学习:STL_vector容器
vector基本概念:
功能:
vector数据结构和数组非常相似,也称为单端数组
vector与普通数组区别:
不同之处在于数组是静态空间,而vector可以动态扩展
动态扩展:
并不是在原空间之后续接新空间,而是找更大的内存空间,然后将原数据拷贝新空间,释放原空间
这张图看起来就是类似栈哇,该容器还有很多函数可以使用,接下来都会用到
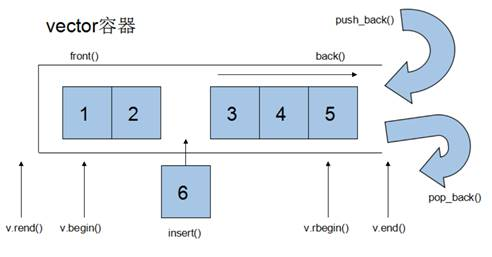
vector容器的迭代器是支持随机访问的迭代器
vector构造函数:
功能描述:创建vector容器
函数原型:
vector<T> v; //采用模板实现类实现,默认构造函数
vector(v.begin(), v.end()); //将v[begin(), end())区间中的元素拷贝给本身。
vector(n, elem); //构造函数将n个elem拷贝给本身。
vector(const vector &vec); //拷贝构造函数。
示例代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
/*
vector<T> v; //采用模板实现类实现,默认构造函数
vector(v.begin(), v.end()); //将v[begin(), end())区间中的元素拷贝给本身。
vector(n, elem); //构造函数将n个elem拷贝给本身。
vector(const vector &vec); //拷贝构造函数。
*/
void vectorPrint(vector<int> v) { //一个打印vector的容器中的值的函数
for (vector<int>::iterator a = v.begin(); a < v.end(); a++) {
cout << (*a);
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01() {
vector<int> v1; //第一种:默认构造函数 无参构造
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i);
}
vectorPrint(v1); //然后进行打印v1
vector<int> v2(v1.begin(),v1.end());//第二种:将v[begin(), end())区间中的元素拷贝给本身。
vectorPrint(v2);
vector<int> v3(5, 100); //第三种:构造函数将n个elem拷贝给本身。
vectorPrint(v3);
vector<int> v4(v1); //第四种:拷贝构造函数。
vectorPrint(v4);
}
int main() {
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
vector赋值操作:
功能描述:给vector容器进行赋值
函数原型:
vector& operator=(const vector &vec);//重载等号操作符
assign(beg, end); //将[beg, end)区间中的数据拷贝赋值给本身。
assign(n, elem); //将n个elem拷贝赋值给本身。
示例代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
/*
vector& operator=(const vector &vec);//重载等号操作符
assign(beg, end); //将[beg, end)区间中的数据拷贝赋值给本身。
assign(n, elem); //将n个elem拷贝赋值给本身。
*/
void toprint(vector<int> v) {
for (vector<int>::iterator a = v.begin(); a < v.end(); a++) {
cout << (*a);
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01() {
vector<int> v1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
v1.push_back(i);
}
toprint(v1);
vector<int> v2 = v1; // 第一种:重载等号操作符
vector<int> v3;
v3.assign(v1.begin(), v1.end()); //因为v1.end() 指向的最后一个元素的后一个,但是assign是左边闭区间 右边开区间,所以我们要多一个那么就是v1.end();
toprint(v3);
v3.assign(10, 100); //第三种:将n个elem拷贝赋值给本身。
toprint(v3);
}
int main() {
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
vector容量和大小:
功能描述:对vector容器的容量和大小操作
函数原型:
empty(); //判断容器是否为空
capacity(); //容器的容量
size(); //返回容器中元素的个数
resize(int num); //重新指定容器的长度为num,若容器变长,则以默认值填充新位置。如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除。
resize(int num, elem); //重新指定容器的长度为num,若容器变长,则以elem值填充新位置。如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除
示例代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
/*
empty(); //判断容器是否为空
capacity(); //容器的容量
size(); //返回容器中元素的个数
resize(int num); //重新指定容器的长度为num,若容器变长,则以默认值填充新位置。如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除。
resize(int num, elem); //重新指定容器的长度为num,若容器变长,则以elem值填充新位置。如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除
*/
void toprint(vector<int> v) {
for (vector<int>::iterator a = v.begin(); a < v.end(); a++) {
cout << (*a);
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01() {
vector<int> v1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
v1.push_back(i);
}
if (v1.empty()) {
cout << "v1容器为空" << endl;
}else {
cout << "v1容器不为空" << endl;
}
cout << v1.capacity() << endl; //打印容器的容量
cout << v1.size() << endl; //打印容器中元素的个数,这里需要知道的就是容器的容量永远都是>=容器的元素个数
cout << &v1[0] << endl;
v1.resize(100); // 上下都打印了v1中的第一个元素的地址,发现其地址已经发生变化了,
cout << &v1[0] << endl;
toprint(v1);
v1.resize(110,100); //重新指定容器的长度为num,若容器变长,则以elem值填充新位置。如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除
toprint(v1);
}
int main() {
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
vector插入和删除:
功能描述:对vector容器进行插入、删除操作
函数原型:
push_back(ele);//尾部插入元素ele
pop_back();//删除最后一个元素
