视觉十四讲:第七讲_3D-2D:P3P
1.P3P
P3P输入数据为三对3D-2D的匹配点,一个单目相机,经过初始化,得到初始的3D点,就可以依次得到后续的姿态和3D点。
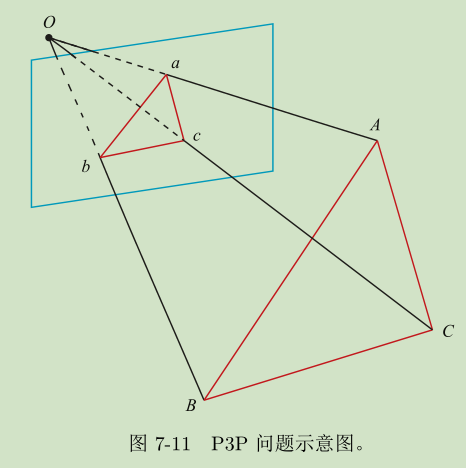
ABC是上一时刻求的的3D点, abc是与上一次时刻的匹配点。利用相似原理,可求出abc在相机坐标下的3D坐标,最后就可以把问题转换为3D-3D坐标的估计问题。
- 问题:只利用3个点,不能运用多余的信息;受噪声影响,存在无匹配,容易算法失败
通常做法是用P3P估计出相机位姿,然后再构建最小二乘优化问题对估计值进行优化调整(Bundle Adjustment)
2.使用Pnp来求解
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
if (argc != 5) {
cout << "usage: pose_estimation_3d2d img1 img2 depth1 depth2" << endl;
return 1;
}
//-- 读取图像
Mat img_1 = imread(argv[1], CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR);
Mat img_2 = imread(argv[2], CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR);
assert(img_1.data && img_2.data && "Can not load images!");
vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_1, keypoints_2;
vector<DMatch> matches;
//获取匹配点
find_feature_matches(img_1, img_2, keypoints_1, keypoints_2, matches);
cout << "一共找到了" << matches.size() << "组匹配点" << endl;
// 建立3D点
Mat d1 = imread(argv[3], CV_LOAD_IMAGE_UNCHANGED); // 第一张图的深度图为16位无符号数,单通道图像
Mat K = (Mat_<double>(3, 3) << 520.9, 0, 325.1, 0, 521.0, 249.7, 0, 0, 1);
vector<Point3f> pts_3d;
vector<Point2f> pts_2d;
for (DMatch m:matches) {
//取出第一张图匹配点的深度数据
//Mat.ptr<>(行)[列]
ushort d = d1.ptr<unsigned short>(int(keypoints_1[m.queryIdx].pt.y))[int(keypoints_1[m.queryIdx].pt.x)];
if (d == 0) // bad depth
continue;
float dd = d / 5000.0;
//将图1的匹配点的像素坐标转相机归一化坐标
Point2d p1 = pixel2cam(keypoints_1[m.queryIdx].pt, K);
//转换为相机坐标的3D点
pts_3d.push_back(Point3f(p1.x * dd, p1.y * dd, dd));
//获取图2的匹配点的像素坐标
pts_2d.push_back(keypoints_2[m.trainIdx].pt);
}
cout << "3d-2d pairs: " << pts_3d.size() << endl;
/**************pnp**************/
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
Mat r, t;
solvePnP(pts_3d, pts_2d, K, Mat(), r, t, false); // 调用OpenCV 的 PnP 求解,可选择EPNP,DLS等方法
Mat R;
cv::Rodrigues(r, R); // r为旋转向量形式,用Rodrigues公式转换为矩阵
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
chrono::duration<double> time_used = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double>>(t2 - t1);
cout << "solve pnp in opencv cost time: " << time_used.count() << " seconds." << endl;
cout << "R=" << endl << R << endl;
cout << "t=" << endl << t << endl;
}
3.使用高斯牛顿法来优化求解
1.构建最小二乘问题:
\(T^{*}=argmin\frac{1}{2} \displaystyle \sum^{n}_{i=1}||u_{i}-\frac{1}{s_{i}}KTP_{i}||^{2}_{2}\)
误差是观测像素点-投影像素点,称为重投影误差
使用高斯牛顿法的重点在于求误差项对于每个优化变量的导数
线性化:\(e(x+\Delta x) \approx e(x) + J^{T}\Delta x\)
高斯的增量方程为: \((\displaystyle \sum^{100}_{i=1} J_{i}(\sigma^{2})^{-1} J_{i}^{T})\Delta x_{k}=\displaystyle \sum^{100}_{i=1} -J_{i}(\sigma^{2})^{-1} e_{i}\)
\(H\Delta x_{k}=b\)
2.求雅可比矩阵:
1.使用非齐次坐标,像素误差e是2维,x为相机位姿是6维,\(J^{T}\)是一个2*6的矩阵。
2.将P变换到相机坐标下为\(P^{'}=[X^{'},Y^{'},Z^{'}]^{T}\),则:\(su=KP^{'}\)
3.消去s得:\(u=f_{x}\frac{X^{'}}{Z^{'}}+c_{x}\) \(v=f_{y}\frac{Y^{'}}{Z^{'}}+c_{y}\)
4.对T左乘扰动量\(\delta \xi\),考虑e的变化关于扰动量的导数。则\(\frac{\partial e}{\partial \delta \xi}= \frac{\partial e}{\partial P^{'}} \frac{\partial P^{'}}{\partial \delta \xi}\)
5.容易得出\(\frac{\partial e}{\partial P^{'}}\) = \(-\left[ \begin{matrix} \frac{f_{x}}{Z^{'}} & 0 & -\frac{f_{x}X^{'}}{Z^{'2}} \\ 0 & \frac{f_{y}}{Z^{'}} & -\frac{f_{y}Y^{'}}{Z^{'2}} \end{matrix} \right]\)
6.由李代数导数得:\(\frac{\partial (TP)}{\partial \delta \xi} = \left[ \begin{matrix} I & -P^{' \Lambda} \\ 0^{T} & 0^{T} \end{matrix} \right]\)
7.在\(P^{'}\)的定义中,取了前三维,所以\(\frac{\partial P^{'}}{\partial \delta \xi} = \left[ \begin{matrix} I & -P^{' \Lambda} \end{matrix} \right]\)
8.将两个式子相乘就可以得到雅可比矩阵:
\(\frac{\partial e}{\partial \delta \xi} = - \left[ \begin{matrix} \frac{f_{x}}{Z^{'}} & 0 & -\frac{f_{x}X^{'}}{Z^{'2}} & -\frac{f_{x}X^{'}Y^{'}}{Z^{'2}} & f_{x} + \frac{f_{x}X^{'2}}{Z^{'2}} &- \frac{f_{x}Y^{'}}{Z^{'}} \\ 0 & \frac{f_{y}}{Z^{'}} & -\frac{f_{y}Y^{'}}{Z^{'2}} & -f_{y} - \frac{f_{y}Y^{'2}}{Z^{'2}} & \frac{f_{y}X^{'}Y^{'}}{Z^{'2}} & \frac{f_{y}X^{'}}{Z^{'}} \end{matrix} \right]\)
