day10-AOP-03
AOP-03
7.AOP-切入表达式
7.1切入表达式的具体使用
1.切入表达式的作用:
通过表达式的方式定义一个或多个具体的连接点。
2.语法细节:
(1)切入表达式的语法格式:
execution([权限修饰符] [返回值类型] [简单类名/全类名] [方法名]([参数列表])
若目标类、接口与该切面类在用同一个包中,可以省略包名,只写简单类名
(2)举例说明:
例子1:
表达式:execution(* com.sina.spring.ArithmeticCalculator.*(..))
含义:ArithmeticCalculator.* :接口中声明的所有方法。第一个 * 代表任意修饰符和任意返回值。 第二个 * 代表任意方法。.. 代表匹配任意数量和任意类型的参数,若目标类、接口与该切面类在用同一个包中,可以省略包名。
例子2:
表达式:execution(public * ArithmeticCalculator.*(..))
含义:ArithmeticCalculator 接口中的所有公有方法
例子3:
表达式:execution(public double ArithmeticCalculator.*(..))
含义:ArithmeticCalculator 接口中返回 double 类型数值的方法
例子4:
表达式:execution(public double ArithmeticCalculator.*(double, ..))
含义:第一个参数为double 类型的方法。.. 匹配任意数量、任意类型的参数。
例子5:
表达式:execution(public double ArithmeticCalculator.*(double, double))
含义:参数类型为double ,double 类型的方法。
(3)在AspectJ中,切入点表达式可以通过 && 或者 || 或者 ! 等操作符结合起来
例子:
表达式:execution(* *.add(int, ..))|| exexution(* *.sub(int, ..))
含义:任意类中第一个参数为 int 类型的 add 方法或 sub 方法
7.2注意事项和细节
切入表达式可以指向(实现了接口的)类的方法,这时切入表达式会对该类/对象生效
切入表达式也可以指向接口的方法,这时切入表达式会对实现了接口的类/对象生效
切入表达式可以对没有实现接口的类进行切入。
这涉及到CGlib动态代理:动态代理jdk的Proxy与spring的CGlib
两个动态代理的区别:
JDK动态代理是面向接口的,只能增强实现类中接口中存在的方法。CGlib是面向父类的,可以增强父类的所有方法
JDK得到的对象是JDK代理对象实例,而CGlib得到的对象是被代理对象的子类
静态代理例子:
一个普通类Car:
package com.li.aop.hw;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author 李
* @version 1.0
*/
@Component
public class Car {
public void run() {
System.out.println("小汽车在running...");
}
}
MyAspect切面类:
package com.li.aop.hw;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* @author 李
* @version 1.0
* 切面类
*/
@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAspect {
//CGlib
//给没有实现接口的一个普通类设置前置通知,其他通知亦可以设置
@Before(value = "execution(public void Car.run())")
public void ok(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("MyAspect前置通知ok()-目标方法-" + methodName +
" 参数-" + Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs()));
}
}
测试类:
package com.li.aop.hw;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
/**
* @author 李
* @version 1.0
*/
public class UsbTest {
@Test
public void UsbAspectTest() {
ApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans08.xml");
//carProxy是 被代理对象的子类
Car carProxy = ioc.getBean(Car.class);
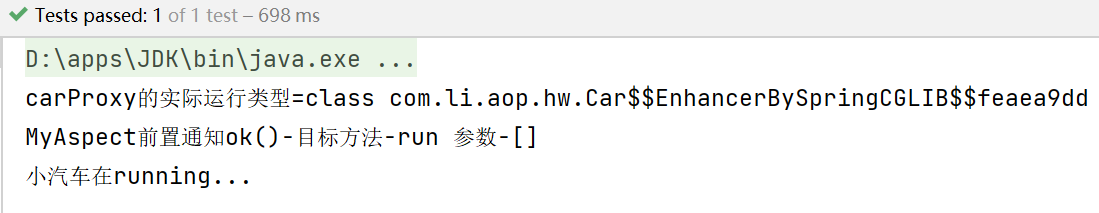
System.out.println("carProxy的实际运行类型=" + carProxy.getClass());
carProxy.run();
}
}
测试结果:
8.AOP-JoinPoint
在切面类的通知方法中,可以通过 JoinPoint对象获取到目标方法的一系列信息:
| JoinPoint对象的方法 | 释义 |
|---|---|
| getSignature().getName() | 获取目标方法名 |
