Java集合--WeakHashMap
转载请注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/admin/EditPosts.aspx?postid=3311092
第1部分 WeakHashMap介绍
WeakHashMap简介
WeakHashMap 继承于AbstractMap,实现了Map接口。
和HashMap一样,WeakHashMap 也是一个散列表,它存储的内容也是键值对(key-value)映射,而且键和值都可以是null。
不过WeakHashMap的键是“弱键”。在 WeakHashMap 中,当某个键不再正常使用时,会被从WeakHashMap中被自动移除。更精确地说,对于一个给定的键,其映射的存在并不阻止垃圾回收器对该键的丢弃,这就使该键成为可终止的,被终止,然后被回收。某个键被终止时,它对应的键值对也就从映射中有效地移除了。
这个“弱键”的原理呢?大致上就是,通过WeakReference和ReferenceQueue实现的。 WeakHashMap的key是“弱键”,即是WeakReference类型的;ReferenceQueue是一个队列,它会保存被GC回收的“弱键”。实现步骤是:
(01) 新建WeakHashMap,将“键值对”添加到WeakHashMap中。
实际上,WeakHashMap是通过数组table保存Entry(键值对);每一个Entry实际上是一个单向链表,即Entry是键值对链表。
(02) 当某“弱键”不再被其它对象引用,并被GC回收时。在GC回收该“弱键”时,这个“弱键”也同时会被添加到ReferenceQueue(queue)队列中。
(03) 当下一次我们需要操作WeakHashMap时,会先同步table和queue。table中保存了全部的键值对,而queue中保存被GC回收的键值对;同步它们,就是删除table中被GC回收的键值对。
这就是“弱键”如何被自动从WeakHashMap中删除的步骤了。
和HashMap一样,WeakHashMap是不同步的。可以使用 Collections.synchronizedMap 方法来构造同步的 WeakHashMap。
WeakHashMap的构造函数
WeakHashMap共有4个构造函数,如下:

// 默认构造函数。
WeakHashMap() // 指定“容量大小”的构造函数
WeakHashMap(int capacity) // 指定“容量大小”和“加载因子”的构造函数
WeakHashMap(int capacity, float loadFactor) // 包含“子Map”的构造函数
WeakHashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> map)

WeakHashMap的API

void clear()
Object clone()
boolean containsKey(Object key)
boolean containsValue(Object value)
Set<Entry<K, V>> entrySet()
V get(Object key)
boolean isEmpty()
Set<K> keySet()
V put(K key, V value)
void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> map)
V remove(Object key)
int size()
Collection<V> values()

第2部分 WeakHashMap数据结构
WeakHashMap的继承关系如下

java.lang.Object
↳ java.util.AbstractMap<K, V>
↳ java.util.WeakHashMap<K, V> public class WeakHashMap<K,V>
extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V> {}

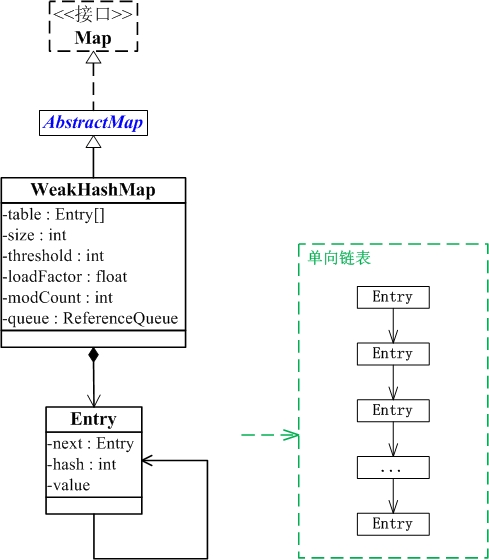
WeakHashMap与Map关系如下图:
从图中可以看出:
(01) WeakHashMap继承于AbstractMap,并且实现了Map接口。
(02) WeakHashMap是哈希表,但是它的键是"弱键"。WeakHashMap中保护几个重要的成员变量:table, size, threshold, loadFactor,modCount, queue。
table是一个Entry[]数组类型,而Entry实际上就是一个单向链表。哈希表的"key-value键值对"都是存储在Entry数组中的。
size是Hashtable的大小,它是Hashtable保存的键值对的数量。
threshold是Hashtable的阈值,用于判断是否需要调整Hashtable的容量。threshold的值="容量*加载因子"。
loadFactor就是加载因子。
modCount是用来实现fail-fast机制的
queue保存的是“已被GC清除”的“弱引用的键”。
第3部分 WeakHashMap源码解析(基于JDK1.6.0_45)
下面对WeakHashMap的源码进行说明

