[LeetCode] Inorder Successor in BST II 二叉搜索树中的中序后继节点之二
Given a binary search tree and a node in it, find the in-order successor of that node in the BST.
The successor of a node p is the node with the smallest key greater than p.val.
You will have direct access to the node but not to the root of the tree. Each node will have a reference to its parent node.
Example 1:
Input:
root = {"$id":"1","left":{"$id":"2","left":null,"parent":{"$ref":"1"},"right":null,"val":1},"parent":null,"right":{"$id":"3","left":null,"parent":{"$ref":"1"},"right":null,"val":3},"val":2}
p = 1
Output: 2
Explanation: 1's in-order successor node is 2. Note that both p and the return value is of Node type.
Example 2:
Input:
root = {"$id":"1","left":{"$id":"2","left":{"$id":"3","left":{"$id":"4","left":null,"parent":{"$ref":"3"},"right":null,"val":1},"parent":{"$ref":"2"},"right":null,"val":2},"parent":{"$ref":"1"},"right":{"$id":"5","left":null,"parent":{"$ref":"2"},"right":null,"val":4},"val":3},"parent":null,"right":{"$id":"6","left":null,"parent":{"$ref":"1"},"right":null,"val":6},"val":5}
p = 6
Output: null
Explanation: There is no in-order successor of the current node, so the answer isnull.
Example 3:
Input:
root = {"$id":"1","left":{"$id":"2","left":{"$id":"3","left":{"$id":"4","left":null,"parent":{"$ref":"3"},"right":null,"val":2},"parent":{"$ref":"2"},"right":{"$id":"5","left":null,"parent":{"$ref":"3"},"right":null,"val":4},"val":3},"parent":{"$ref":"1"},"right":{"$id":"6","left":null,"parent":{"$ref":"2"},"right":{"$id":"7","left":{"$id":"8","left":null,"parent":{"$ref":"7"},"right":null,"val":9},"parent":{"$ref":"6"},"right":null,"val":13},"val":7},"val":6},"parent":null,"right":{"$id":"9","left":{"$id":"10","left":null,"parent":{"$ref":"9"},"right":null,"val":17},"parent":{"$ref":"1"},"right":{"$id":"11","left":null,"parent":{"$ref":"9"},"right":null,"val":20},"val":18},"val":15}
p = 15
Output: 17
Example 4:
Input:
root = {"$id":"1","left":{"$id":"2","left":{"$id":"3","left":{"$id":"4","left":null,"parent":{"$ref":"3"},"right":null,"val":2},"parent":{"$ref":"2"},"right":{"$id":"5","left":null,"parent":{"$ref":"3"},"right":null,"val":4},"val":3},"parent":{"$ref":"1"},"right":{"$id":"6","left":null,"parent":{"$ref":"2"},"right":{"$id":"7","left":{"$id":"8","left":null,"parent":{"$ref":"7"},"right":null,"val":9},"parent":{"$ref":"6"},"right":null,"val":13},"val":7},"val":6},"parent":null,"right":{"$id":"9","left":{"$id":"10","left":null,"parent":{"$ref":"9"},"right":null,"val":17},"parent":{"$ref":"1"},"right":{"$id":"11","left":null,"parent":{"$ref":"9"},"right":null,"val":20},"val":18},"val":15}
p = 13
Output: 15
Note:
- If the given node has no in-order successor in the tree, return
null. - It's guaranteed that the values of the tree are unique.
- Remember that we are using the
Nodetype instead ofTreeNodetype so their string representation are different.
Follow up:
Could you solve it without looking up any of the node's values?
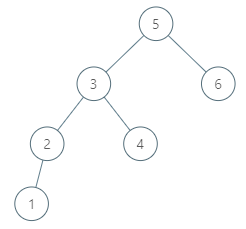
这道题是之前的那道 Inorder Successor in BST 的后续,之前那道题给了我们树的根结点,而这道题并没有确定给我们根结点,只是给了树的任意一个结点,然后让求给定结点的中序后继结点。这道题比较好的一点就是例子给的比较详尽,基本覆盖到了大部分的情况,包括一些很 tricky 的情况。首先来看例子1,结点1的中序后继结点是2,因为中序遍历的顺序是左-根-右。还是例子1,结点2的中序后续结点是3,这样我们就知道中序后续结点可以是其父结点或者右子结点。再看例子2,结点6的中序后续结点是空,因为其已经是中序遍历的最后一个结点了,所以没有后续结点。例子3比较 tricky,结点 15 的中序后续结点不是其右子结点,而是其右子结点的左子结点 17,这样才符合左-根-右的顺序。例子4同样 tricky,结点 13 的中序后继结点并不是其亲生父结点,而是其祖爷爷结点 15。
好,看完了这四个例子,我们应该心里有些数了吧。后继结点出现的位置大致可以分为两类,一类是在子孙结点中,另一类是在祖先结点中。仔细观察例子不难发现,当某个结点存在右子结点时,其中序后继结点就在子孙结点中,反之则在祖先结点中。这样我们就可以分别来处理,当右子结点存在时,我们需要找到右子结点的最左子结点,这个不难,就用个 while 循环就行了。当右子结点不存在,我们就要找到第一个比其值大的祖先结点,也是用个 while 循环去找即可,参见代码如下:
解法一:
class Solution {
public:
Node* inorderSuccessor(Node* node) {
if (!node) return nullptr;
Node *res = nullptr;
if (node->right) {
res = node->right;
while (res && res->left) res = res->left;
} else {
res = node->parent;
while (res && res->val < node->val) res = res->parent;
}
return res;
}
};
本题的 Follow up 让我们不要访问结点值,那么上面的解法就不行了。因为当 node 没有右子结点时,我们没法通过比较结点值来找到第一个大于 node 的祖先结点。虽然不能比较结点值了,我们还是可以通过 node 相对于其 parent 的位置来判断,当 node 是其 parent 的左子结点时,我们知道此时 parent 的结点值一定大于 node,因为这是二叉搜索树的性质。若 node 是其 parent 的右子结点时,则将 node 赋值为其 parent,继续向上找,直到其 parent 结点不存在了,此时说明不存在大于 node 值的祖先结点,这说明 node 是 BST 的最后一个结点了,没有后继结点,直接返回 nullptr 即可,参见代码如下:
解法二:
class Solution {
public:
Node* inorderSuccessor(Node* node) {
if (!node) return nullptr;
if (node->right) {
node = node->right;
while (node && node->left) node = node->left;
return node;
}
while (node) {
if (!node->parent) return nullptr;
if (node == node->parent->left) return node->parent;
node = node->parent;
}
return node;
}
};
Github 同步地址:
https://github.com/grandyang/leetcode/issues/510
类似题目:
参考资料:
https://leetcode.com/problems/inorder-successor-in-bst-ii/
LeetCode All in One 题目讲解汇总(持续更新中...)