3.程序:
void bundleAdjustmentGaussNewton(
const VecVector3d &points_3d,
const VecVector2d &points_2d,
const Mat &K,
Sophus::SE3d &pose) {
typedef Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 1> Vector6d;
const int iterations = 10;
double cost = 0, lastCost = 0;
double fx = K.at<double>(0, 0);
double fy = K.at<double>(1, 1);
double cx = K.at<double>(0, 2);
double cy = K.at<double>(1, 2);
for (int iter = 0; iter < iterations; iter++) {
Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 6> H = Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 6>::Zero();
Vector6d b = Vector6d::Zero();
cost = 0;
// compute cost
for (int i = 0; i < points_3d.size(); i++) {
//世界坐标转为相机坐标
Eigen::Vector3d pc = pose * points_3d[i];
double inv_z = 1.0 / pc[2];
double inv_z2 = inv_z * inv_z;
//相机坐标转为像素坐标
Eigen::Vector2d proj(fx * pc[0] / pc[2] + cx, fy * pc[1] / pc[2] + cy);
Eigen::Vector2d e = points_2d[i] - proj; //误差,观测值-预测值,反之取负
cost += e.squaredNorm(); //误差里的每项平方和
Eigen::Matrix<double, 2, 6> J;
//雅可比矩阵赋值
J << -fx * inv_z,
0,
fx * pc[0] * inv_z2,
fx * pc[0] * pc[1] * inv_z2,
-fx - fx * pc[0] * pc[0] * inv_z2,
fx * pc[1] * inv_z,
0,
-fy * inv_z,
fy * pc[1] * inv_z2,
fy + fy * pc[1] * pc[1] * inv_z2,
-fy * pc[0] * pc[1] * inv_z2,
-fy * pc[0] * inv_z;
H += J.transpose() * J;
b += -J.transpose() * e;
}
Vector6d dx;
dx = H.ldlt().solve(b);
if (isnan(dx[0])) {
cout << "result is nan!" << endl;
break;
}
if (iter > 0 && cost >= lastCost) {
// cost increase, update is not good
cout << "cost: " << cost << ", last cost: " << lastCost << endl;
break;
}
// update your estimation
//更新位姿
pose = Sophus::SE3d::exp(dx) * pose;
lastCost = cost;
cout << "iteration " << iter << " cost=" << std::setprecision(12) << cost << endl;
//范数,误差足够小
if (dx.norm() < 1e-6) {
// converge
break;
}
}
cout << "pose by g-n: \n" << pose.matrix() << endl;
}
4.使用g2o来进行BA优化
- 节点(待优化的变量): 第二个相机的位姿 \(T \in SE(3)\)
- 边(误差): 每个3D在第二个相机中的投影
1.构建节点和边框架:
// 曲线模型的顶点,模板参数:优化变量维度和数据类型
class VertexPose : public g2o::BaseVertex<6, Sophus::SE3d> {
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW;
// 初始化
virtual void setToOriginImpl() override {
_estimate = Sophus::SE3d();
}
//更新估计值
virtual void oplusImpl(const double *update) override {
Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 1> update_eigen;
update_eigen << update[0], update[1], update[2], update[3], update[4], update[5];
_estimate = Sophus::SE3d::exp(update_eigen) * _estimate;
}
virtual bool read(istream &in) override {}
virtual bool write(ostream &out) const override {}
};
// 误差模型 模板参数:观测值维度,类型,连接顶点类型
class EdgeProjection : public g2o::BaseUnaryEdge<2, Eigen::Vector2d, VertexPose> {
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW;
//输入的变量:位姿,相机内参
EdgeProjection(const Eigen::Vector3d &pos, const Eigen::Matrix3d &K) : _pos3d(pos), _K(K) {}
//计算误差
virtual void computeError() override {
const VertexPose *v = static_cast<VertexPose *> (_vertices[0]);
//获取估计值
Sophus::SE3d T = v->estimate();
//将3D世界坐标转为相机像素坐标
Eigen::Vector3d pos_pixel = _K * (T * _pos3d);
//归一化
pos_pixel /= pos_pixel[2];
//计算误差
_error = _measurement - pos_pixel.head<2>();
}
//计算雅可比矩阵,公式上面已推导
virtual void linearizeOplus() override {
const VertexPose *v = static_cast<VertexPose *> (_vertices[0]);
Sophus::SE3d T = v->estimate();
//世界坐标转化为相机坐标
Eigen::Vector3d pos_cam = T * _pos3d;
//获取相机内参
double fx = _K(0, 0);
double fy = _K(1, 1);
double cx = _K(0, 2);
double cy = _K(1, 2);
double X = pos_cam[0];
double Y = pos_cam[1];
double Z = pos_cam[2];
double Z2 = Z * Z;
//传入雅可比矩阵参数
_jacobianOplusXi
<< -fx / Z, 0, fx * X / Z2, fx * X * Y / Z2, -fx - fx * X * X / Z2, fx * Y / Z,
0, -fy / Z, fy * Y / (Z * Z), fy + fy * Y * Y / Z2, -fy * X * Y / Z2, -fy * X / Z;
}
virtual bool read(istream &in) override {}
virtual bool write(ostream &out) const override {}
private:
Eigen::Vector3d _pos3d;