1 package java.util;
2 import java.lang.ref.WeakReference;
3 import java.lang.ref.ReferenceQueue;
4
5 public class WeakHashMap<K,V>
6 extends AbstractMap<K,V>
7 implements Map<K,V> {
8
9 // 默认的初始容量是16,必须是2的幂。
10 private static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16;
11
12 // 最大容量(必须是2的幂且小于2的30次方,传入容量过大将被这个值替换)
13 private static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
14
15 // 默认加载因子
16 private static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
17
18 // 存储数据的Entry数组,长度是2的幂。
19 // WeakHashMap是采用拉链法实现的,每一个Entry本质上是一个单向链表
20 private Entry[] table;
21
22 // WeakHashMap的大小,它是WeakHashMap保存的键值对的数量
23 private int size;
24
25 // WeakHashMap的阈值,用于判断是否需要调整WeakHashMap的容量(threshold = 容量*加载因子)
26 private int threshold;
27
28 // 加载因子实际大小
29 private final float loadFactor;
30
31 // queue保存的是“已被GC清除”的“弱引用的键”。
32 // 弱引用和ReferenceQueue 是联合使用的:如果弱引用所引用的对象被垃圾回收,Java虚拟机就会把这个弱引用加入到与之关联的引用队列中
33 private final ReferenceQueue<K> queue = new ReferenceQueue<K>();
34
35 // WeakHashMap被改变的次数
36 private volatile int modCount;
37
38 // 指定“容量大小”和“加载因子”的构造函数
39 public WeakHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
40 if (initialCapacity < 0)
41 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Initial Capacity: "+
42 initialCapacity);
43 // WeakHashMap的最大容量只能是MAXIMUM_CAPACITY
44 if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
45 initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
46
47 if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
48 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Load factor: "+
49 loadFactor);
50 // 找出“大于initialCapacity”的最小的2的幂
51 int capacity = 1;
52 while (capacity < initialCapacity)
53 capacity <<= 1;
54 // 创建Entry数组,用来保存数据
55 table = new Entry[capacity];
56 // 设置“加载因子”
57 this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
58 // 设置“WeakHashMap阈值”,当WeakHashMap中存储数据的数量达到threshold时,就需要将WeakHashMap的容量加倍。
59 threshold = (int)(capacity * loadFactor);
60 }
61
62 // 指定“容量大小”的构造函数
63 public WeakHashMap(int initialCapacity) {
64 this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
65 }
66
67 // 默认构造函数。
68 public WeakHashMap() {
69 this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR;
70 threshold = (int)(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY);
71 table = new Entry[DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY];
72 }
73
74 // 包含“子Map”的构造函数
75 public WeakHashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
76 this(Math.max((int) (m.size() / DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR) + 1, 16),
77 DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
78 // 将m中的全部元素逐个添加到WeakHashMap中
79 putAll(m);
80 }
81
82 // 键为null的mask值。
83 // 因为WeakReference中允许“null的key”,若直接插入“null的key”,将其当作弱引用时,会被删除。
84 // 因此,这里对于“key为null”的清空,都统一替换为“key为NULL_KEY”,“NULL_KEY”是“静态的final常量”。
85 private static final Object NULL_KEY = new Object();
86
87 // 对“null的key”进行特殊处理
88 private static Object maskNull(Object key) {
89 return (key == null ? NULL_KEY : key);
90 }
91
92 // 还原对“null的key”的特殊处理
93 private static <K> K unmaskNull(Object key) {
94 return (K) (key == NULL_KEY ? null : key);
95 }
96
97 // 判断“x”和“y”是否相等
98 static boolean eq(Object x, Object y) {
99 return x == y || x.equals(y);
100 }
101
102 // 返回索引值
103 // h & (length-1)保证返回值的小于length
104 static int indexFor(int h, int length) {
105 return h & (length-1);
106 }
107
108 // 清空table中无用键值对。原理如下:
109 // (01) 当WeakHashMap中某个“弱引用的key”由于没有再被引用而被GC收回时,
110 // 被回收的“该弱引用key”也被会被添加到"ReferenceQueue(queue)"中。
111 // (02) 当我们执行expungeStaleEntries时,
112 // 就遍历"ReferenceQueue(queue)"中的所有key
113 // 然后就在“WeakReference的table”中删除与“ReferenceQueue(queue)中key”对应的键值对
114 private void expungeStaleEntries() {
115 Entry<K,V> e;
116 while ( (e = (Entry<K,V>) queue.poll()) != null) {
117 int h = e.hash;
118 int i = indexFor(h, table.length);
119
120 Entry<K,V> prev = table[i];
121 Entry<K,V> p = prev;
122 while (p != null) {
123 Entry<K,V> next = p.next;
124 if (p == e) {
125 if (prev == e)
126 table[i] = next;
127 else
128 prev.next = next;
129 e.next = null; // Help GC
130 e.value = null; // " "
131 size--;
132 break;
133 }
134 prev = p;
135 p = next;
136 }
137 }
138 }
139
140 // 获取WeakHashMap的table(存放键值对的数组)
141 private Entry[] getTable() {
142 // 删除table中“已被GC回收的key对应的键值对”
143 expungeStaleEntries();
144 return table;
145 }
146
147 // 获取WeakHashMap的实际大小
148 public int size() {
149 if (size == 0)