insert(const_iterator pos, ele); //迭代器指向位置pos插入元素ele
insert(const_iterator pos, int count,ele);//迭代器指向位置pos插入count个元素ele
erase(const_iterator pos); //删除迭代器指向的元素
erase(const_iterator start, const_iterator end);//删除迭代器从start到end之间的元素
clear(); //删除容器中所有元素
示例代码:
#include <vector>
void printVector(vector<int>& v) {
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++) {
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
//插入和删除
void test01()
{
vector<int> v1;
//尾插
v1.push_back(10);
v1.push_back(20);
v1.push_back(30);
v1.push_back(40);
v1.push_back(50);
printVector(v1);
//尾删
v1.pop_back();
printVector(v1);
//插入
v1.insert(v1.begin(), 100);
printVector(v1);
v1.insert(v1.begin(), 2, 1000);
printVector(v1);
//删除
v1.erase(v1.begin());
printVector(v1);
//清空
v1.erase(v1.begin(), v1.end());
v1.clear();
printVector(v1);
}
int main() {
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
vector数据存取:
功能描述:对vector中的数据的存取操作
函数原型:
at(int idx); //返回索引idx所指的数据
operator[]; //返回索引idx所指的数据
front(); //返回容器中第一个数据元素
back(); //返回容器中最后一个数据元素
示例代码:
#include <vector>
void test01()
{
vector<int>v1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < v1.size(); i++)
{
cout << v1[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < v1.size(); i++)
{
cout << v1.at(i) << " ";
}
cout << endl;
cout << "v1的第一个元素为: " << v1.front() << endl;
cout << "v1的最后一个元素为: " << v1.back() << endl;
}
int main() {
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
总结:
1、除了用迭代器获取vector容器中元素,[ ]和at也可以
2、front返回容器第一个元素
3、back返回容器最后一个元素
vector互换容器:
功能描述:实现两个容器内元素进行互换
函数原型:
swap(vec); // 将vec与本身的元素互换
示例代码:
#include <vector>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void printVector(vector<int>& v) {
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++) {
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
vector<int>v1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i);
}
printVector(v1);
cout << "当前v1的容量 " << v1.capacity() << " 大小 " << v1.size() << endl;
vector<int>v2;
for (int i = 20; i > 0; i--)
{
v2.push_back(i);
}
printVector(v2);
cout << "当前v2的容量 " << v2.capacity() << " 大小 " << v2.size() << endl;
//互换容器
cout << "互换后" << endl;
v1.swap(v2);
cout << "当前v1的容量 " << v1.capacity() << " 大小 " << v1.size() << endl;
cout << "当前v2的容量 " << v2.capacity() << " 大小 " << v2.size() << endl;
printVector(v1);
printVector(v2);
}
void test02()
{
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
v.push_back(i);
}
cout << "v的容量为:" << v.capacity() << endl;
cout << "v的大小为:" << v.size() << endl;
v.resize(3);
cout << "v的容量为:" << v.capacity() << endl; //虽然重新指定了大小,但是发现容量还是原来这么大
cout << "v的大小为:" << v.size() << endl;
//为了不浪费这么大的空间,可以采取swap收缩内存的操作
vector<int>(v).swap(v); //vector<int>(v) 这句话生成了一个匿名对象,以当前的v的大小为初始化那么当前的v为3,然后进行swap操作 与当前的v进行capacity和size互换
//因为匿名对象的特性,交换完就会释放匿名对象
cout << "v的容量为:" << v.capacity() << endl;
cout << "v的大小为:" << v.size() << endl;
}
int main() {
//test01();
test02();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
vector预留空间:
功能描述:减少vector在动态扩展容量时的扩展次数
函数原型:
reserve(int len);//容器预留len个元素长度,预留位置不初始化,元素不可访问。
示例代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
void toprint(vector<int> v) {
for (vector<int>::iterator a = v.begin(); a < v.end(); a++)
{
cout << (*a);
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01() {
vector<int> v1;
v1.reserve(10000); //预留一万个,这样vector容器就不会在10000之前随着元素的扩大而重新开辟新的空间进行储存
int num = 0;
int * p = NULL;
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
v1.push_back(i);
if (p != &v1[0]) {
p = &v1[0];
num++;
}
}
cout << num << endl;
}
int main() {
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
学习:STL_vector容器的更多相关文章
- Spring.NET依赖注入框架学习--实例化容器常用方法
Spring.NET依赖注入框架学习---实例化容器常用方法 本篇学习实例化Spring.NET容器的俩种方式 1.通过XmlObjectFactory创建一个Spring.NET容器 IResour ...