Eigen::Matrix3d _K;
};
2.组成图优化:
void bundleAdjustmentG2O(
const VecVector3d &points_3d,
const VecVector2d &points_2d,
const Mat &K,
Sophus::SE3d &pose) {
// 构建图优化,先设定g2o
typedef g2o::BlockSolver<g2o::BlockSolverTraits<6, 3>> BlockSolverType; // 位姿维度为6,误差维度为3
typedef g2o::LinearSolverDense<BlockSolverType::PoseMatrixType> LinearSolverType; // 线性求解器类型
// 梯度下降方法,可以从GN, LM, DogLeg 中选
auto solver = new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmGaussNewton(
g2o::make_unique<BlockSolverType>(g2o::make_unique<LinearSolverType>()));
g2o::SparseOptimizer optimizer; // 图模型
optimizer.setAlgorithm(solver); // 设置求解器
optimizer.setVerbose(true); // 打开调试输出
// 往图中添加节点
VertexPose *vertex_pose = new VertexPose(); // camera vertex_pose
vertex_pose->setId(0);
vertex_pose->setEstimate(Sophus::SE3d());
optimizer.addVertex(vertex_pose);
// K 相机内参
Eigen::Matrix3d K_eigen;
K_eigen <<
K.at<double>(0, 0), K.at<double>(0, 1), K.at<double>(0, 2),
K.at<double>(1, 0), K.at<double>(1, 1), K.at<double>(1, 2),
K.at<double>(2, 0), K.at<double>(2, 1), K.at<double>(2, 2);
// edges 边
int index = 1;
for (size_t i = 0; i < points_2d.size(); ++i) {
auto p2d = points_2d[i];
auto p3d = points_3d[i];
EdgeProjection *edge = new EdgeProjection(p3d, K_eigen);
edge->setId(index);
edge->setVertex(0, vertex_pose); // 设置连接的顶点
edge->setMeasurement(p2d); //传入观测值
edge->setInformation(Eigen::Matrix2d::Identity()); // 信息矩阵
optimizer.addEdge(edge);
index++;
}
//执行优化
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
optimizer.setVerbose(true);
optimizer.initializeOptimization();
optimizer.optimize(10);
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
chrono::duration<double> time_used = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double>>(t2 - t1);
cout << "optimization costs time: " << time_used.count() << " seconds." << endl;
//获取结果
cout << "pose estimated by g2o =\n" << vertex_pose->estimate().matrix() << endl;
pose = vertex_pose->estimate();
}
5.完整代码
#include <iostream>
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2/calib3d/calib3d.hpp>
#include <Eigen/Core>
#include <g2o/core/base_vertex.h>
#include <g2o/core/base_unary_edge.h>
#include <g2o/core/sparse_optimizer.h>
#include <g2o/core/block_solver.h>
#include <g2o/core/solver.h>
#include <g2o/core/optimization_algorithm_gauss_newton.h>
#include <g2o/solvers/dense/linear_solver_dense.h>
#include <sophus/se3.hpp>
#include <chrono>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
void find_feature_matches(
const Mat &img_1, const Mat &img_2,
std::vector<KeyPoint> &keypoints_1,
std::vector<KeyPoint> &keypoints_2,
std::vector<DMatch> &matches);
// 像素坐标转相机归一化坐标
Point2d pixel2cam(const Point2d &p, const Mat &K);
// BA by g2o
//STL容器中的元素是Eigen的数据结构,例如这里定义一个vector容器,元素是Vector2d
typedef vector<Eigen::Vector2d, Eigen::aligned_allocator<Eigen::Vector2d>> VecVector2d;
typedef vector<Eigen::Vector3d, Eigen::aligned_allocator<Eigen::Vector3d>> VecVector3d;
void bundleAdjustmentG2O(
const VecVector3d &points_3d,
const VecVector2d &points_2d,
const Mat &K,
Sophus::SE3d &pose
);
// BA by gauss-newton
void bundleAdjustmentGaussNewton(
const VecVector3d &points_3d,
const VecVector2d &points_2d,
const Mat &K,
Sophus::SE3d &pose
);
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
if (argc != 5) {
cout << "usage: pose_estimation_3d2d img1 img2 depth1 depth2" << endl;
return 1;
}
//-- 读取图像
Mat img_1 = imread(argv[1], CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR);
Mat img_2 = imread(argv[2], CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR);
assert(img_1.data && img_2.data && "Can not load images!");
vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_1, keypoints_2;
vector<DMatch> matches;
//获取匹配点
find_feature_matches(img_1, img_2, keypoints_1, keypoints_2, matches);
cout << "一共找到了" << matches.size() << "组匹配点" << endl;
