rtp header
rtp协议基于udp传输,流媒体音视频数据被封装在rtp中,通过rtp协议进行实时的传输。
一、rtp协议头格式

The RTP header has a minimum size of 12 bytes. After the header, optional header extensions may be present. This is followed by the RTP payload, the format of which is determined by the particular class of application.[20] The fields in the header are as follows:
- Version: (2 bits) Indicates the version of the protocol. Current version is 2.[21]
- P (Padding): (1 bit) Used to indicate if there are extra padding bytes at the end of the RTP packet. A padding might be used to fill up a block of certain size, for example as required by an encryption algorithm. The last byte of the padding contains the number of padding bytes that were added (including itself).[13]:12[21]
- X (Extension): (1 bit) Indicates presence of an Extension header between standard header and payload data. This is application or profile specific.[21]
- CC (CSRC count): (4 bits) Contains the number of CSRC identifiers (defined below) that follow the fixed header.[13]:12
- M (Marker): (1 bit) Used at the application level and defined by a profile. If it is set, it means that the current data has some special relevance for the application.[13]:13
- PT (Payload type): (7 bits) Indicates the format of the payload and determines its interpretation by the application. This is specified by an RTP profile. For example, see RTP Profile for audio and video conferences with minimal control(RFC 3551).[22]
- Sequence number: (16 bits) The sequence number is incremented by one for each RTP data packet sent and is to be used by the receiver to detect packet loss and to restore packet sequence. The RTP does not specify any action on packet loss; it is left to the application to take appropriate action. For example, video applications may play the last known frame in place of the missing frame.[23] According to RFC 3550, the initial value of the sequence number should be random to make known-plaintext attacks on encryption more difficult.[13]:13 RTP provides no guarantee of delivery, but the presence of sequence numbers makes it possible to detect missing packets.[1]
- Timestamp: (32 bits) Used by the receiver to play back the received samples at appropriate time and interval. When several media streams are present, the timestamps may be independent in each stream.[b] The granularity of the timing is application specific. For example, an audio application that samples data once every 125 µs (8 kHz, a common sample rate in digital telephony) would use that value as its clock resolution. Video streams typically use a 90 kHz clock. The clock granularity is one of the details that is specified in the RTP profile for an application.[23]
- SSRC: (32 bits) Synchronization source identifier uniquely identifies the source of a stream. The synchronization sources within the same RTP session will be unique.[13]:15
- CSRC: (32 bits each, number indicated by CSRC count field) Contributing source IDs enumerate contributing sources to a stream which has been generated from multiple sources.[13]:15
- Header extension: (optional, presence indicated by Extension field) The first 32-bit word contains a profile-specific identifier (16 bits) and a length specifier (16 bits) that indicates the length of the extension (EHL = extension header length) in 32-bit units, excluding the 32 bits of the extension header.[13]:17
上面针对rtp头的解释,最为重要的就是seq 和 timestamp,seq需要保证连续,timestamp对视频数据来说,需要时间毫秒数 x 90,
对于音频则是时间毫秒数 x 80
二、rtp协议头定义
rtp协议头字节序为网络字节序,也就是大端模式:
rfc3550中的rtp头结构体定义
/*
* RTP data header
*/
typedef struct {
unsigned int version:; /* protocol version */
unsigned int p:; /* padding flag */
unsigned int x:; /* header extension flag */
unsigned int cc:; /* CSRC count */
unsigned int m:; /* marker bit */
unsigned int pt:; /* payload type */
unsigned int seq:; /* sequence number */
u_int32 ts; /* timestamp */
u_int32 ssrc; /* synchronization source */
u_int32 csrc[]; /* optional CSRC list */
} rtp_hdr_t;
rtp封包时,一般设置version, payloadtype,seq,timestamp,ssrc 即可。
可以按照大端模式直接填充上述的结构体
也可以直接封包,下面的例子:
// Prepare the 12 byte RTP header
RtpBuf[] = 0x80; // RTP version
RtpBuf[] = 0x1a + (marker_bit << ); // JPEG payload (26) and marker bit
RtpBuf[] = m_SequenceNumber >> ;
RtpBuf[] = m_SequenceNumber & 0x0FF; // each packet is counted with a sequence counter
RtpBuf[] = (m_Timestamp & 0xFF000000) >> ; // each image gets a timestamp
RtpBuf[] = (m_Timestamp & 0x00FF0000) >> ;
RtpBuf[] = (m_Timestamp & 0x0000FF00) >> ;
RtpBuf[] = (m_Timestamp & 0x000000FF);
RtpBuf[] = 0x13; // 4 byte SSRC (sychronization source identifier)
RtpBuf[] = 0xf9; // we just an arbitrary number here to keep it simple
RtpBuf[] = 0x7e;
RtpBuf[] = 0x67;
三、wireshark抓包出的rdp包,可以根据包头的版本号和负载类型筛选出rtp包
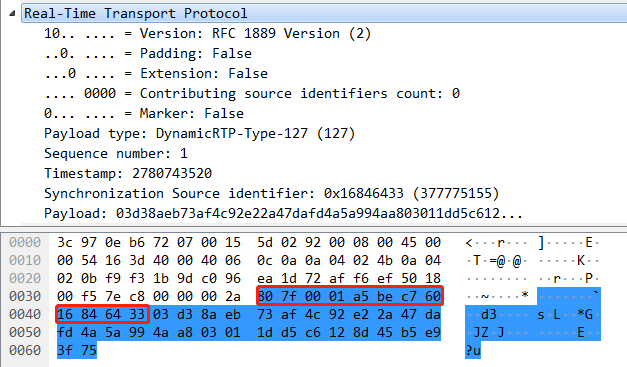
0x80 =1000 0000 version = 2
0x7f =1111 1111
0x00 01 = 0000 0000 0000 0001 seq = 1
0xa5 be c7 60 = 10100101101111101100011101100000 timestamp = 2780743520
引用:
1、https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Real-time_Transport_Protocol
2、https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3550
rtp header的更多相关文章
- (转载)H.264码流的RTP封包说明
H.264的NALU,RTP封包说明(转自牛人) 2010-06-30 16:28 H.264 RTP payload 格式 H.264 视频 RTP 负载格式 1. 网络抽象层单元类型 (NALU) ...