| getSignature().getDeclaringType().getSimpleName() | 获取目标方法所属类的简单类名 |
| getSignature().getDeclaringTypeName() | 获取目标方法所属类的全类名 |
| getSignature().getModifiers() | 获取目标方法声明类型(public/private/protected) |
| getArgs() | 获取传入目标方法的参数,返回一个数组 |
| getTarget() | 获取被代理的对象 |
| getThis() | 获取代理对象自己 |
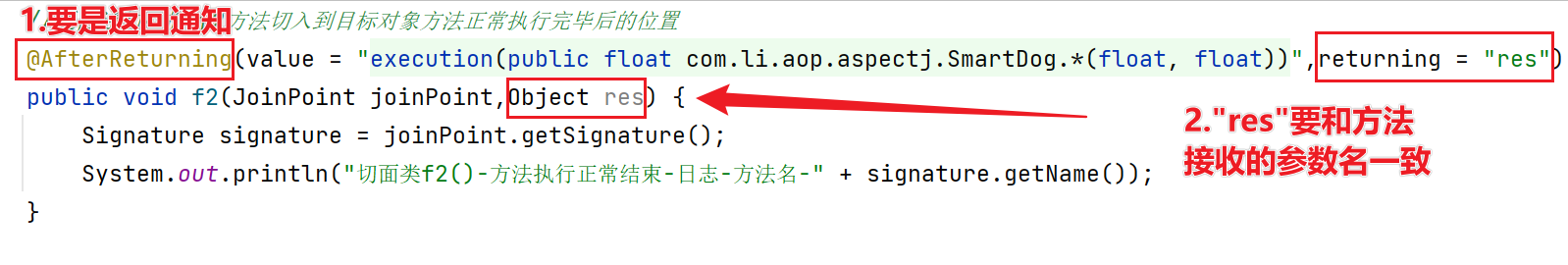
9.AOP-返回通知获取结果
- 在返回通知 @AfterReturning 中,可以获取目标方法返回的结果。
我们在 @AfterReturning (返回通知)的注解源码中可以看到有一个returning属性。通过 returning 属性可以获取目标方法执行完毕后,返回的结果。
底层大概是:在反射执行目标方法时,将目标方法返回的结果赋给 returning 的定义的变量,然后赋给切入方法同名的参数。

例子
必须在返回通知中,才能获取目标方法的返回值
returning 属性定义的变量,要和切入方法接收的参数名称一致。
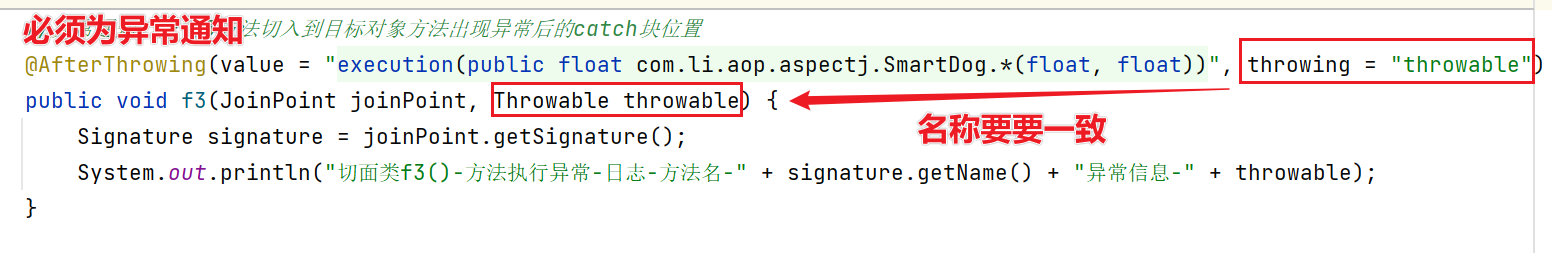
10.AOP-异常通知中获取异常
- 在异常通知中,可以获取目标方法出现异常的信息
异常通知 @AfterThrowing 中有一个throwing 的属性,它可以接收异常信息

例子
11.AOP-环绕通知
- 环绕通知可以完成其他四个通知要做的事情(了解即可)
以AOP-02-6.2 快速入门为例子
接口为 SmartAnimal.java,实现类为 SmartDog.java
切面类为 SmartAnimalAspect2.java:
package com.li.aop.aspectj;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author 李
* @version 1.0
* 切面类-这里主要演示环绕通知
*/
@Aspect
@Component
public class SmartAnimalAspect2 {
//环绕通知
/**
* 1.@Around 表示环绕通知,它可以完成其他四个通知的功能
* 2.value = "execution(...)" 切入表达式
* 3.doAround() 表示要切入的方法,调用结构为 try-catch-finally
*
* @param joinPoint 如果是环绕通知,需要用到 ProceedingJoinPoint
* @return
*/
@Around(value = "execution(public float com.li.aop.aspectj.SmartDog.getSum(float, float))")
public Object doAround(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) {
Object result = null;
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
try {
//1.相当于前置通知完成的事情
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
List<Object> argList = Arrays.asList(args);
System.out.println("AOP 环绕通知 " + methodName + "方法开始了--参数有:" + argList);
//在环绕通知中一定要调用 joinPoint.proceed()来执行目标方法
result = joinPoint.proceed();
//2.相当于返回通知完成的事情
System.out.println("AOP 环绕通知 " + methodName + "方法结束了--结果是:" + result);
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
//3.相当于异常通知完成的事情
System.out.println("AOP 环绕通知 " + methodName + "方法抛异常了--异常对象:" + throwable);
} finally {
//4.相当于最终通知完成的事情
System.out.println("AOP 环绕通知 " + methodName + "方法最终结束了...");
}
return result;
}
}
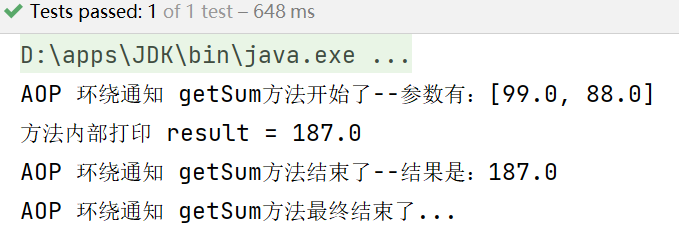
测试方法:
@Test
public void testDoAround(){
//得到ioc容器
ApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans07.xml");
//获取代理对象
SmartAnimal smartAnimal = ioc.getBean(SmartAnimal.class);
//执行方法
smartAnimal.getSum(99,88);
}
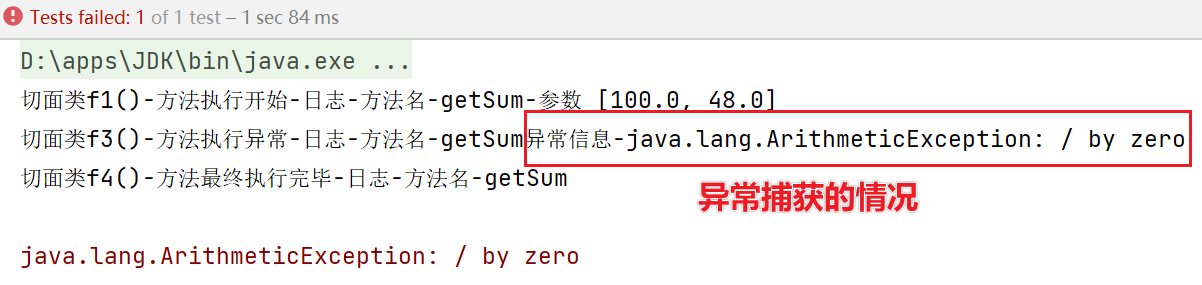
测试结果:
12.AOP-切入点表达式重用
切入点表达式重用
为了统一管理切入点表达式,可以使用切入点表达式重用/复用技术。