// 建立3D点
Mat d1 = imread(argv[3], CV_LOAD_IMAGE_UNCHANGED); // 第一张图的深度图为16位无符号数,单通道图像
Mat K = (Mat_<double>(3, 3) << 520.9, 0, 325.1, 0, 521.0, 249.7, 0, 0, 1);
vector<Point3f> pts_3d;
vector<Point2f> pts_2d;
for (DMatch m:matches) {
//取出第一张图匹配点的深度数据
ushort d = d1.ptr<unsigned short>(int(keypoints_1[m.queryIdx].pt.y))[int(keypoints_1[m.queryIdx].pt.x)];
if (d == 0) // bad depth
continue;
float dd = d / 5000.0;
//将图1的匹配点的像素坐标转相机归一化坐标
Point2d p1 = pixel2cam(keypoints_1[m.queryIdx].pt, K);
//转换为相机坐标的3D点
pts_3d.push_back(Point3f(p1.x * dd, p1.y * dd, dd));
//获取图2的匹配点的像素坐标
pts_2d.push_back(keypoints_2[m.trainIdx].pt);
}
cout << "3d-2d pairs: " << pts_3d.size() << endl;
/**************pnp**************/
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
Mat r, t;
solvePnP(pts_3d, pts_2d, K, Mat(), r, t, false); // 调用OpenCV 的 PnP 求解,可选择EPNP,DLS等方法
Mat R;
cv::Rodrigues(r, R); // r为旋转向量形式,用Rodrigues公式转换为矩阵
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
chrono::duration<double> time_used = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double>>(t2 - t1);
cout << "solve pnp in opencv cost time: " << time_used.count() << " seconds." << endl;
cout << "R=" << endl << R << endl;
cout << "t=" << endl << t << endl;
/********************************/
VecVector3d pts_3d_eigen;
VecVector2d pts_2d_eigen;
//
for (size_t i = 0; i < pts_3d.size(); ++i) {
//图1的3D点
pts_3d_eigen.push_back(Eigen::Vector3d(pts_3d[i].x, pts_3d[i].y, pts_3d[i].z));
//图2的2D点
pts_2d_eigen.push_back(Eigen::Vector2d(pts_2d[i].x, pts_2d[i].y));
}
//高斯牛顿法优化
cout << "calling bundle adjustment by gauss newton" << endl;
Sophus::SE3d pose_gn;
t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
bundleAdjustmentGaussNewton(pts_3d_eigen, pts_2d_eigen, K, pose_gn);
t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
time_used = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double>>(t2 - t1);
cout << "solve pnp by gauss newton cost time: " << time_used.count() << " seconds." << endl;
//g2o优化
cout << "calling bundle adjustment by g2o" << endl;
Sophus::SE3d pose_g2o;
t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
bundleAdjustmentG2O(pts_3d_eigen, pts_2d_eigen, K, pose_g2o);
t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
time_used = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double>>(t2 - t1);
cout << "solve pnp by g2o cost time: " << time_used.count() << " seconds." << endl;
return 0;
}
void find_feature_matches(const Mat &img_1, const Mat &img_2,
std::vector<KeyPoint> &keypoints_1,
std::vector<KeyPoint> &keypoints_2,
std::vector<DMatch> &matches) {
//-- 初始化
Mat descriptors_1, descriptors_2;
// used in OpenCV3
Ptr<FeatureDetector> detector = ORB::create();
Ptr<DescriptorExtractor> descriptor = ORB::create();
// use this if you are in OpenCV2
// Ptr<FeatureDetector> detector = FeatureDetector::create ( "ORB" );
// Ptr<DescriptorExtractor> descriptor = DescriptorExtractor::create ( "ORB" );
Ptr<DescriptorMatcher> matcher = DescriptorMatcher::create("BruteForce-Hamming");
//-- 第一步:检测 Oriented FAST 角点位置
detector->detect(img_1, keypoints_1);
detector->detect(img_2, keypoints_2);
//-- 第二步:根据角点位置计算 BRIEF 描述子
descriptor->compute(img_1, keypoints_1, descriptors_1);
descriptor->compute(img_2, keypoints_2, descriptors_2);
//-- 第三步:对两幅图像中的BRIEF描述子进行匹配,使用 Hamming 距离
vector<DMatch> match;
// BFMatcher matcher ( NORM_HAMMING );
matcher->match(descriptors_1, descriptors_2, match);
//-- 第四步:匹配点对筛选
double min_dist = 10000, max_dist = 0;
//找出所有匹配之间的最小距离和最大距离, 即是最相似的和最不相似的两组点之间的距离
for (int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++) {
double dist = match[i].distance;
if (dist < min_dist) min_dist = dist;
if (dist > max_dist) max_dist = dist;
}
printf("-- Max dist : %f \n", max_dist);
printf("-- Min dist : %f \n", min_dist);
//当描述子之间的距离大于两倍的最小距离时,即认为匹配有误.但有时候最小距离会非常小,设置一个经验值30作为下限.