- 5.docker学习之容器
容器创建 我们已经知道,镜像是只读的,而基于镜像创建出来的容器是可读写的,所以,一般我们实际中,会经常使用对应镜像创建容器并且使用这些容器.同样,如果我们想要使用容器,那么我们必须首先需要创建容器.而 ...
- c++学习之容器细枝末节(2)
从昨天到现在,还依然停留在容器的学习上,现在写例程代码顺手多了,看来写代码还是要多多练习才能有感觉. 经过一天的学习,有一下几点知识点让我觉得很有意义: (1)删除容器中的元素的时候,pop_fron ...
- c++学习之容器细枝末节(1)
对照着c++primier 开始学习第九章容器,把课后习题当做练习,虽然是看过书上的讲解,但是做题编程的时候,一些需要注意的地方还是难免有遗漏. 一下是几点印象比较深刻的总结: (1)前几章只学了ve ...
- ###STL学习--关联容器
点击查看Evernote原文. #@author: gr #@date: 2014-08-23 #@email: forgerui@gmail.com STL中的关联容器. ###stl学习 |--迭 ...
- 创建ApplicationContext与BeanFactory时的区别-Spring源码学习之容器的基本实现
传送门 可以加载XML两种方法 使用 BeanFactory 加载 XML BeanFactory bf = new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResource(&quo ...
- 侯捷STL学习(十)--容器hashtable探索(unordered set/map)
layout: post title: 侯捷STL学习(十) date: 2017-07-23 tag: 侯捷STL --- 第二十三节 容器hashtable探索 hashtable冲突(碰撞)处理 ...
- spring源码学习之容器的基本实现
最近想拿出一部分时间来学习一下spring的源码,还特意买了一本书结合来看,当然主要是学习并跟着作者的思路来踏上学习spring的源码的道路,特意在此记录一下,<spring源码深度解析> ...
- laravel学习:容器绑定与解析
1.在服务容器中注册类(bind) $this->app->bind('sender','MailSender');//$this->app成为服务容器. 2.从服务容器生成类( ...
随机推荐
- spring.profiles.active=@profiles.active@的含义
spring.profiles.active=@profiles.active@ ,其实是配合 maven profile进行选择不同配置文件进行启动. 当执行 mvn clean package - ...
- memcpy() 实现循环缓冲区数据的读写
使用memcpy()函数做循环缓冲区的读写 首先对mencpy函数做个简单的介绍 下面是 memcpy() 函数的声明 void *memcpy(void *str1, const void *str ...
- SQL系列(七)—— 相似(like)
在看like之前先了解下通配符和搜索模式: 通 配 符 ( wildcard) 用来匹配值的一部分的特殊字符. 搜索模式(search pattern) 由字面值.通配符或两者组合构成的搜索条件. 目 ...
- SQL Server的常用提示
在SQL Server中,有许多SQL语句的提示,本文总结一些比较常用的提示. OPTION LOOP/MERGE/HASH JOIN提示 该提示可以改变整个SQL语句中所有JOIN的关联算法,所以请 ...
- php 计算文件大小
计算文件大小 主要计算文件的 size 大小,默认的为Bytes的,所以运用三元运算符,来进行转换. 转换成 Bytes->KB->MB->GB /** * @param $size ...
- 使用PS打开图片的常见姿势
我们经常会使用PS对现有的图片进行编辑.所以每个人都会经历打开图片这一步骤. 下面为大家介绍一下PS打开图片的这一步的常见方式吧: 第一种:使用文件资源管理器(也就是双击我的电脑弹出来的窗口) 第二种 ...
- 上传文件大小与时间 Web.Config文件 httpRuntime 限制
httpRuntime <httpRuntime executionTimeout="90" maxRequestLength="40960" useF ...
- 通过Ldap实现人事系统组织人事和AD的同步
项目需求:同步人事系统的组织架构-对应AD的OU树同步人事系统的员工-对应AD的用户 创建OU 名字不能重复,需要父级路径(parentOrganizeUnit)以及新ou的名字(name),如果最父 ...
- C#里面如何判断一个Object是否是某种类型
第一种方法 var isA = oldObject.GetType() == typeof(Dictionary<string, string>) 第二种方法 var isB = oldO ...
- 重温拉格朗日乘子法和KKT条件
在求取有约束条件的优化问题时,拉格朗日乘子法(Lagrange Multiplier) 和KKT条件是非常重要的两个求取方法,对于等式约束的优化问题,可以应用拉格朗日乘子法去求取最优值:如果含有不等式 ...