以AOP-02-6.2 快速入门为例子
接口为 SmartAnimal.java,实现类为 SmartDog.java
切面类为 SmartAnimalAspect.java:
package com.li.aop.aspectj;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.Signature;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* @author 李
* @version 1.0
* 切面类
*/
@Aspect
@Component
public class SmartAnimalAspect {
//定义一个切入点,在后面使用时可以直接引用,提高复用性
@Pointcut(value = "execution(public float com.li.aop.aspectj.SmartDog.*(float, float))")
public void myPointCut() {
}
//前置通知
//@Before(value = "execution(public float com.li.aop.aspectj.SmartDog.*(float, float))")
//这里我们使用定义好的切入点
@Before(value = "myPointCut()")
public void f1(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
//通过连接点对象joinPoint 拿到方法签名
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("切面类f1()-方法执行开始-日志-方法名-" + signature.getName() +
"-参数 " + Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs()));
}
//返回通知
//@AfterReturning(value = "execution(public float com.li.aop.aspectj.SmartDog.*(float, float))", returning = "res")
@AfterReturning(value = "myPointCut()", returning = "res")
public void f2(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object res) {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("切面类f2()-方法执行正常结束-日志-方法名-" + signature.getName());
System.out.println("目标方法返回的结果=" + res);
}
//异常通知
//@AfterThrowing(value = "execution(public float com.li.aop.aspectj.SmartDog.*(float, float))", throwing = "throwable")
@AfterThrowing(value = "myPointCut()", throwing = "throwable")
public void f3(JoinPoint joinPoint, Throwable throwable) {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("切面类f3()-方法执行异常-日志-方法名-" + signature.getName() + "异常信息-" + throwable);
}
//最终通知
//@After(value = "execution(public float com.li.aop.aspectj.SmartDog.*(float, float))")
@After(value = "myPointCut()")
public void f4(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("切面类f4()-方法最终执行完毕-日志-方法名-" + signature.getName());
}
}
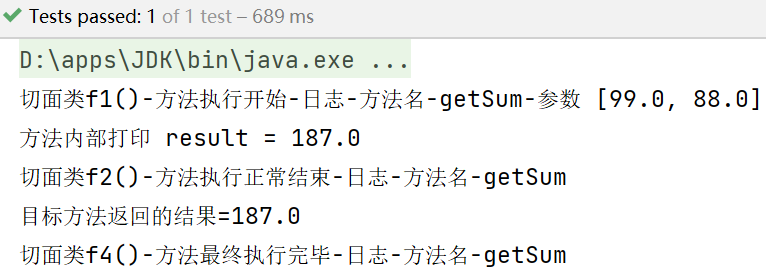
测试:
@Test
public void test(){
//得到ioc容器
ApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans07.xml");
//获取代理对象
SmartAnimal smartAnimal = ioc.getBean(SmartAnimal.class);
//执行方法
smartAnimal.getSum(99,88);
}
测试结果:
13.AOP-切面优先级问题
如果同一个方法,有多个切面在同一个切入点切入,那么执行的优先级如何控制?
答:在切面类声明时,使用@Order注解控制优先级:n值越小,优先级越高
@Order(value=n) //n值越小,优先级越高
例子-以AOP-02-6.2 快速入门为例子
接口为 SmartAnimal.java,实现类为 SmartDog.java,两个切面类: SmartAnimalAspect.java 和 SmartAnimalAspect2.java
SmartAnimalAspect.java:
package com.li.aop.aspectj;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.Signature;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* @author 李
* @version 1.0
* 切面类1
*/
@Aspect
@Component
@Order(value = 2)//表示该切面类执行的顺序,value越小,优先级越高
public class SmartAnimalAspect {
//定义一个切入点,在后面使用时可以直接引用,提高复用性
@Pointcut(value = "execution(public float com.li.aop.aspectj.SmartDog.*(float, float))")
public void myPointCut() {
}
//前置通知
@Before(value = "myPointCut()")
public void f1(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
//通过连接点对象joinPoint 拿到方法签名
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("切面类1-f1()-方法执行开始-日志-方法名-" + signature.getName() +
"-参数 " + Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs()));
}
//返回通知
@AfterReturning(value = "myPointCut()", returning = "res")
public void f2(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object res) {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("切面类1-f2()-方法执行正常结束-日志-方法名-" + signature.getName() + " 目标方法返回的结果=" + res);
}
//异常通知
@AfterThrowing(value = "myPointCut()", throwing = "throwable")
public void f3(JoinPoint joinPoint, Throwable throwable) {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("切面类1-f3()-方法执行异常-日志-方法名-" + signature.getName() + "异常信息-" + throwable);
}
//最终通知
@After(value = "myPointCut()")
public void f4(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("切面类1-f4()-方法最终执行完毕-日志-方法名-" + signature.getName());
}
}
SmartAnimalAspect2.java:
package com.li.aop.aspectj;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.Signature;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* @author 李
* @version 1.0
* 切面类 2
*/
@Aspect
@Component
@Order(value = 1)
public class SmartAnimalAspect2 {
@Before(value = "execution(public float com.li.aop.aspectj.SmartDog.*(float, float))")
public void f1(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("切面类2-f1()-方法执行开始-日志-方法名-" + signature.getName() +
"-参数 " + Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs()));
}
//返回通知:
@AfterReturning(value = "execution(public float com.li.aop.aspectj.SmartDog.*(float, float))", returning = "res")
public void f2(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object res) {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("切面类2-f2()-方法执行正常结束-日志-方法名-" + signature.getName() + " 目标方法返回的结果=" + res);
}
//异常通知:
@AfterThrowing(value = "execution(public float com.li.aop.aspectj.SmartDog.*(float, float))", throwing = "throwable")