for (int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++) {
if (match[i].distance <= max(2 * min_dist, 30.0)) {
matches.push_back(match[i]);
}
}
}
Point2d pixel2cam(const Point2d &p, const Mat &K) {
return Point2d
(
(p.x - K.at<double>(0, 2)) / K.at<double>(0, 0),
(p.y - K.at<double>(1, 2)) / K.at<double>(1, 1)
);
}
void bundleAdjustmentGaussNewton(
const VecVector3d &points_3d,
const VecVector2d &points_2d,
const Mat &K,
Sophus::SE3d &pose) {
typedef Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 1> Vector6d;
const int iterations = 10;
double cost = 0, lastCost = 0;
double fx = K.at<double>(0, 0);
double fy = K.at<double>(1, 1);
double cx = K.at<double>(0, 2);
double cy = K.at<double>(1, 2);
for (int iter = 0; iter < iterations; iter++) {
Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 6> H = Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 6>::Zero();
Vector6d b = Vector6d::Zero();
cost = 0;
// compute cost
for (int i = 0; i < points_3d.size(); i++) {
//世界坐标转为相机坐标
Eigen::Vector3d pc = pose * points_3d[i];
double inv_z = 1.0 / pc[2];
double inv_z2 = inv_z * inv_z;
//相机坐标转为像素坐标
Eigen::Vector2d proj(fx * pc[0] / pc[2] + cx, fy * pc[1] / pc[2] + cy);
Eigen::Vector2d e = points_2d[i] - proj; //误差,观测值-预测值,反之取负
cost += e.squaredNorm(); //误差里的每项平方和
Eigen::Matrix<double, 2, 6> J;
//雅可比矩阵赋值
J << -fx * inv_z,
0,
fx * pc[0] * inv_z2,
fx * pc[0] * pc[1] * inv_z2,
-fx - fx * pc[0] * pc[0] * inv_z2,
fx * pc[1] * inv_z,
0,
-fy * inv_z,
fy * pc[1] * inv_z2,
fy + fy * pc[1] * pc[1] * inv_z2,
-fy * pc[0] * pc[1] * inv_z2,
-fy * pc[0] * inv_z;
H += J.transpose() * J;
b += -J.transpose() * e;
}
Vector6d dx;
dx = H.ldlt().solve(b);
if (isnan(dx[0])) {
cout << "result is nan!" << endl;
break;
}
if (iter > 0 && cost >= lastCost) {
// cost increase, update is not good
cout << "cost: " << cost << ", last cost: " << lastCost << endl;
break;
}
// update your estimation
//更新位姿
pose = Sophus::SE3d::exp(dx) * pose;
lastCost = cost;
cout << "iteration " << iter << " cost=" << std::setprecision(12) << cost << endl;
if (dx.norm() < 1e-6) {
// converge
break;
}
}
cout << "pose by g-n: \n" << pose.matrix() << endl;
}
/// vertex and edges used in g2o ba
class VertexPose : public g2o::BaseVertex<6, Sophus::SE3d> {
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW;
virtual void setToOriginImpl() override {
_estimate = Sophus::SE3d();
}
/// left multiplication on SE3
virtual void oplusImpl(const double *update) override {
Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 1> update_eigen;
update_eigen << update[0], update[1], update[2], update[3], update[4], update[5];
_estimate = Sophus::SE3d::exp(update_eigen) * _estimate;
}
virtual bool read(istream &in) override {}
virtual bool write(ostream &out) const override {}
};
class EdgeProjection : public g2o::BaseUnaryEdge<2, Eigen::Vector2d, VertexPose> {
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW;
EdgeProjection(const Eigen::Vector3d &pos, const Eigen::Matrix3d &K) : _pos3d(pos), _K(K) {}
virtual void computeError() override {
const VertexPose *v = static_cast<VertexPose *> (_vertices[0]);
Sophus::SE3d T = v->estimate();
Eigen::Vector3d pos_pixel = _K * (T * _pos3d);
pos_pixel /= pos_pixel[2];
_error = _measurement - pos_pixel.head<2>();
}
virtual void linearizeOplus() override {
const VertexPose *v = static_cast<VertexPose *> (_vertices[0]);
Sophus::SE3d T = v->estimate();
