Java原理之HashMap
一下JDK1.7测试没问题,1.8就不一样了,应该散列的更优化。
最近看了很多java底层之HashMap的原理,根据自己的实现如下:
package com.gmq.chapter02; import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map; /**
* Created by gmq on 2017/08/24.
*
* @version 1.0
* @since 2017/08/24 09:25
*/
public class TestHashMap { public static void main(String[] args) { HashMap hashMap = new HashMap();//line1
hashMap.put(null,"null");//null
hashMap.put("one","hello1");//line2
hashMap.put("two","hello2");//line3
hashMap.put("three","hello3");//line4
hashMap.put("four","hello4");//line5
hashMap.put("five","hello5");//line6
hashMap.put("six","hello6");//line7
hashMap.put("seven","hello7");//line8 System.out.println(hashMap.size());
System.out.println(hashMap.get(null));
System.out.println(hashMap.get("one"));
System.out.println(hashMap.get("two"));
System.out.println(hashMap.get("three"));
System.out.println(hashMap.get("four"));
System.out.println(hashMap.get("five"));
System.out.println(hashMap.get("six"));
System.out.println(hashMap.get("seven")); }
}
通过仔细debug得到这些key-value在底层的存储如下:
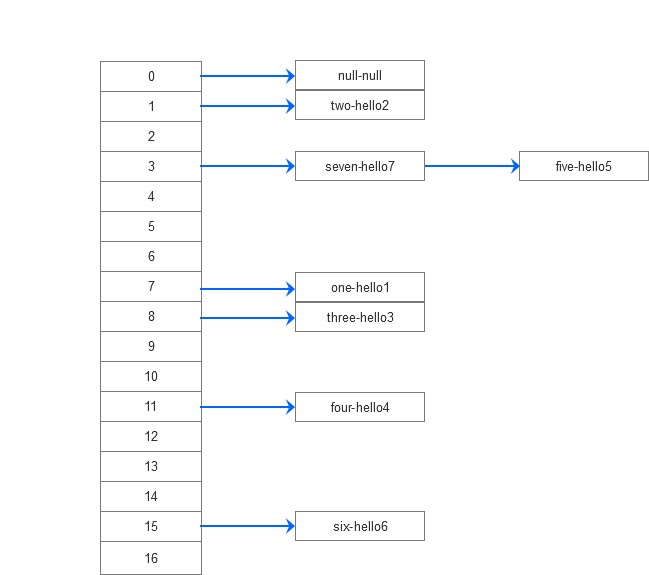
hashmap底层数组,数组每个元素是一个链表,Entry<K,V>是hashMap的内部链表。
/**
* Creates new entry.
*/
Entry(int h, K k, V v, Entry<K,V> n) {
value = v;
next = n;
key = k; hash = h;
}
createEntry:
void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex];
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
size++;
}
在数组中增加新元素,如果元素中已经有,则新元素前面,老的放到后面next,形成链表。
| 代码 | hashcode | index | key | value | next |
| hashMap.put(null,"null"); | 0 | 0 | null | null | null |
| hashMap.put("one","hello1") | 11583 | 7 | one | hello1 | null |
| hashMap.put("two","hello2"); | 122353 | 1 | two | hello2 | null |
| hashMap.put("three","hello3"); | 116905880 | 8 | three | hello3 | null |
| hashMap.put("four","hello4"); | 3370515 | 11 | four | hello4 | null |
| hashMap.put("five","hello5"); | 2970851 | five | hello5 | null | |
| hashMap.put("six","hello6"); | 107599 | 15 | six | hello6 | null |
| hashMap.put("seven","hello7"); | 11543427 | seven | hello7 | Entry<"five","hello5"> |
由上可知,hashmap的底层是数组+链表:数组的元素是链表,如果key的hashCode的hash相同,则放到链表上,再取的时候for循环数组元素的链表即可。
hashmap遵循:怎么put进去的,就怎么取。
存(put):hashcode(key)-》hash--》indexFor--》最终索引位置
取(get):hashcode(key)-》hash--》indexFor--》最终索引位置
存和取调用的是同样的hash,故存取时间复杂度未O(1).
hashmap的hash是为了散列,更均匀的获取数组下标。
=========================================参考博文========================================
我是参考了:http://www.cnblogs.com/yangqiangyu/p/5276629.html
Java你可能不知道的事(3)HashMap
概述
HashMap对于做Java的小伙伴来说太熟悉了。估计你们每天都在使用它。它为什么叫做HashMap?它的内部是怎么实现的呢?为什么我们使用的时候很多情况都是用String作为它的key呢?带着这些疑问让我们来了解HashMap!
HashMap介绍
1、介绍
HashMap是一个用”KEY”-“VALUE”来实现数据存储的类。你可以用一个”key”去存储数据。当你想获得数据的时候,你可以通过”key”去得到数据。所以你可以把HashMap当作一个字典。 那么HashMap的名字从何而来呢?其实HashMap的由来是基于Hasing技术(Hasing),Hasing就是将很大的字符串或者任何对象转换成一个用来代表它们的很小的值,这些更短的值就可以很方便的用来方便索引、加快搜索。
在讲解HashMap的存储过程之前还需要提到一个知识点
我们都知道在Java中每个对象都有一个hashcode()方法用来返回该对象的 hash值。HashMap中将会用到对象的hashcode方法来获取对象的hash值。
2、关系
图1展示了HashMap的类结构关系。
HashMap继承了AbstractMap,并且支持序列化和反序列化。由于实现了Clonable接口,也就支持clone()方法来复制一个对象。今天主要说HashMap的内部实现,这里就不对序列化和clone做讲解了。
3、内部介绍
上面的图很清晰的说明了HashMap内部的实现原理。就好比一个篮子,篮子里装了很多苹果,苹果里包含了自己的信息和另外一个苹果的引用
1、和上图显示的一样,HashMap内部包含了一个Entry类型的数组table, table里的每一个数据都是一个Entry对象。
2、再来看table里面存储的Entry类型,Entry类里包含了hashcode变量,key,value 和另外一个Entry对象。为什么要有一个Entry对象呢?其实如果你看过linkedList的源码,你可能会知道这就是一个链表结构。通过我找到你,你再找到他。不过这里的Entry并不是LinkedList,它是单独为HashMap服务的一个内部单链表结构的类。
3、那么Entry是一个单链表结构的意义又是什么呢?在我们了解了HashMap的存储过程之后,你就会很清楚了,接着让我们来看HashMap怎么工作的。
HashMap的存储过程
下面分析一段代码的HashMap存储过程。(这里只是作为演示的例子,并没有真实的去取到了Hash值,如果你有需要可以通过Debug来得到key的Hash值)

