达拉草201771010105《面向对象程序设计(java)》第十周学习总结
达拉草201771010105《面向对象程序设计(java)》第十周学习总结
实验十 泛型程序设计技术
实验时间 2018-11-1
第一部分:理论知识
泛型:也称参数化类型(parameterizedtype), 就是在定义类、接口和方法时,通过类型参数指 示将要处理的对象类型。(如ArrayList类)
泛型程序设计(Genericprogramming):编写 代码可以被很多不同类型的对象所重用。
泛型类的定义:
1.一个泛型类(genericclass)就是具有一个或多 个类型变量的类,即创建用类型作为参数的类。 如一个泛型类定义格式如下: classGenerics<K,V> 其中的K和V是类中的可变类型参数。
2. Pair类引入了一个类型变量T,用尖括号(<>) 括起来,并放在类名的后面。
3.泛型类可以有多个类型变量。例如: publicclassPair<T,U>{…}
4.类定义中的类型变量用于指定方法的返回类型以 及域、局部变量的类型。
泛型方法:
1. 泛型方法 –除了泛型类外,还可以只单独定义一个方法作 为泛型方法,用于指定方法参数或者返回值为 泛型类型,留待方法调用时确定。
2.泛型方法可以声明在泛型类中,也可以声明在 普通类中。
通配符类型;
通配符 –“?”符号表明参数的类型可以是任何一种类 型,它和参数T的含义是有区别的。T表示一种 未知类型,而“?”表示任何一种类型。这种 通配符一般有以下三种用法:
1.单独的?,用于表示任何类型。
2.? extends type,表示带有上界。
3.? super type,表示带有下界。
泛型中<TextendsObject>,extends并不代表继 承,它是类型范围限制。
泛型类不是协变的。
1、实验目的与要求
(1) 理解泛型概念;
(2) 掌握泛型类的定义与使用;
(3) 掌握泛型方法的声明与使用;
(4) 掌握泛型接口的定义与实现;
(5)了解泛型程序设计,理解其用途。
2、实验内容和步骤
实验1: 导入第8章示例程序,测试程序并进行代码注释。
测试程序1:
l 编辑、调试、运行教材311、312页 代码,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 在泛型类定义及使用代码处添加注释;
l 掌握泛型类的定义及使用。
package pair1; /**
* @version 1.00 2004-05-10
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class Pair<T> //Pair类引入了一个类型变量T {
private T first;
private T second; public Pair() { first = null; second = null; }
public Pair(T first, T second) { this.first = first; this.second = second; } public T getFirst() { return first; }
public T getSecond() { return second; } public void setFirst(T newValue) { first = newValue; }
public void setSecond(T newValue) { second = newValue; }
}
package pair1; /**
* @version 1.01 2012-01-26
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class PairTest1
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String[] words = { "Mary", "had", "a", "little", "lamb" };
Pair<String> mm = ArrayAlg.minmax(words);
System.out.println("min = " + mm.getFirst());
System.out.println("max = " + mm.getSecond());
}
} class ArrayAlg//泛型类
{
/**
* Gets the minimum and maximum of an array of strings.
* @param a an array of strings
* @return a pair with the min and max value, or null if a is null or empty
*/
public static Pair<String> minmax(String[] a)
{
if (a == null || a.length == 0) return null;
String min = a[0];
String max = a[0];
for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++)
{
if (min.compareTo(a[i]) > 0) min = a[i];
if (max.compareTo(a[i]) < 0) max = a[i];
}
return new Pair<>(min, max);//调用泛型类对象
}
}
程序运行结果如下:
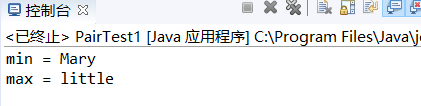
测试程序2:
l 编辑、调试运行教材315页 PairTest2,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 在泛型程序设计代码处添加相关注释;
l 掌握泛型方法、泛型变量限定的定义及用途。
package pair2; import java.time.*; /**
* @version 1.02 2015-06-21
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class PairTest2
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LocalDate[] birthdays =
{
LocalDate.of(1906, 12, 9), // G. Hopper
LocalDate.of(1815, 12, 10), // A. Lovelace
LocalDate.of(1903, 12, 3), // J. von Neumann
LocalDate.of(1910, 6, 22), // K. Zuse
};
Pair<LocalDate> mm = ArrayAlg.minmax(birthdays);
System.out.println("min = " + mm.getFirst());
System.out.println("max = " + mm.getSecond());
}
} class ArrayAlg
{
/**
Gets the minimum and maximum of an array of objects of type T.