150 return 0;
151 // 删除table中“已被GC回收的key对应的键值对”
152 expungeStaleEntries();
153 return size;
154 }
155
156 public boolean isEmpty() {
157 return size() == 0;
158 }
159
160 // 获取key对应的value
161 public V get(Object key) {
162 Object k = maskNull(key);
163 // 获取key的hash值。
164 int h = HashMap.hash(k.hashCode());
165 Entry[] tab = getTable();
166 int index = indexFor(h, tab.length);
167 Entry<K,V> e = tab[index];
168 // 在“该hash值对应的链表”上查找“键值等于key”的元素
169 while (e != null) {
170 if (e.hash == h && eq(k, e.get()))
171 return e.value;
172 e = e.next;
173 }
174 return null;
175 }
176
177 // WeakHashMap是否包含key
178 public boolean containsKey(Object key) {
179 return getEntry(key) != null;
180 }
181
182 // 返回“键为key”的键值对
183 Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) {
184 Object k = maskNull(key);
185 int h = HashMap.hash(k.hashCode());
186 Entry[] tab = getTable();
187 int index = indexFor(h, tab.length);
188 Entry<K,V> e = tab[index];
189 while (e != null && !(e.hash == h && eq(k, e.get())))
190 e = e.next;
191 return e;
192 }
193
194 // 将“key-value”添加到WeakHashMap中
195 public V put(K key, V value) {
196 K k = (K) maskNull(key);
197 int h = HashMap.hash(k.hashCode());
198 Entry[] tab = getTable();
199 int i = indexFor(h, tab.length);
200
201 for (Entry<K,V> e = tab[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
202 // 若“该key”对应的键值对已经存在,则用新的value取代旧的value。然后退出!
203 if (h == e.hash && eq(k, e.get())) {
204 V oldValue = e.value;
205 if (value != oldValue)
206 e.value = value;
207 return oldValue;
208 }
209 }
210
211 // 若“该key”对应的键值对不存在于WeakHashMap中,则将“key-value”添加到table中
212 modCount++;
213 Entry<K,V> e = tab[i];
214 tab[i] = new Entry<K,V>(k, value, queue, h, e);
215 if (++size >= threshold)
216 resize(tab.length * 2);
217 return null;
218 }
219
220 // 重新调整WeakHashMap的大小,newCapacity是调整后的单位
221 void resize(int newCapacity) {
222 Entry[] oldTable = getTable();
223 int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
224 if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
225 threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
226 return;
227 }
228
229 // 新建一个newTable,将“旧的table”的全部元素添加到“新的newTable”中,
230 // 然后,将“新的newTable”赋值给“旧的table”。
231 Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity];
232 transfer(oldTable, newTable);
233 table = newTable;
234
235 if (size >= threshold / 2) {
236 threshold = (int)(newCapacity * loadFactor);
237 } else {
238 // 删除table中“已被GC回收的key对应的键值对”
239 expungeStaleEntries();
240 transfer(newTable, oldTable);
241 table = oldTable;
242 }
243 }
244
245 // 将WeakHashMap中的全部元素都添加到newTable中
246 private void transfer(Entry[] src, Entry[] dest) {
247 for (int j = 0; j < src.length; ++j) {
248 Entry<K,V> e = src[j];
249 src[j] = null;
250 while (e != null) {
251 Entry<K,V> next = e.next;
252 Object key = e.get();
253 if (key == null) {
254 e.next = null; // Help GC
255 e.value = null; // " "
256 size--;
257 } else {
258 int i = indexFor(e.hash, dest.length);
259 e.next = dest[i];
260 dest[i] = e;
261 }
262 e = next;
263 }
264 }
265 }
266
267 // 将"m"的全部元素都添加到WeakHashMap中
268 public void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
269 int numKeysToBeAdded = m.size();
270 if (numKeysToBeAdded == 0)
271 return;
272
273 // 计算容量是否足够,
274 // 若“当前实际容量 < 需要的容量”,则将容量x2。
275 if (numKeysToBeAdded > threshold) {
276 int targetCapacity = (int)(numKeysToBeAdded / loadFactor + 1);
277 if (targetCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
278 targetCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
279 int newCapacity = table.length;
280 while (newCapacity < targetCapacity)
281 newCapacity <<= 1;
282 if (newCapacity > table.length)
283 resize(newCapacity);
284 }
285
286 // 将“m”中的元素逐个添加到WeakHashMap中。
287 for (Map.Entry<? extends K, ? extends V> e : m.entrySet())
288 put(e.getKey(), e.getValue());
289 }
290
291 // 删除“键为key”元素
292 public V remove(Object key) {
293 Object k = maskNull(key);
294 // 获取哈希值。
295 int h = HashMap.hash(k.hashCode());
296 Entry[] tab = getTable();
297 int i = indexFor(h, tab.length);
298 Entry<K,V> prev = tab[i];
299 Entry<K,V> e = prev;
300
301 // 删除链表中“键为key”的元素
302 // 本质是“删除单向链表中的节点”
303 while (e != null) {
304 Entry<K,V> next = e.next;
305 if (h == e.hash && eq(k, e.get())) {
306 modCount++;
307 size--;
308 if (prev == e)
309 tab[i] = next;
310 else
311 prev.next = next;
312 return e.value;
313 }
314 prev = e;
315 e = next;
316 }
317
318 return null;