public void f3(JoinPoint joinPoint, Throwable throwable) {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("切面类2-f3()-方法执行异常-日志-方法名-" + signature.getName() + "异常信息-" + throwable);
}
//最终通知:
@After(value = "execution(public float com.li.aop.aspectj.SmartDog.*(float, float))")
public void f4(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("切面类2-f4()-方法最终执行完毕-日志-方法名-" + signature.getName());
}
}
测试方法:
@Test
public void smartDogTestByAspectj() {
//得到Spring容器
ApplicationContext ioc =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans07.xml");
//通过接口类型来获得注入的SmartDog对象(实际上是代理对象proxy)
SmartAnimal smartAnimal = ioc.getBean(SmartAnimal.class);
smartAnimal.getSum(100, 48);
}
测试结果:

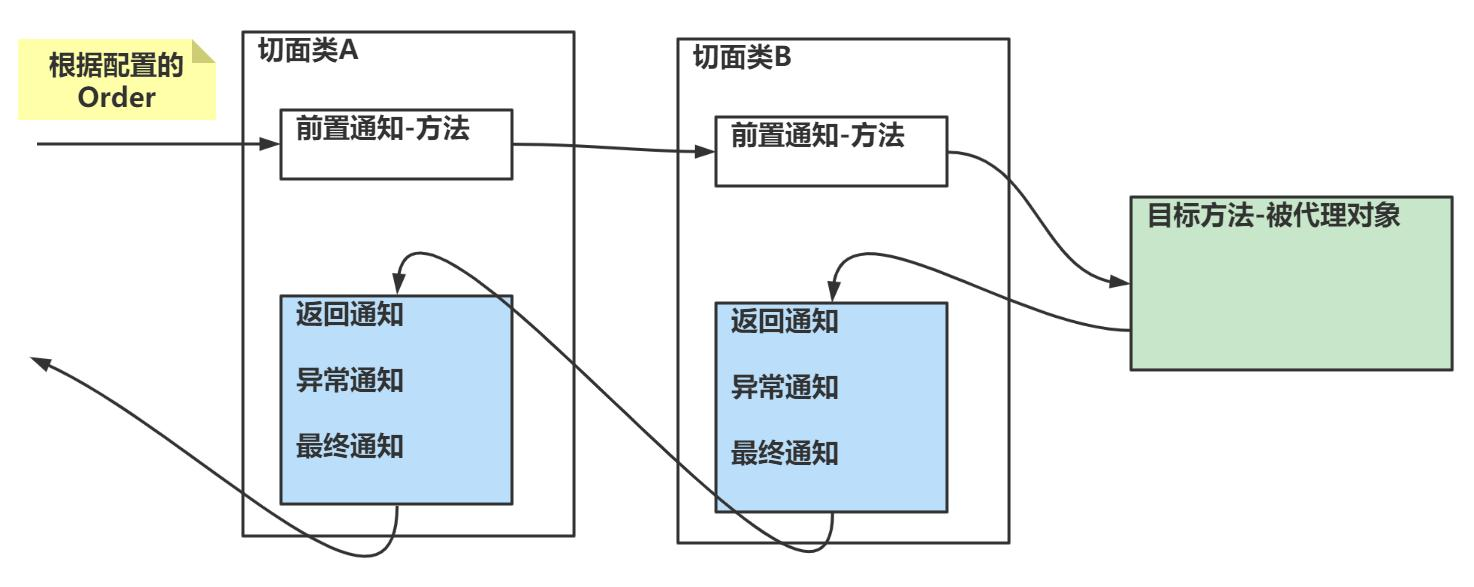
注意事项和细节:
不能理解成:优先级高的切面类,每个消息通知都先执行。
真实的执行顺序和 Filter 过滤器链式调用类似:
14.基于XML配置AOP
前面我们都是通过注解来配置aop的,在spring中,同样支持通过xml的方式来配置aop
例子
1.SmartAnimal 接口:
package com.li.aop.xml;
/**
* @author 李
* @version 1.0
*/
public interface SmartAnimal {
//求和
float getSum(float a, float b);
//求差
float getSub(float a, float b);
}
2.SmartDog 实现类:
package com.li.aop.xml;
/**
* @author 李
* @version 1.0
*/
public class SmartDog implements SmartAnimal {
@Override
public float getSum(float a, float b) {
float result = a + b;
System.out.println("方法内部打印 result = " + result);
return result;
}
@Override
public float getSub(float a, float b) {
float result = a - b;
System.out.println("方法内部打印 result = " + result);
return result;
}
}
3.SmartAnimalAspect 切面类:
package com.li.aop.xml;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.Signature;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* @author 李
* @version 1.0
* 这是一个切面类,使用xml的方法配置
*/
public class SmartAnimalAspect {
public void showBeginLog(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("xml-showBeginLog()-方法执行开始-日志-方法名-" + signature.getName() +
"-参数 " + Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs()));
}
public void showSuccessEndLog(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object res) {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("xml-showSuccessEndLog()-方法执行正常结束-日志-方法名-" + signature.getName() + " 目标方法返回的结果=" + res);
}
public void showExceptionLog(JoinPoint joinPoint, Throwable throwable) {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("xml-showExceptionLog()-方法执行异常-日志-方法名-" + signature.getName() + "异常信息-" + throwable);
}
public void showFinallyEndLog(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("xml-showFinallyEndLog()-方法最终执行完毕-日志-方法名-" + signature.getName());
