[HNOI2018]毒瘤
Description
从前有一名毒瘤。
毒瘤最近发现了量产毒瘤题的奥秘。考虑如下类型的数据结构题:给出一个数组,要求支持若干种奇奇怪怪的修改操作(比如区间加一个数,或者区间开平方),并支持询问区间和。毒瘤考虑了\(n\)个这样的修改操作,并编号为\(1\sim n\)。当毒瘤要出数据结构题的时候,他就将这些修改操作中选若干个出来,然后出成一道题。
当然了,这样出的题有可能不可做。通过精妙的数学推理,毒瘤揭露了这些修改操作的关系:有\(m\)对“互相排斥”的修改操作,第\(i\)对是第\(u_i\)个操作和第\(v_i\)个操作。当一道题同时含有\(u_i\)和\(v_i\)这两个操作时,这道题就会变得不可做。另一方面,一道题中不包含任何“互相排斥”的修改操作时,这个题就是可做的。此外,毒瘤还发现了一个规律:\(m-n\)是一个很小的数字,且任意两个修改操作都是连通的。两个修改操作\(a,b\)是连通的,当且仅当存在若干操作\(t_0,t_1,...,t_l\),使得\(t_0=a,t_l=b\),且对\(1\leqslant i\leqslant l\),\(t_{i-1}\)和\(t_i\)都是“互相排斥”的修改操作。
一堆“互相排斥”的修改操作称为互斥对。现在毒瘤想知道,给定值\(n\)和\(m\)个互斥对,他共能出出多少道可做的不同的数据结构题。两道数据结构题是不同的,当且仅当有一个修改操作在其中一道题中存在,而在另一道题中不存在。
Input
第一行为正整数\(n,m\)。
接下来\(m\)行,每行两个正整数\(u,v\),代表一对“互相排斥”的修改操作。
Output
输出一行一个整数,代表毒瘤可以出的可做的不同的“互相排斥”的修改操作的个数。这个数可能很大,所以只输出模998244353后的值。
Sample Input 1
3 2
1 2
2 3
Sample Output 1
5
Sample Input 2
6 8
1 2
1 3
1 4
2 4
3 5
4 5
4 6
1 6
Sample Output 2
16
Sample Input 3
12 18
12 6
3 11
8 6
2 9
10 4
1 8
6 2
11 5
10 6
12 2
9 3
7 6
2 7
3 2
7 3
5 6
2 11
12 1
Sample Output 3
248
HINT
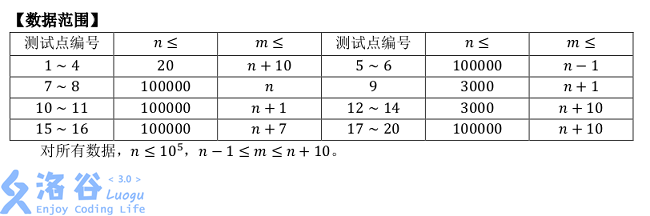
首先考虑\(m=n-1\)的情况,我们直接做一遍tree dp,设\(f[u][0/1]\)表示点\(u\)选或不选的方案数,转移即为$$\begin{cases}f[u][0]=\prod\limits_{u\rightarrow v}(f[v][0]+f[v][1])\f[u][1]=\prod\limits_{u\rightarrow v}f[v][0]\end{cases}$$
这样我们可以得到10pts的好成绩,那么多出来的非树边如何处理?因为最多只有11条非树边,暴力枚举端点状态,只有\((1,0),(0,0),(0,1)\)三种,但其实只要枚举一个点选或不选,\((0,0)\)和\((0,1)\)可以合并起来,复杂度\(O(2^{m-n+1}n)\),可以得到75pts的好成绩
如何拿满分?我们发现上面的算法重复计算了很多状态,我们把非树边影响的点取出来,记为关键点,影响dp值的只有这些点,我们把这些关键点(至多22个)建立一棵虚树,dp方程可以转化为$$\begin{cases}f[u][0]=\prod\limits_{u\rightarrow v}k_{u\rightarrow v,0,0}\times f[v][0]+k_{u\rightarrow v,0,1}\times f[v][1]\f[u][1]=\prod\limits_{u\rightarrow v}k_{u\rightarrow v,1,0}\times f[v][0]+k_{u\rightarrow v,1,1}\times f[v][1]\end{cases}$$
其实可以发现,\(k_{u\rightarrow v,0/1,0/1}\)是不会变化的,那么我们就先预处理出系数,如何求?\(v\)在原树上暴力向上跳,累计统计系数即可,记得统计的时候不能重复统计
这样转移的复杂度是\(O(n)\)的,对于虚树上的边我们暴力枚举状态,然后转移,记\(s\)为关键点数,则复杂度为\(O(n+s2^s)\)
/*program from Wolfycz*/
#include<cmath>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#define Fi first
#define Se second
#define MK make_pair
#define inf 0x7f7f7f7f
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned int ui;
typedef pair<int,int> pii;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
inline char gc(){
static char buf[1000000],*p1=buf,*p2=buf;
return p1==p2&&(p2=(p1=buf)+fread(buf,1,1000000,stdin),p1==p2)?EOF:*p1++;
}
inline int frd(){
int x=0,f=1; char ch=gc();
for (;ch<'0'||ch>'9';ch=gc()) if (ch=='-') f=-1;