@param a an array of objects of type T
@return a pair with the min and max value, or null if a is
null or empty
*/
public static <T extends Comparable> Pair<T> minmax(T[] a) //加了上界约束的泛型方法
{
if (a == null || a.length == 0) return null;
T min = a[0];
T max = a[0];
for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++)
{
if (min.compareTo(a[i]) > 0) min = a[i];
if (max.compareTo(a[i]) < 0) max = a[i];
}
return new Pair<>(min, max);
}
}
程序运行结果如下;
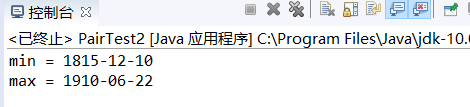
测试程序3:
l 用调试运行教材335页 PairTest3,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 了解通配符类型的定义及用途。
package pair3; import java.time.*; public class Employee
{
private String name;
private double salary;
private LocalDate hireDay; public Employee(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day)//构造器
{
this.name = name;
this.salary = salary;
hireDay = LocalDate.of(year, month, day);
} public String getName()//访问器
{
return name;
} public double getSalary()//访问器
{
return salary;
} public LocalDate getHireDay()
{
return hireDay;
} public void raiseSalary(double byPercent)
{
double raise = salary * byPercent / 100;
salary += raise;
}
}
package pair3; public class Manager extends Employee
{
private double bonus; /**
@param name the employee's name
@param salary the salary
@param year the hire year
@param month the hire month
@param day the hire day
*/
public Manager(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day)
{
super(name, salary, year, month, day);
bonus = 0;
} public double getSalary()//访问器
{
double baseSalary = super.getSalary();
return baseSalary + bonus;
} public void setBonus(double b)//更改器
{
bonus = b;
} public double getBonus()
{
return bonus;
}
}
package pair3; /**
* @version 1.00 2004-05-10
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class Pair<T> //Pair类引入了一个类型变量T {
private T first;
private T second; public Pair() { first = null; second = null; }
public Pair(T first, T second) { this.first = first; this.second = second; } public T getFirst() { return first; }
public T getSecond() { return second; } public void setFirst(T newValue) { first = newValue; }
public void setSecond(T newValue) { second = newValue; }
}
package pair3; /**
* @version 1.01 2012-01-26
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class PairTest3
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Manager ceo = new Manager("Gus Greedy", 800000, 2003, 12, 15);
Manager cfo = new Manager("Sid Sneaky", 600000, 2003, 12, 15);
Pair<Manager> buddies = new Pair<>(ceo, cfo);
printBuddies(buddies); ceo.setBonus(1000000);
cfo.setBonus(500000);
Manager[] managers = { ceo, cfo }; Pair<Employee> result = new Pair<>();
minmaxBonus(managers, result);
System.out.println("first: " + result.getFirst().getName()
+ ", second: " + result.getSecond().getName());
maxminBonus(managers, result);
System.out.println("first: " + result.getFirst().getName()
+ ", second: " + result.getSecond().getName());
} public static void printBuddies(Pair<? extends Employee> p)//表明带有上界
{
Employee first = p.getFirst();
Employee second = p.getSecond();
System.out.println(first.getName() + " and " + second.getName() + " are buddies.");
} public static void minmaxBonus(Manager[] a, Pair<? super Manager> result)//表明带有下界
{
if (a.length == 0) return;
Manager min = a[0];
Manager max = a[0];
for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++)
{
if (min.getBonus() > a[i].getBonus()) min = a[i];
if (max.getBonus() < a[i].getBonus()) max = a[i];
}
result.setFirst(min);
result.setSecond(max);
} public static void maxminBonus(Manager[] a, Pair<? super Manager> result)//表明带有下界
{
minmaxBonus(a, result);
PairAlg.swapHelper(result); // OK--swapHelper captures wildcard type
}
// Can't write public static <T super manager> ...