319 }
320
321 // 删除“键值对”
322 Entry<K,V> removeMapping(Object o) {
323 if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
324 return null;
325 Entry[] tab = getTable();
326 Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry)o;
327 Object k = maskNull(entry.getKey());
328 int h = HashMap.hash(k.hashCode());
329 int i = indexFor(h, tab.length);
330 Entry<K,V> prev = tab[i];
331 Entry<K,V> e = prev;
332
333 // 删除链表中的“键值对e”
334 // 本质是“删除单向链表中的节点”
335 while (e != null) {
336 Entry<K,V> next = e.next;
337 if (h == e.hash && e.equals(entry)) {
338 modCount++;
339 size--;
340 if (prev == e)
341 tab[i] = next;
342 else
343 prev.next = next;
344 return e;
345 }
346 prev = e;
347 e = next;
348 }
349
350 return null;
351 }
352
353 // 清空WeakHashMap,将所有的元素设为null
354 public void clear() {
355 while (queue.poll() != null)
356 ;
357
358 modCount++;
359 Entry[] tab = table;
360 for (int i = 0; i < tab.length; ++i)
361 tab[i] = null;
362 size = 0;
363
364 while (queue.poll() != null)
365 ;
366 }
367
368 // 是否包含“值为value”的元素
369 public boolean containsValue(Object value) {
370 // 若“value为null”,则调用containsNullValue()查找
371 if (value==null)
372 return containsNullValue();
373
374 // 若“value不为null”,则查找WeakHashMap中是否有值为value的节点。
375 Entry[] tab = getTable();
376 for (int i = tab.length ; i-- > 0 ;)
377 for (Entry e = tab[i] ; e != null ; e = e.next)
378 if (value.equals(e.value))
379 return true;
380 return false;
381 }
382
383 // 是否包含null值
384 private boolean containsNullValue() {
385 Entry[] tab = getTable();
386 for (int i = tab.length ; i-- > 0 ;)
387 for (Entry e = tab[i] ; e != null ; e = e.next)
388 if (e.value==null)
389 return true;
390 return false;
391 }
392
393 // Entry是单向链表。
394 // 它是 “WeakHashMap链式存储法”对应的链表。
395 // 它实现了Map.Entry 接口,即实现getKey(), getValue(), setValue(V value), equals(Object o), hashCode()这些函数
396 private static class Entry<K,V> extends WeakReference<K> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
397 private V value;
398 private final int hash;
399 // 指向下一个节点
400 private Entry<K,V> next;
401
402 // 构造函数。
403 Entry(K key, V value,
404 ReferenceQueue<K> queue,
405 int hash, Entry<K,V> next) {
406 super(key, queue);
407 this.value = value;
408 this.hash = hash;
409 this.next = next;
410 }
411
412 public K getKey() {
413 return WeakHashMap.<K>unmaskNull(get());
414 }
415
416 public V getValue() {
417 return value;
418 }
419
420 public V setValue(V newValue) {
421 V oldValue = value;
422 value = newValue;
423 return oldValue;
424 }
425
426 // 判断两个Entry是否相等
427 // 若两个Entry的“key”和“value”都相等,则返回true。
428 // 否则,返回false
429 public boolean equals(Object o) {
430 if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
431 return false;
432 Map.Entry e = (Map.Entry)o;
433 Object k1 = getKey();
434 Object k2 = e.getKey();
435 if (k1 == k2 || (k1 != null && k1.equals(k2))) {
436 Object v1 = getValue();
437 Object v2 = e.getValue();
438 if (v1 == v2 || (v1 != null && v1.equals(v2)))
439 return true;
440 }
441 return false;
442 }
443
444 // 实现hashCode()
445 public int hashCode() {
446 Object k = getKey();
447 Object v = getValue();
448 return ((k==null ? 0 : k.hashCode()) ^
449 (v==null ? 0 : v.hashCode()));
450 }
451
452 public String toString() {
453 return getKey() + "=" + getValue();
454 }
455 }
456
457 // HashIterator是WeakHashMap迭代器的抽象出来的父类,实现了公共了函数。
458 // 它包含“key迭代器(KeyIterator)”、“Value迭代器(ValueIterator)”和“Entry迭代器(EntryIterator)”3个子类。
459 private abstract class HashIterator<T> implements Iterator<T> {
460 // 当前索引
461 int index;
462 // 当前元素
463 Entry<K,V> entry = null;
464 // 上一次返回元素
465 Entry<K,V> lastReturned = null;
466 // expectedModCount用于实现fast-fail机制。
467 int expectedModCount = modCount;
468
469 // 下一个键(强引用)
470 Object nextKey = null;
471
472 // 当前键(强引用)
473 Object currentKey = null;
474
475 // 构造函数
476 HashIterator() {
477 index = (size() != 0 ? table.length : 0);
478 }
479
480 // 是否存在下一个元素
481 public boolean hasNext() {
482 Entry[] t = table;
483
484 // 一个Entry就是一个单向链表
485 // 若该Entry的下一个节点不为空,就将next指向下一个节点;
486 // 否则,将next指向下一个链表(也是下一个Entry)的不为null的节点。
487 while (nextKey == null) {
488 Entry<K,V> e = entry;
489 int i = index;
490 while (e == null && i > 0)
491 e = t[--i];
492 entry = e;
493 index = i;
494 if (e == null) {
495 currentKey = null;
496 return false;
497 }
498 nextKey = e.get(); // hold on to key in strong ref
499 if (nextKey == null)
500 entry = entry.next;
501 }
502 return true;