for (;ch>='0'&&ch<='9';ch=gc()) x=(x<<3)+(x<<1)+ch-'0';
return x*f;
}
inline int read(){
int x=0,f=1; char ch=getchar();
for (;ch<'0'||ch>'9';ch=getchar()) if (ch=='-') f=-1;
for (;ch>='0'&&ch<='9';ch=getchar()) x=(x<<3)+(x<<1)+ch-'0';
return x*f;
}
inline void print(int x){
if (x<0) putchar('-'),x=-x;
if (x>9) print(x/10);
putchar(x%10+'0');
}
const int N=1e5,Mod=998244353;
struct S1{
int x,y;
S1(){x=y=0;}
void insert(int _x,int _y){x=_x,y=_y;}
}NT[15];//Not in Tree
int NT_cnt,dfn[N+10];
bool cmp(int x,int y){return dfn[x]<dfn[y];}
struct S2{
int pre[(N<<1)+10],now[N+10],child[(N<<1)+10],tot,Time;
int fa[N+10],size[N+10],deep[N+10],Rem[N+10],top[N+10],f[N+10][2];
bool vis[N+10];
void join(int x,int y){pre[++tot]=now[x],now[x]=tot,child[tot]=y;}
void insert(int x,int y){join(x,y),join(y,x);}
void dfs(int x){
deep[x]=deep[fa[x]]+1,size[x]=1;
for (int p=now[x],son=child[p];p;p=pre[p],son=child[p]){
if (son==fa[x]) continue;
fa[son]=x,dfs(son);
size[x]+=size[son];
if (size[Rem[x]]<size[son]) Rem[x]=son;
}
}
void build(int x){
if (!x) return;
dfn[x]=++Time;
top[x]=Rem[fa[x]]==x?top[fa[x]]:x;
build(Rem[x]);
for (int p=now[x],son=child[p];p;p=pre[p],son=child[p]){
if (son==fa[x]||son==Rem[x]) continue;
build(son);
}
}
int LCA(int x,int y){
while (top[x]!=top[y]){
if (deep[top[x]]<deep[top[y]]) swap(x,y);
x=fa[top[x]];
}
return deep[x]<deep[y]?x:y;
}
void dp(int x){//在原树上dp一次,处理出原本的dp系数f
f[x][0]=f[x][1]=1;
for (int p=now[x],son=child[p];p;p=pre[p],son=child[p]){
if (son==fa[x]) continue;
dp(son);
f[x][1]=1ll*f[x][1]*f[son][0]%Mod;
f[x][0]=1ll*f[x][0]*(f[son][0]+f[son][1])%Mod;
}
}
int work(int x,int y,int xv,int yv){//deep[x]<deep[y]
//暴力上跳,求出边的系数
static int tmp[2];
tmp[yv]=1,tmp[yv^1]=0;
while (x!=y){
vis[y]=1;
for (int p=now[y],son=child[p];p;p=pre[p],son=child[p]){
if (son==fa[y]||vis[son]) continue;
tmp[1]=1ll*tmp[1]*f[son][0]%Mod;
tmp[0]=1ll*tmp[0]*(f[son][0]+f[son][1])%Mod;
}
swap(tmp[0],tmp[1]);
tmp[0]=(tmp[0]+tmp[1])%Mod;
//f[x][1]=f[son][0];
//f[x][0]=f[son][0]+f[son][1];
//向上跳一次要按如上方法转移,所以tmp数组需要按如上方法处理
y=fa[y];
}
return tmp[xv];
}
pii work(int x){//处理关键点在虚树上应有的值
static int tmp[2];
tmp[0]=tmp[1]=1;
for (int p=now[x],son=child[p];p;p=pre[p],son=child[p]){
if (son==fa[x]||vis[son]) continue;
vis[son]=1;
tmp[1]=1ll*tmp[1]*f[son][0]%Mod;
tmp[0]=1ll*tmp[0]*(f[son][0]+f[son][1])%Mod;
}
return MK(tmp[0],tmp[1]);
}
}HLD;//Heavy Light Decomposition
const int M=22;
struct S3{
