VC 运行时库的引用区别 /MD、/MDd 和 /MT、/MTd和DllMain函数
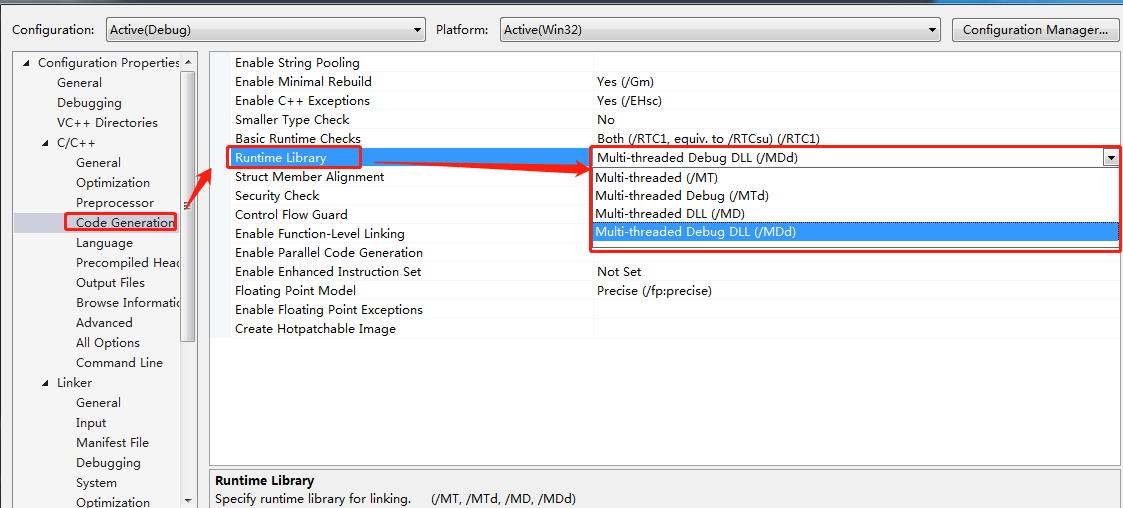
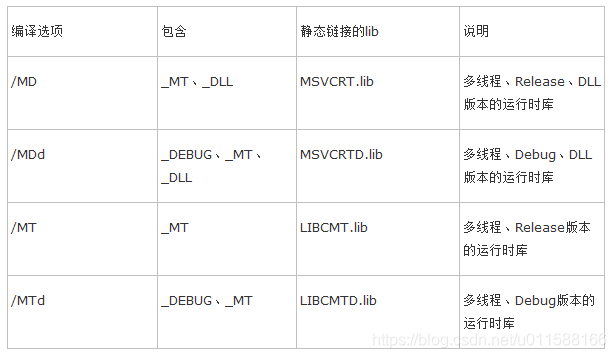
/MT和/MTd表示采用多线程CRT库的静态lib版本。该选项会在编译时将运行时库以静态lib的形式完全嵌入。该选项生成的可执行文件运行时不需要运行时库dll的参加,会获得轻微的性能提升,但最终生成的二进制代码因链入庞大的运行时库实现而变得非常臃肿。当某项目以静态链接库的形式嵌入到多个项目,则可能造成运行时库的内存管理有多份,最终将导致致命的“Invalid Address specified to RtlValidateHeap”问题。另外托管C++和CLI中不再支持/MT和/MTd选项。
/MD和/MDd表示采用多线程CRT库的动态dll版本,会使应用程序使用运行时库特定版本的多线程DLL。链接时将按照传统VC链接dll的方式将运行时库MSVCRxx.DLL的导入库MSVCRT.lib链接,在运行时要求安装了相应版本的VC运行时库可再发行组件包(当然把这些运行时库dll放在应用程序目录下也是可以的)。 因/MD和/MDd方式不会将运行时库链接到可执行文件内部,可有效减少可执行文件尺寸。当多项目以MD方式运作时,其内部会采用同一个堆,内存管理将被简化,跨模块内存管理问题也能得到缓解。
结论:/MD和/MDd将是潮流所趋,/ML和/MLd方式请及时放弃,/MT和/MTd在非必要时最好也不要采用了
DllMain函数(说白了一般就是在加载卸载DLL时被调用)
MSDN官方说明:DllMain entry point (Process.h) - Win32 apps | Microsoft Docs
An optional entry point into a dynamic-link library (DLL). When the system starts or terminates a process or thread, it calls the entry-point function for each loaded DLL using the first thread of the process. The system also calls the entry-point function for a DLL when it is loaded or unloaded using the LoadLibrary and FreeLibrary functions.
