初探Tomcat的架构设计

Tomcat 作为 servlet 容器实现,它是基于 Java 语言开发的轻量级应用服务器。因为 Tomcat 作为应用服务器,它有着完全开源,轻量,性能稳定,部署成本低等优点,所以它成为目前 Java 开发应用部署的首选,几乎每个Java Web开发者都有使用过,但是,你对 Tomcat 的整体设计有进行过了解和思考吗?
本文将基于 Tomcat8 进行分析,具体版本为 Tomcat8 当前官网最新修改(2019-11-21 09:28)的版本 v8.5.49
总体结构
Tomcat 的总体结构中有很多模块,下图列出我们将要进行分析结构中的主要模块。其中主要分析的是Service,Connector,Engine,Host,Context,Wrapper。为避免图层看着太乱,下图中n代表该组件可允许存在多个。
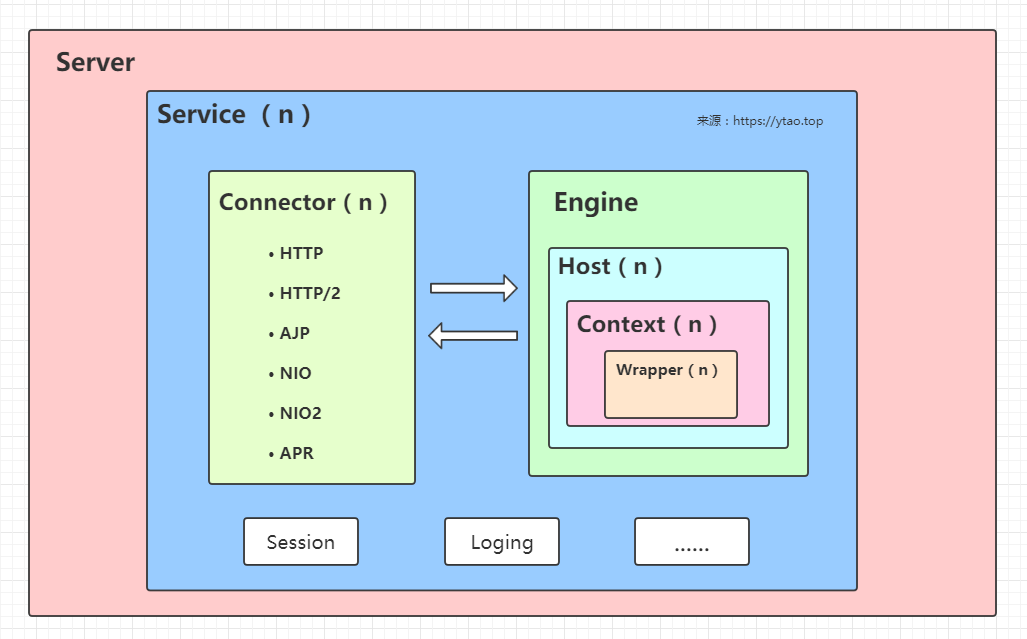
如上图所描述的是:Server 是 tomcat 服务器,在 Server 中可以存在多个服务 Service 。每个服务中可有多个连接器和一个 Servlet 引擎 Engine,一个 Service 中多个连接器对应一个 Engine。 每个 Engine 中,可存在多个域名,这里可用虚拟主机的概念来表示 Host。每个 Host 中可以存在多个应用 Context。
Server,Service,Connector,Engine,Host,Context,Wrapper 它们之间的关系,除了Connector和Engine,它们是平行关系,其它的都是存在包含关系。同时,它们也都继承了 Lifecycle 接口,该接口提供的是生命周期的管理,里面包括:初始化(init),启动(start),停止(stop),销毁(destroy)。当它的父容器启动时,会调用它子容器的启动,停止也是一样的。
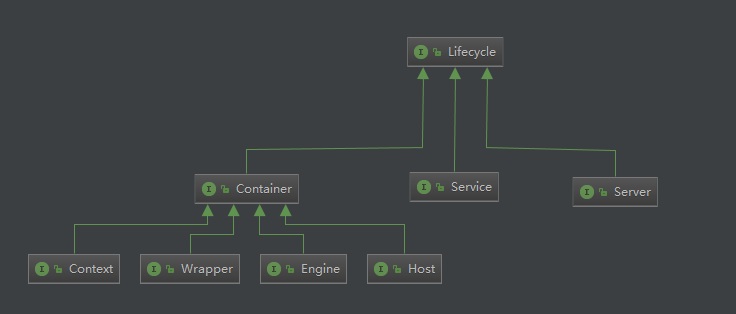
上图中,还可以看到,Engine,Host,Context,Wrapper 都继承自 Container。它有个backgroundProcess()方法,后台异步处理,所以继承它后可以方便的创建异步线程。
在 Tomcat7 中,有看到 Service 持有的是 Container,而不是 Engine。估计这也是为什么在当前版本中添加 Engine 方法名叫setContainer。
Server
Tomcat 源码中有提供org.apache.catalina.Server接口,对应的默认实现类为org.apache.catalina.core.StandardServer,接口里面提供有如下图方法。
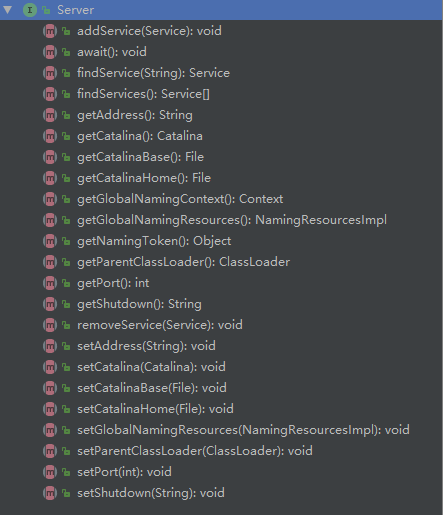
上图中可以知道 Server 做的工作:对 Service,Address,Port,Catalina 以及全局命名资源的管理操作。
Server 在进行初始化的时候,会加载我们 server.xml 中配置的数据。

这里对其中的 Service 操作的addService向定义的服务集添加新服务进行分析:
// 保存服务的服务集
private Service services[] = new Service[0];
final PropertyChangeSupport support = new PropertyChangeSupport(this);
@Override
public void addService(Service service) {
// 相互关联
service.setServer(this);
// 利用同步锁,防止并发访问 来源:https://ytao.top
synchronized (servicesLock) {
Service results[] = new Service[services.length + 1];
// copy 旧的服务到新的数组中
System.arraycopy(services, 0, results, 0, services.length);
// 添加新的 service
results[services.length] = service;
services = results;
// 如果当前 server 已经启动,那么当前添加的 service 就开始启动
if (getState().isAvailable()) {
try {
service.start();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
// Ignore
}
}
// 使用观察者模式,当被监听对象属性值发生变化时通知监听器,remove 是也会调用。
support.firePropertyChange("service", null, service);