int pre[(M<<2)+10],now[N+10],child[(M<<2)+10],tot,m;
int V[(M<<2)+10][2][2];//V[p][i][j]: p:u->v i:u(0/1) j:v(0/1)
int vis[N+10];//special point(0/1); normal point(-1)
int f[N+10][2],g[N+10][2],A[M+10];
void join(int x,int y){pre[++tot]=now[x],now[x]=tot,child[tot]=y;}
void insert(int x,int y){join(x,y),join(y,x);}
void rebuild(){
static int stack[(M<<1)+10],top=0;
for (int i=1;i<=NT_cnt;i++) A[++m]=NT[i].x,A[++m]=NT[i].y;
sort(A+1,A+1+m);
m=unique(A+1,A+1+m)-A-1;
stack[++top]=1;
sort(A+1,A+1+m,cmp);
for (int i=1;i<=m;i++){
int x=A[i],lca=HLD.LCA(x,stack[top]);
if (x==1) continue;
if (lca==stack[top]){
stack[++top]=x;
continue;
}
while (true){
int y=stack[top-1];
if (dfn[y]>=dfn[lca]) insert(stack[top--],y);
else{
if (lca==stack[top]) break;
insert(stack[top],lca);
stack[top]=lca; break;
}
}
stack[++top]=x;
}
while (top>1){
insert(stack[top-1],stack[top]);
top--;
}
}
void prepare(int x,int fa){
for (int p=now[x],son=child[p];p;p=pre[p],son=child[p]){
if (son==fa) continue;
prepare(son,x);
for (int i=0;i<2;i++)
for (int j=0;j<2;j++)
V[p][i][j]=HLD.work(x,son,i,j);
}
//求出每个点本身应有的dp值,边的系数只考虑边,不考虑端点
pii tmp=HLD.work(x);
g[x][0]=tmp.Fi,g[x][1]=tmp.Se;
}
void dp(int x,int fa){
if (vis[x]==-1) f[x][0]=g[x][0],f[x][1]=g[x][1];
else f[x][vis[x]]=g[x][vis[x]],f[x][vis[x]^1]=0;
for (int p=now[x],son=child[p];p;p=pre[p],son=child[p]){
if (son==fa) continue;
dp(son,x);
f[x][1]=1ll*f[x][1]*(1ll*f[son][0]*V[p][1][0]%Mod+1ll*f[son][1]*V[p][1][1]%Mod)%Mod;
f[x][0]=1ll*f[x][0]*(1ll*f[son][0]*V[p][0][0]%Mod+1ll*f[son][1]*V[p][0][1]%Mod)%Mod;
}
}
void work(){
rebuild();
prepare(1,0);
memset(vis,255,sizeof(vis));
int Ans=0;
for (int sta=0;sta<1<<m;sta++){
for (int i=1;i<=m;i++) vis[A[i]]=(sta>>(i-1))&1;
bool flag=1;
for (int i=1;i<=NT_cnt;i++){
if (vis[NT[i].x]&&vis[NT[i].y]){
flag=0;
break;
}
}
if (!flag) continue;
dp(1,0);
Ans=(Ans+(f[1][0]+f[1][1])%Mod)%Mod;
}
printf("%d\n",Ans);
}
}VT;//Virtual Tree
struct S4{
int fa[N+10];
S4(){for (int i=1;i<=N;i++) fa[i]=i;}
int find(int x){return x==fa[x]?x:fa[x]=find(fa[x]);}
}DSU;//Disjoint Set Union
int main(){
int n=read(),m=read();
for (int i=1;i<=m;i++){
int x=read(),y=read(),fx,fy;
if ((fx=DSU.find(x))!=(fy=DSU.find(y))){
DSU.fa[fx]=fy;
HLD.insert(x,y);
}else NT[++NT_cnt].insert(x,y);
}
HLD.dfs(1),HLD.build(1),HLD.dp(1);
VT.work();
return 0;
}
[HNOI2018]毒瘤的更多相关文章
- 【BZOJ5287】[HNOI2018]毒瘤(动态规划,容斥)
[BZOJ5287][HNOI2018]毒瘤(动态规划,容斥) 题面 BZOJ 洛谷 题解 考场上想到的暴力做法是容斥: 因为\(m-n\le 10\),所以最多会多出来\(11\)条非树边. 如果就 ...
