c语言实行泛型hashmap
代码出处:A simple string hashmap in C https://github.com/petewarden/c_hashmap
main.c
(main2是官方源代码,main是博主写的代码,实现了String类型及Char类型的存取,看官可以根据以下代码触类旁通,限于博主的c语言
功底有限,此处的实现仅为poc代码,不保证严谨性以及稳定性,如果使用到生产环境请多斟酌,测试,如果你有更完善的代码分享,将感激不尽)
/*
* A unit test and example of how to use the simple C hashmap
*/ #include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <assert.h> #include "hashmap.h" #define KEY_MAX_LENGTH (256)
#define KEY_PREFIX ("somekey")
#define KEY_COUNT (1024*1024) typedef struct data_struct_s
{
char key_string[KEY_MAX_LENGTH];
int number;
} data_struct_t; typedef struct data_struct_String
{
char key_string[KEY_MAX_LENGTH];
char str[];
} ds_String; typedef struct data_struct_Char
{
char key_string[KEY_MAX_LENGTH];
char ch;
}ds_Char; void hashmap_putString(map_t *map, ds_String *string)
{
hashmap_put(map, string->key_string, string);
}
void hashmap_getStringValue(map_t *map, char* key)
{
ds_String *out;
hashmap_get(map, key, (void**)(&out)); printf("key:%s, value:%s\n", out->key_string, out->str);
} void hashmap_putChar(map_t *map, ds_Char *ch)
{
hashmap_put(map, ch->key_string, ch);
}
void hashmap_getCharValue(map_t *map, char* key)
{
ds_Char *out;
hashmap_get(map, key, (void**)(&out)); printf("key:%s, value:%c\n", out->key_string, out->ch);
}
int main()
{
map_t mymap;
mymap = hashmap_new(); ds_String *str; ds_Char *ch; str = malloc(sizeof(ds_String)); ch = malloc(sizeof(ds_Char)); //写入String值
snprintf(str->key_string, KEY_MAX_LENGTH, "%s%d", "str", );
strcpy(str->str, "hello World");
hashmap_putString(mymap, str);
hashmap_getStringValue(mymap, str->key_string); //写入Char
ch->ch = 'A';
snprintf(ch->key_string, KEY_COUNT, "%s%d", "ch", );
hashmap_putChar(mymap, ch);
hashmap_getCharValue(mymap, ch->key_string);
} int main2(char* argv, int argc)
{
int index;
int error;
map_t mymap;
char key_string[KEY_MAX_LENGTH];
data_struct_t* value; mymap = hashmap_new(); /* First, populate the hash map with ascending values */
for (index = ; index<KEY_COUNT; index += )
{
/* Store the key string along side the numerical value so we can free it later */
value = malloc(sizeof(data_struct_t));
snprintf(value->key_string, KEY_MAX_LENGTH, "%s%d", KEY_PREFIX, index);
value->number = index; error = hashmap_put(mymap, value->key_string, value);
assert(error == MAP_OK);
} /* Now, check all of the expected values are there */
for (index = ; index<KEY_COUNT; index += )
{
snprintf(key_string, KEY_MAX_LENGTH, "%s%d", KEY_PREFIX, index); error = hashmap_get(mymap, key_string, (void**)(&value)); /* Make sure the value was both found and the correct number */
assert(error == MAP_OK);
assert(value->number == index);
} /* Make sure that a value that wasn't in the map can't be found */
snprintf(key_string, KEY_MAX_LENGTH, "%s%d", KEY_PREFIX, KEY_COUNT); error = hashmap_get(mymap, key_string, (void**)(&value)); /* Make sure the value was not found */
assert(error == MAP_MISSING); /* Free all of the values we allocated and remove them from the map */
for (index = ; index<KEY_COUNT; index += )
{
snprintf(key_string, KEY_MAX_LENGTH, "%s%d", KEY_PREFIX, index); error = hashmap_get(mymap, key_string, (void**)(&value));
assert(error == MAP_OK); error = hashmap_remove(mymap, key_string);
assert(error == MAP_OK); free(value);
} /* Now, destroy the map */
hashmap_free(mymap); return ;
}
输出结果
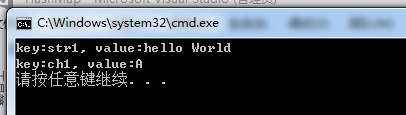
hashmap.h
/*
* Generic hashmap manipulation functions
*
* Originally by Elliot C Back - http://elliottback.com/wp/hashmap-implementation-in-c/
*
* Modified by Pete Warden to fix a serious performance problem, support strings as keys
* and removed thread synchronization - http://petewarden.typepad.com
*/
#ifndef __HASHMAP_H__
#define __HASHMAP_H__ #define MAP_MISSING -3 /* No such element */
#define MAP_FULL -2 /* Hashmap is full */
#define MAP_OMEM -1 /* Out of Memory */
#define MAP_OK 0 /* OK */ /*
* any_t is a pointer. This allows you to put arbitrary structures in
* the hashmap.
