照标准的缩进格式的结构输出。
同时我们通过下面代码可以分别获取所有的链接,以及文字内容:
for link in soup.find_all('a'):
print(link.get('href'))
print(soup.get_text())
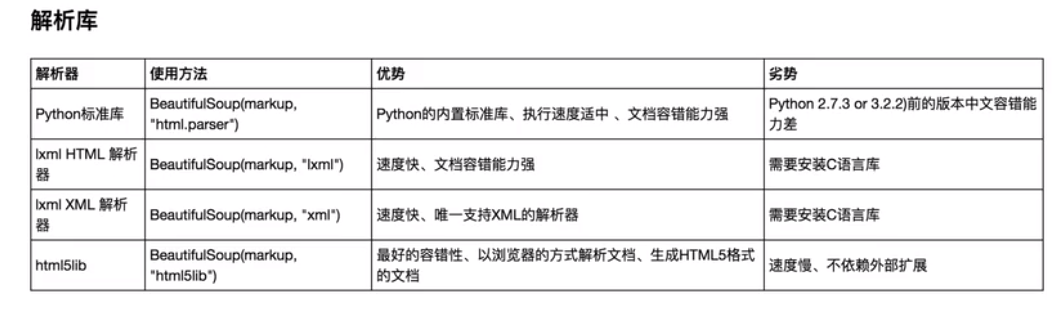
解析器
Beautiful Soup支持Python标准库中的HTML解析器,还支持一些第三方的解析器,如果我们不安装它,则 Python 会使用 Python默认的解析器,lxml 解析器更加强大,速度更快,推荐安装。
下面是常见解析器:
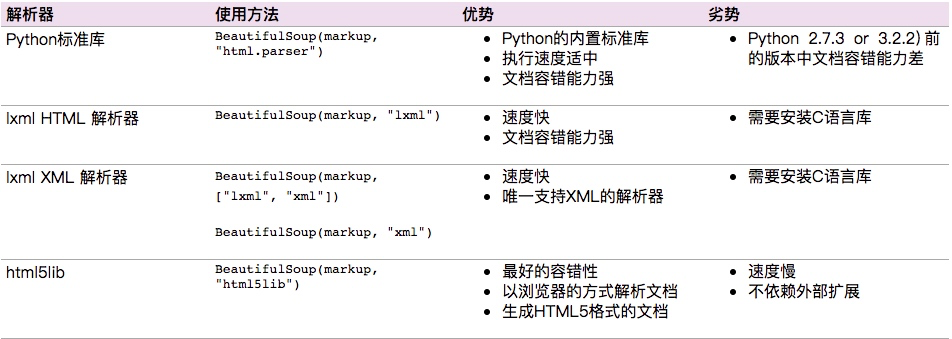
推荐使用lxml作为解析器,因为效率更高. 在Python2.7.3之前的版本和Python3中3.2.2之前的版本,必须安装lxml或html5lib, 因为那些Python版本的标准库中内置的HTML解析方法不够稳定.
子节点和子孙节点
contents的使用
通过下面例子演示:
html = """
<html>
<head>
<title>The Dormouse's story</title>
</head>
<body>
<p class="story">
Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">
<span>Elsie</span>
</a>
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a>
and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>
and they lived at the bottom of a well.
</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
""" from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html,'lxml')
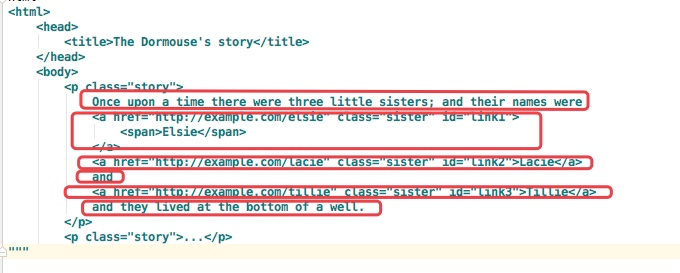
print(soup.p.contents)
['\n Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were\n ', <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">
<span>Elsie</span>
</a>, '\n', <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>, '\n and\n ', <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>, '\n and they lived at the bottom of a well.\n ']
结果是将p标签下的所有子标签存入到了一个列表中
列表中会存入如下元素
children的使用
通过下面的方式也可以获取p标签下的所有子节点内容和通过contents获取的结果是一样的,但是不同的地方是soup.p.children是一个迭代对象,而不是列表,只能通过循环的方式获取素有的信息
html = """
<html>
<head>
<title>The Dormouse's story</title>
</head>
<body>
<p class="story">
Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">
<span>Elsie</span>
</a>
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a>
and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>
and they lived at the bottom of a well.