}
}
源码中可以看到,向服务器中添加服务后,随机会启动服务,实则也服务启动入口。
Service
Service 的主要职责就是将 Connector 和 Engine 的组装在一起。两者分开的目的也就是使请求监听和请求处理进行解耦,能拥有更好的扩展性。每个 Service 都是相互独立的,但是共享一个JVM和系统类库。这里提供了org.apache.catalina.Service接口和默认实现类org.apache.catalina.coreStandardService。
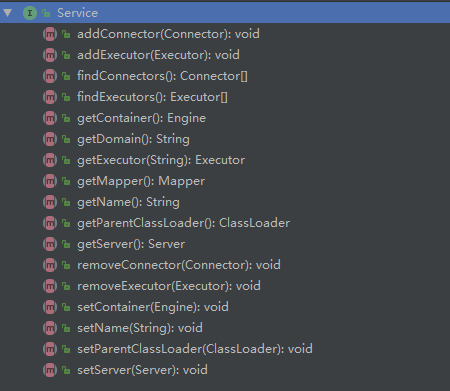
在实现类 StandardService 中,主要分析setContainer和addConnector两个方法。
private Engine engine = null;
protected final MapperListener mapperListener = new MapperListener(this);
@Override
public void setContainer(Engine engine) {
Engine oldEngine = this.engine;
// 判断当前 Service 是否有关联 Engine
if (oldEngine != null) {
// 如果当前 Service 有关联 Engine,就去掉当前关联的 Engine
oldEngine.setService(null);
}
// 如果当前新的 Engine 不为空,那么 Engine 关联当前 Service,这里是个双向关联
this.engine = engine;
if (this.engine != null) {
this.engine.setService(this);
}
// 如果当前 Service 启动了,那么就开始启动当前新的 Engine
if (getState().isAvailable()) {
if (this.engine != null) {
try {
this.engine.start();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardService.engine.startFailed"), e);
}
}
// 重启 MapperListener ,获取一个新的 Engine ,一定是当前入参的 Engine
try {
mapperListener.stop();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardService.mapperListener.stopFailed"), e);
}
try {
mapperListener.start();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardService.mapperListener.startFailed"), e);
}
// 如果当前 Service 之前有 Engine 关联,那么停止之前的 Engine
if (oldEngine != null) {
try {
oldEngine.stop();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardService.engine.stopFailed"), e);
}
}
}
// Report this property change to interested listeners
support.firePropertyChange("container", oldEngine, this.engine);
}
/**
* 实现方式和 StandardServer#addService 类似,不在细述
* 注意,Connector 这里没有像 Engine 一样与 Service 实现双向关联
*/
@Override
public void addConnector(Connector connector) {
synchronized (connectorsLock) {
connector.setService(this);
Connector results[] = new Connector[connectors.length + 1];
System.arraycopy(connectors, 0, results, 0, connectors.length);
results[connectors.length] = connector;
connectors = results;
if (getState().isAvailable()) {
try {