503 }
504
505 // 获取下一个元素
506 protected Entry<K,V> nextEntry() {
507 if (modCount != expectedModCount)
508 throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
509 if (nextKey == null && !hasNext())
510 throw new NoSuchElementException();
511
512 lastReturned = entry;
513 entry = entry.next;
514 currentKey = nextKey;
515 nextKey = null;
516 return lastReturned;
517 }
518
519 // 删除当前元素
520 public void remove() {
521 if (lastReturned == null)
522 throw new IllegalStateException();
523 if (modCount != expectedModCount)
524 throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
525
526 WeakHashMap.this.remove(currentKey);
527 expectedModCount = modCount;
528 lastReturned = null;
529 currentKey = null;
530 }
531
532 }
533
534 // value的迭代器
535 private class ValueIterator extends HashIterator<V> {
536 public V next() {
537 return nextEntry().value;
538 }
539 }
540
541 // key的迭代器
542 private class KeyIterator extends HashIterator<K> {
543 public K next() {
544 return nextEntry().getKey();
545 }
546 }
547
548 // Entry的迭代器
549 private class EntryIterator extends HashIterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
550 public Map.Entry<K,V> next() {
551 return nextEntry();
552 }
553 }
554
555 // WeakHashMap的Entry对应的集合
556 private transient Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet = null;
557
558 // 返回“key的集合”,实际上返回一个“KeySet对象”
559 public Set<K> keySet() {
560 Set<K> ks = keySet;
561 return (ks != null ? ks : (keySet = new KeySet()));
562 }
563
564 // Key对应的集合
565 // KeySet继承于AbstractSet,说明该集合中没有重复的Key。
566 private class KeySet extends AbstractSet<K> {
567 public Iterator<K> iterator() {
568 return new KeyIterator();
569 }
570
571 public int size() {
572 return WeakHashMap.this.size();
573 }
574
575 public boolean contains(Object o) {
576 return containsKey(o);
577 }
578
579 public boolean remove(Object o) {
580 if (containsKey(o)) {
581 WeakHashMap.this.remove(o);
582 return true;
583 }
584 else
585 return false;
586 }
587
588 public void clear() {
589 WeakHashMap.this.clear();
590 }
591 }
592
593 // 返回“value集合”,实际上返回的是一个Values对象
594 public Collection<V> values() {
595 Collection<V> vs = values;
596 return (vs != null ? vs : (values = new Values()));
597 }
598
599 // “value集合”
600 // Values继承于AbstractCollection,不同于“KeySet继承于AbstractSet”,
601 // Values中的元素能够重复。因为不同的key可以指向相同的value。
602 private class Values extends AbstractCollection<V> {
603 public Iterator<V> iterator() {
604 return new ValueIterator();
605 }
606
607 public int size() {
608 return WeakHashMap.this.size();
609 }
610
611 public boolean contains(Object o) {
612 return containsValue(o);
613 }
614
615 public void clear() {
616 WeakHashMap.this.clear();
617 }
618 }
619
620 // 返回“WeakHashMap的Entry集合”
621 // 它实际是返回一个EntrySet对象
622 public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() {
623 Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> es = entrySet;
624 return es != null ? es : (entrySet = new EntrySet());
625 }
626
627 // EntrySet对应的集合
628 // EntrySet继承于AbstractSet,说明该集合中没有重复的EntrySet。
629 private class EntrySet extends AbstractSet<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
630 public Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> iterator() {
631 return new EntryIterator();
632 }
633
634 // 是否包含“值(o)”
635 public boolean contains(Object o) {
636 if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
637 return false;
638 Map.Entry e = (Map.Entry)o;
639 Object k = e.getKey();
640 Entry candidate = getEntry(e.getKey());
641 return candidate != null && candidate.equals(e);
642 }
643
644 // 删除“值(o)”
645 public boolean remove(Object o) {
646 return removeMapping(o) != null;
647 }
648
649 // 返回WeakHashMap的大小
650 public int size() {
651 return WeakHashMap.this.size();
652 }
653
654 // 清空WeakHashMap
655 public void clear() {
656 WeakHashMap.this.clear();
657 }
658
659 // 拷贝函数。将WeakHashMap中的全部元素都拷贝到List中
660 private List<Map.Entry<K,V>> deepCopy() {
661 List<Map.Entry<K,V>> list = new ArrayList<Map.Entry<K,V>>(size());
662 for (Map.Entry<K,V> e : this)
663 list.add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<K,V>(e));
664 return list;
665 }
666
667 // 返回Entry对应的Object[]数组
668 public Object[] toArray() {
669 return deepCopy().toArray();
670 }
671
672 // 返回Entry对应的T[]数组(T[]我们新建数组时,定义的数组类型)
673 public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {
674 return deepCopy().toArray(a);
675 }
676 }
677 }