}
}
4.xml容器文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!--使用xml配置完成aop编程-->
<!--配置一个切面类对象 bean-->
<bean class="com.li.aop.xml.SmartAnimalAspect" id="smartAnimalAspect"/>
<!--配置一个SmartDog对象-->
<bean class="com.li.aop.xml.SmartDog" id="smartDog"/>
<!--配置切面类 (注意要引入aop名称空间)-->
<aop:config>
<!--先配置切入点-->
<aop:pointcut id="myPointCut" expression="execution(public float com.li.aop.xml.SmartDog.*(float, float))"/>
<!--配置切面的前置/返回/异常/最终通知-->
<aop:aspect ref="smartAnimalAspect" order="10">
<!--配置前置通知-->
<aop:before method="showBeginLog" pointcut-ref="myPointCut"/>
<!--配置返回通知-->
<aop:after-returning method="showSuccessEndLog" pointcut-ref="myPointCut" returning="res"/>
<!--配置异常通知-->
<aop:after-throwing method="showExceptionLog" pointcut-ref="myPointCut" throwing="throwable"/>
<!--最终通知-->
<aop:after method="showFinallyEndLog" pointcut-ref="myPointCut"/>
<!--还可以配置环绕通知...-->
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>
5.测试类:
package com.li.aop.xml;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
/**
* @author 李
* @version 1.0
* 测试类
*/
public class AopAspectjXMLTest {
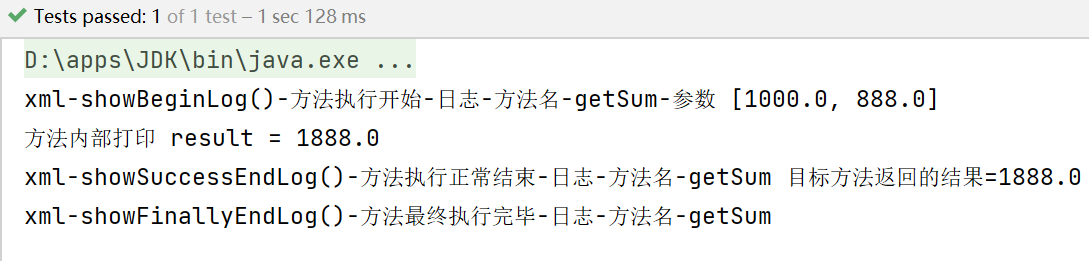
@Test
public void testAspectjByXML() {
ApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans09.xml");
SmartAnimal smartAnimalProxy = ioc.getBean(SmartAnimal.class);
smartAnimalProxy.getSum(1000, 888);
}
}
测试结果:
15.aop练习
请编写一个Cal接口,该接口有两个方法:
- cal1(int n),计算1 + 2 + ... + n
- cal2(int n),计算1 * 2 *... * n
Cal 实现类为 MyCal
请分别使用注解方式和xml配置的方式,完成aop编程
- 在执行 cal2 前打印开始执行的时间,在执行完后打印时间
- 在执行 cal2 前打印开始执行的时间,在执行完后打印时间
(1)xml配置的方式:
Cal:
package com.li.aop.hw2;
/**
* @author 李
* @version 1.0
*/
public interface Cal {
//累加
public void cal1(int n);
//累乘
public void cal2(int n);
}
MyCal:
package com.li.aop.hw2;
/**
* @author 李
* @version 1.0
*/
public class MyCal implements Cal {
@Override
public void cal1(int n) {
int result = 0;
if (n >= 1) {
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
result += i;
}
System.out.println("cal1-result=" + result);
return;
}
System.out.println("cal1-参数有误");
}
@Override
public void cal2(int n) {
int result = 1;
if (n >= 1) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
result *= i;
}
System.out.println("cal2-result=" + result);
return;
}
System.out.println("cal2-参数有误");
}
}
切面类:
package com.li.aop.hw2;
/**
* @author 李
* @version 1.0
* 切面类
*/
public class CalAspect {
//前置通知
public void beforeTime() {
