893E - Counting Arrays
3 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
You are given two positive integer numbers x and y. An array F is called an y-factorization of x iff the following conditions are met:
- There are y elements in F, and all of them are integer numbers;
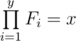 .
.
You have to count the number of pairwise distinct arrays that are y-factorizations of x. Two arrays A and B are considered different iff there exists at least one index i (1 ≤ i ≤ y) such that Ai ≠ Bi. Since the answer can be very large, print it modulo 109 + 7.
The first line contains one integer q (1 ≤ q ≤ 105) — the number of testcases to solve.
Then q lines follow, each containing two integers xi and yi (1 ≤ xi, yi ≤ 106). Each of these lines represents a testcase.
Print q integers. i-th integer has to be equal to the number of yi-factorizations of xi modulo 109 + 7.
- 2
6 3
4 2
- 36
6
In the second testcase of the example there are six y-factorizations:
- { - 4, - 1};
- { - 2, - 2};
- { - 1, - 4};
- {1, 4};
- {2, 2};
- {4, 1}.
题意:给出x,y。求满足含有y个元素的之积是x的数列个数。
思路:排列组合,插空法。
代码:
- #include<bits/stdc++.h>
- #define db double
- #define ll long long
- #define vec vector<ll>
- #define Mt vector<vec>
- #define ci(x) scanf("%d",&x)
- #define cd(x) scanf("%lf",&x)
- #define cl(x) scanf("%lld",&x)
- #define pi(x) printf("%d\n",x)
- #define pd(x) printf("%f\n",x)
- #define pl(x) printf("%lld\n",x)
- #define rep(i,x,y) for(int i=x;i<=y;i++)
- #define debug puts("-------------");
- const int N = 1e6 + ;
- const int mod = 1e9 + ;
- const int MOD = mod-;
- const db eps = 1e-;
- const db PI = acos(-1.0);
- using namespace std;
- bool v[N];
- int pri[N];
- ll F[N], Finv[N], inv[N];//F是阶乘,Finv是逆元的阶乘
- int p=;
- void init()
- {
- memset(v,,sizeof(v));
- for(int i=;i<;i++){
- if(!v[i]) pri[p++]=i;
- for(int j=*i;j<;j+=i) {v[j]=;}
- }
- inv[] = ;
- for(int i = ; i < ; i ++){
- inv[i] = (mod - mod / i) * 1ll * inv[mod % i] % mod;
- }
- F[] = Finv[] = ;
- for(int i = ; i < ; i ++){
- F[i] = F[i-] * 1ll * i % mod;
- Finv[i] = Finv[i-] * 1ll* inv[i] % mod;
- }
- }
- ll C(ll n, ll m){ //comb(n, m)就是C(n, m)
- if(m < || m > n) return ;
- return F[n] * 1ll * Finv[n - m] % mod * Finv[m] % mod;
- }
- ll qpow(ll x,ll n)
- {
- ll ans=;
- x%=mod;
- while(n){
- if(n&) ans=ans*x%mod;
- x=x*x%mod;
- n>>=;
- }
- return ans;
- }
- int main(){
- int q;
- ci(q);
- init();
- for(int i=;i<q;i++)
- {
- ll x,y;
- cl(x),cl(y);
- ll ans=qpow(,y-);
- if(x==){
- pl(qpow(, y - ));
- continue;
- }
- vector<int> e;e.clear();
- map<int,int> mp;mp.clear();
- int id=;
- while(x>){
- if(x%pri[id]==){
- int n=;
- while(x%pri[id]==) n++,x/=pri[id];
- ans=ans*C(n+y-,y-)%mod;
- }
- id++;
- if(pri[id]>){
- if(x>) ans=ans*y%mod;
- break;
- }
- }
- pl(ans);
- }
- return ;
- }
893E - Counting Arrays的更多相关文章
- Codeforces 893E - Counting Arrays
893E - Counting Arrays 思路:质因子分解. 对于每个质因子,假设它有k个,那么求把它分配到y个数上的方案数. 相当于把k个小球分配到y个盒子里的方案数. 这个问题可以用隔板法(插 ...
- Codeforces 893E Counting Arrays:dp + 线性筛 + 分解质因数 + 组合数结论
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/893/E 题意: 共q组数据(q <= 10^5),每组数据给定x,y(x,y <= 10^6 ...