HashMap hashMap = new HashMap();//line1
hashMap.put("one","hello1");//line2
hashMap.put("two","hello2");//line3
hashMap.put("three","hello3");//line4
hashMap.put("four","hello4");//line5
hashMap.put("five","hello5");//line6
hashMap.put("six","hello6");//line7
hashMap.put("seven","hello7");//line8

put操作的伪代码可以表示如下:
public V put(K key, V value){
int hash = hash(key);
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
//在table[i]的地方添加一个包含hash,key,value信息的Entry类。
}
下面我们来看上面代码的过程
1、line1创建了一个HashMap,所以我们来看构造函数
/**
* Constructs an empty <tt>HashMap</tt> with the default initial capacity
* (16) and the default load factor (0.75).
*/
public HashMap() {
this(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
}空构造函数调用了它自己的另一个构造函数,注释说明了构建了一个初始容量的空HashMap,那我们就来看它另外一个构造函数。

public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " +
initialCapacity);
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
threshold = initialCapacity;
init();
}
void init() {
}

上面的代码只是简单的给loadFactor(其实是数组不够用来扩容的)和threshold(内部数组的初始化容量),init()是一个空方法。所以现在数组table还是一个空数组。

/**
* An empty table instance to share when the table is not inflated.
*/
static final Entry<?,?>[] EMPTY_TABLE = {}; /**
* The table, resized as necessary. Length MUST Always be a power of two.
*/
transient Entry<K,V>[] table = (Entry<K,V>[]) EMPTY_TABLE;

2、接下来到了line2的地方, hashMap.put(“one”,”hello1”);在这里先提一下put方法源码:

public V put(K key, V value) {
if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) {
inflateTable(threshold);//如果是空的,加载
}
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
int hash = hash(key);获取hash值
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);生成索引
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
//遍历已存在的Entry,如果要存入的key和hash值都一样就覆盖。
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
//添加一个节点
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}