Example
BOOL WINAPI DllMain(HINSTANCE hinstDLL, // handle to DLL moduleDWORD fdwReason, // reason for calling functionLPVOID lpReserved ) // reserved{// Perform actions based on the reason for calling.switch( fdwReason ){case DLL_PROCESS_ATTACH:// Initialize once for each new process.// Return FALSE to fail DLL load.break;case DLL_THREAD_ATTACH:// Do thread-specific initialization.break;case DLL_THREAD_DETACH:// Do thread-specific cleanup.break;case DLL_PROCESS_DETACH:// Perform any necessary cleanup.break;}return TRUE; // Successful DLL_PROCESS_ATTACH.}
This is an example from the Dynamic-Link Library Entry-Point Function.
Warning
There are significant limits on what you can safely do in a DLL entry point. See General Best Practices for specific Windows APIs that are unsafe to call in DllMain. If you need anything but the simplest initialization then do that in an initialization function for the DLL. You can require applications to call the initialization function after DllMain has run and before they call any other functions in the DLL.
Syntax
BOOL WINAPI DllMain(_In_ HINSTANCE hinstDLL,_In_ DWORD fdwReason,_In_ LPVOID lpvReserved);
Parameters
hinstDLL [in]
-
A handle to the DLL module. The value is the base address of the DLL. The HINSTANCE of a DLL is the same as the HMODULE of the DLL, so hinstDLL can be used in calls to functions that require a module handle.
fdwReason [in]
-
The reason code that indicates why the DLL entry-point function is being called. This parameter can be one of the following values.
TABLE 1 Value Meaning - DLL_PROCESS_ATTACH
- 1
The DLL is being loaded into the virtual address space of the current process as a result of the process starting up or as a result of a call to LoadLibrary. DLLs can use this opportunity to initialize any instance data or to use the TlsAlloc function to allocate a thread local storage (TLS) index.
The lpReserved parameter indicates whether the DLL is being loaded statically or dynamically.- DLL_PROCESS_DETACH
- 0
The DLL is being unloaded from the virtual address space of the calling process because it was loaded unsuccessfully or the reference count has reached zero (the processes has either terminated or called FreeLibrary one time for each time it called LoadLibrary).
The lpReserved parameter indicates whether the DLL is being unloaded as a result of a FreeLibrary call, a failure to load, or process termination.
The DLL can use this opportunity to call the TlsFree function to free any TLS indices allocated by using TlsAlloc and to free any thread local data.
Note that the thread that receives the DLL_PROCESS_DETACH notification is not necessarily the same thread that received the DLL_PROCESS_ATTACH notification.- DLL_THREAD_ATTACH
- 2
The current process is creating a new thread. When this occurs, the system calls the entry-point function of all DLLs currently attached to the process. The call is made in the context of the new thread. DLLs can use this opportunity to initialize a TLS slot for the thread. A thread calling the DLL entry-point function with DLL_PROCESS_ATTACH does not call the DLL entry-point function with DLL_THREAD_ATTACH.
Note that a DLL's entry-point function is called with this value only by threads created after the DLL is loaded by the process. When a DLL is loaded using LoadLibrary, existing threads do not call the entry-point function of the newly loaded DLL.- DLL_THREAD_DETACH
- 3
A thread is exiting cleanly. If the DLL has stored a pointer to allocated memory in a TLS slot, it should use this opportunity to free the memory. The system calls the entry-point function of all currently loaded DLLs with this value. The call is made in the context of the exiting thread.
lpvReserved [in]
-
If fdwReason is DLL_PROCESS_ATTACH, lpvReserved is NULL for dynamic loads and non-NULL for static loads.
If fdwReason is DLL_PROCESS_DETACH, lpvReserved is NULL if FreeLibrary has been called or the DLL load failed and non-NULL if the process is terminating.
Return value
When the system calls the DllMain function with the DLL_PROCESS_ATTACH value, the function returns TRUE if it succeeds or FALSE if initialization fails. If the return value is FALSE when DllMain is called because the process uses the LoadLibrary function, LoadLibrary returns NULL. (The system immediately calls your entry-point function with DLL_PROCESS_DETACH and unloads the DLL.) If the return value is FALSE when DllMain is called during process initialization, the process terminates with an error. To get extended error information, call GetLastError.
When the system calls the DllMain function with any value other than DLL_PROCESS_ATTACH, the return value is ignored.
Remarks
DllMain is a placeholder for the library-defined function name. You must specify the actual name you use when you build your DLL. For more information, see the documentation included with your development tools.