connector.start();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
log.error(sm.getString(
"standardService.connector.startFailed",
connector), e);
}
}
// Report this property change to interested listeners
support.firePropertyChange("connector", null, connector);
}
}
Connector
Connector 主要用于接收请求,然后交给 Engine 处理请求,处理完后再给 Connector 去返回给客户端。当前使用版本支持的协议有:HTTP,HHTP/2,AJP,NIO,NIO2,APR
主要的功能包括:
- 监听服务器端口来读取客户端的请求。
- 解析协议并交给对应的容器处理请求。
- 返回处理后的信息给客户端
Connector 对应服务器 server.xml 中配置信息的例子:
<Connector port="8080" protocol="HTTP/1.1"
connectionTimeout="20000"
redirectPort="8443" />
这里通过配置监听的端口号port,指定处理协议protocol,以及重定向地址redirectPort。
协议处理类型通过实例化连接器时设置:
public Connector() {
// 无参构造,下面 setProtocol 中默认使用HTTP/1.1
this(null);
}
public Connector(String protocol) {
// 设置当前连接器协议处理类型
setProtocol(protocol);
// 实例化协议处理器,并保存到当前 Connector 中
ProtocolHandler p = null;
try {
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(protocolHandlerClassName);
p = (ProtocolHandler) clazz.getConstructor().newInstance();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error(sm.getString(
"coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerInstantiationFailed"), e);
} finally {
this.protocolHandler = p;
}
if (Globals.STRICT_SERVLET_COMPLIANCE) {
uriCharset = StandardCharsets.ISO_8859_1;
} else {
uriCharset = StandardCharsets.UTF_8;
}
}
/**
* 这个设置再 tomcat9 中被移除,改为必配项
*/
public void setProtocol(String protocol) {
boolean aprConnector = AprLifecycleListener.isAprAvailable() &&
AprLifecycleListener.getUseAprConnector();
// 这里指定了默认协议和 HTTP/1.1 一样
if ("HTTP/1.1".equals(protocol) || protocol == null) {
if (aprConnector) {
setProtocolHandlerClassName("org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11AprProtocol");
} else {
setProtocolHandlerClassName("org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11NioProtocol");
}
} else if ("AJP/1.3".equals(protocol)) {
if (aprConnector) {
setProtocolHandlerClassName("org.apache.coyote.ajp.AjpAprProtocol");
} else {
setProtocolHandlerClassName("org.apache.coyote.ajp.AjpNioProtocol");
}
} else {
// 最后如果不是通过指定 HTTP/1.1,AJP/1.3 类型的协议,就通过类名实例化一个协议处理器