说明:WeakHashMap和HashMap都是通过"拉链法"实现的散列表。它们的源码绝大部分内容都一样,这里就只是对它们不同的部分就是说明。
WeakReference是“弱键”实现的哈希表。它这个“弱键”的目的就是:实现对“键值对”的动态回收。当“弱键”不再被使用到时,GC会回收它,WeakReference也会将“弱键”对应的键值对删除。
“弱键”是一个“弱引用(WeakReference)”,在Java中,WeakReference和ReferenceQueue 是联合使用的。在WeakHashMap中亦是如此:如果弱引用所引用的对象被垃圾回收,Java虚拟机就会把这个弱引用加入到与之关联的引用队列中。 接着,WeakHashMap会根据“引用队列”,来删除“WeakHashMap中已被GC回收的‘弱键’对应的键值对”。
另外,理解上面思想的重点是通过 expungeStaleEntries() 函数去理解。
第4部分 WeakHashMap遍历方式
4.1 遍历WeakHashMap的键值对
第一步:根据entrySet()获取WeakHashMap的“键值对”的Set集合。
第二步:通过Iterator迭代器遍历“第一步”得到的集合。

// 假设map是WeakHashMap对象
// map中的key是String类型,value是Integer类型
Integer integ = null;
Iterator iter = map.entrySet().iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry)iter.next();
// 获取key
key = (String)entry.getKey();
// 获取value
integ = (Integer)entry.getValue();
}

