感知器基础原理及python实现
简单版本,按照李航的《统计学习方法》的思路编写

数据采用了著名的sklearn自带的iries数据,最优化求解采用了SGD算法。
预处理增加了标准化操作。
'''
perceptron classifier created on 2019.9.14
author: vince
'''
import pandas
import numpy
import logging
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score '''
perceptron classifier Attributes
w: ld-array = weights after training
l: list = number of misclassification during each iteration
'''
class Perceptron:
def __init__(self, eta = 0.01, iter_num = 50, batch_size = 1):
'''
eta: float = learning rate (between 0.0 and 1.0).
iter_num: int = iteration over the training dataset.
batch_size: int = gradient descent batch number,
if batch_size == 1, used SGD;
if batch_size == 0, use BGD;
else MBGD;
''' self.eta = eta;
self.iter_num = iter_num;
self.batch_size = batch_size; def train(self, X, Y):
'''
train training data.
X:{array-like}, shape=[n_samples, n_features] = Training vectors,
where n_samples is the number of training samples and
n_features is the number of features.
Y:{array-like}, share=[n_samples] = traget values.
'''
self.w = numpy.zeros(1 + X.shape[1]);
self.l = numpy.zeros(self.iter_num);
for iter_index in range(self.iter_num):
for sample_index in range(X.shape[0]):
if (self.activation(X[sample_index]) != Y[sample_index]):
logging.debug("%s: pred(%s), label(%s), %s, %s" % (sample_index,
self.net_input(X[sample_index]) , Y[sample_index],
X[sample_index, 0], X[sample_index, 1]));
self.l[iter_index] += 1;
for sample_index in range(X.shape[0]):
if (self.activation(X[sample_index]) != Y[sample_index]):
self.w[0] += self.eta * Y[sample_index];
self.w[1:] += self.eta * numpy.dot(X[sample_index], Y[sample_index]);
break;
logging.info("iter %s: %s, %s, %s, %s" %
(iter_index, self.w[0], self.w[1], self.w[2], self.l[iter_index])); def activation(self, x):
return numpy.where(self.net_input(x) >= 0.0 , 1 , -1); def net_input(self, x):
return numpy.dot(x, self.w[1:]) + self.w[0]; def predict(self, x):
return self.activation(x); def main():