源码很简单,先判断table如果是空的,就初始化数组table,接着如果key是null就单独处理。否则的话就得到key的hash值再生成索引,这里用了indexFor()方法生成索引是因为:hash值一般都很大,是不适合我们的数组的。来看indexFor方法
/**
* Returns index for hash code h.
*/
static int indexFor(int h, int length) {
// assert Integer.bitCount(length) == 1 : "length must be a non-zero power of 2";
return h & (length-1);
}就是一个&操作,这样返回的值比较小适合我们的数组。
继续 line2put操作,因为开始table是空数组,所以会进入 inflateTable(threshold)方法,其实这个方法就是出实话数组容量,初始化长度是16,这个长度是在开始的构造方法赋值的。
所以,现在空数组变成了长度16的数组了,就像下图一样。
接着由于我们的key不为null,到了获取hash值和索引,这里假设int hash = hash(key)和int i = indexFor(hash, table.length)生成的索引i为hash=2306996,i = 4;那么就会在table索引为4的位置新建一个Entry,对应的代码是addEntry(hash, key, value, i);到此结果如下图:
新建的Entry内部的变量分别是,hash,key,value,和指向下一节点的next Entry。
3、继续来看line3,line3和line2一样,而且数组不为空直接hash(key)和index。所以直接看图了
4、到了line4,这里line4情况有点特殊,我们假设line4里key生成的hashcode产生的index也为4,比如hash(“three”) 的值 63281940
hash&(15)产生的index为4。这种情况由于之前的位置已经有Entry了,所以遍历Entry如果key和hashcode都相同,就直接替换,否则新添加一个Entry,来看一下对应源码

public V put(K key, V value) {
...//一些代码
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
//for循环里判断如果hash和key都一样直接替换。
modCount++;
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);//没有重复的话就addEntry
return null;
}

上面代码先判断是否需要替换,不需要就调用了addEntry方法。来看addEntry

void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) {
resize(2 * table.length);
hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0;
bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length);
}//判断数组容量是否足够,不足够扩容
createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);
}

里面又调用了createEntry

void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex];
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
size++;
//获取当前节点,然后新建一个含有当前hash,key,value信息的一个节点,并且该节点的Entry指向了前一个Entry并赋值给table[index],成为了最新的节点Entry,同时将size加1。
}

到这里相信大家很清楚了。来看看图:
5、到这里之后的代码都在上面的分析情况当中。我就不一一画图了,直接给出程序执行到最后的图
line5到line8
| 代码 | hashcode | index | key | value | next |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hashMap.put(“four”,”hello4”); | 54378290 | 9 | four | hello4 | null |
| hashMap.put(“five”,”hello5”); | 39821723 | 8 | five | hello5 | null |
| hashMap.put(“six”,”hello6”); | 86726537 | 4 | six | hello6 | line4产生的Entry |
| hashMap.put(“seven”,”hello7”); | 28789082 | 2 | seven | hello7 | line3产生的Entry |
结果图如下:
到此put 操作就结束了,再来看看取
HashMap的取值过程
我们通过hashMap.get(K key) 来获取存入的值,key的取值很简单了。我们通过数组的index直接找到Entry,然后再遍历Entry,当hashcode和key都一样就是我们当初存入的值啦。看源码:

public V get(Object key) {
if (key == null)
return getForNullKey();
Entry<K,V> entry = getEntry(key);
return null == entry ? null : entry.getValue();
}

调用getEntry(key)拿到entry ,然后返回entry的value,来看getEntry(key)方法

final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) {
if (size == 0) {
return null;
}
int hash = (key == null) ? 0 : hash(key);
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)];
e != null;
e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
}
return null;
}

按什么规则存的就按什么规则取,获取到hash,再获取index,然后拿到Entry遍历,hash相等的情况下,如果key相等就知道了我们想要的值。
再get方法中有null的判断,null取hash值总是0,再getNullKey(K key)方法中,也是按照遍历方法来查找的。
到这你肯定明白了为什么HashMap可以用null做key。
了解的存储取值过程和内部实现,其它的方法自己看看源码很好理解,在此就不一一解释了。
几个问题
问题1、HashMap是基于key的hashcode的存储的,如果两个不同的key产生的hashcode一样取值怎么办?
看了上面的分析,你肯定知道,再数组里面有链表结构的Entry来实现,通过遍历所有的Entry,比较key来确定到底是哪一个value;
问题2、HashMap是基于key的hashcode的存储的,如果两个key一样产生的hashcode一样怎么办?
在put操作的时候会遍历所有Entry,如果有key相等的则替换。所以get的时候只会有一个
问题3、我们总是习惯用一个String作为HashMap的key,这是为什么呢?其它的类可以做为HashMap的key吗?
这里因为String是不可以变的,并且java为它实现了hashcode的缓存技术。我们在put和get中都需要获取key的hashcode,这些方法的效率很大程度上取决于获取hashcode的,所以用String的原因:1、它是不可变的。2、它实现了hashcode的缓存,效率更高。如果你对String不了解可以看:Java你可能不知道的事-String
问题4、可变的对象能作为HashMap的key吗?
可变的对象是可以当做HashMap的key的,只是你要确保你可变变量的改变不会改变hashcode。比如以下代码