*/
typedef void *any_t; /*
* PFany is a pointer to a function that can take two any_t arguments
* and return an integer. Returns status code..
*/
typedef int (*PFany)(any_t, any_t); /*
* map_t is a pointer to an internally maintained data structure.
* Clients of this package do not need to know how hashmaps are
* represented. They see and manipulate only map_t's.
*/
typedef any_t map_t; /*
* Return an empty hashmap. Returns NULL if empty.
*/
extern map_t hashmap_new(); /*
* Iteratively call f with argument (item, data) for
* each element data in the hashmap. The function must
* return a map status code. If it returns anything other
* than MAP_OK the traversal is terminated. f must
* not reenter any hashmap functions, or deadlock may arise.
*/
extern int hashmap_iterate(map_t in, PFany f, any_t item); /*
* Add an element to the hashmap. Return MAP_OK or MAP_OMEM.
*/
extern int hashmap_put(map_t in, char* key, any_t value); /*
* Get an element from the hashmap. Return MAP_OK or MAP_MISSING.
*/
extern int hashmap_get(map_t in, char* key, any_t *arg); /*
* Remove an element from the hashmap. Return MAP_OK or MAP_MISSING.
*/
extern int hashmap_remove(map_t in, char* key); /*
* Get any element. Return MAP_OK or MAP_MISSING.
* remove - should the element be removed from the hashmap
*/
extern int hashmap_get_one(map_t in, any_t *arg, int remove); /*
* Free the hashmap
*/
extern void hashmap_free(map_t in); /*
* Get the current size of a hashmap
*/
extern int hashmap_length(map_t in); #endif __HASHMAP_H__
hashmap.c
/*
* Generic map implementation.
*/
#include "hashmap.h" #include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h> #define INITIAL_SIZE (256)
#define MAX_CHAIN_LENGTH (8) /* We need to keep keys and values */
typedef struct _hashmap_element{
char* key;
int in_use;
any_t data;
} hashmap_element; /* A hashmap has some maximum size and current size,
* as well as the data to hold. */
typedef struct _hashmap_map{
int table_size;
int size;
hashmap_element *data;
} hashmap_map; /*
* Return an empty hashmap, or NULL on failure.
*/
map_t hashmap_new() {
hashmap_map* m = (hashmap_map*) malloc(sizeof(hashmap_map));
if(!m) goto err; m->data = (hashmap_element*) calloc(INITIAL_SIZE, sizeof(hashmap_element));
if(!m->data) goto err; m->table_size = INITIAL_SIZE;
m->size = ; return m;
err:
if (m)
hashmap_free(m);
return NULL;
} /* The implementation here was originally done by Gary S. Brown. I have
borrowed the tables directly, and made some minor changes to the
crc32-function (including changing the interface). //ylo */ /* ============================================================= */
/* COPYRIGHT (C) 1986 Gary S. Brown. You may use this program, or */
/* code or tables extracted from it, as desired without restriction. */
/* */
/* First, the polynomial itself and its table of feedback terms. The */
/* polynomial is */
/* X^32+X^26+X^23+X^22+X^16+X^12+X^11+X^10+X^8+X^7+X^5+X^4+X^2+X^1+X^0 */
/* */