System.out.println("开始执行计算 "+System.currentTimeMillis());
}
//返回通知
public void returningTime() {
System.out.println("结束执行计算 "+System.currentTimeMillis());
}
}
xml容器配置文件:
<!--配置实现类对象bean-->
<bean class="com.li.aop.hw2.MyCal" id="myCal"/>
<!--配置切面类对象bean-->
<bean class="com.li.aop.hw2.CalAspect" id="calAspect"/>
<aop:config>
<!--配置切入点表达式-->
<aop:pointcut id="myPointCut" expression="execution(public void com.li.aop.hw2.MyCal.*(int))"/>
<!--配置切面类-->
<aop:aspect ref="calAspect">
<!--前置通知-->
<aop:before method="beforeTime" pointcut-ref="myPointCut"/>
<!--返回通知-->
<aop:after-returning method="returningTime" pointcut-ref="myPointCut"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
测试方法:
@Test
public void myCalTest() {
ApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans10.xml");
//因为这里只有一个实现对象,因此用类型获取
Cal myCalProxy = ioc.getBean(Cal.class);
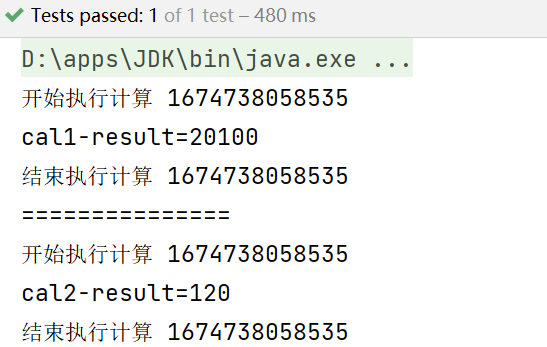
myCalProxy.cal1(200);
System.out.println("===============");
myCalProxy.cal2(5);
}
测试结果:
(2)基于注解的配置方式
Cal 接口不变,在MyCal 实现类上添加 @Component 注解:
@Component
public class MyCal implements Cal {...}
切面类:
package com.li.aop.hw2;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.Signature;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author 李
* @version 1.0
* 切面类
*/
@Component
@Aspect
public class CalAspect {
//前置通知
//如果切面类和目标类在同一个包,可以省略包名
@Before(value = "execution(public void com.li.aop.hw2.Cal.*(int))")
public void beforeTime(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println(signature.getName() + " 开始时间: " + System.currentTimeMillis());
}
//返回通知
@AfterReturning(value = "execution(public void com.li.aop.hw2.Cal.*(int))")
public void returningTime(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println(signature.getName() + " 结束时间: " + System.currentTimeMillis());
}
}
xml容器配置文件:
<!--配置要扫描的包-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.li.aop.hw2"/>
<!--开启基于注解的aop功能-->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
测试方法不变:
@Test
public void myCalTest() {
ApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans10.xml");
//因为这里只有一个实现对象,因此用类型获取
//又因为是代理对象,因此使用接口类型获取
Cal myCalProxy = ioc.getBean(Cal.class);
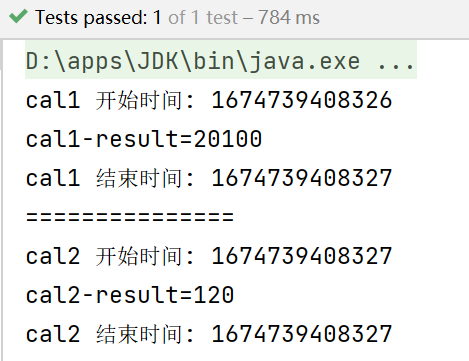
myCalProxy.cal1(200);
System.out.println("===============");
myCalProxy.cal2(5);
}
测试结果:
day10-AOP-03的更多相关文章
- Spring AspectJ基于注解的AOP实现
对于AOP这种编程思想,很多框架都进行了实现.Spring就是其中之一,可以完成面向切面编程.然而,AspectJ也实现了AOP的功能,且实现方式更为简捷,使用更加方便,而且还支持注解式开发.所以,S ...