Eigen::Vector3d pos_cam = T * _pos3d;
double fx = _K(0, 0);
double fy = _K(1, 1);
double cx = _K(0, 2);
double cy = _K(1, 2);
double X = pos_cam[0];
double Y = pos_cam[1];
double Z = pos_cam[2];
double Z2 = Z * Z;
_jacobianOplusXi
<< -fx / Z, 0, fx * X / Z2, fx * X * Y / Z2, -fx - fx * X * X / Z2, fx * Y / Z,
0, -fy / Z, fy * Y / (Z * Z), fy + fy * Y * Y / Z2, -fy * X * Y / Z2, -fy * X / Z;
}
virtual bool read(istream &in) override {}
virtual bool write(ostream &out) const override {}
private:
Eigen::Vector3d _pos3d;
Eigen::Matrix3d _K;
};
void bundleAdjustmentG2O(
const VecVector3d &points_3d,
const VecVector2d &points_2d,
const Mat &K,
Sophus::SE3d &pose) {
// 构建图优化,先设定g2o
typedef g2o::BlockSolver<g2o::BlockSolverTraits<6, 3>> BlockSolverType; // pose is 6, landmark is 3
typedef g2o::LinearSolverDense<BlockSolverType::PoseMatrixType> LinearSolverType; // 线性求解器类型
// 梯度下降方法,可以从GN, LM, DogLeg 中选
auto solver = new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmGaussNewton(
g2o::make_unique<BlockSolverType>(g2o::make_unique<LinearSolverType>()));
g2o::SparseOptimizer optimizer; // 图模型
optimizer.setAlgorithm(solver); // 设置求解器
optimizer.setVerbose(true); // 打开调试输出
// vertex
VertexPose *vertex_pose = new VertexPose(); // camera vertex_pose
vertex_pose->setId(0);
vertex_pose->setEstimate(Sophus::SE3d());
optimizer.addVertex(vertex_pose);
// K
Eigen::Matrix3d K_eigen;
K_eigen <<
K.at<double>(0, 0), K.at<double>(0, 1), K.at<double>(0, 2),
K.at<double>(1, 0), K.at<double>(1, 1), K.at<double>(1, 2),
K.at<double>(2, 0), K.at<double>(2, 1), K.at<double>(2, 2);
// edges
int index = 1;
for (size_t i = 0; i < points_2d.size(); ++i) {
auto p2d = points_2d[i];
auto p3d = points_3d[i];
EdgeProjection *edge = new EdgeProjection(p3d, K_eigen);
edge->setId(index);
edge->setVertex(0, vertex_pose);
edge->setMeasurement(p2d);
edge->setInformation(Eigen::Matrix2d::Identity());
optimizer.addEdge(edge);
index++;
}
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
optimizer.setVerbose(true);
optimizer.initializeOptimization();
optimizer.optimize(10);
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
chrono::duration<double> time_used = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double>>(t2 - t1);
cout << "optimization costs time: " << time_used.count() << " seconds." << endl;
cout << "pose estimated by g2o =\n" << vertex_pose->estimate().matrix() << endl;
pose = vertex_pose->estimate();
}
CMakeLists.txt:
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8)
project(3d2d)
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS} -std=c++11")
list(APPEND CMAKE_MODULE_PATH ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/cmake)
include_directories(inc)
aux_source_directory(src DIR_SRCS)
SET(SOUR_FILE ${DIR_SRCS})
find_package(OpenCV 3 REQUIRED)
find_package(G2O REQUIRED)
find_package(Sophus REQUIRED)
include_directories(
${OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIRS}
${G2O_INCLUDE_DIRS}
${Sophus_INCLUDE_DIRS}
"/usr/include/eigen3/"
)
add_executable(3d2d ${SOUR_FILE})
target_link_libraries(3d2d ${OpenCV_LIBS})
target_link_libraries(3d2d g2o_core g2o_stuff)
cmake文件夹:FindG2O.cmake
# Find the header files
FIND_PATH(G2O_INCLUDE_DIR g2o/core/base_vertex.h
${G2O_ROOT}/include
$ENV{G2O_ROOT}/include
$ENV{G2O_ROOT}
/usr/local/include
/usr/include
/opt/local/include
/sw/local/include
/sw/include
NO_DEFAULT_PATH
)