[LeetCode] Inorder Successor in BST II 二叉搜索树中的中序后继节点之二的更多相关文章
- [LeetCode] Inorder Successor in BST 二叉搜索树中的中序后继节点
Given a binary search tree and a node in it, find the in-order successor of that node in the BST. No ...
- [LeetCode] 285. Inorder Successor in BST 二叉搜索树中的中序后继节点
Given a binary search tree and a node in it, find the in-order successor of that node in the BST. Th ...
- [Swift]LeetCode285. 二叉搜索树中的中序后继节点 $ Inorder Successor in BST
Given a binary search tree and a node in it, find the in-order successor of that node in the BST. Th ...
- 给定一个二叉搜索树的根节点 root 和一个值 key,删除二叉搜索树中的 key 对应的节点,并保证二叉搜索树的性质不变。返回二叉搜索树(有可能被更新)的根节点的引用
一般来说,删除节点可分为两个步骤: 首先找到需要删除的节点: 如果找到了,删除它. 说明: 要求算法时间复杂度为 O(h),h 为树的高度. 示例: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,7] ...
- [Swift]LeetCode450. 删除二叉搜索树中的节点 | Delete Node in a BST
Given a root node reference of a BST and a key, delete the node with the given key in the BST. Retur ...
- Java实现 LeetCode 450 删除二叉搜索树中的节点
450. 删除二叉搜索树中的节点 给定一个二叉搜索树的根节点 root 和一个值 key,删除二叉搜索树中的 key 对应的节点,并保证二叉搜索树的性质不变.返回二叉搜索树(有可能被更新)的根节点的引 ...
- 刷题-力扣-230. 二叉搜索树中第K小的元素
230. 二叉搜索树中第K小的元素 题目链接 来源:力扣(LeetCode) 链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/kth-smallest-element-in-a ...
- LeetCode Inorder Successor in BST
原题链接在这里:https://leetcode.com/problems/inorder-successor-in-bst/ Given a binary search tree and a nod ...
- [LeetCode] Delete Node in a BST 删除二叉搜索树中的节点
Given a root node reference of a BST and a key, delete the node with the given key in the BST. Retur ...
随机推荐
- Python学习笔记-CGI编程(如何在IIS上挂Python开发的Webservice)
一.如何用Python开发一个简单的Webservice 利用python的cgi编程,可以传入参数将结果输出. 定义需要编码以及需要引用的模块 #conding=utf-8 #修正中文乱码 impo ...
- MySql8.0+全新身份验证方式
我们在安装MySql8.0+的版本时MySql将会询问我们是否选择全新的身份验证方式,如下图 ⒈第一个是MySql推荐我们使用的强密码加密模式来进行身份验证 MySql8支持基于SHA256改进的更强 ...
- Linux启动activemq失败
第一种情况: 在网上查找错误,通过./activemq console命令可以查看到activemq启动的错误信息,另外在data/activemq.log文件中可以查看到错误日志. java.io. ...
- JAVA学习笔记(2)—— java初始化三个原则
1. 初始化原则 (1) 静态对象(变量)优先于非静态对象(变量)初始化,其中静态对象(变量)初始化一次,非静态对象(变量)可能会初始化多次. (2) 父类优先于子类初始化 (3) 按照成 ...
- 使用scrapy爬虫,爬取起点小说网的案例
爬取的页面为https://book.qidian.com/info/1010734492#Catalog 爬取的小说为凡人修仙之仙界篇,这边小说很不错. 正文的章节如下图所示 其中下面的章节为加密部 ...
- Spring Cloud微服务集成配置中心
1. 搭建Spring Cloud Config配置中心(见上一篇博客) 2. 创建微服务项目bounter-simon-app,pom文件如下: <?xml version="1.0 ...
- linux常见故障处理
目录 一. 文件和目录类 1.1 File exist 文件已经存在 1.2 No such file or directory 没有这个文件或目录(这个东西不存在) 1.3 command not ...
- ArrayList源码学习
1.ArrayList:基于数据实现,允许出现空值和重复元素,当ArrayList中添加的元素数量大于底层数组容量是,会通过扩容机制重新生成一个更大的数组.(非线程安全) 2.源码分析 构造函数 /* ...
- 【webpack系列】从零搭建 webpack4+react 脚手架(一)
搭建一个React工程的方式有很多,官方也有自己的脚手架,如果你和我一样,喜欢刨根究底,从零开始自己一行一行代码创建一个React脚手架项目,那你就来对地方了.本教程是针对React新手,以及对web ...
- 前端校验插件——Validator简单使用
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> ...