- AspectJ对AOP的实现
一:你应该明白的知识 1.对于AOP这种编程思想,很多框架都进行了实现.Spring就是其中之一,可以完成面向切面编程.然而,AspectJ也实现了AOP的功能,且实现方式更为简捷,使用更加方便,而且 ...
- 第03章 AOP前奏
第03章 AOP前奏 提出问题 ●情景:数学计算器 ●要求 ①执行加减乘除运算 ②日志:在程序执行期间追踪正在发生的活动 ③验证:希望计算器只能处理正数的运算 ●常规实现 ●问题 ○代码混乱:越来越多 ...
- struts2.1笔记03:AOP编程和拦截器概念的简介
1.AOP编程 AOP编程,也叫面向切面编程(也叫面向方面):Aspect Oriented Programming(AOP),是目前软件开发中的一个热点,也是Spring框架中的一个重要内容.利用A ...
- Spring学习03——AOP Demo
切面类StudentServiceAspect.java package com.su.advice; import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint; import org.as ...
- spring:AOP面向切面编程(注解)03
使用注解写aop时最好使用环绕通知写 切面类: /** * 用于记录日志的工具类,它里面提供了公共的代码 */ @Component("logger") @Aspect //表示当 ...
- 04 Spring:01.Spring框架简介&&02.程序间耦合&&03.Spring的 IOC 和 DI&&08.面向切面编程 AOP&&10.Spring中事务控制
spring共四天 第一天:spring框架的概述以及spring中基于XML的IOC配置 第二天:spring中基于注解的IOC和ioc的案例 第三天:spring中的aop和基于XML以及注解的A ...
- Spring AOP学习笔记03:AOP的核心实现之获取增强器
上文讲了spring是如何开启AOP的,简单点说就是将AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator这个类注册到容器中,因为这个类最终实现了BeanPostProcess ...
- 03—AOP基本配置
- Spring的IOC和AOP之深剖
今天,既然讲到了Spring 的IOC和AOP,我们就必须要知道 Spring主要是两件事: 1.开发Bean:2.配置Bean.对于Spring框架来说,它要做的,就是根据配置文件来创建bean实例 ...
随机推荐
- NLP之基于Seq2Seq和注意力机制的句子翻译
Seq2Seq(Attention) @ 目录 Seq2Seq(Attention) 1.理论 1.1 机器翻译 1.1.1 模型输出结果处理 1.1.2 BLEU得分 1.2 注意力模型 1.2.1 ...
- 8.gitlab服务器搭建(基于centos7)
gitlab服务硬件要求 建议服务器最低配置:2核 2G以上内存(不包含2GB,2GB内存运行的时候内存直接爆掉) 官网给出的推荐配置:4核 4GB内存 支持500个用户,8核 8GB内存 支持100 ...
- 第一百零七篇:基本数据类型(undefined,null,boolean类型)
好家伙, 本篇内容为<JS高级程序设计>第三章学习笔记 1.数据类型 ECMAScript有6种简单数据类型(称为原始类型): Undefined, Null, Boolean, Numb ...
- kafka-consumer-groups 命令行工具使用手册
kafka-consumer-groups 命令行工具使用手册 该手册原文出自 $KAFKA_HOME\bin\windows\kafka-consumer-groups.bat --help 命令的 ...
- 嵌入式-C语言基础:指针是存放变量的地址,那为什么要区分类型?
指针是存放变量的地址,那为什么要区分类型?不能所有类型的变量都用一个类型吗?下面用一个例子来说明这个问题. #include<stdio.h> int main() { int a=0x1 ...
- K8S之prometheus-operator监控
prometheus-operator 1. Prometheus Operator介绍 介绍文章:http://t.zoukankan.com/twobrother-p-11164391.html ...
- C语言算法入门
2018年11月2日 leetcode的确是一个不错的网站,希望能提升自己的算法力 int* twoSum(int* nums, int numsSize, int target) { } 出现的第 ...
- 带你从入门到精通学习WireShark
个人名片: 因为云计算成为了监控工程师 个人博客:念舒_C.ying CSDN主页️:念舒_C.ying 带你从入门到精通学习WireShark 一.什么是WireShark? 二.WireShar ...
- float16与float32转换
// based on https://gist.github.com/martin-kallman/5049614 // float32 // Martin Kallman // // Fast h ...
- PDF、视频格式缩略图获取(pdf2img)
PDF.视频格式缩略图获取(pdf2img) 获取pdf缩略图 导入依赖: <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.pdfbox</groupI ...