public class TestMemory {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap hashMap = new HashMap();
TestKey testKey = new TestKey();
testKey.setAddress("sdfdsf");//line3
hashMap.put(testKey,"hello");
testKey.setAddress("sdfsdffds");//line5
System.out.println(hashMap.get(testKey));
}
}
public class TestKey {
String name;
String address;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
if (name==null){
return 0;
}
return name.hashCode();
}
}
Java原理之HashMap的更多相关文章
- Java中的HashMap的工作原理是什么?
问答题23 /120 Java中的HashMap的工作原理是什么? 参考答案 Java中的HashMap是以键值对(key-value)的形式存储元素的.HashMap需要一个hash函数,它使用ha ...
- Java源码——HashMap的源码分析及原理学习记录
学习HashMap时,需要带着这几个问题去,会有很大的收获: 一.什么是哈希表 二.HashMap实现原理 三.为何HashMap的数组长度一定是2的次幂? 四.重写equals方法需同时重写hash ...
- Java基础系列--HashMap(JDK1.8)
原创作品,可以转载,但是请标注出处地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/V1haoge/p/10022092.html Java基础系列-HashMap 1.8 概述 HashMap是 ...
- java数据结构之hashMap
初学JAVA的时候,就记得有句话两个对象的hashCode相同,不一定equal,但是两个对象equal,hashCode一定相同,当时一直不理解是什么意思,最近在极客时间上学习了课程<数据结构 ...
- 杨晓峰-Java核心技术-9 HashMap Hashtable TreeMap MD
目录 第9讲 | 对比Hashtable.HashMap.TreeMap有什么不同? 典型回答 考点分析 知识扩展 Map 整体结构 有序 Map HashMap 源码分析 容量.负载因子和树化 精选 ...
- 沉淀再出发:java中的HashMap、ConcurrentHashMap和Hashtable的认识
沉淀再出发:java中的HashMap.ConcurrentHashMap和Hashtable的认识 一.前言 很多知识在学习或者使用了之后总是会忘记的,但是如果把这些只是背后的原理理解了,并且记忆下 ...
- 【转】Java集合:HashMap源码剖析
Java集合:HashMap源码剖析 一.HashMap概述二.HashMap的数据结构三.HashMap源码分析 1.关键属性 2.构造方法 3.存储数据 4.调 ...
- 死磕Java之聊聊HashMap源码(基于JDK1.8)
死磕Java之聊聊HashMap源码(基于JDK1.8) http://cmsblogs.com/?p=4731 为什么面试要问hashmap 的原理
- java jdk 中HashMap的源码解读
HashMap是我们在日常写代码时最常用到的一个数据结构,它为我们提供key-value形式的数据存储.同时,它的查询,插入效率都非常高. 在之前的排序算法总结里面里,我大致学习了HashMap的实现 ...
随机推荐
- Spring整合Redis时报错:java.util.NoSuchElementException: Unable to validate object
我在Spring整合Redis时报错,我是犯了一个很低级的错误! 我设置了Redis的访问密码,在Spring的配置文件却没有配置密码这一项,配置上密码后,终于不报错了!
- SQL字符串分割解析
常用以下三种: [1]substring( expression ,start , length ): [2]CHARINDEX ( expression1 , expression2 [ , sta ...
- JavaScript 之 ScriptManager.RegisterStartupScript的应用
如果页面中不用Ajax,cs中运行某段js代码方式可以是: Page.ClientScript.RegisterStartupScript(Page.GetType(), "", ...
- java线程同步实的现方式
为何要使用同步? java允许多线程并发控制,当多个线程同时操作一个可共享的资源变量时(如数据的增删改查), 将会导致数据不准确,相互之间产生冲突,因此加入同步锁以避免在该线程没有完成操作之前,被其他 ...
- The Builder pattern simulates named optional parameters(Java)
the Builder pattern is a good choice when designing classes whose constructors or static factories w ...
- 6、redis之使用spring-data-redis的Template
POM: <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.o ...
- Web工程中各类地址的写法
1)总体原则 在java web开发中,只要是url地址,那么最好以“/”开头,也就是绝对路径的方式.那么这个“/”到底代表什么呢? 如果“/”是给服务器用的,则代表当前web工程:如果是给浏览器用的 ...
- Qt Installer Framework 使用说明(三)
目录 6.Qt Installer Framework 示例 7.参考 Reference 配置文件 Configuration File 配置文件元素的简要说明 Summary of Configu ...
- Window10激活
Windows10激活,通过kms激活. 01.安装对应版本的秘钥 专业版:W269N-WFGWX-YVC9B-4J6C9-T83GX 企业版:NPPR9-FWDCX-D2C8J-H872K-2YT4 ...
- Oracle 中TNS的作用
什么是TNS? TNS是Oracle Net的一部分,专门用来管理和配置Oracle数据库和client连接的一个工具,在大多数情况下client和数据库要通讯,必须配置TNS,当然在少数情况下,不用 ...