During initial process startup or after a call to LoadLibrary, the system scans the list of loaded DLLs for the process. For each DLL that has not already been called with the DLL_PROCESS_ATTACH value, the system calls the DLL's entry-point function. This call is made in the context of the thread that caused the process address space to change, such as the primary thread of the process or the thread that called LoadLibrary. Access to the entry point is serialized by the system on a process-wide basis. Threads in DllMain hold the loader lock so no additional DLLs can be dynamically loaded or initialized.
If the DLL's entry-point function returns FALSE following a DLL_PROCESS_ATTACH notification, it receives a DLL_PROCESS_DETACH notification and the DLL is unloaded immediately. However, if the DLL_PROCESS_ATTACH code throws an exception, the entry-point function will not receive the DLL_PROCESS_DETACH notification.
There are cases in which the entry-point function is called for a terminating thread even if the entry-point function was never called with DLL_THREAD_ATTACH for the thread:
- The thread was the initial thread in the process, so the system called the entry-point function with the DLL_PROCESS_ATTACH value.
- The thread was already running when a call to the LoadLibrary function was made, so the system never called the entry-point function for it.
When a DLL is unloaded from a process as a result of an unsuccessful load of the DLL, termination of the process, or a call to FreeLibrary, the system does not call the DLL's entry-point function with the DLL_THREAD_DETACH value for the individual threads of the process. The DLL is only sent a DLL_PROCESS_DETACH notification. DLLs can take this opportunity to clean up all resources for all threads known to the DLL.
When handling DLL_PROCESS_DETACH, a DLL should free resources such as heap memory only if the DLL is being unloaded dynamically (the lpReserved parameter is NULL). If the process is terminating (the lpvReserved parameter is non-NULL), all threads in the process except the current thread either have exited already or have been explicitly terminated by a call to the ExitProcess function, which might leave some process resources such as heaps in an inconsistent state. In this case, it is not safe for the DLL to clean up the resources. Instead, the DLL should allow the operating system to reclaim the memory.
If you terminate a process by calling TerminateProcess or TerminateJobObject, the DLLs of that process do not receive DLL_PROCESS_DETACH notifications. If you terminate a thread by calling TerminateThread, the DLLs of that thread do not receive DLL_THREAD_DETACH notifications.
The entry-point function should perform only simple initialization or termination tasks. It must not call the LoadLibrary or LoadLibraryEx function (or a function that calls these functions), because this may create dependency loops in the DLL load order. This can result in a DLL being used before the system has executed its initialization code. Similarly, the entry-point function must not call the FreeLibrary function (or a function that calls FreeLibrary) during process termination, because this can result in a DLL being used after the system has executed its termination code.
Because Kernel32.dll is guaranteed to be loaded in the process address space when the entry-point function is called, calling functions in Kernel32.dll does not result in the DLL being used before its initialization code has been executed. Therefore, the entry-point function can call functions in Kernel32.dll that do not load other DLLs. For example, DllMain can create synchronization objects such as critical sections and mutexes, and use TLS. Unfortunately, there is not a comprehensive list of safe functions in Kernel32.dll.
Calling functions that require DLLs other than Kernel32.dll may result in problems that are difficult to diagnose. For example, calling User, Shell, and COM functions can cause access violation errors, because some functions load other system components. Conversely, calling functions such as these during termination can cause access violation errors because the corresponding component may already have been unloaded or uninitialized.
Because DLL notifications are serialized, entry-point functions should not attempt to communicate with other threads or processes. Deadlocks may occur as a result.
For information on best practices when writing a DLL, see https://docs.microsoft.com/windows/win32/dlls/dynamic-link-library-best-practices.
If your DLL is linked with the C run-time library (CRT), the entry point provided by the CRT calls the constructors and destructors for global and static C++ objects. Therefore, these restrictions for DllMain also apply to constructors and destructors and any code that is called from them.
Consider calling DisableThreadLibraryCalls when receiving DLL_PROCESS_ATTACH, unless your DLL is linked with static C run-time library (CRT).
Requirements
| Requirement | Value |
|---|---|
| Minimum supported client | Windows XP [desktop apps only] |
| Minimum supported server | Windows Server 2003 [desktop apps only] |
| Header |
|
VC 运行时库的引用区别 /MD、/MDd 和 /MT、/MTd和DllMain函数的更多相关文章
- VC 运行时库 /MD、/MDd 和 /MT、/MTd
这里总结下他们的区别,后面的那个'd'是代表DEBUG版本,没有'd'的就是RELEASE版本了. 首先说/MT /MT是 "multithread, static version ” 意思 ...