- 自己动手写RTP服务器——关于RTP协议
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/baby313/article/details/7353605 本文会带领着你一步步动手实现一个简单的RTP传输服务器,旨在了解RTP流媒体传输协议以及 ...
- H.264 基础及 RTP 封包详解
转自:http://my.oschina.net/u/1431835/blog/393315 一. h264基础概念 1.NAL.Slice与frame意思及相互关系 1 frame的数据可以分为多个 ...
- RTMP/RTP/RTSP/RTCP的区别
RTCP RTMP/RTP/RTSP/RTCP的区别 http://blog.csdn.net/frankiewang008/article/details/7665547 流媒体协议介绍(rtp/r ...
- 庖丁解牛-----Live555源码彻底解密(RTP解包)
Live555 客户端解包 以testRTSPClient.cpp为例讲解: Medium<-MediaSource<-FramedSource<-RTPSource<-Mul ...
- 庖丁解牛-----Live555源码彻底解密(RTP打包)
本文主要讲解live555的服务端RTP打包流程,根据MediaServer讲解RTP的打包流程,所以大家看这篇文章时,先看看下面这个链接的内容; 庖丁解牛-----Live555源码彻底解密(根据M ...
- 基于RTP的H264视频数据打包解包类
from:http://blog.csdn.net/dengzikun/article/details/5807694 最近考虑使用RTP替换原有的高清视频传输协议,遂上网查找有关H264视频RTP打 ...
- 用实例分析H264 RTP payload
用实例分析H264 RTP payload H264的RTP中有三种不同的基本负载(Single NAL,Non-interleaved,Interleaved) 应用程序可以使用第一个字节来识别. ...
- RTP封装h264
网络抽象层单元类型 (NALU): NALU头由一个字节组成,它的语法如下: +---------------+ |0|1|2|3|4|5|6|7| +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+ ...
随机推荐
- nginx proxy_pass后的url加不加/的区别
在nginx中配置proxy_pass时,当在后面的url加上了/,相当于是绝对根路径,则nginx不会把location中匹配的路径部分代理走;如果没有/,则会把匹配的路径部分也给代理走. 下面四种 ...
- mysql 入门 jdbc
在java程序中连接mysql,先要到mysql的网站上面去下载驱动,并且安装,默认安装在c盘(我的都是默认安装,目录为C:\Program Files\MySQL\MySQL Connector J ...
- plsql Developer 登录oracle出现 initialization error
plsql Developer 登录oracle出现 initialization error 原因:plsql没有64位的,32位的plsql连接64位的oracle才会报错 解决方案:到oracl ...
- Java理论学时第六节。课后作业。
package Fuction; class Grandparent { public Grandparent() { System.out.println("GrandParent Cre ...
- Mining Twitter Data with Python
目录 1.Collecting data 1.1 Register Your App 1.2 Accessing the Data 1.3 Streaming 2.Text Pre-processin ...
- node-webkit学习(1)hello world
)hello world 文/玄魂 目录 node-webkit学习(1)hello world 前言 1.1 环境安装 1.1.1 windows下的安装 1.1.2 linux环境下的安装 1 ...
- WPF用户控件库 嵌入外部(VLC)exe
综合网上资源完成的自己的第一篇博客 ------------------------------------------------------------------------ 网上类似的贴子挺多 ...
- 背水一战 Windows 10 (59) - 控件(媒体类): Image, MediaElement
[源码下载] 背水一战 Windows 10 (59) - 控件(媒体类): Image, MediaElement 作者:webabcd 介绍背水一战 Windows 10 之 控件(媒体类) Im ...
- 深入解析SQL Server高可用镜像实现原理
本文来自网易云社区 SQL Server 是windows平台.NET架构下标配数据库解决方案,与Oracle.MySQL共同构成了DB-Engines Ranking的第一阵营,在国内外企业市场中有 ...
- 【BZOJ5290】 [Hnoi2018]道路
BZOJ5290 [Hnoi2018]道路 前言 这道题目我竟然没有在去年省选切? 我太菜了. Solution 对题面进行一个语文透彻解析,发现这是一个二叉树,乡村都是叶子节点,城市都有两个儿子.( ...