/* Note that we take it "backwards" and put the highest-order term in */
/* the lowest-order bit. The X^32 term is "implied"; the LSB is the */
/* X^31 term, etc. The X^0 term (usually shown as "+1") results in */
/* the MSB being 1. */
/* */
/* Note that the usual hardware shift register implementation, which */
/* is what we're using (we're merely optimizing it by doing eight-bit */
/* chunks at a time) shifts bits into the lowest-order term. In our */
/* implementation, that means shifting towards the right. Why do we */
/* do it this way? Because the calculated CRC must be transmitted in */
/* order from highest-order term to lowest-order term. UARTs transmit */
/* characters in order from LSB to MSB. By storing the CRC this way, */
/* we hand it to the UART in the order low-byte to high-byte; the UART */
/* sends each low-bit to hight-bit; and the result is transmission bit */
/* by bit from highest- to lowest-order term without requiring any bit */
/* shuffling on our part. Reception works similarly. */
/* */
/* The feedback terms table consists of 256, 32-bit entries. Notes: */
/* */
/* The table can be generated at runtime if desired; code to do so */
/* is shown later. It might not be obvious, but the feedback */
/* terms simply represent the results of eight shift/xor opera- */
/* tions for all combinations of data and CRC register values. */
/* */
/* The values must be right-shifted by eight bits by the "updcrc" */
/* logic; the shift must be unsigned (bring in zeroes). On some */
/* hardware you could probably optimize the shift in assembler by */
/* using byte-swap instructions. */
/* polynomial $edb88320 */
/* */
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------- */ static unsigned long crc32_tab[] = {
0x00000000L, 0x77073096L, 0xee0e612cL, 0x990951baL, 0x076dc419L,
0x706af48fL, 0xe963a535L, 0x9e6495a3L, 0x0edb8832L, 0x79dcb8a4L,
0xe0d5e91eL, 0x97d2d988L, 0x09b64c2bL, 0x7eb17cbdL, 0xe7b82d07L,
0x90bf1d91L, 0x1db71064L, 0x6ab020f2L, 0xf3b97148L, 0x84be41deL,
0x1adad47dL, 0x6ddde4ebL, 0xf4d4b551L, 0x83d385c7L, 0x136c9856L,
0x646ba8c0L, 0xfd62f97aL, 0x8a65c9ecL, 0x14015c4fL, 0x63066cd9L,
0xfa0f3d63L, 0x8d080df5L, 0x3b6e20c8L, 0x4c69105eL, 0xd56041e4L,
0xa2677172L, 0x3c03e4d1L, 0x4b04d447L, 0xd20d85fdL, 0xa50ab56bL,
0x35b5a8faL, 0x42b2986cL, 0xdbbbc9d6L, 0xacbcf940L, 0x32d86ce3L,
0x45df5c75L, 0xdcd60dcfL, 0xabd13d59L, 0x26d930acL, 0x51de003aL,
0xc8d75180L, 0xbfd06116L, 0x21b4f4b5L, 0x56b3c423L, 0xcfba9599L,
0xb8bda50fL, 0x2802b89eL, 0x5f058808L, 0xc60cd9b2L, 0xb10be924L,
0x2f6f7c87L, 0x58684c11L, 0xc1611dabL, 0xb6662d3dL, 0x76dc4190L,
0x01db7106L, 0x98d220bcL, 0xefd5102aL, 0x71b18589L, 0x06b6b51fL,
0x9fbfe4a5L, 0xe8b8d433L, 0x7807c9a2L, 0x0f00f934L, 0x9609a88eL,
0xe10e9818L, 0x7f6a0dbbL, 0x086d3d2dL, 0x91646c97L, 0xe6635c01L,
0x6b6b51f4L, 0x1c6c6162L, 0x856530d8L, 0xf262004eL, 0x6c0695edL,
0x1b01a57bL, 0x8208f4c1L, 0xf50fc457L, 0x65b0d9c6L, 0x12b7e950L,
0x8bbeb8eaL, 0xfcb9887cL, 0x62dd1ddfL, 0x15da2d49L, 0x8cd37cf3L,