setProtocolHandlerClassName(protocol);
}
}
ProtocolHandler 是一个协议处理器,针对不同的请求,提供不同实现。实现类 AbstractProtocol 在初始化时,会在最后调用一个抽象类 AbstractEndpoint 初始化来启动线程来监听服务器端口,当接收到请求后,调用 Processor 读取请求,然后交给 Engine 处理请求。
Engine
Engine 对应的是,org.apache.catalina.Engine接口和org.apache.catalina.core.StandardEngine默认实现类。
Engine 的功能也比较简单,处理容器关系的关联。
但是实现类中的addChild()不是指的子 Engine,而是只能是 Host。同时没有父容器,setParent是不允许操作设置的。
@Override
public void addChild(Container child) {
// 添加的子容器必须是 Host
if (!(child instanceof Host))
throw new IllegalArgumentException
(sm.getString("standardEngine.notHost"));
super.addChild(child);
}
@Override
public void setParent(Container container) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException
(sm.getString("standardEngine.notParent"));
}
server.xml 可以配置我们的数据:
<!-- 配置默认Host,及jvmRoute -->
<Engine name="Catalina" defaultHost="localhost" jvmRoute="jvm1">
Host
Host 表示一个虚拟主机。应为我们的服务器可设置多个域名,比如 demo.ytao.top,dev.ytao.top。那么我们就要设置两个不同 Host 来处理不同域名的请求。当过来的请求域名为 demo.ytao.top 时,那么它就会去找该域名 Host 下的 Context。
所以我们的 server.xml 配置文件也提供该配置:
<!-- name 设置的时虚拟主机域名 -->
<Host name="localhost" appBase="webapps"
unpackWARs="true" autoDeploy="true">
Context
到 Context 这里来,就拥有 Servlet 的运行环境,Engine,Host都是主要维护容器关系,不具备运行环境。
我们暂且可将 Context 理解为一个应用,例如我们在根目录下有 ytao-demo-1 和 ytao-demo-2 两个应用,那么这里就是有两个 Context。
这里主要介绍的addChild方法,该添加的子容器是 Wrapper:
@Override
public void addChild(Container child) {
// Global JspServlet
Wrapper oldJspServlet = null;
// 这里添加的子容器只能时 Wrapper
if (!(child instanceof Wrapper)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException
(sm.getString("standardContext.notWrapper"));
}
// 判断子容器 Wrapper 是否为 JspServlet
boolean isJspServlet = "jsp".equals(child.getName());
// Allow webapp to override JspServlet inherited from global web.xml.
if (isJspServlet) {
oldJspServlet = (Wrapper) findChild("jsp");
if (oldJspServlet != null) {
removeChild(oldJspServlet);
}
}
super.addChild(child);
// 将servlet映射添加到Context组件
if (isJspServlet && oldJspServlet != null) {
/*
* The webapp-specific JspServlet inherits all the mappings
* specified in the global web.xml, and may add additional ones.