4.2 遍历WeakHashMap的键
第一步:根据keySet()获取WeakHashMap的“键”的Set集合。
第二步:通过Iterator迭代器遍历“第一步”得到的集合。

// 假设map是WeakHashMap对象
// map中的key是String类型,value是Integer类型
String key = null;
Integer integ = null;
Iterator iter = map.keySet().iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
// 获取key
key = (String)iter.next();
// 根据key,获取value
integ = (Integer)map.get(key);
}

4.3 遍历WeakHashMap的值
第一步:根据value()获取WeakHashMap的“值”的集合。
第二步:通过Iterator迭代器遍历“第一步”得到的集合。

// 假设map是WeakHashMap对象
// map中的key是String类型,value是Integer类型
Integer value = null;
Collection c = map.values();
Iterator iter= c.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
value = (Integer)iter.next();
}

WeakHashMap遍历测试程序如下:

1 import java.util.Map;
2 import java.util.Random;
3 import java.util.Iterator;
4 import java.util.WeakHashMap;
5 import java.util.HashSet;
6 import java.util.Map.Entry;
7 import java.util.Collection;
8
9 /*
10 * @desc 遍历WeakHashMap的测试程序。
11 * (01) 通过entrySet()去遍历key、value,参考实现函数:
12 * iteratorHashMapByEntryset()
13 * (02) 通过keySet()去遍历key、value,参考实现函数:
14 * iteratorHashMapByKeyset()
15 * (03) 通过values()去遍历value,参考实现函数:
16 * iteratorHashMapJustValues()
17 *
18 * @author skywang
19 */
20 public class WeakHashMapIteratorTest {
21
22 public static void main(String[] args) {
23 int val = 0;
24 String key = null;
25 Integer value = null;
26 Random r = new Random();
27 WeakHashMap map = new WeakHashMap();
28
29 for (int i=0; i<12; i++) {
30 // 随机获取一个[0,100)之间的数字
31 val = r.nextInt(100);
32
33 key = String.valueOf(val);
34 value = r.nextInt(5);
35 // 添加到WeakHashMap中
36 map.put(key, value);
37 System.out.println(" key:"+key+" value:"+value);
38 }
39 // 通过entrySet()遍历WeakHashMap的key-value
40 iteratorHashMapByEntryset(map) ;
41
42 // 通过keySet()遍历WeakHashMap的key-value
43 iteratorHashMapByKeyset(map) ;
44
45 // 单单遍历WeakHashMap的value
46 iteratorHashMapJustValues(map);
47 }
48
49 /*
50 * 通过entry set遍历WeakHashMap
51 * 效率高!
52 */
53 private static void iteratorHashMapByEntryset(WeakHashMap map) {
54 if (map == null)
55 return ;
56
57 System.out.println("\niterator WeakHashMap By entryset");
58 String key = null;
59 Integer integ = null;
60 Iterator iter = map.entrySet().iterator();
61 while(iter.hasNext()) {
62 Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry)iter.next();
63
64 key = (String)entry.getKey();
65 integ = (Integer)entry.getValue();
66 System.out.println(key+" -- "+integ.intValue());
67 }
68 }
69
70 /*
71 * 通过keyset来遍历WeakHashMap
72 * 效率低!
73 */
74 private static void iteratorHashMapByKeyset(WeakHashMap map) {
75 if (map == null)
76 return ;
77
78 System.out.println("\niterator WeakHashMap By keyset");
79 String key = null;
80 Integer integ = null;
81 Iterator iter = map.keySet().iterator();
82 while (iter.hasNext()) {
83 key = (String)iter.next();
84 integ = (Integer)map.get(key);
85 System.out.println(key+" -- "+integ.intValue());
86 }
87 }
88
89
90 /*
91 * 遍历WeakHashMap的values
92 */
93 private static void iteratorHashMapJustValues(WeakHashMap map) {
94 if (map == null)
95 return ;
96
97 Collection c = map.values();
98 Iterator iter= c.iterator();
99 while (iter.hasNext()) {
100 System.out.println(iter.next());
101 }
102 }
103 }

第5部分 WeakHashMap示例
下面通过实例来学习如何使用WeakHashMap

1 import java.util.Iterator;
2 import java.util.Map;
3 import java.util.WeakHashMap;
4 import java.util.Date;
5 import java.lang.ref.WeakReference;
6
7 /**
8 * @desc WeakHashMap测试程序
9 *
10 * @author skywang
11 * @email kuiwu-wang@163.com
12 */
13 public class WeakHashMapTest {
14
15 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
16 testWeakHashMapAPIs();
17 }
18
19 private static void testWeakHashMapAPIs() {
20 // 初始化3个“弱键”
21 String w1 = new String("one");
22 String w2 = new String("two");
23 String w3 = new String("three");
24 // 新建WeakHashMap
25 Map wmap = new WeakHashMap();
26
27 // 添加键值对
28 wmap.put(w1, "w1");
29 wmap.put(w2, "w2");
30 wmap.put(w3, "w3");
31
32 // 打印出wmap
33 System.out.printf("\nwmap:%s\n",wmap );
34
35 // containsKey(Object key) :是否包含键key
36 System.out.printf("contains key two : %s\n",wmap.containsKey("two"));
37 System.out.printf("contains key five : %s\n",wmap.containsKey("five"));
38
39 // containsValue(Object value) :是否包含值value
40 System.out.printf("contains value 0 : %s\n",wmap.containsValue(new Integer(0)));
41
42 // remove(Object key) : 删除键key对应的键值对
43 wmap.remove("three");
44
45 System.out.printf("wmap: %s\n",wmap );
46
47
48
49 // ---- 测试 WeakHashMap 的自动回收特性 ----
50
51 // 将w1设置null。
52 // 这意味着“弱键”w1再没有被其它对象引用,调用gc时会回收WeakHashMap中与“w1”对应的键值对
53 w1 = null;
54 // 内存回收。这里,会回收WeakHashMap中与“w1”对应的键值对
55 System.gc();
56
57 // 遍历WeakHashMap
58 Iterator iter = wmap.entrySet().iterator();
59 while (iter.hasNext()) {
60 Map.Entry en = (Map.Entry)iter.next();
61 System.out.printf("next : %s - %s\n",en.getKey(),en.getValue());
62 }
63 // 打印WeakHashMap的实际大小
64 System.out.printf(" after gc WeakHashMap size:%s\n", wmap.size());
65 }
66 }

运行结果:

wmap:{three=w3, one=w1, two=w2}
contains key two : true
contains key five : false
contains value 0 : false
wmap: {one=w1, two=w2}
next : two - w2
after gc WeakHashMap size:1

