佳文赏析:How to uninstall Linux
来源:https://www.dedoimedo.com/computers/linux-uninstall.html
This article was suggested to me by a reader called krishna. I realized this was a very important, very common topic - and quite often so easily overlooked by Linux users all over the world. It stands to logic, really. You install an operating system - so you expect to be able to uninstall it, undo the installation, remove the operating system without any trace left to its presence. How do you do that in Linux?
While the idea is a very logical, it is very difficult to answer. This is probably the reason why so many Linux users never bothered answering it. Not to worry. In this tutorial, I will teach you how you can fully and safely remove Linux installations from your system and remain with a bootable, working machine. Let's begin.

Install Linux
The first step in getting Linux onto your system is by downloading a distribution of your choice, burning the .iso image to a CD, booting a computer from the CD, and then installing the distribution. To learn how to do that, please refer to my myriad Linux reviews and tutorials, all of which explain in great, rich detail the installation procedure for different distributions. Now let's examine several test cases.

Single operating system
This is one of the most common solutions that most people will use. A single instance of an operating system is installed.
Two operating systems in a dual boot configuration
This is another very common scenario. Many new Linux users will be recent converts, all of which have previously and are currently using Windows. Many will keep their Windows installation and use Linux as a second or secondary operating system alongside their existing Windows installation. This configuration is known as dual boot. Please refer to this tutorial to learn how it can be created.

More than two operating systems
This configuration is usually used by power users, who will have several Windows releases and several Linux distributions and possibly other operating systems installed on their machine. Practically, there is very little difference between a dual-boot and a multiple-boot system.
Understand how things work
Whichever configuration you choose, it is important to understand how things work. When you install an operating system, several things are done.
Disk layout is changed
Disks are logically divided into sections called partitions. Operating systems are installed onto these partitions, when they requires at least one and usually no more than a single partition to install to. To better understand partitioning, please read the very extensive GParted tutorial.

The partitions are also formatted with one or another filesystem type, which is a logical data structure method that allows operating systems to interact with the hard disk. For example, NTFS is a Windows filesystem, EXT3 is a Linux filesystem.
A bootloader is installed
When you start your computer, the first thing you see is the BIOS screen. After that, an operating system boots. But who does it do that? Well, the answer is simple.
Hard disks contain sectors, physical parcels onto which logical data is written in the form of a filesystem operations. The very first sector is reserved for a tiny bit of code called the bootloader, which contains a basic set of instructions required to kickstart the operating system boot. The first sector is called the Master Boot Record (MBR) and it points to the active partition where important files necessary for the booting of the operating system can be found.
Every operating system installs this or that bootloader. Windows uses the NT Loader (NTLDR). Linux uses the popular GRUB. Reading my tutorial linked to the left will grant you a much deeper understanding into how GRUB works. So the boot sequence goes like this:
- BIOS looks for the first bootable device (hard disk) and initiates it.
- The MBR is read and the relevant partition is chosen.
- Boot files on the relevant partitions are loaded into memory and the booting of the system begins.
Boot process
The boot process is accompanied by visual cues that allow the user to interact with the system. The first is the BIOS menu, where you can change the boot order of your devices, enable and disable peripherals and other tasks.

Next comes a bootloader menu. On Windows, you do not usually see this menu, as it's hidden from view when there's only one operating system installed. On Linux, the menu is normally displayed, usually offering several boot options.