*/
String[] jspMappings = oldJspServlet.findMappings();
for (int i=0; jspMappings!=null && i<jspMappings.length; i++) {
addServletMappingDecoded(jspMappings[i], child.getName());
}
}
}
这里也就是每个应用中的 Servlet 管理中心。
Wrapper
Wrapper 是一个 Servlet 的管理中心,它拥有 Servlet 的整个生命周期,它是没有子容器的,因为它自己就是最底层的容器了。
这里主要对 Servlet 加载的分析:
public synchronized Servlet loadServlet() throws ServletException {
// 如果已经实例化或者用实例化池,就直接返回
if (!singleThreadModel && (instance != null))
return instance;
PrintStream out = System.out;
if (swallowOutput) {
SystemLogHandler.startCapture();
}
Servlet servlet;
try {
long t1=System.currentTimeMillis();
// 如果 servlet 类名为空,直接抛出 Servlet 异常
if (servletClass == null) {
unavailable(null);
throw new ServletException
(sm.getString("standardWrapper.notClass", getName()));
}
// 从 Context 中获取 Servlet
InstanceManager instanceManager = ((StandardContext)getParent()).getInstanceManager();
try {
servlet = (Servlet) instanceManager.newInstance(servletClass);
} catch (ClassCastException e) {
unavailable(null);
// Restore the context ClassLoader
throw new ServletException
(sm.getString("standardWrapper.notServlet", servletClass), e);
} catch (Throwable e) {
e = ExceptionUtils.unwrapInvocationTargetException(e);
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(e);
unavailable(null);
// Added extra log statement for Bugzilla 36630:
// https://bz.apache.org/bugzilla/show_bug.cgi?id=36630
if(log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(sm.getString("standardWrapper.instantiate", servletClass), e);
}
// Restore the context ClassLoader
throw new ServletException
(sm.getString("standardWrapper.instantiate", servletClass), e);
}
// 加载声明了 MultipartConfig 注解的信息
if (multipartConfigElement == null) {
MultipartConfig annotation =
servlet.getClass().getAnnotation(MultipartConfig.class);
if (annotation != null) {
multipartConfigElement =
new MultipartConfigElement(annotation);
}
}
// 对 servlet 类型进行检查
if (servlet instanceof ContainerServlet) {
((ContainerServlet) servlet).setWrapper(this);
}
classLoadTime=(int) (System.currentTimeMillis() -t1);
if (servlet instanceof SingleThreadModel) {
if (instancePool == null) {
instancePool = new Stack<>();
}
singleThreadModel = true;
}
// 初始化 servlet
initServlet(servlet);
fireContainerEvent("load", this);
loadTime=System.currentTimeMillis() -t1;
} finally {
if (swallowOutput) {
String log = SystemLogHandler.stopCapture();
if (log != null && log.length() > 0) {
if (getServletContext() != null) {
getServletContext().log(log);
} else {
out.println(log);
}
}
}
}
return servlet;
}
这里加载 Servlet,如果该 Servlet 没有被实例化过,那么一定要加载一个。
到目前为止,大致介绍了 Tomcat8 的主要组件,对 Tomcat 的整体架构也有个大致了解了,Tomcat 源码进行重构后,可读性确实要好很多,建议大家可以去尝试分析下,里面的使用的一些设计模式,我们在实际编码过程中,还是有一定的借鉴意义。
个人博客: [https://ytao.top](https://ytao.top)
我的公众号 ytao

初探Tomcat的架构设计的更多相关文章
- Tomcat 架构原理解析到架构设计借鉴
Tomcat 发展这么多年,已经比较成熟稳定.在如今『追新求快』的时代,Tomcat 作为 Java Web 开发必备的工具似乎变成了『熟悉的陌生人』,难道说如今就没有必要深入学习它了么?学习它我们又 ...
- Tomcat 第三篇:总体架构设计
Tomcat 总体架构设计 在开始这篇文章的时候,忽然发现上一篇内容的题目不是很合适,不应该叫启动流程,更确切的应该是叫启动脚本. 在最开始,先介绍下 Tomcat 的总体设计,先有一个大概的印象,对 ...
- Tomcat详解系列(2) - 理解Tomcat架构设计
Tomcat - 理解Tomcat架构设计 前文我们已经介绍了一个简单的Servlet容器是如何设计出来,我们就可以开始正式学习Tomcat了,在学习开始,我们有必要站在高点去看看Tomcat的架构设 ...