- [bzoj5287] [HNOI2018]毒瘤
题目描述 从前有一名毒瘤. 毒瘤最近发现了量产毒瘤题的奥秘.考虑如下类型的数据结构题:给出一个数组,要求支持若干种奇奇怪怪的修改操作(比如区间加一个数,或者区间开平方),并支持询问区间和.毒瘤考虑了n ...
- bzoj 5287: [Hnoi2018]毒瘤
Description Solution \(dfs\) 出一棵生成树之后,多出来的边就都是反祖边了 把反祖边两个端点都拿出来,就会得到最多 \(k=2*(m-n+1)\) 个关键点 除了关键点以外的 ...
- BZOJ.5287.[AHOI HNOI2018]毒瘤(虚树 树形DP)
BZOJ LOJ 洛谷 设\(f[i][0/1]\)表示到第\(i\)个点,不选/选这个点的方案数.对于一棵树,有:\[f[x][0]=\prod_{v\in son[x]}(f[v][0]+f[v] ...
- BZOJ5287 HNOI2018毒瘤(虚树+树形dp)
显然的做法是暴力枚举非树边所连接两点的选或不选,大力dp.考场上写的是最暴力的O(3n-mn),成功比大众分少10分.容斥或者注意到某些枚举是不必要的就能让底数变成2.但暴力的极限也就到此为止. 每次 ...
- HNOI2018毒瘤
题面链接 luogu sol 这篇博是骗访问量的QwQ. 考虑树怎么做,简单容斥.诸如\(f[u][0]=\prod (f[v][0]+f[v][1]),f[u][1]=\prod f[v][0]\) ...
- [BZOJ5287][HNOI2018]毒瘤(虚树DP)
暴力枚举非树边取值做DP可得75. 注意到每次枚举出一个容斥状态的时候,都要做大量重复操作. 建立虚树,预处理出虚树上两点间的转移系数.也可动态DP解决. 树上倍增.动态DP.虚树DP似乎是这种问题的 ...
- 【比赛】HNOI2018 毒瘤
虚树+dp 直接看zlttttt的强大题解 zlttttt的题解看这里 #include<bits/stdc++.h> #define ui unsigned int #define ll ...
- BZOJ 5287: [Hnoi2018]毒瘤 动态dp(LCT+矩阵乘法)
自己 yy 了一个动态 dp 做法,应该是全网唯一用 LCT 写的. code: #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define ll long long #define ...
随机推荐
- iOS 开发之 - 关闭键盘 退出键盘 的5种方式
iOS 开发之 - 关闭键盘 退出键盘 的5种方式 1.点击编辑区以外的地方(UIView) 2.点击编辑区域以外的地方(UIControl) 3.使用制作收起键盘的按钮 4.使用判断输入字元 5 ...
- BZOJ 4976: 宝石镶嵌 背包
4976: 宝石镶嵌 Time Limit: 2 Sec Memory Limit: 128 MB Description 魔法师小Q拥有n个宝石,每个宝石的魔力依次为w_1,w_2,...,w_n ...
- C# delegate Action<T> lambda表达式
转载以记录:http://blog.csdn.net/educast/article/details/7219854 在使用 Action<T> 委托时,不必显式定义一个封装只有一个参数的 ...
- 成本函数计算方法J
J = 1/(2*m) * sum((X*theta - y).^2); OR
- amazon lightsail
https://51.ruyo.net/6038.html https://aws.amazon.com/cn/lightsail/
- 一步一步学Silverlight 2系列(21):如何在Silverlight中调用JavaScript
概述 Silverlight 2 Beta 1版本发布了,无论从Runtime还是Tools都给我们带来了很多的惊喜,如支持框架语言Visual Basic, Visual C#, IronRuby, ...
- npm 基本命令行
npm是随同NodeJS一起安装的包管理工具. 检查版本 npm -v 升级npm npm install npm -g 使用淘宝镜像升级 cnpm install npm -g npm instal ...
- COCOS2DX场景切换特效
cocos2d-x 3.0中场景切换特效比较多,而且游戏开发中也经常需要用到这些特效,来使场景切换时不至于那么干巴,遂这里汇总一下,开发中使用. 百牛信息技术bainiu.ltd整理发布于博客园 场景 ...
- Start Developing Mac Apps -- App Design 应用程序设计
App Design Apps do not exist on their own. They not only interact seamlessly with their environment, ...
- HDU 5882 Balanced Game (水题)
题意:问 nnn 个手势的石头剪刀布游戏是否能保证出每种手势胜率都一样. 析:当每种手势的攻防个数完全相等才能保证平衡,所以容易得出 nnn 是奇数时游戏平衡,否则不平衡. 也就是说打败 i 的和 i ...