Java集合--WeakHashMap的更多相关文章
- Java 集合系列13之 WeakHashMap详细介绍(源码解析)和使用示例
概要 这一章,我们对WeakHashMap进行学习.我们先对WeakHashMap有个整体认识,然后再学习它的源码,最后再通过实例来学会使用WeakHashMap.第1部分 WeakHashMap介绍 ...
- Java 集合系列14之 Map总结(HashMap, Hashtable, TreeMap, WeakHashMap等使用场景)
概要 学完了Map的全部内容,我们再回头开开Map的框架图. 本章内容包括:第1部分 Map概括第2部分 HashMap和Hashtable异同第3部分 HashMap和WeakHashMap异同 转 ...
- Java 集合系列 13 WeakHashMap
java 集合系列目录: Java 集合系列 01 总体框架 Java 集合系列 02 Collection架构 Java 集合系列 03 ArrayList详细介绍(源码解析)和使用示例 Java ...
- Java 集合 持有引用 & WeakHashMap
Java 集合 持有引用 & WeakHashMap @author ixenos 摘要:强引用.弱引用.WeakHashMap动态回收步骤 Reference引用对象 可获得的(reacha ...
- 死磕 java集合之WeakHashMap源码分析
欢迎关注我的公众号"彤哥读源码",查看更多源码系列文章, 与彤哥一起畅游源码的海洋. 简介 WeakHashMap是一种弱引用map,内部的key会存储为弱引用,当jvm gc的时 ...
- Java集合框架List,Map,Set等全面介绍
Java集合框架的基本接口/类层次结构: java.util.Collection [I]+--java.util.List [I] +--java.util.ArrayList [C] +- ...
- Java 集合框架
Java集合框架大致可以分为五个部分:List列表,Set集合.Map映射.迭代器.工具类 List 接口通常表示一个列表(数组.队列.链表 栈),其中的元素 可以重复 的是:ArrayList 和L ...
- Java 集合系列目录(Category)
下面是最近总结的Java集合(JDK1.6.0_45)相关文章的目录. 01. Java 集合系列01之 总体框架 02. Java 集合系列02之 Collection架构 03. Java 集合系 ...
- Java集合源码分析(一)
Java集合工具包位于Java.util包下,包含了很多常用的数据结构,如数组.链表.栈.队列.集合.哈希表等.学习Java集合框架下大致可以分为如下五个部分:List列表.Set集合.Map映射.迭 ...
随机推荐
- Python函数或者类的时间参数的默认值设为datetime.date.today()引起的问题
定义了函数def main(start_date=datetime.date.today(), end_date=datetime.date.today()): pass 函数在项目启动后, end_ ...
- Linux集群环境准备及20项基础优化
中小规模集群架构: 1.什么是集群? 简单地说,集群就是一堆机器 做同一件事, 例如:京东(www.jd.com)提供卖东西服务这就是一件事,可能是几千台服务器,在背后运转支撑这个网站. www.ba ...
- 【leetcode算法-简单】27. 移除元素
[题目描述] 给定一个数组 nums 和一个值 val,你需要原地移除所有数值等于 val 的元素,返回移除后数组的新长度. 不要使用额外的数组空间,你必须在原地修改输入数组并在使用 O(1) 额外空 ...
- C5. Spring 服务的注册与发现(Spring Cloud Eureka)
[概述] Eureka 作为 Spring Cloud 分布式解决方案中重要的一环,实现了服务的注册与发现等功能.Eureka 包括 Eureka Server 和 Eureka Client,具体的 ...
- 【基本优化实践】【1.6】在sql server修改且移动数据库文件位置
在master数据库中,SQL Server提供系统扩展的存储过程,其中有一些存储过程的命名以xp_开头,用于处理操作系统的文件. 一,判断文件是否存在 存储过程sys.xp_fileexist 用于 ...
- if语句、while和for循环
一.if语句 1.多路分支 if 条件1: 代码块1 elif 条件2: 代码块2 else: 代码块3 #python会执行第一次测试为真的语句,如果所有测试都为假,就执行else部分(本例) 2. ...
- 十三、GPIO子系统
由于之后的触摸屏驱动分析中使用到了GPIO子系统和i2c子系统,因此在分析触摸屏驱动之前我准备把这两个子系统进行简单分析. 之前我们使用GPIO引脚的方式并不是推荐的方式,当我们更改某一bit时,很有 ...
- SAS学习笔记46 宏变量的可使用范围
全局宏变量 在宏程序内部,除了使用%GLOBAL语句创建.在某些情况下,还可以直接使用DATA步中的CALL SYMPUT创建. 在一个宏程序中,在包含CALL SYMPUT的DATA步程序之前,如果 ...
- SAS学习笔记31 SAS随机分组方法及实现
随机分组方法包括: 简单随机化(simple randomization) 区组随机化(block randomization) 分层随机化(stratified randomization) 分层区 ...
- docker系列3--dockerd配置文件
dockerd启动配置 docker通信方式选择 docker默认以sock文件方式提供接口,要开放tcp接口远程调用,需要修改配置文件: The Docker daemon can listen f ...