</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
""" from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html,'lxml')
print(soup.p.children)
for child in soup.p.children:
print(child)
结果:
<list_iterator object at 0x000001AD777B49B0>
Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">
<span>Elsie</span>
</a>
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>
and
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>
and they lived at the bottom of a well.
html = """
<html>
<head>
<title>The Dormouse's story</title>
</head>
<body>
<p class="story">
Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">
<span>Elsie</span>
</a>
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a>
and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>
and they lived at the bottom of a well.
</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
""" from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html,'lxml')
print(soup.p.children)
for i,child in enumerate(soup.p.children): #enumerate 枚举
print(i,child)
结果:
<list_iterator object at 0x000001AD778605F8>
0
Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were 1 <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">
<span>Elsie</span>
</a>
2 3 <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>
4
and 5 <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>
6
and they lived at the bottom of a well.
通过contents以及children都是获取子节点,如果想要获取子孙节点可以通过descendants
print(soup.descendants)同时这种获取的结果也是一个迭代器
获取子孙节点
html = """
<html>
<head>
<title>The Dormouse's story</title>
</head>
<body>
<p class="story">
Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">
<span>Elsie</span>
</a>
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a>
and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>
and they lived at the bottom of a well.
</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
""" from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html,'lxml')
print(soup.p.descendants)
for i,child in enumerate(soup.p.descendants):
print(i,child)
结果:
<generator object Tag.descendants at 0x000001AD777B3A98>
0
Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were 1 <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">
<span>Elsie</span>
</a>
2 3 <span>Elsie</span>
4 Elsie
5 6 7 <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>
8 Lacie
9
and 10 <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>
11 Tillie
12
and they lived at the bottom of a well.
父节点和祖先节点
通过soup.a.parent就可以获取父节点的信息
html = """
<html>
<head>
<title>The Dormouse's story</title>
</head>
<body>
<p class="story">
Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">
<span>Elsie</span>
</a>
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a>
and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>
and they lived at the bottom of a well.
</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
""" from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html,'lxml')
print(soup.a.parent)
结果:
<p class="story">
Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">
<span>Elsie</span>
</a>
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>
and
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>
and they lived at the bottom of a well.
</p>
通过list(enumerate(soup.a.parents))可以获取祖先节点,这个方法返回的结果是一个列表,会分别将a标签的父节点的信息存放到列表中,以及父节点的父节点也放到列表中,并且最后还会讲整个文档放到列表中,所有列表的最后一个元素以及倒数第二个元素都是存的整个文档的信息
祖先节点:
html = """
<html>
<head>
<title>The Dormouse's story</title>
</head>
<body>
<p class="story">
Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">
<span>Elsie</span>
</a>
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a>
and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>
and they lived at the bottom of a well.
</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
""" from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html,'lxml')
print(list(enumerate(soup.a.parents)))
结果:
[(0, <p class="story">
Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">
<span>Elsie</span>
</a>
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>
and
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>
and they lived at the bottom of a well.
</p>), (1, <body>
<p class="story">
Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">
<span>Elsie</span>
</a>
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>
and
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>
and they lived at the bottom of a well.
</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
</body>), (2, <html>
<head>
<title>The Dormouse's story</title>
</head>
<body>
<p class="story">
Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">
<span>Elsie</span>
</a>
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>
and
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>
and they lived at the bottom of a well.
</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
</body></html>), (3, <html>
<head>
<title>The Dormouse's story</title>
</head>
<body>
<p class="story">
Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">
<span>Elsie</span>
</a>
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>
and
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>
and they lived at the bottom of a well.
</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
</body></html>)]
兄弟节点
soup.a.next_siblings 获取后面的兄弟节点
soup.a.previous_siblings 获取前面的兄弟节点
soup.a.next_sibling 获取下一个兄弟标签
souo.a.previous_sinbling 获取上一个兄弟标签
html = """
<html>
<head>
<title>The Dormouse's story</title>
</head>
<body>
<p class="story">
Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">
<span>Elsie</span>
</a>
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a>
and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>
and they lived at the bottom of a well.