- Educational Codeforces Round 33 (Rated for Div. 2) E. Counting Arrays
题目链接 题意:给你两个数x,yx,yx,y,让你构造一些长为yyy的数列,让这个数列的累乘为xxx,输出方案数. 思路:考虑对xxx进行质因数分解,设某个质因子PiP_iPi的的幂为kkk,则这个 ...
- Educational Codeforces Round 33
# Who = Penalty * A B C D E F 479 arkethos 4 247 + 00:08 + 00:19 +1 00:59 +2 01:41 479 ne-leo ...
- counting elements--codility
lesson 4: counting elements 1. FrogRiverOne 2. PermCheck 3. MissingInteger 4. MaxCounters lesson 4: ...
- 排序算法六:计数排序(Counting sort)
前面介绍的几种排序算法,都是基于不同位置的元素比较,算法平均时间复杂度理论最好值是θ(nlgn). 今天介绍一种新的排序算法,计数排序(Counting sort),计数排序是一个非基于比较的线性时间 ...
- 【算法】计数排序(Counting Sort)(八)
计数排序(Counting Sort) 计数排序不是基于比较的排序算法,其核心在于将输入的数据值转化为键存储在额外开辟的数组空间中. 作为一种线性时间复杂度的排序,计数排序要求输入的数据必须是有确定范 ...
- Java程序员的日常—— Arrays工具类的使用
这个类在日常的开发中,还是非常常用的.今天就总结一下Arrays工具类的常用方法.最常用的就是asList,sort,toStream,equals,copyOf了.另外可以深入学习下Arrays的排 ...
- 使用 Arrays 类操作 Java 中的数组
Arrays 类是 Java 中提供的一个工具类,在 java.util 包中.该类中包含了一些方法用来直接操作数组,比如可直接实现数组的排序.搜索等(关于类和方法的相关内容在后面的章节中会详细讲解滴 ...
随机推荐
- spring数组注入
数组注入 public class MyCollection { private String[]array; private List<String>list; ...
- 《Head First 设计模式》之单件模式
单件模式(Singleton) ——确保一个类只有一个实例,并提供全局访问点. 有一些对象其实我们只需要一个,比如线程池.缓存.对话框.处理偏好设置和注册表的对象.日志对象.如果制造出多个实例,就会导 ...
- 从零开始的全栈工程师——js篇2.16
js操作css样式 div.style.width=“200px” 在div标签内我们添加了一个style属性 并设定了width值 这种写法会给标签带来了大量的style属性 跟实际项目是不符的 我 ...
- JavaScript获取样式值的几种方法学习总结
本人经过整理总结出以下获取样式值的方法,如有错误请各位大佬指正. 有四种方法:style,currentStyle,getComputedStyle,rules 与 cssRules方法. 1. st ...
- Linux下安装maven和nexus
Linux下安装maven1.首先到Maven官网下载安装文件,目前最新版本为3.0.3,下载文件为apache-maven-3.0.3-bin.tar.gz,下载可以使用wget命令: 2.进入下载 ...
- java Vamei快速教程17 多线程
作者:Vamei 出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/vamei 欢迎转载,也请保留这段声明.谢谢! 多线程 多线程(multiple thread)是计算机实现多任务并行处理的一种方 ...
- Mac Office 2016 卸载
https://support.office.com/zh-cn/article/%E5%8D%B8%E8%BD%BD-Office-2016-for-Mac-eefa1199-5b58-43af-8 ...
- [VC]vc中socket编程步骤
sockets(套接字)编程有三种,流式套接字(SOCK_STREAM),数据报套接字(SOCK_DGRAM),原始套接字(SOCK_RAW): 基于TCP的socket编程是采用的流式套接字.在这个 ...
- 分布式版本控制系统git
最近看到这篇文章,简洁易懂,特摘抄至https://www.cnblogs.com/bgwhite/p/9403233.html 供大家提供参考. git可以说是世界上最先进的版本控制系统,大多语句的 ...
- dubbo + zookeeper 配置
Dubbo与Zookeeper.SpringMVC整合和使用 windows环境介绍: myeclipse 10 jdk1.6 tomcat 6.0.35 一.安装Zookeeper 1.通过链接 ...