0xfbd44c65L, 0x4db26158L, 0x3ab551ceL, 0xa3bc0074L, 0xd4bb30e2L,
0x4adfa541L, 0x3dd895d7L, 0xa4d1c46dL, 0xd3d6f4fbL, 0x4369e96aL,
0x346ed9fcL, 0xad678846L, 0xda60b8d0L, 0x44042d73L, 0x33031de5L,
0xaa0a4c5fL, 0xdd0d7cc9L, 0x5005713cL, 0x270241aaL, 0xbe0b1010L,
0xc90c2086L, 0x5768b525L, 0x206f85b3L, 0xb966d409L, 0xce61e49fL,
0x5edef90eL, 0x29d9c998L, 0xb0d09822L, 0xc7d7a8b4L, 0x59b33d17L,
0x2eb40d81L, 0xb7bd5c3bL, 0xc0ba6cadL, 0xedb88320L, 0x9abfb3b6L,
0x03b6e20cL, 0x74b1d29aL, 0xead54739L, 0x9dd277afL, 0x04db2615L,
0x73dc1683L, 0xe3630b12L, 0x94643b84L, 0x0d6d6a3eL, 0x7a6a5aa8L,
0xe40ecf0bL, 0x9309ff9dL, 0x0a00ae27L, 0x7d079eb1L, 0xf00f9344L,
0x8708a3d2L, 0x1e01f268L, 0x6906c2feL, 0xf762575dL, 0x806567cbL,
0x196c3671L, 0x6e6b06e7L, 0xfed41b76L, 0x89d32be0L, 0x10da7a5aL,
0x67dd4accL, 0xf9b9df6fL, 0x8ebeeff9L, 0x17b7be43L, 0x60b08ed5L,
0xd6d6a3e8L, 0xa1d1937eL, 0x38d8c2c4L, 0x4fdff252L, 0xd1bb67f1L,
0xa6bc5767L, 0x3fb506ddL, 0x48b2364bL, 0xd80d2bdaL, 0xaf0a1b4cL,
0x36034af6L, 0x41047a60L, 0xdf60efc3L, 0xa867df55L, 0x316e8eefL,
0x4669be79L, 0xcb61b38cL, 0xbc66831aL, 0x256fd2a0L, 0x5268e236L,
0xcc0c7795L, 0xbb0b4703L, 0x220216b9L, 0x5505262fL, 0xc5ba3bbeL,
0xb2bd0b28L, 0x2bb45a92L, 0x5cb36a04L, 0xc2d7ffa7L, 0xb5d0cf31L,
0x2cd99e8bL, 0x5bdeae1dL, 0x9b64c2b0L, 0xec63f226L, 0x756aa39cL,
0x026d930aL, 0x9c0906a9L, 0xeb0e363fL, 0x72076785L, 0x05005713L,
0x95bf4a82L, 0xe2b87a14L, 0x7bb12baeL, 0x0cb61b38L, 0x92d28e9bL,
0xe5d5be0dL, 0x7cdcefb7L, 0x0bdbdf21L, 0x86d3d2d4L, 0xf1d4e242L,
0x68ddb3f8L, 0x1fda836eL, 0x81be16cdL, 0xf6b9265bL, 0x6fb077e1L,
0x18b74777L, 0x88085ae6L, 0xff0f6a70L, 0x66063bcaL, 0x11010b5cL,
0x8f659effL, 0xf862ae69L, 0x616bffd3L, 0x166ccf45L, 0xa00ae278L,
0xd70dd2eeL, 0x4e048354L, 0x3903b3c2L, 0xa7672661L, 0xd06016f7L,
0x4969474dL, 0x3e6e77dbL, 0xaed16a4aL, 0xd9d65adcL, 0x40df0b66L,
0x37d83bf0L, 0xa9bcae53L, 0xdebb9ec5L, 0x47b2cf7fL, 0x30b5ffe9L,
0xbdbdf21cL, 0xcabac28aL, 0x53b39330L, 0x24b4a3a6L, 0xbad03605L,
0xcdd70693L, 0x54de5729L, 0x23d967bfL, 0xb3667a2eL, 0xc4614ab8L,
0x5d681b02L, 0x2a6f2b94L, 0xb40bbe37L, 0xc30c8ea1L, 0x5a05df1bL,
0x2d02ef8dL
}; /* Return a 32-bit CRC of the contents of the buffer. */ unsigned long crc32(const unsigned char *s, unsigned int len)
{
unsigned int i;
unsigned long crc32val; crc32val = ;
for (i = ; i < len; i ++)
{
crc32val =
crc32_tab[(crc32val ^ s[i]) & 0xff] ^
(crc32val >> );
}
return crc32val;
} /*
* Hashing function for a string
*/
unsigned int hashmap_hash_int(hashmap_map * m, char* keystring){ unsigned long key = crc32((unsigned char*)(keystring), strlen(keystring)); /* Robert Jenkins' 32 bit Mix Function */
key += (key << );
key ^= (key >> );
key += (key << );
key ^= (key >> );
key += (key << );
key ^= (key >> );
key += (key << );
key ^= (key >> ); /* Knuth's Multiplicative Method */
key = (key >> ) * ; return key % m->table_size;
} /*
* Return the integer of the location in data
* to store the point to the item, or MAP_FULL.