# Macro to unify finding both the debug and release versions of the
# libraries; this is adapted from the OpenSceneGraph FIND_LIBRARY
# macro.
MACRO(FIND_G2O_LIBRARY MYLIBRARY MYLIBRARYNAME)
FIND_LIBRARY("${MYLIBRARY}_DEBUG"
NAMES "g2o_${MYLIBRARYNAME}_d"
PATHS
${G2O_ROOT}/lib/Debug
${G2O_ROOT}/lib
$ENV{G2O_ROOT}/lib/Debug
$ENV{G2O_ROOT}/lib
NO_DEFAULT_PATH
)
FIND_LIBRARY("${MYLIBRARY}_DEBUG"
NAMES "g2o_${MYLIBRARYNAME}_d"
PATHS
~/Library/Frameworks
/Library/Frameworks
/usr/local/lib
/usr/local/lib64
/usr/lib
/usr/lib64
/opt/local/lib
/sw/local/lib
/sw/lib
)
FIND_LIBRARY(${MYLIBRARY}
NAMES "g2o_${MYLIBRARYNAME}"
PATHS
${G2O_ROOT}/lib/Release
${G2O_ROOT}/lib
$ENV{G2O_ROOT}/lib/Release
$ENV{G2O_ROOT}/lib
NO_DEFAULT_PATH
)
FIND_LIBRARY(${MYLIBRARY}
NAMES "g2o_${MYLIBRARYNAME}"
PATHS
~/Library/Frameworks
/Library/Frameworks
/usr/local/lib
/usr/local/lib64
/usr/lib
/usr/lib64
/opt/local/lib
/sw/local/lib
/sw/lib
)
IF(NOT ${MYLIBRARY}_DEBUG)
IF(MYLIBRARY)
SET(${MYLIBRARY}_DEBUG ${MYLIBRARY})
ENDIF(MYLIBRARY)
ENDIF( NOT ${MYLIBRARY}_DEBUG)
ENDMACRO(FIND_G2O_LIBRARY LIBRARY LIBRARYNAME)
# Find the core elements
FIND_G2O_LIBRARY(G2O_STUFF_LIBRARY stuff)
FIND_G2O_LIBRARY(G2O_CORE_LIBRARY core)
# Find the CLI library
FIND_G2O_LIBRARY(G2O_CLI_LIBRARY cli)
# Find the pluggable solvers
FIND_G2O_LIBRARY(G2O_SOLVER_CHOLMOD solver_cholmod)
FIND_G2O_LIBRARY(G2O_SOLVER_CSPARSE solver_csparse)
FIND_G2O_LIBRARY(G2O_SOLVER_CSPARSE_EXTENSION csparse_extension)
FIND_G2O_LIBRARY(G2O_SOLVER_DENSE solver_dense)
FIND_G2O_LIBRARY(G2O_SOLVER_PCG solver_pcg)
FIND_G2O_LIBRARY(G2O_SOLVER_SLAM2D_LINEAR solver_slam2d_linear)
FIND_G2O_LIBRARY(G2O_SOLVER_STRUCTURE_ONLY solver_structure_only)
FIND_G2O_LIBRARY(G2O_SOLVER_EIGEN solver_eigen)
# Find the predefined types
FIND_G2O_LIBRARY(G2O_TYPES_DATA types_data)
FIND_G2O_LIBRARY(G2O_TYPES_ICP types_icp)
FIND_G2O_LIBRARY(G2O_TYPES_SBA types_sba)
FIND_G2O_LIBRARY(G2O_TYPES_SCLAM2D types_sclam2d)
FIND_G2O_LIBRARY(G2O_TYPES_SIM3 types_sim3)
FIND_G2O_LIBRARY(G2O_TYPES_SLAM2D types_slam2d)
FIND_G2O_LIBRARY(G2O_TYPES_SLAM3D types_slam3d)
# G2O solvers declared found if we found at least one solver
SET(G2O_SOLVERS_FOUND "NO")
IF(G2O_SOLVER_CHOLMOD OR G2O_SOLVER_CSPARSE OR G2O_SOLVER_DENSE OR G2O_SOLVER_PCG OR G2O_SOLVER_SLAM2D_LINEAR OR G2O_SOLVER_STRUCTURE_ONLY OR G2O_SOLVER_EIGEN)
SET(G2O_SOLVERS_FOUND "YES")
ENDIF(G2O_SOLVER_CHOLMOD OR G2O_SOLVER_CSPARSE OR G2O_SOLVER_DENSE OR G2O_SOLVER_PCG OR G2O_SOLVER_SLAM2D_LINEAR OR G2O_SOLVER_STRUCTURE_ONLY OR G2O_SOLVER_EIGEN)
# G2O itself declared found if we found the core libraries and at least one solver
SET(G2O_FOUND "NO")
IF(G2O_STUFF_LIBRARY AND G2O_CORE_LIBRARY AND G2O_INCLUDE_DIR AND G2O_SOLVERS_FOUND)
SET(G2O_FOUND "YES")
ENDIF(G2O_STUFF_LIBRARY AND G2O_CORE_LIBRARY AND G2O_INCLUDE_DIR AND G2O_SOLVERS_FOUND)
视觉十四讲:第七讲_3D-2D:P3P的更多相关文章
- 视觉slam十四讲第七章课后习题6
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,转载请注明出处: http://www.cnblogs.com/newneul/p/8545450.html 6.在PnP优化中,将第一个相机的观测也考虑进来,程序应如何 ...
- 视觉slam十四讲第七章课后习题7
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,转载请注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/newneul/p/8544369.html 7.题目要求:在ICP程序中,将空间点也作为优化变量考虑进来 ...