} class PairAlg
{
public static boolean hasNulls(Pair<?> p)
{
return p.getFirst() == null || p.getSecond() == null;
} public static void swap(Pair<?> p) { swapHelper(p); } public static <T> void swapHelper(Pair<T> p)
{
T t = p.getFirst();
p.setFirst(p.getSecond());
p.setSecond(t);
}
}
程序运行结果如下:
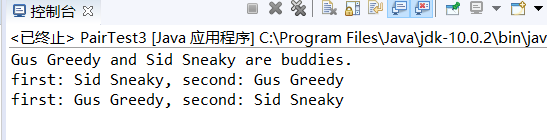
实验2:编程练习:
编程练习1:实验九编程题总结
l 实验九编程练习1总结(从程序总体结构说明、模块说明,目前程序设计存在的困难与问题三个方面阐述)。
l 实验九编程练习2总结(从程序总体结构说明、模块说明,目前程序设计存在的困难与问题三个方面阐述)。
1 import java.io.BufferedReader;
2 import java.io.File;
3 import java.io.FileInputStream;
4 import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
5 import java.io.IOException;
6 import java.io.InputStreamReader;
7 import java.util.ArrayList;
8 import java.util.Arrays;
9 import java.util.Collections;
10 import java.util.Scanner;
11
12 public class Moom{
13 private static ArrayList<Mest> studentlist;
14 public static void main(String[] args) {
15 studentlist = new ArrayList<>();
16 Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
17 File file = new File("D:\\身份证号.txt");
18 try {
19 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
20 BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(fis));
21 String temp = null;
22 while ((temp = in.readLine()) != null) {
23
24 Scanner linescanner = new Scanner(temp);
25
26 linescanner.useDelimiter(" ");
27 String name = linescanner.next();
28 String number = linescanner.next();
29 String sex = linescanner.next();
30 String age = linescanner.next();
31 String province =linescanner.nextLine();
32 Mest student = new Mest();
33 student.setName(name);
34 student.setnumber(number);
35 student.setsex(sex);
36 int a = Integer.parseInt(age);
37 student.setage(a);
38 student.setprovince(province);
39 studentlist.add(student);
40
41 }
42 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
43 System.out.println("学生信息文件找不到");
44 e.printStackTrace();
45 } catch (IOException e) {
46 System.out.println("学生信息文件读取错误");
47 e.printStackTrace();
48 }
49 boolean isTrue = true;
50 while (isTrue) {
51
52 System.out.println("1:字典排序");
53 System.out.println("2:输出年龄最大和年龄最小的人");
54 System.out.println("3:寻找老乡");
55 System.out.println("4:寻找年龄相近的人");
56 System.out.println("5:退出");
57 String m = scanner.next();
58 switch (m) {
59 case "1":
60 Collections.sort(studentlist);
61 System.out.println(studentlist.toString());
62 break;
63 case "2":
64 int max=0,min=100;
65 int j,k1 = 0,k2=0;
66 for(int i=1;i<studentlist.size();i++)
67 {
68 j=studentlist.get(i).getage();
69 if(j>max)
70 {
71 max=j;
72 k1=i;
73 }
74 if(j<min)
75 {
76 min=j;
77 k2=i;
78 }
79
80 }
81 System.out.println("年龄最大:"+studentlist.get(k1));
82 System.out.println("年龄最小:"+studentlist.get(k2));
83 break;
84 case "3":
85 System.out.println("家庭住址:");
86 String find = scanner.next();
87 String place=find.substring(0,3);
88 for (int i = 0; i <studentlist.size(); i++)
89 {
90 if(studentlist.get(i).getprovince().substring(1,4).equals(place))
91 System.out.println("province"+studentlist.get(i));
92 }
93 break;
94
95 case "4":
96 System.out.println("年龄:");
97 int yourage = scanner.nextInt();
98 int near=agematched(yourage);
99 int value=yourage-studentlist.get(near).getage();
100 System.out.println(""+studentlist.get(near));
101 break;
102 case "5":
103 isTrue = false;
104 System.out.println("退出程序!");
105 break;
106 default:
107 System.out.println("输入错误");
108
109 }
110 }
111 }
112 public static int agematched(int age) {
113 int j=0,min=53,value=0,k=0;
114 for (int i = 0; i < studentlist.size(); i++)
115 {
116 value=studentlist.get(i).getage()-age;
117 if(value<0) value=-value;
118 if (value<min)
119 {
120 min=value;
121 k=i;
122 }
123 }
124 return k;
125 }
126
127 }
1 public class Mest implements Comparable<Mest> {
2
3 private String name;
4 private String number ;
5 private String sex ;
6 private int age;
7 private String province;
8
9 public String getName() {
10 return name;
11 }
12 public void setName(String name) {
13 this.name = name;
14 }
15 public String getnumber() {
16 return number;
17 }
18 public void setnumber(String number) {
19 this.number = number;
20 }
21 public String getsex() {
22 return sex ;
23 }
24 public void setsex(String sex ) {
25 this.sex =sex ;
26 }
27 public int getage() {
28
29 return age;
30 }
31 public void setage(int age) {
32
33 this.age= age;
34 }
35
36 public String getprovince() {
37 return province;
38 }
39 public void setprovince(String province) {
40 this.province=province ;
41 }
42
43 public int compareTo(Mest o) {
44 return this.name.compareTo(o.getName());
45 }
46
47 public String toString() {
48 return name+"\t"+sex+"\t"+age+"\t"+number+"\t"+province+"\n";
49 }
50
51 }
程序总体结构说明和模块说明:程序分一个主类和一个Mest类,Mest类实现Comparable接口。
目前程序设计存在的困难与问题:对编写程序还有很多不懂得地方,文件捕获错误的代码用的不是很熟练。
l 实验九编程练习2总结(从程序总体结构说明、模块说明,目前程序设计存在的困难与问题三个方面阐述)。
1 package MM;
2
3 import java.util.Random;
4 import java.util.Scanner;
5
6 import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
7
8 import java.io.PrintWriter;
9
10 public class Demo{
11 public static void main(String[] args)
12 {
13
14 MNM counter=new MNM();//与其它类建立联系
15 PrintWriter out=null;
16 try {
17 out=new PrintWriter("D:/text.txt");
18
19 }catch(FileNotFoundException e) {
20 e.printStackTrace();
21 }
22 int sum=0;
23
24 for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
25 {
26 int a=new Random().nextInt(100);
27 int b=new Random().nextInt(100);
28 Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
29 //in.close();
30
31 switch((int)(Math.random()*4))
32
33 {
34
35 case 0:
36 System.out.println( ""+a+"+"+b+"=");
37
38 int M = in.nextInt();
39 out.println(a+"+"+b+"="+M);
40 if (M == counter.add(a, b)) {
41 sum += 10;
42 System.out.println("答案正确");
43 }
44 else {
45 System.out.println("答案错误");
46 }
47
48 break ;
49 case 1:
50 if(a<b)
51 {
52 int temp=a;
53 a=b;
54 b=temp;
55 }//为避免减数比被减数大的情况
56
57 System.out.println(""+a+"-"+b+"=");
58 /*while((a-b)<0)
59 {
60 b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
61
62 }*/
63 int N= in.nextInt();
64
65 out.println(a+"-"+b+"="+N);
66 if (N == counter.reduce(a, b)) {
67 sum += 10;
68 System.out.println("答案正确");
69 }
70 else {
71 System.out.println("答案错误");
72 }
73
74 break ;
75
76
77
78
79 case 2:
80
81 System.out.println(""+a+"*"+b+"=");
82 int c = in.nextInt();
83 out.println(a+"*"+b+"="+c);
84 if (c == counter.multiply(a, b)) {
85 sum += 10;
86 System.out.println("答案正确");
87 }
88 else {
89 System.out.println("答案错误");
90 }
91 break;
92 case 3:
93
94
95 System.out.println(""+a+"/"+b+"=");
96 while(b==0)
97 { b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
98 }
99 int c0= in.nextInt();
100 out.println(a+"/"+b+"="+c0);
101 if (c0 == counter.devision(a, b)) {