</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
""" from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html,'lxml')
print(list(enumerate(soup.a.next_siblings)))
print(list(enumerate(soup.a.previous_siblings)))
结果:
[(0, '\n'), (1, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>),
(2, '\n and\n '), (3, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>),
(4, '\n and they lived at the bottom of a well.\n ')]
[(0, '\n Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were\n ')]
标准选择器
find_all
find_all(name,attrs,recursive,text,**kwargs)
可以根据标签名,属性,内容查找文档
name的用法
html='''
<div class="panel">
<div class="panel-heading">
<h4>Hello</h4>
</div>
<div class="panel-body">
<ul class="list" id="list-1">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
<li class="element">Jay</li>
</ul>
<ul class="list list-small" id="list-2">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
'''
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
print(soup.find_all('ul'))
print('--------------------')
print(type(soup.find_all('ul')[0]))
结果返回的是一个列表的方式
[<ul class="list" id="list-1">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
<li class="element">Jay</li>
</ul>, <ul class="list list-small" id="list-2">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
</ul>]
-----------------------
<class 'bs4.element.Tag'>
同时我们是可以针对结果再次find_all,从而获取所有的li标签信息,层层嵌套的方法
html='''
<div class="panel">
<div class="panel-heading">
<h4>Hello</h4>
</div>
<div class="panel-body">
<ul class="list" id="list-1">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
<li class="element">Jay</li>
</ul>
<ul class="list list-small" id="list-2">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
'''
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
for ul in soup.find_all('ul'):
print(ul.find_all('li'))
结果:
[<li class="element">Foo</li>, <li class="element">Bar</li>, <li class="element">Jay</li>]
[<li class="element">Foo</li>, <li class="element">Bar</li>]
attrs
例子如下:
html='''
<div class="panel">
<div class="panel-heading">
<h4>Hello</h4>
</div>
<div class="panel-body">
<ul class="list" id="list-1" name="elements">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
<li class="element">Jay</li>
</ul>
<ul class="list list-small" id="list-2">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
'''
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
print(soup.find_all(attrs={'id': 'list-1'}))
print(soup.find_all(attrs={'name': 'elements'}))
结果:
[<ul class="list" id="list-1" name="elements">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
<li class="element">Jay</li>
</ul>]
[<ul class="list" id="list-1" name="elements">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
<li class="element">Jay</li>
</ul>]
html='''
<div class="panel">
<div class="panel-heading">
<h4>Hello</h4>
</div>
<div class="panel-body">
<ul class="list" id="list-1" name="elements">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
<li class="element">Jay</li>
</ul>
<ul class="list list-small" id="list-2">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
'''
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
print(soup.find_all(id='list-1'))
print(soup.find_all(class_='element'))
结果:
[<ul class="list" id="list-1" name="elements">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
<li class="element">Jay</li>
</ul>]
[<li class="element">Foo</li>, <li class="element">Bar</li>, <li class="element">Jay</li>,
<li class="element">Foo</li>, <li class="element">Bar</li>]
attrs可以传入字典的方式来查找标签,但是这里有个特殊的就是class,因为class在python中是特殊的字段,所以如果想要查找class相关的可以更改attrs={'class_':'element'}或者soup.find_all('',{"class":"element}),特殊的标签属性可以不写attrs,例如id
text
例子如下:
html='''
<div class="panel">
<div class="panel-heading">
<h4>Hello</h4>
</div>
<div class="panel-body">
<ul class="list" id="list-1">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
<li class="element">Jay</li>
</ul>
<ul class="list list-small" id="list-2">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
'''
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
print(soup.find_all(text='Foo'))
