Why DDD and layered architecture
As a developer, you may think that your job is to write code. However, Software development is not a product pipeline. If all developers just simply add new features and don’t care about design, software development and maintenance will become more and more complicated. A developer’s job is to solve a problem through software, and coding is just one aspect of software development. Good design and communication are just as important.
Domain driven design(or DDD) is such approach focused on clear communication and shared domain knowledge.
The importance of the shared model knowledge
Before attempting to solve a problem it’s important that we understand the problem correctly. Obviously, if our understanding of the problem is incomplete or distorted, then we won’t to be able to provide a useful solution. And sadly, of course, it’s the developers’ understanding, not the domain experts’s understanding. that gets released to production.
What if the domain experts,the development team, other stakeholders share the same model? In this case there is no translation from the domain expert’s requirements to the code. The code is designed to reflect the shared model directly.
.png)
The benefits of this approach can be:
- Faster time to market
- More business value
- Less waste
- Easier maintenance and evolution
Understanding the Domain through business events
A DDD approach to gathering requirements will emphasize building a shared understanding between developers and domain experts.
How to do that? Business logic is not static, it’s a process of transformation, so understanding how it changes is a good starting point. the transformation point of the process is also called domain event. For example “the order submitted” is a domain event will kick off the order selling process.
Use Event storming to discover the domain
There are a number of ways to discover events in a domain, but one that is particularly suitable for a DDD approach is Event Storming, which is a collaborative process for discovering business events and their associated workflows. TW Xi’an team did several workshops for Event Storming in the past days.
Partitioning the Domain into Subdomains
After Event storming we have a good understanding of what the various business processes are. But the big picture is still quite chaotic. The next step is partitioning the problem domain into smaller subdomains When faced with a large problem, it’s natural to break it into smaller components that can be addressed separately.
We have a large problem: Selling domain, Can we break it into smaller pieces?
Yes, we can. We can split it to various aspects of the Order, Charge, Authentication, Availability …, We will call each of these areas a domain.
Creating a solution Using Bounded contexts
Understanding the problem doesn’t mean that building a solution is easy. The solution can’t possibly represent all the information in the original domain. We should only capture the information that is relevant to solving a particular problem. Everything else is irrelevant.
We therefore need to create a distinction between a “problem space” and a “solution space” and they must be treated as two different things. To build the solution we will create a model for the problem domain, extracting only the aspects of the domain that are relevant and then re-creating them in our solution space as bounded context.
1. Why context
Because each context represents some specialized knowledge in the solution. Within the context, we share a common language and the design is coherent and unified.
2. Why bounded
In the real world, domains have fuzzy boundaries, but in the world of software we want to reduce coupling between separate subsystems so that they can evolve independently.
Creating a ubiquitous language
The set of concepts and vocabulary that is shared between everyone on the team is called the Ubiquitous Language. This is the language that defines the shared model for the business domain. The language should used everywhere in the project, not just in the requirements but in the design, and most importantly, in the source code.
Finally, it’s important to realize that you often cannot have a single Ubiquitous language that covers all domains and contexts.
We called User in Authentication domain but called Customer in Order domain.
Domain modeling
We have now got a basic understanding of Domain, but how to document them?
we should use visual diagrams, but these are often hard to work with and not detailed enough to capture some of the subtleties of the domain.
If you have a lot of database experience, your first instinct might be think about tables and the relationships between them. You might envision a Order table, an order line table, and Customer, Contact tables. And then you’ll probably want to describe the relationships between them by foreign key, But if you do this, you are making a mistake. In DDD we let the domain drive the design, not a database schema.
In DDD terminology this step called Domain modeling, For developer we should use code to modeling these domains.
Other concepts
As you know DDD is a large topic, We can not describe all the concepts in here. But you should understand that the core idea of DDD is using code to create a business model that can be shared with domain experts.
Other concepts like Entity, ValueObject, AggregateRoot, CQRS, EventSourcing, MicroService etc require you constantly practice to understand.
Layered architecture
For implementing DDD, we need to design our architecture to achieve this goal. The reason we will split whole system into multiple layers is Separation of Concerns and Single Responsibility Principle. The general idea is that we split persistence, rendering api and application logic to different layers and let developers focus on design and writing domain logic.
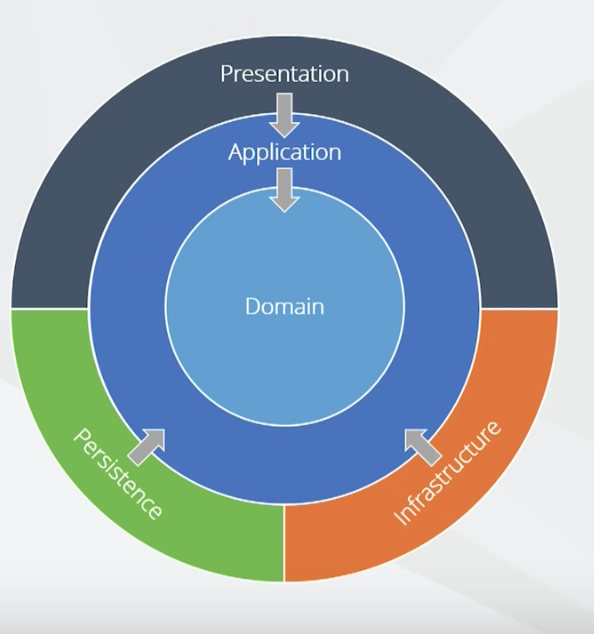
Domain Layer
We have the domain layer and business logic at the center, The domain layer will contain enterprise business logic and types.