102 sum += 10;
103 System.out.println("答案正确");
104 }
105 else {
106 System.out.println("答案错误");
107 }
108
109 break;
110
111
112 }
113 }
114 System.out.println("totlescore:"+sum);
115 out.println(sum);
116
117 out.close();
118 }
119 }
1 package MM;
2
3 public class MNM{
4 public int add(int a,int b)
5 {
6 return a+b;
7 }
8 public int reduce(int a,int b)
9 {
10 if((a-b)>0)
11 return a-b;
12 else return 0;
13 }
14 public int multiply(int a,int b)
15 {
16 return a*b;
17 }
18 public int devision(int a,int b)
19 {
20 if(b!=0)
21 return a/b;
22 else return 0;
23
24 }
25 }
程序总体结构:Demo类实现MNM类的功能。
模块说明:随机生成100以内的加减乘除四则运算,输入答案,程序检查答案是否正确。
目前程序设计存在的困难与问题:对于除法运算还存在输出一些问题。
编程练习2:采用泛型程序设计技术改进实验九编程练习2,使之可处理实数四则运算,其他要求不变。
package MM; import java.util.Random;
import java.util.Scanner; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.PrintWriter; public class Demo{
public static void main(String[] args)
{ MNM counter=new MNM();//与其它类建立联系
PrintWriter out=null;
try {
out=new PrintWriter("D:/text.txt"); }catch(FileNotFoundException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
int sum=0; for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
{
int a=new Random().nextInt(100);
int b=new Random().nextInt(100);
Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
//in.close(); switch((int)(Math.random()*4)) { case 0:
System.out.println( ""+a+"+"+b+"="); int M = in.nextInt();
System.out.println(a+"+"+b+"="+M);
if (M == counter.add(a, b)) {
sum += 10;
System.out.println("答案正确");
}
else {
System.out.println("答案错误");
} break ;
case 1:
if(a<b)
{
int temp=a;
a=b;
b=temp;
}//为避免减数比被减数大的情况 System.out.println(""+a+"-"+b+"=");
/*while((a-b)<0)
{
b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); }*/
int N= in.nextInt(); System.out.println(a+"-"+b+"="+N);
if (N == counter.reduce(a, b))
{
sum += 10;
System.out.println("答案正确");
}
else {
System.out.println("答案错误");
} break ; case 2:
System.out.println(""+a+"*"+b+"=");
int c = in.nextInt();
System.out.println(a+"*"+b+"="+c);
if (c == counter.multiply(a, b)) {
sum += 10;
System.out.println("答案正确");
}
else {
System.out.println("答案错误");
}
break;
case 3: while(b==0)
{ b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);//满足分母不为0
}
while(a%b!=0)
{
a = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
}
System.out.println(""+a+"/"+b+"=");
while(b==0)
{ b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
}
int c0= in.nextInt();
System.out.println(a+"/"+b+"="+c0);
if (c0 == counter.devision(a, b)) {
sum += 10;
System.out.println("答案正确");
}
else {
System.out.println("答案错误");
} break; }
}
System.out.println("totlescore:"+sum);
System.out.println(sum); out.close();
}
}
package MM;
public class MNM <T>{
private T a;
private T b;
public void MNM()
{
a=null;
b=null;
}
public MNM(T a,T b)
{
this.a=a;
this.b=b;
}
public MNM() {
// TODO 自动生成的构造函数存根
}
public int add(int a,int b)
{
return a+b;
}
public int reduce(int a,int b)
{
if((a-b)>0)
return a-b;
else return 0;
}
public int multiply(int a,int b)
{
return a*b;
}
public int devision(int a,int b)
{
if(b!=0&&a%b==0)
return a/b;
else
return 0;
}
}
程序运行结果如下:

实验总结:
在这一周的学习中我们主要学习的是泛型程序设计,泛型接口的定义,泛型变量的限定以及通配符类型及使用方法,然后这周的编程练习主要是对之前的程序进行改进,通过编程练习将这周学过泛型程序设计运用到程序中。
达拉草201771010105《面向对象程序设计(java)》第十周学习总结的更多相关文章
- 201771010134杨其菊《面向对象程序设计java》第九周学习总结
第九周学习总结 第一部分:理论知识 异常.断言和调试.日志 1.捕获 ...