- Nginx及其架构设计
1.1. 什么是 Nginx Nginx 是俄罗斯人编写的十分轻量级的 HTTP 服务器,Nginx,它的发音为“engine X”,是一个高性能的HTTP和反向代理服务器,同时也是一个 IMAP/P ...
- Tomcat 系统架构与设计模式,第 2 部分: 设计模式分析(转载)
简介: 这个分为两个部分的系列文章研究了 Apache Tomcat 服务器的系统架构以及其运用的很多经典设计模式.第 1 部分 分析了 Tomcat 的工作原理,第 2 部分将分析 Tomcat 中 ...
- 【Tomcat】Tomcat 系统架构与设计模式,第 2 部分: 设计模式分析
这个分为两个部分的系列文章研究了 Apache Tomcat 服务器的系统架构以及其运用的很多经典设计模式.第 1 部分 分析了 Tomcat 的工作原理,第 2 部分将分析 Tomcat 中运用的许 ...
- 浅读tomcat架构设计和tomcat启动过程(1)
一图甚千言,这张图真的是耽搁我太多时间了: 下面的tomcat架构设计代码分析,和这张图息息相关. 使用maven搭建本次的环境,贴出pom.xml完整内容: <?xml version=&qu ...
- 浅读tomcat架构设计之tomcat生命周期(2)
浅读tomcat架构设计和tomcat启动过程(1) https://www.cnblogs.com/piaomiaohongchen/p/14977272.html tomcat通过org.apac ...
- 浅读tomcat架构设计之tomcat容器Container(3)
浅读tomcat架构设计和tomcat启动过程(1) https://www.cnblogs.com/piaomiaohongchen/p/14977272.html 浅读tomcat架构设计之tom ...
随机推荐
- [Tutorial]综述阅读笔记 <Visual Odometry PartII_Introduce about BA>
目录 Visual Odometry: Part II - Matching, Robustness, and Applications ---- paper notes 特征点的选择与匹配 特征点匹 ...
- 过滤身份证号和grep复习
一.把身份证号过滤出来 我们还是从一道面试题说起. 请从test.txt文件当中过滤出正确的的身份证号码 [root@localhost test.dir]# cat test.txt 赵 37083 ...
- 201871010101-陈来弟《面向对象程序设计(Java)》第八周学习总结
实验七 接口的定义与使用 第一部分:理论知识 一.接口.lambda和内部类: Comparator与comparable接口: 1.comparable接口的方法是compareTo,只有一个参数 ...
- 安装禅道提示:ERROR: 您访问的域名 192.168.110.128 没有对应的公司
您访问的域名 192.168.110.128 没有对应的公司. in /usr/local/nginx/html/zentaopms/module/common/model.php on line 8 ...
- Window包管理工具scoop
自定义安装路径安装 scoop安装应用路径 目标目录是D:\Program Files\Scoop,在PowerShell命令控制台中运行: [environment]::setEnvironment ...
- windows上传文件到 linux的hdfs
一.windows上传文件到 linux的hdfs 1.先在 centos 上开启 hdfs, 用 jps 可以看到下面信息, 说明完成开启 2.在win上配置 hadoop (https://www ...
- 个人网站 & 博客
www.ykmimi.com (测试使用) http://www.implements.fun/ (测试使用) http://www.java-developer.cn/ (测试使用,预备论坛) ...
- [LeetCode] 617. Merge Two Binary Trees 合并二叉树
Given two binary trees and imagine that when you put one of them to cover the other, some nodes of t ...
- [LeetCode] 57. Insert Interval 插入区间
Given a set of non-overlapping intervals, insert a new interval into the intervals (merge if necessa ...
- GreenPlum 大数据平台--集群恢复
一,问题描述 :::: gpinitstandby:greenplum01:gpadmin-[ERROR]:-Cannot use -n option when standby master has ...