logging.basicConfig(level = logging.INFO,
format = '%(asctime)s %(filename)s[line:%(lineno)d] %(levelname)s %(message)s',
datefmt = '%a, %d %b %Y %H:%M:%S'); iris = load_iris(); features = iris.data[:99, [0, 2]];
# normalization
features_std = numpy.copy(features);
for i in range(features.shape[1]):
features_std[:, i] = (features_std[:, i] - features[:, i].mean()) / features[:, i].std(); labels = numpy.where(iris.target[:99] == 0, -1, 1); # 2/3 data from training, 1/3 data for testing
train_features, test_features, train_labels, test_labels = train_test_split(
features_std, labels, test_size = 0.33, random_state = 23323); logging.info("train set shape:%s" % (str(train_features.shape))); p = Perceptron(); p.train(train_features, train_labels); test_predict = numpy.array([]);
for feature in test_features:
predict_label = p.predict(feature);
test_predict = numpy.append(test_predict, predict_label); score = accuracy_score(test_labels, test_predict);
logging.info("The accruacy score is: %s "% (str(score))); #plot
x_min, x_max = train_features[:, 0].min() - 1, train_features[:, 0].max() + 1;
y_min, y_max = train_features[:, 1].min() - 1, train_features[:, 1].max() + 1;
plt.xlim(x_min, x_max);
plt.ylim(y_min, y_max);
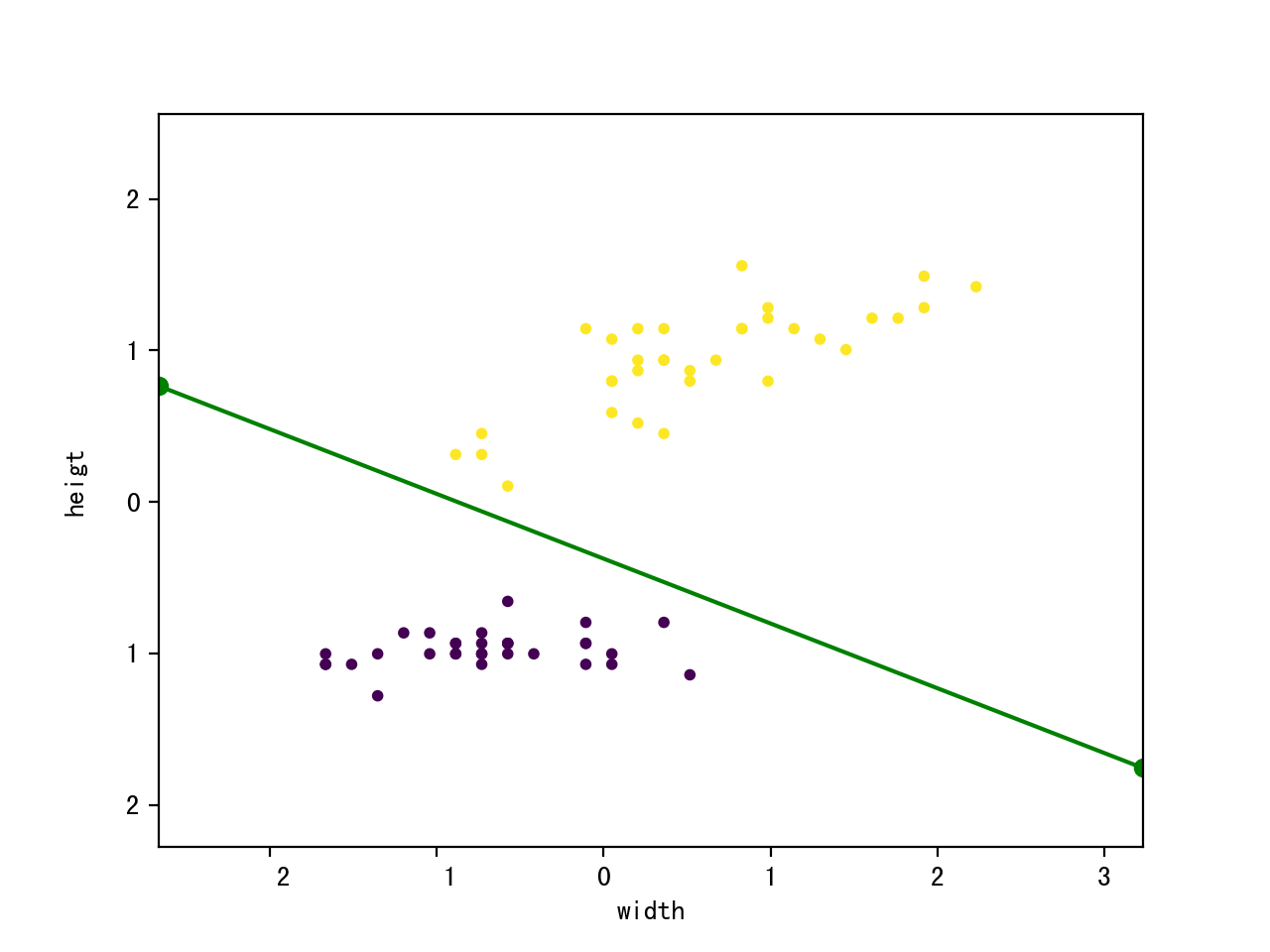
plt.xlabel("width");
plt.ylabel("heigt"); plt.scatter(train_features[:, 0], train_features[:, 1], c = train_labels, marker = 'o', s = 10); k = - p.w[1] / p.w[2];
d = - p.w[0] / p.w[2]; plt.plot([x_min, x_max], [k * x_min + d, k * x_max + d], "go-"); plt.show(); if __name__ == "__main__":
main();
感知器基础原理及python实现的更多相关文章
- 机器学习之感知器算法原理和Python实现
(1)感知器模型 感知器模型包含多个输入节点:X0-Xn,权重矩阵W0-Wn(其中X0和W0代表的偏置因子,一般X0=1,图中X0处应该是Xn)一个输出节点O,激活函数是sign函数. (2)感知器学 ...
- 机器学习:Python实现单层Rosenblatt感知器
如果对Rosenblatt感知器不了解,可以先查看下相关定义,然后对照下面的代码来理解. 代码中详细解释了各步骤的含义,有些涉及到了数学公式的解释. 这篇文章是以理解Rosenblatt感知器的原理为 ...
- RBF神经网络学习算法及与多层感知器的比较
对于RBF神经网络的原理已经在我的博文<机器学习之径向基神经网络(RBF NN)>中介绍过,这里不再重复.今天要介绍的是常用的RBF神经网络学习算法及RBF神经网络与多层感知器网络的对比. ...