- 201871010132-张潇潇《面向对象程序设计(java)》第一周学习总结
面向对象程序设计(Java) 博文正文开头 项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cn ...
- 扎西平措 201571030332《面向对象程序设计 Java 》第一周学习总结
<面向对象程序设计(java)>第一周学习总结 正文开头: 项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 ...
- 杨其菊201771010134《面向对象程序设计Java》第二周学习总结
第三章 Java基本程序设计结构 第一部分:(理论知识部分) 本章主要学习:基本内容:数据类型:变量:运算符:类型转换,字符串,输入输出,控制流程,大数值以及数组. 1.基本概念: 1)标识符:由字母 ...
- 201871010124 王生涛《面向对象程序设计JAVA》第一周学习总结
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/xbsf/ ...
- 201871010115——马北《面向对象程序设计JAVA》第二周学习总结
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p ...
- 201777010217-金云馨《面向对象程序设计(Java)》第二周学习总结
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p ...
- 201871010132——张潇潇《面向对象程序设计JAVA》第二周学习总结
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p ...
- 201771010123汪慧和《面向对象程序设计Java》第二周学习总结
一.理论知识部分 1.标识符由字母.下划线.美元符号和数字组成, 且第一个符号不能为数字.标识符可用作: 类名.变量名.方法名.数组名.文件名等.第二部分:理论知识学习部分 2.关键字就是Java语言 ...
- 达拉草201771010105《面向对象程序设计(java)》第三周学习总结
达拉草201771010105«面向对象程序设计(java)»第三周学习总结 第一部分:实验部分 1.实验目的与要求 (1)进一步掌握Eclipse集成开发环境下java程序开发基本步骤: (2)熟 ...
随机推荐
- Vue项目中跨域问题解决
后台更改header 使用http-proxy-middleware 代理解决(项目使用vue-cli脚手架搭建) Jquery jsonp 一.后台更改header header('Access-C ...
- Java多线程常见概念
进程和线程的区别 进程是资源分配的最小单位,线程是CPU调度的最小单位 线程不能看做独立应用,而进程可以 进程有独立的地址空间,互相不影响,线程只是进程的不同执行路径 线程没有独立的地址空间,多进程的 ...
- $.proxy和$.extend
$.proxy用法详解 参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/alice626/p/6004864.html jQuery中的$.proxy官方描述为: 描述:接受一个函数,然后返回一 ...
- shell_clean_log
apache日志每天进行轮转: vim /usr/local/apache2/conf/extar/httpd-vhosts.conf...ErrorLog "| /usr/local/ap ...
- AUTOSAR 架构
AUTOSAR 软件架构 1.AUTOSAR 软件 2.AUTOSAR 运行时环境(RTE) 3.AUTOSAR 基本软件 (BSW) 1.服务:诊断协议等系统服务及NVRAM管理 2.通信:CAN. ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然C语言开发:数据类型
#include <stdio.h> #include <limits.h> int main() { printf("int 存储大小 : %lu \n" ...
- Java发送邮箱
smtp与pop3 SMTP(Simple Mail Transfer Protocol)即简单邮件传输协议 SMTP 服务器就是遵循 SMTP 协议的发送邮件服务器 POP3是Post Office ...
- LeetCode No.76,77,78
No.76 MinWindow 最小覆盖子串 题目 给你一个字符串 S.一个字符串 T,请在字符串 S 里面找出:包含 T 所有字母的最小子串. 示例 输入: S = "ADOBECODEB ...
- Tomcat远程调试模式及利用Eclipse远程链接调试
1.启动tomcat到调试模式 进入到tomcat的bin目录下,执行命令./catalina.sh jpda run 启动日记会提示打开调试端口默认为8000 2.调试Eclipse远程连接tomc ...
- String的compareTo用法
String的compareTo其实就是依次比较两个字符串ASC码.如果两个字符的ASC码相等则继续后续比较,否则直接返回两个ASC的差值.如果两个字符串完全一样,则返回0.来看一下代码. publi ...