结果返回的是查到的所有的text='Foo'的文本
['Foo', 'Foo']
find
find(name,attrs,recursive,text,**kwargs)
find返回的匹配结果的第一个元素
html='''
<div class="panel">
<div class="panel-heading">
<h4>Hello</h4>
</div>
<div class="panel-body">
<ul class="list" id="list-1">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
<li class="element">Jay</li>
</ul>
<ul class="list list-small" id="list-2">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
'''
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
print(soup.find('ul'))
print(type(soup.find('ul')))
print(soup.find('page'))
结果:
<ul class="list" id="list-1">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
<li class="element">Jay</li>
</ul>
<class 'bs4.element.Tag'>
None
其他一些类似的用法:
find_parents()返回所有祖先节点,find_parent()返回直接父节点。
find_next_siblings()返回后面所有兄弟节点,find_next_sibling()返回后面第一个兄弟节点。
find_previous_siblings()返回前面所有兄弟节点,find_previous_sibling()返回前面第一个兄弟节点。
find_all_next()返回节点后所有符合条件的节点, find_next()返回第一个符合条件的节点
find_all_previous()返回节点后所有符合条件的节点, find_previous()返回第一个符合条件的节点
CSS选择器
通过select()直接传入CSS选择器就可以完成选择
熟悉前端的人对CSS可能更加了解,其实用法也是一样的
标签1,标签2 找到所有的标签1和标签2
标签1 标签2 找到标签1内部的所有的标签2
[attr] 可以通过这种方法找到具有某个属性的所有标签
[atrr=value] 例子[target=_blank]表示查找所有target=_blank的标签
前面加 .表示class #表示id ,选择标签不需要加
html='''
<div class="panel">
<div class="panel-heading">
<h4>Hello</h4>
</div>
<div class="panel-body">
<ul class="list" id="list-1">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
<li class="element">Jay</li>
</ul>
<ul class="list list-small" id="list-2">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
'''
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
print(soup.select('.panel .panel-heading'))
print(soup.select('ul li'))
print(soup.select('#list-2 .element'))
print(type(soup.select('ul')[0]))
结果:
[<div class="panel-heading">
<h4>Hello</h4>
</div>]
[<li class="element">Foo</li>, <li class="element">Bar</li>, <li class="element">Jay</li>,
<li class="element">Foo</li>, <li class="element">Bar</li>]
[<li class="element">Foo</li>, <li class="element">Bar</li>]
<class 'bs4.element.Tag'>
获取内容
通过get_text()就可以获取文本内容
html='''
<div class="panel">
<div class="panel-heading">
<h4>Hello</h4>
</div>
<div class="panel-body">
<ul class="list" id="list-1">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
<li class="element">Jay</li>
</ul>
<ul class="list list-small" id="list-2">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
'''
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
for li in soup.select('li'):
print(li.get_text())
结果:
Foo
Bar
Jay
Foo
Bar
获取属性
或者属性的时候可以通过[属性名]或者attrs[属性名]
html='''
<div class="panel">
<div class="panel-heading">
<h4>Hello</h4>
</div>
<div class="panel-body">
<ul class="list" id="list-1">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
<li class="element">Jay</li>
</ul>
<ul class="list list-small" id="list-2">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
'''
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
for ul in soup.select('ul'):
print(ul)
print('---------------')
print(ul['id'])
print('---------------')
print(ul.attrs['id'])
print('***************')
结果:
<ul class="list" id="list-1">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
<li class="element">Jay</li>
</ul>
---------------
list-1
---------------
list-1
***************
<ul class="list list-small" id="list-2">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
</ul>
---------------
list-2
---------------
list-2
***************
总结
推荐使用lxml解析库,必要时使用html.parser
标签选择筛选功能弱但是速度快
建议使用find()、find_all() 查询匹配单个结果或者多个结果
如果对CSS选择器熟悉建议使用select()
记住常用的获取属性和文本值的方法
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/zhaof/p/6930955.html
python-BeautifulSoup库详解的更多相关文章
- Python turtle库详解
Python turtle库详解 Turtle库是Python语言中一个很流行的绘制图像的函数库,想象一个小乌龟,在一个横轴为x.纵轴为y的坐标系原点,(0,0)位置开始,它根据一组函数指令的控制,在 ...
- python爬虫知识点总结(六)BeautifulSoup库详解
官方学习文档:https://www.crummy.com/software/BeautifulSoup/bs4/doc.zh/ 一.什么时BeautifulSoup? 答:灵活又方便的网页解析库,处 ...
- Python optparser库详解
一直以来对optparser不是特别的理解,今天就狠下心,静下心研究了一下这个库.当然了,不敢说理解的很到位,但是足以应付正常的使用了.废话不多说,开始今天的分享吧. 简介 optparse模块主要用 ...