Application Layer
Contains application logic and types.
The difference between Domain layer and application layers is Domain layer can be invoked by application layer, But domain layer don't know application layer.
Infrastructure Layer
Focus on persistence by database or api
Invert of Control
We don't want to let business logic to be dependent on concerns such as infrastructure and persistence so we invert these dependencies, so infrastructure, persistence and presentation all take a dependency on that center area.
The way we did is we added our abstraction and interfaces inside the core and then infrastructure and persistence implement those abstractions. For example, for persistence, if we were creating a repository there, there would be an IRepository used in the core and in persistence we will implement that IRepository. The result of this design is domain layer doesn't have any dependency on anything, We will got below benefit:
- It's highly testable, We can actually test the core without UI
- It's independent of persistence, whatever you persist data by database or api
- Independent of external system
Why DDD and layered architecture的更多相关文章
- 2.2 DDD Layers & Clean Architecture DDD分层和简洁架构
DDD Layers & Clean Architecture DDD分层和简洁架构 There are four fundamental layers of a Domain Driven ...
- Layered Architecture 分层架构
分层的价值在于每一层都只代表程序中的某一特定方面.这种限制使每个方面的设计都更具有内聚性,更容易解释. 大多数成功的架构使用的都是包括下面这四个概念层的某个版本
- NLayer Architecture in abp
https://aspnetboilerplate.com/Pages/Documents/NLayer-Architecture Introduction The layering of an ap ...
- WCF - Architecture
WCF - Architecture WCF has a layered architecture that offers ample support for developing various d ...
- 架构:The Onion Architecture : part 3(洋葱架构:第三篇)(转载)
In my previous installments, I described what has become my approach to defining the architecture fo ...
- 架构:The Onion Architecture : part 1(洋葱架构:第一篇)(转载)
原文地址:http://jeffreypalermo.com/blog/the-onion-architecture-part-1/. I've spoken several times about ...
- Architecture Patterns
This chapter provides guidelines for using architecture patterns. Introduction Patterns for system a ...
- MASA Framework - DDD设计(2)
目录 MASA Framework - 整体设计思路 MASA Framework - EventBus设计 MASA Framework - MASA Framework - DDD设计(1) MA ...
- DotNet 资源大全中文版(Awesome最新版)
Awesome系列的.Net资源整理.awesome-dotnet是由quozd发起和维护.内容包括:编译器.压缩.应用框架.应用模板.加密.数据库.反编译.IDE.日志.风格指南等. 算法与数据结构 ...
随机推荐
- Dancing Links 学习笔记
Dancing Links 本周的AI引论作业布置了一道数独 加了奇怪剪枝仍然TLE的Candy?不得不去学了dlx dlxnb! Exact cover 设全集X,X的若干子集的集合为S.精确覆盖是 ...
- PIL库自我学习总结及应用(美白,磨皮,搞笑图片处理)
Hello!今天我们来学习一下这个神奇的图片处理的第三方函数库——PIL库 (本blog部分图片及代码来自网络) 这是一个支持图像存储.显示和处理的函数库,它能够处理几乎所有图像格式,可以完成对图像的 ...
- [LeetCode] Lemonade Change 买柠檬找零
At a lemonade stand, each lemonade costs $5. Customers are standing in a queue to buy from you, and ...
- Hadoop集群搭建-HA高可用(手动切换模式)(四)
步骤和集群规划 1)保存完全分布式模式配置 2)在full配置的基础上修改为高可用HA 3)第一次启动HA 4)常规启动HA 5)运行wordcount 集群规划: centos虚拟机:node-00 ...
- Servlet 自定义标签
自定义标签 1)用户定义的一种jsp标记,当一个含有自定义标签的jsp页面被jsp引擎编译成servlet时,tag标签被转化成了对一个称为 标签处理类 的对象的操作.于是,当jsp页面被jsp引擎转 ...
- 一个帮助理解python星号的例子
- create-react-app创建的项目中registerServiceWorker.js文件的作用
使用React官方的脚手架工具create-react-app创建的项目,目录中会存在registerServiceWorker.js这个文件,这个文件的作用是什么呢? 这个文件可以使用也可以不使用, ...
- Hibernate4集成spring4报错----No Session found for current thread
在编写一个Hibernate4集成spring4的小demo的时候出现了该错误: org.hibernate.HibernateException: No Session found for curr ...
- return和throw某些特性相似
拷贝构造函数的调用拷贝构造函数会在以下三中情况下被调用(1)当类的一个对象去初始化该类的另一个对象时 int main(){ Point a(1,2); Point b(a);//用对象a初始化对象b ...
- ThreadLocal及InheritableThreadLocal的原理剖析
我们知道,线程的不安全问题,主要是由于多线程并发读取一个变量而引起的,那么有没有一种办法可以让一个变量是线程独有的呢,这样不就可以解决线程安全问题了么.其实JDK已经为我们提供了ThreadLocal ...