*/
int hashmap_hash(map_t in, char* key){
int curr;
int i; /* Cast the hashmap */
hashmap_map* m = (hashmap_map *) in; /* If full, return immediately */
if(m->size >= (m->table_size/)) return MAP_FULL; /* Find the best index */
curr = hashmap_hash_int(m, key); /* Linear probing */
for(i = ; i< MAX_CHAIN_LENGTH; i++){
if(m->data[curr].in_use == )
return curr; if(m->data[curr].in_use == && (strcmp(m->data[curr].key,key)==))
return curr; curr = (curr + ) % m->table_size;
} return MAP_FULL;
} /*
* Doubles the size of the hashmap, and rehashes all the elements
*/
int hashmap_rehash(map_t in){
int i;
int old_size;
hashmap_element* curr; /* Setup the new elements */
hashmap_map *m = (hashmap_map *) in;
hashmap_element* temp = (hashmap_element *)
calloc( * m->table_size, sizeof(hashmap_element));
if(!temp) return MAP_OMEM; /* Update the array */
curr = m->data;
m->data = temp; /* Update the size */
old_size = m->table_size;
m->table_size = * m->table_size;
m->size = ; /* Rehash the elements */
for(i = ; i < old_size; i++){
int status; if (curr[i].in_use == )
continue; status = hashmap_put(m, curr[i].key, curr[i].data);
if (status != MAP_OK)
return status;
} free(curr); return MAP_OK;
} /*
* Add a pointer to the hashmap with some key
*/
int hashmap_put(map_t in, char* key, any_t value){
int index;
hashmap_map* m; /* Cast the hashmap */
m = (hashmap_map *) in; /* Find a place to put our value */
index = hashmap_hash(in, key);
while(index == MAP_FULL){
if (hashmap_rehash(in) == MAP_OMEM) {
return MAP_OMEM;
}
index = hashmap_hash(in, key);
} /* Set the data */
m->data[index].data = value;
m->data[index].key = key;
m->data[index].in_use = ;
m->size++; return MAP_OK;
} /*
* Get your pointer out of the hashmap with a key
*/
int hashmap_get(map_t in, char* key, any_t *arg){
int curr;
int i;
hashmap_map* m; /* Cast the hashmap */
m = (hashmap_map *) in; /* Find data location */
curr = hashmap_hash_int(m, key); /* Linear probing, if necessary */
for(i = ; i<MAX_CHAIN_LENGTH; i++){ int in_use = m->data[curr].in_use;
if (in_use == ){
if (strcmp(m->data[curr].key,key)==){
*arg = (m->data[curr].data);
return MAP_OK;
}
} curr = (curr + ) % m->table_size;
} *arg = NULL; /* Not found */
return MAP_MISSING;
} /*
* Iterate the function parameter over each element in the hashmap. The
* additional any_t argument is passed to the function as its first
* argument and the hashmap element is the second.
*/
int hashmap_iterate(map_t in, PFany f, any_t item) {
int i; /* Cast the hashmap */
hashmap_map* m = (hashmap_map*) in; /* On empty hashmap, return immediately */
if (hashmap_length(m) <= )
return MAP_MISSING; /* Linear probing */
for(i = ; i< m->table_size; i++)
if(m->data[i].in_use != ) {
any_t data = (any_t) (m->data[i].data);
int status = f(item, data);
if (status != MAP_OK) {
return status;
}
} return MAP_OK;
} /*
* Remove an element with that key from the map
*/
int hashmap_remove(map_t in, char* key){
int i;
int curr;
hashmap_map* m; /* Cast the hashmap */
m = (hashmap_map *) in; /* Find key */
curr = hashmap_hash_int(m, key); /* Linear probing, if necessary */
for(i = ; i<MAX_CHAIN_LENGTH; i++){ int in_use = m->data[curr].in_use;
if (in_use == ){
if (strcmp(m->data[curr].key,key)==){
/* Blank out the fields */
m->data[curr].in_use = ;
m->data[curr].data = NULL;
m->data[curr].key = NULL; /* Reduce the size */
m->size--;
return MAP_OK;
}
}
curr = (curr + ) % m->table_size;
} /* Data not found */
return MAP_MISSING;
} /* Deallocate the hashmap */
void hashmap_free(map_t in){
hashmap_map* m = (hashmap_map*) in;
free(m->data);
free(m);
} /* Return the length of the hashmap */
int hashmap_length(map_t in){
hashmap_map* m = (hashmap_map *) in;
if(m != NULL) return m->size;
else return ;
}
c语言实行泛型hashmap的更多相关文章
- C++应该被看成是个语言集合——四种语言(C语言,OO语言,泛型语言,STL)
至少有三种语言: 一,C++ is C 二,C++ is an OO language 三,C++ is a genetic programming language 有的童鞋觉得难,可能是没有看清楚 ...