- python爬虫知识点详解
python爬虫知识点总结(一)库的安装 python爬虫知识点总结(二)爬虫的基本原理 python爬虫知识点总结(三)urllib库详解 python爬虫知识点总结(四)Requests库的基本使 ...
- Python爬虫系列-Urllib库详解
Urllib库详解 Python内置的Http请求库: * urllib.request 请求模块 * urllib.error 异常处理模块 * urllib.parse url解析模块 * url ...
- Python 字符串方法详解
Python 字符串方法详解 本文最初发表于赖勇浩(恋花蝶)的博客(http://blog.csdn.net/lanphaday),如蒙转载,敬请保留全文完整,切勿去除本声明和作者信息. ...
- Python--urllib3库详解1
Python--urllib3库详解1 Urllib3是一个功能强大,条理清晰,用于HTTP客户端的Python库,许多Python的原生系统已经开始使用urllib3.Urllib3提供了很多pyt ...
- python/ORM操作详解
一.python/ORM操作详解 ===================增==================== models.UserInfo.objects.create(title='alex ...
- Python开发技术详解PDF
Python开发技术详解(高清版)PDF 百度网盘 链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1F5J9mFfHKgwhkC5KuPd0Pw 提取码:xxy3 复制这段内容后打开百度网盘手 ...
- Python环境搭建详解(Window平台)
前言 Python,是一种面向对象的解释型计算机程序设计语言,是纯粹的自由软件,Python语法简洁清晰,特色是强制用空白符作为语句缩进,具有丰富和强大的库,它常被称为胶水语言. Python是一种解 ...
随机推荐
- 自动化测试基础篇--Selenium元素定位
摘自https://www.cnblogs.com/sanzangTst/p/7457111.html 一.Selenium元素定位的重要性: Web自动化测试的操作:获取UI页面的元素,对元素进行操 ...
- 看到一个想收藏的的AJAX小列子
用户登录的验证可以使用 form 表单提交,也可以使用 ajax 技术异步提交. AJAX 即 Asynchronous Javascript And XML(异步 JavaScript 和 XML) ...
- Windows重启显卡驱动热键说明
Windows 有一个秘密的快捷键,可以重启显卡驱动程序.如果你的电脑经常“冻屏”,可以在重启电脑之前试试这个快捷键,它可以修复冻屏,否则就只能强制重启电脑了. 这个组合快捷键将重启 Win10 和 ...
- C++ 中operator用法:隐式类型转换
[转]C++ operator两种用法 C++,有时它的确是个耐玩的东东,就比如operator,它有两种用法,一种是operator overloading(操作符重载),一种是operator c ...
- 用sed实现wc -w的功能
版权申明:本文为博主窗户(Colin Cai)原创,欢迎转帖.如要转贴,必须注明原文网址 http://www.cnblogs.com/Colin-Cai/p/7663831.html 作者:窗户 Q ...
- Node爬虫之初体验
记得之前就听说过爬虫,个人初步理解就是从网页中抓取一些有用的数据,存储到本地,今天就当是小牛试刀,拿来溜溜...... 实现需求: 抓取课程数据,输入url后并在浏览器端以一定的数据格式显示出来(如下 ...
- Linux之文档与目录结构
Linux文件系统结构 Linux目录结构的组织形式和Windows有很大的不同.首先Linux没有“盘(C盘.D盘.E盘)”的概念.已经建立文件系统的硬盘分区被挂载到某一个目录下,用户通过操作目录来 ...
- 【Linux基础】VI 编辑器基本使用方法
vi编辑器是所有Unix及Linux系统下标准的编辑器.对Unix及Linux系统的任何版本,vi编辑器是完全相同的,它是Linux中最基本的文本编辑器. 第一章vi的三种模式 第二章vi文本编辑器 ...
- spark SQL读取ORC文件从Driver启动到开始执行Task(或stage)间隔时间太长(计算Partition时间太长)且产出orc单个文件中stripe个数太多问题解决方案
1.背景: 控制上游文件个数每天7000个,每个文件大小小于256M,50亿条+,orc格式.查看每个文件的stripe个数,500个左右,查询命令:hdfs fsck viewfs://hadoop ...
- Vue指令v-for之遍历输出JavaScript数组,json对象的几种方式
定义数据: <script> new Vue({ el:"#test", data:{ message:"infor", list:["a ...