- VC运行时库(/MD、/MT等)
VC项目属性→配置属性→C/C++→代码生成→运行时库 可以采用的方式有:多线程(/MT).多线程调试(/MTd).多线程DLL(/MD).多线程调试DLL(/MDd).单线程(/ML).单线程调试( ...
- VC运行时库/MD、/MDd、/MT、/MTd说明
http://blog.csdn.net/holybin/article/details/26134153 VC运行时库设置:VC项目属性->配置属性->C/C++->代码生成-&g ...
- vs2015部署---下一代VC运行时库系统:the Universal CRT
前言 其实the Universal CRT(通用C运行时库)已经不能算是“下一代”,因为它已经在前两年伴随着Visual Studio 2015和Windows10发布.但是由于之前使用VS2015 ...
- /MD, /MDD, /ML, /MT,/MTD(使用运行时库)
1. VC编译选项 多线程(/MT)多线程调试(/MTd)多线程 DLL (/MD)多线程调试 DLL (/MDd) 2. C 运行时库 ...
- 定位vc运行时库问题 依赖问题,屡试不爽的一招
用vc 菜单 文件| 打开|指定EXE或DLL,如有指定运行时库,则PE文件的资源中可以看到manifest 配置节 然后据此判断EXE依赖的运行时库, 再根据编译选项调整 运行时库设置
- VC编译选项 md /mdd /ml /mt/mtd
VC编译选项 多线程(/MT)多线程调试(/MTd)多线程 DLL (/MD)多线程调试 DLL (/MDd)C 运行时库 库文件Single threa ...
- VC C运行时库(CRTL)的几个版本及选用
分类: Windows 2008-12-23 10:01 987人阅读 评论(0) 收藏 举报ciostreammfclibrary多线程import最近做项目碰到了一个关于在动态库中使用MFC以及在 ...
- [转帖]运行时库(runtime library)
运行时库(runtime library) https://blog.csdn.net/xitie8523/article/details/82712105 没学过这些东西 或者当时上课没听 又或者 ...
- Visual C++中对运行时库的支持
原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/wqvbjhc/article/details/6612099 一.什么是C运行时库 1)C运行时库就是 C run-time library,是 ...
随机推荐
- C# 报表接口样例,简单实用
//连接视图名称,视图在数据库写好<%@ WebHandler Language="C#" Class="GetwmsReport" %> usin ...
- 以图搜图(demo创建流程)
window10添加向量数据库以及调用 创建docker 1,在windows功能中打开Hyper-V 和 容器 2,进入https://www.docker.com/ ,下载windows版本进行安 ...
- leecode64. 最小路径和(动态规划)
64. 最小路径和 给定一个包含非负整数的 m x n 网格 grid ,请找出一条从左上角到右下角的路径,使得路径上的数字总和为最小. 说明:每次只能向下或者向右移动一步. 示例 1: 输入:gri ...
- 微信小程序 table表格 固定表头和首列 右侧表格可以左右滚动(多种表格演练)
https://blog.csdn.net/m0_61073617/article/details/124430213
- Python爬取网页上想要的数据
1.源代码如下 from urllib.request import urlopen,Request import urllib.request import re from bs4 import B ...
- csv文件导入数据库中文乱码
在向数据库的表中导入csv数据时,出现了中文乱码的问题,解决办法是在选择编码格式时选择10008 (MAC - Simplified Chinese GB 2312)即可
- Mac上好用的app们
记录下自己在mac上用的一些很不错的app,大多免费. 排名随缘. 不定期更新. Amphetamine 来源 AppStore 说明 欢迎使用Amphetamine,一款为macOS打造的最棒的防睡 ...
- lowcodeEngine设计器源码简析(创建流程,主要对象), 怎么生成一个左侧面板
lowcodeEngine 怎么生成一个左侧面板 初始化流程 如何生成一个左侧面板 初始化插件时往skeleton.leftArea新增按钮,新增按钮时往skeleton.leftFloatArea新 ...
- HCIP-ICT实战进阶08-以太网链路的聚合和集群
HCIP-ICT实战进阶08-以太网链路的聚合和集群 1 网络可靠性需求 网络可靠性可以从设备.链路多个层面实现, 保持当前设备或链路出现单点或者多点故障时保证网络服务不间断的能力. 网络可靠性 设备 ...
- Linux 第六节( 磁盘系统,挂载,分区,格式化)
/dev/st0 磁带机 /dev/lp 打印机 /dev/cdrom 光驱 /dev/sd scsi接口硬盘 sata接口硬盘 U盘(sda,sdb,sdc 分别对应 ...