- 视觉slam学习之路(一)看高翔十四讲所遇到的问题
目前实验室做机器人,主要分三个方向,定位导航,建图,图像识别,之前做的也是做了下Qt上位机,后面又弄红外识别,因为这学期上课也没怎么花时间在项目,然后导师让我们确定一个方向来,便于以后发论文什么. ...
- 浅读《视觉SLAM十四讲:从理论到实践》--操作1--初识SLAM
下载<视觉SLAM十四讲:从理论到实践>源码:https://github.com/gaoxiang12/slambook 第二讲:初识SLAM 2.4.2 Hello SLAM(书本P2 ...
- 高翔《视觉SLAM十四讲》从理论到实践
目录 第1讲 前言:本书讲什么:如何使用本书: 第2讲 初始SLAM:引子-小萝卜的例子:经典视觉SLAM框架:SLAM问题的数学表述:实践-编程基础: 第3讲 三维空间刚体运动 旋转矩阵:实践-Ei ...
- 高博-《视觉SLAM十四讲》
0 讲座 (1)SLAM定义 对比雷达传感器和视觉传感器的优缺点(主要介绍视觉SLAM) 单目:不知道尺度信息 双目:知道尺度信息,但测量范围根据预定的基线相关 RGBD:知道深度信息,但是深度信息对 ...
- 《视觉SLAM十四讲》第2讲
目录 一 视觉SLAM中的传感器 二 经典视觉SLAM框架 三 SLAM问题的数学表述 注:原创不易,转载请务必注明原作者和出处,感谢支持! 本讲主要内容: (1) 视觉SLAM中的传感器 (2) 经 ...
- 《视觉SLAM十四讲》第1讲
目录 一 视觉SLAM 注:原创不易,转载请务必注明原作者和出处,感谢支持! 一 视觉SLAM 什么是视觉SLAM? SLAM是Simultaneous Localization and Mappin ...
- 视觉SLAM十四讲:从理论到实践 两版 PDF和源码
视觉SLAM十四讲:从理论到实践 第一版电子版PDF 链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1SuuSpavo_fj7xqTYtgHBfw提取码:lr4t 源码github链接:htt ...
- 《SLAM十四讲》个人学习知识点梳理
0.引言 从六月末到八月初大概一个月时间一直在啃SLAM十四讲[1]这本书,这本书把SLAM中涉及的基本知识点都涵盖了,所以在这里做一个复习,对这本书自己学到的东西做一个梳理. 书本地址:http:/ ...
随机推荐
- ssh免交互
sshpass -p the_password ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no root@domainname_or_ip remote_command #远程执行命 ...
- Spring Security(1)
您好,我是湘王,这是我的博客园,欢迎您来,欢迎您再来- 虽然说互联网是一个非常开发.几乎没有边界的信息大海,但说起来有点奇怪的是,每个稍微有点规模的互联网应用都有自己的权限系统,而权限的本质却是是封闭 ...
- i春秋SQLi
打开题目网页是个很简单的登录网页 先查看源码,抓包 都没找到可用的信息 依我所见这里应该就是一个注入 但是怎么输入都会回显username错误 直到输入admin 尝试admin# Admin'# ...
- Python3 Scrapy 框架学习
1.安装scrapy 框架 windows 打开cmd输入 pip install Scrapy 2.新建一个项目: 比如这里我新建的项目名为first scrapy startproject fir ...
- day23 约束 & 锁 & 范式
考点: 乐观锁=>悲观锁=>锁 表与表的对应关系 一对一:学生与手机号,一个学生对一个手机号 一对多:班级与学生,一个班级对应多个学生 多对一: 多对多:学生与科目,一个学生对应多个科目, ...
- Windows 10 读取bitlocker加密的硬盘出现参数错误怎么解决?
我为了数据安全,用windows专业版的bitlocker加密了一个固态硬盘SSD做的移动硬盘(u盘同理),在家里电脑(windows10 家庭版)打开的时候出现了参数错误 即使密码输入正确还是这个错 ...
- js-day05-对象
为什么要学习对象 没有对象时,保存网站用户信息时不方便,很难区别 对象是什么 1.对象是一种数据类型 2.无序的数据集合 对象有什么特点 1.无序的数据的集合 2.可以详细的描述某个事物' 对象使用 ...
- JavaScript入门⑤-欲罢不能的对象原型与继承-全网一般图文版
JavaScript入门系列目录 JavaScript入门①-基础知识筑基 JavaScript入门②-函数(1)基础{浅出} JavaScript入门③-函数(2)原理{深入}执行上下文 JavaS ...
- 个人电脑公网IPv6配置
一.前言 自己当时以低价买的阿里ECS云服务器马上要过期了,对于搭建个人博客.NAS这样服务器的需求购买ECS服务器成本太高了,刚好家里有台小型的桌面式笔记本,考虑用作服务器,但是公网IPv4的地址实 ...
- 像go 一样 打造.NET 单文件应用程序的编译器项目bflat 发布 7.0版本
现代.NET和C#在低级/系统程序以及与C/C++/Rust等互操作方面的能力完全令各位刮目相看了,有人用C#开发的64位操作系统: GitHub - nifanfa/MOOS: C# x64 ope ...