After this stage, you reach your desktop and things are just the way you know them. However, it is important that you remember the sequence of events that took place.
Operating systems are not self-sustained entities. They require the presence of several factors to be able to function, namely the hard disk and the partitioning layout, which the operating system uses for permanent storage of its files, the bootloader that points to the right files and allows the system to boot, the BIOS, which recognizes and properly initializes the hardware. Take away any one of these and your system will not boot.
Another very critical thing to remember is that on a machine with no operating system installed, nothing will happen past the BIOS stage. Since the hard disks are empty, there is no boot sector and no bootloader installed in it. Therefore, once BIOS initializes the primary boot device, nothing will happen. The boot sequence will simply fail.
This means that uninstalling an operating system usually means leaving your machine unbootable. It is important for you to remember this. The only way to maintain desktop functionality is if there's more than a single operating system installed. You remove one or more, but that's ok, as long as there's at least one instance of an operating system capable of completing the boot sequence. Now that we understand what uninstalling an operating system means, let's do it.
Uninstall Linux
Operating systems will not work without their boot files or if they are never called by the bootloader. Therefore, to remove the presence of an operating system, it is enough to dereference is from the bootloader menu. Alternatively, you can also delete its files or replace them with another operating system. So let's examine our test cases again.
Single operating system
If you have a single operating system, removing it will render the machine unbootable. So any which way you to choose to get rid of is perfectly acceptable. This method is true for just about any operating system, including Windows.
- You can delete all the files on the disks; this will render the system unbootable.(note: “rm -rf /*” can be used)
- You can format the partitions where the operating system is installed.
- You can delete the partitions where the operating system is installed or even delete the entire partition table.
- You can uninstall the bootloader.
- You can install another operating system on top of the existing one, simply overwriting its files.
Two operating systems in a dual boot configuration
This is the case that really interests us. We will focus on the classic case - Windows and Linux. If you've read my GRUB tutorial, you will have learned by now that GRUB install itself into the MBR and replaces the Windows bootloader that existed there.
When you uninstall Linux, which we will do shortly, you remove the GRUB stage2 from the system. GRUB stage2 contains the crucial files that allow it to boot your installed instances of Linux or transfer the boot control to Windows. This means that by removing Linux, you will also cripple the Windows installation. It will be intact, but unbootable.
This is because the Linux bootloader will still be present after you remove the Linux installation. To restore Windows functionality, you will have to install the Windows bootloader again. It will overwrite the GRUB present in the MBR and you'll be back to being able to use Windows once more. Now, to uninstall Linux, there are several options:
- You can boot from a live CD and delete or format the Linux partitions.
- You can boot into Windows and delete or format the Linux partitions.
Now, please note that by default, Windows cannot read data from partitions formatted in Linux filesystems like EXT3, EXT4, JFS, ReiserFS, and others, however the Disk Management utility can see these partitions. It will label them as Unknown.

There is a way to allow Windows to be able to read and write to Linux filesystems. Please read this tutorial for more details.

Furthermore, to learn more how to work with the Disk Management utility in Windows, please read my How to partition and format hard disks in Windows article.
To remove Linux, open the Disk Management utility, select the partition(s) where Linux is installed and then format them or delete them. If you delete the partitions, the device will have all its space freed. To make good use of the free space, create a new partition and format it.

But our work is not done. There's the bootloader issue to fix.
Fix the bootloader
This needs to be done on next reboot. What you need to do is restore the Master Boot Record. There are several tools that can do the trick, I will mention just two:
Super Grub Disk
Super Grub Disk is intended to run from a floppy disk or CD and is used for system rescue. Most importantly, it can be used to restore boot loaders, including GRUB, LILO and even Windows boot loader.
Ultimate Boot CD for Windows
This is one of the most important tools a Windows user can have. It is a complete bootable Windows kernel, packaged with tens of useful utilities in a range of categories. Most importantly, UBCD4WIN can fix the MBR quickly and easily. If you have a Windows CD, you can also boot from it, go into the Recovery Console and manually restore the MBR, although this is a procedure for more advanced users. Let's take a look at each option separately.
Windows Recovery Console
Boot from Window CD. After a while, you'll reach the screen where you have to choose between a setup and the Recovery Console. Press R to get into the Recovery Console.


Provide the administrator's password when asked:

Then simply type the following command:
After that, write quit to exit and reboot. And that's it.
Ultimate Boot CD for Windows
This mighty tool also has the Recovery Console, so you can use it the same way you did before. Or you can boot into the live desktop and use a number of tools.