- C语言泛型编程——泛型冒泡排序
在实际编程中,常常会需要一些方法(函数),比如排序,它们具体实现基本一致,仅仅只有参数类型不同, 那么可不可以有一种通用的函数,不管是什么类型的参数都可以通用呢? 泛型编程:泛型即是指具有在多种数据类 ...
- Java泛型的历史
为什么Java泛型会有当前的缺陷? 之前的章节里已经说明了Java泛型擦除会导致的问题,C++和C#的泛型都是在运行时存在的,难道Java天然不支持“真正的泛型”吗? 事实上,在Java1.5在200 ...
- Java泛型
什么是泛型? 泛型(Generic type 或者 generics)是对 Java 语言的类型系统的一种扩展,以支持创建可以按类型进行参数化的类.可以把类型参数看作是使用参数化类型时指定的类型的一个 ...
- Java泛型总结
1. 什么是泛型?泛型(Generic type 或者 generics)是对 Java 语言的类型系统的一种扩展,以支持创建可以按类型进行参数化的类.可以把类型参数看作是使用参数化类型时指定的类型的 ...
- Java泛型的好处
java 泛型是java SE 1.5的新特性,泛型的本质是参数化类型,也就是说所操作的数据类型被指定为一个参数.这种参数类型可以用在类.接口和方法的创建中,分别称为泛型类.泛型接口.泛型方法. ...
- java泛型的讲解
java泛型 什么是泛型? 泛型(Generic type 或者 generics)是对 Java 语言的类型系统的一种扩展,以支持创建可以按类型进行参数化的类.可以把类型参数看作是使用参数化类型时指 ...
- java中的泛型(转)
什么是泛型? 泛型(Generic type 或者 generics)是对 Java 语言的类型系统的一种扩展,以支持创建可以按类型进行参数化的类.可以把类型参数看作是使用参数化类型时指定的类型的一个 ...
- java泛型【收藏】
什么是泛型? 泛型(Generic type 或者 generics)是对 Java 语言的类型系统的一种扩展,以支持创建可以按类型进行参数化的类.可以把类型参数看作是使用参数化类型时指定的类型的一个 ...
随机推荐
- java——多线程—启动线程
继承Thread启动线程 package com.mycom.继承Thread启动线程; /** * * 继承Thread类启动线程的步骤 * 1.定义自定义线程类并继承Thread * 2.重写ru ...
- Ubuntu系统---安装搜狗输入法
Ubuntu_搜狗输入法 第一步: 1,下载搜狗输入法的安装包. 下载地址为:http://pinyin.sogou.com/linux/ ,如下图,要选择与自己系统位数一致的安装包,我的系统是64位 ...
- Django 外键、多对多插入数据方法
models.py class UserInfo(models.Model): username = models.CharField(max_length=64,db_column='usernam ...
- 五分钟彻底搞懂你一直没明白的Linux内存管理
现在的服务器大部分都是运行在Linux上面的,所以,作为一个程序员有必要简单地了解一下系统是如何运行的.对于内存部分需要知道: 地址映射 内存管理的方式 缺页异常 先来看一些基本的知识,在进程看来,内 ...
- FFmpeg常用命令学习笔记(二)录制命令
录制命令 1.FFmpeg录屏命令 ffmpeg -f avfoundation -i 1 -r 30 out.yuv -f:指定使用avfoundation采集数据 -i:指定从哪采集数据,它是一个 ...
- linux学习19 shell脚本基础-bash脚本编程基础及配置文件
一.shell脚本编程 1.编程语言的分类,根据运行方式 a.编译运行:源代码 --> 编译器(编译) --> 程序文件 C语言: b.解释运行:源代码 --> 运行时启动解释器,由 ...
- C#新增按钮
代码亲测可用,似乎不需要“ADD”,如下:form_load段:for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){btn = new Button();btn.Parent = this ...
- cookie和Session是啥?
HTTP是无状态(stateless)协议 http协议是无状态协议即不保存状态. 无状态协议的优点: 由于不需要保存记录,所以减少服务器的CPU和内存的资源的消耗.毕竟客户端一多起来保存记录的话对于 ...
- fatal: refusing to merge unrelated histories(git pull)
https://blog.csdn.net/lindexi_gd/article/details/52554159 (refusing to merge unrelated histories) ht ...
- [引用]MATLAB中的fft后为何要用fftshift
原文地址:MATLAB中的fft后为何要用fftshift fft是一维傅里叶变换,即将时域信号转换为频域. fftshift是针对频域的,将FFT的DC分量移到频谱中心,重新排列fft,fft1和… ...