- 感知器做二分类的原理及python实现
本文目录: 1. 感知器 2. 感知器的训练法则 3. 梯度下降和delta法则 4. python实现 1. 感知器[1] 人工神经网络以感知器(perceptron)为基础.感知器以一个实数值向量 ...
- python之感知器-从零开始学深度学习
感知器-从零开始学深度学习 未来将是人工智能和大数据的时代,是各行各业使用人工智能在云上处理大数据的时代,深度学习将是新时代的一大利器,在此我将从零开始记录深度学习的学习历程. 我希望在学习过程中做到 ...
- 【转】【python】装饰器的原理
写在前面: 在开发OpenStack过程中,经常可以看到代码中的各种注解,自己也去查阅了资料,了解了这是python中的装饰器,因为弱类型的语言可以将函数当成返回值返回,这就是装饰器的原理. 虽然说知 ...
- 机器学习 —— 基础整理(六)线性判别函数:感知器、松弛算法、Ho-Kashyap算法
这篇总结继续复习分类问题.本文简单整理了以下内容: (一)线性判别函数与广义线性判别函数 (二)感知器 (三)松弛算法 (四)Ho-Kashyap算法 闲话:本篇是本系列[机器学习基础整理]在time ...
- 感知器算法--python实现
写在前面: 参考: 1 <统计学习方法>第二章感知机[感知机的概念.误分类的判断] http://pan.baidu.com/s/1hrTscza 2 点到面的距离 3 梯度 ...
- Python开发基础-Day7-闭包函数和装饰器基础
补充:全局变量声明及局部变量引用 python引用变量的顺序: 当前作用域局部变量->外层作用域变量->当前模块中的全局变量->python内置变量 global关键字用来在函数或其 ...
随机推荐
- 量化投资学习笔记37——《Python机器学习应用》课程笔记10
用KNN算法来进行数字识别,还是用sklearn自带的digits数据集. coding:utf-8 KNN算法实现手写识别 from sklearn import neighbors from sk ...
- css手写一个表头固定
Bootstrap,layui等前端框架里面都对表头固定,表格滚动有实现,偏偏刚入职的公司选择了手动渲染表格,后期又觉得表格数据拉太长想要做表头固定.为了避免对代码改动太大,所以决定手写表头固定 主要 ...
- notepad++ 字符处理: 字符前后删除 或 删除未包含字符串的行
字符串前后删除 删除str之后的所有字符用,打开替换(Ctrl+H) :str.*$ 删除str之前的所有字符用:^.*str 如果是其他字符就把str替换为其他字符 ---------------- ...
- 浅析SIEM、态势感知平台、安全运营中心
近年来SIEM.态势感知平台.安全运营中心等概念炒的火热,有的人认为这都是安全管理产品,这些产品就是一回事,有人认为还是有所区分.那么到底什么是SIEM.什么是态势感知平台.什么是安全运营中心,他们之 ...
- Node的require和module.exports
node编程中最重要的思想之一就是模块,在 Node.js 模块系统中,每个文件都被视为独立的模块.这是这个思想,让javascript的大规模工程成为可能.模块化编程在前端大肆盛行,在node中导出 ...
- Druid未授权(弱口令)的一些利用方式
Druid简介 1.Druid是阿里巴巴数据库事业部出品,为监控而生的数据库连接池. 2.Druid提供的监控功能,监控SQL的执行时间.监控Web URI的请求.Session监控. Druid可能 ...
- 最全Redis基础知识
NoSQL概述 什么是NoSQL NoSQL不仅仅是SQL,它是Not Only SQL 的缩写,也是众多非关系型数据库的统称NoSQL和关系型数据库一样,也是用来存储数据的仓库. 为什么需要NoSQ ...
- 【原创】(求锤得锤的故事)Redis锁从面试连环炮聊到神仙打架。
这是why技术的第38篇原创文章 又到了一周一次的分享时间啦,老规矩,还是先荒腔走板的聊聊生活. 有上面的图是读大学的时候,一次自行车骑行途中队友抓拍的我的照片.拍照的地方,名字叫做牛背山,一个名字很 ...
- asyncio在爬虫中的使用
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # 协程基础.py import asyncio import time async def request(url): print("正在请 ...
- 03.文件I/O
UNIX系统中的大多数文件I/O只需用到5个函数:open.read.write.lseek和close. 本章所说明的函数称为不带缓冲的I/O.不带缓冲指的是每个read和write都调用内核中的一 ...