Under Programs > Disk Tools > Partition, you will find both MBRWizard and MbrFix.
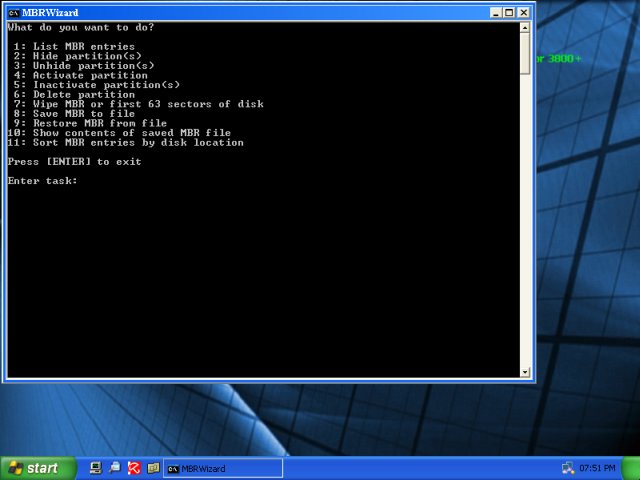

Super GRUB Disk
Super GRUB Disk also lets you fix the bootloader, be it LILO, GRUB or NTLDR. Just burn the .iso and let it boot. The main menu is very ugly, but it's quite simple to follow:

That's it. From now on, the principle is the same for three, four or a million operating systems. Just follow the same train of actions.
Conclusion
Uninstalling operating systems is not a simple thing. It's a complicated issue that requires quite a bit of knowledge, including the understanding of how computers work, the boot sequence, the hard disk & partitioning vocabulary, the bootloader.
It comes as no small wonder that so many people avoid this topic. Furthermore, it does hurt many Linux users that one of their peers should abandon the world of freedom and whatnot and go back to using Microsoft software.
Regardless what your motives are, this tutorial provides you with the tools necessary to remove Linux installations from your system and still maintain a bootable, operable machine. I would very much like to believe that no Linux user would ever take a step back and abandon his/her distribution, but in a real world, this happens and having the right tools for the task guarantees a painless transition. I hope you've learned something new. Enjoy.
佳文赏析:How to uninstall Linux的更多相关文章
- 一文让你熟练掌握Linux的ncat(nc)命令
一文让你熟练掌握Linux的ncat(nc)命令 ncat 或者说 nc 是一款功能类似 cat 的工具,但是是用于网络的.它是一款拥有多种功能的 CLI 工具,可以用来在网络上读.写以及重定向数据. ...
- 佳文分享:CAP定理
1976年6月4号,周5,在远离音乐会大厅的一个楼上的房间内,在位于Manchester的Lesser Free Trade Hall ,Sex Pistols 乐队(注:Sex Pistols的经理 ...
- PythonWeb 服务部署文档及迁移到Linux相关
pythonWeb的部署(Django+Uwsgi): 1. 部署服务器上需要的Python3.6环境: 安装集成了python3.6 和pip ,virtualenv虚拟环境 的Anaconda(A ...
- NetBean 远程开发的好文1 --> NetBeans的远程Linux C开发实践
from: http://blog.csdn.net/jacktan/article/details/9268535 一直以来总觉得NetBeans生活在Eclipse的阴影下,同样做为一款不错的基 ...
- 一文带你彻底理解Linux的各种终端类型及概念
每天使用Linux每天都要接触到Bash,使用Bash时似乎永远都让人摸不着头脑的概念就是终端,坐在这台运行着Linux的机器的显示器前面,这个显示器就是终端的输出,而插在机器上的USB键盘或者PS/ ...
- Linux 文档与目录结构
Linux之文档与目录结构 Linux文件系统结构 Linux目录结构的组织形式和Windows有很大的不同.首先Linux没有“盘(C盘.D盘.E盘)”的概念.已经建立文件系统的硬盘分区被挂载到 ...
- Linux之文档与目录结构 目录的相关操作 Linux的文件系统
Linux之文档与目录结构 Linux文件系统结构 Linux目录结构的组织形式和Windows有很大的不同.首先Linux没有“盘(C盘.D盘.E盘)”的概念.已经建立文件系统的硬盘分区被挂载到 ...
- Linux之文档与目录结构 (/ 用法, 相对路径,绝对路径)
Linux之文档与目录结构 Linux文件系统结构 Linux目录结构的组织形式和Windows有很大的不同.首先Linux没有“盘(C盘.D盘.E盘)”的概念.已经建立文件系统的硬盘分区被挂载到 ...
- (转)linux下进程的进程最大数、最大线程数、进程打开的文件数和ulimit命令修改硬件资源限制
ulimit命令查看和更改系统限制 ulimit命令详解 ulimit用于shell启动进程所占用的资源,可以用来设置系统的限制 语法格式 ulimit [-acdfHlmnpsStvw] [size ...
随机推荐
- Harbor配置https认证
Harbor配置https认证由于Harbor不附带任何证书,它默认使用HTTP来提供注册表请求.但是,强烈建议为任何生产环境启用安全性.因为测试使用,使用自签名证书: 1.创建CA证书 首先创建个目 ...
- 200行代码,7个对象——让你了解ASP.NET Core框架的本质
2019年1月19日,微软技术(苏州)俱乐部成立,我受邀在成立大会上作了一个名为<ASP.NET Core框架揭秘>的分享.在此次分享中,我按照ASP.NET Core自身的运行原理和设计 ...
- DotNetCore跨平台~在appsettings.json里自定义配置项
回到目录 DotNetCore里一切都是依赖注入的,对于appsettings这个可扩展的配置对象也不例外,它位于项目根目录,一般在startup里去注册它,在类中通过构造方法注入来获取当前的对象,以 ...
- .Net Core Web Api 上传女朋友的照片到微软云Azure Storage
前言 实现一个Web Api,把女朋友照片保存到Azure云的storage里. Image Upload Api 在对应的Api Controller里,加上attribute: [Consumes ...
- 并发系列(4)之 AbstractQueuedSynchronizer 源码分析
本文将主要讲述 AbstractQueuedSynchronizer 的内部结构和实现逻辑,在看本文之前最好先了解一下 CLH 队列锁,AbstractQueuedSynchronizer 就是根据 ...
- 【转载】假设有以下代码 String s = “hello”; 阿里巴巴笔试题
原文链接点这里 equals 源码如下: 分析: //true equal用于比较两个对象的值是否相同,和内存地址无关
- PyTorch入门(一)向量
什么是PyTorch? PyTorch是Facebook人工智能团队开发的一个机器学习和深度学习工具,用于处理大规模图像分析,包括物体检测,分割与分类.但是它的功能不仅限于此.它与其它深度学习框架 ...
- 学JAVA第十六 天,JAVA多态
今天老师讲了多态的使用 多态是同一个行为具有多个不同表现形式或形态的能力. 多态的优点: 1. 消除类型之间的耦合关系 2. 可替换性 3. 可扩充性 4. 接口性 5. 灵活性 6. 简化性 我个 ...
- java_异常
一.什么是异常? 1.当程序”运行后”,当jvm遇到一些无法处理的情况,例如:整数/0,这就表示jvm遇到一种”异常情况”. 通常jvm能够识别这些异常并在控制台打印异常信息,并结束程序 2.为了解决 ...
- 2.python中self详解(程序适用于python3版本)
先介绍下Python中的类和实例面向对象最重要的概念就是类(class)和实例(instance),类(class)是抽象的模板,比如学生这个抽象的事物,可以用一个Student类来表示.而实例是根据 ...
