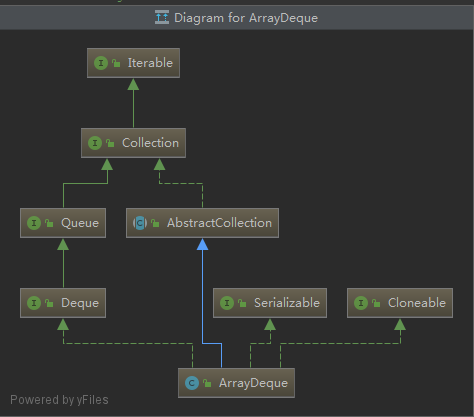
jdk1.8-ArrayDeque
public class ArrayDeque<E> extends AbstractCollection<E>
implements Deque<E>, Cloneable, Serializable
/**
* The array in which the elements of the deque are stored.
* The capacity of the deque is the length of this array, which is
* always a power of two. The array is never allowed to become
* full, except transiently within an addX method where it is
* resized (see doubleCapacity) immediately upon becoming full,
* thus avoiding head and tail wrapping around to equal each
* other. We also guarantee that all array cells not holding
* deque elements are always null.
*
* 存放元素的Object[]数组(底层数据结构)
*/
transient Object[] elements; // non-private to simplify nested class access
/**
* The index of the element at the head of the deque (which is the
* element that would be removed by remove() or pop()); or an
* arbitrary number equal to tail if the deque is empty.
*
* 队首元素所在位置
*/
transient int head;
/**
* The index at which the next element would be added to the tail
* of the deque (via addLast(E), add(E), or push(E)).
*
* 队尾元素所在位置
*/
transient int tail;
/**
* The minimum capacity that we'll use for a newly created deque.
* Must be a power of 2.
*
* 容量最小值,2的次幂,默认为8
*/
private static final int MIN_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 8;
/**
* Allocates empty array to hold the given number of elements.
*
* @param numElements the number of elements to hold
*
* 寻找numElements的最近的二次幂值initialCapacity
* new一个长度为initialCapacity的新Object[]数组
*/
private void allocateElements(int numElements) {
int initialCapacity = MIN_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
// Find the best power of two to hold elements.
// Tests "<=" because arrays aren't kept full.
if (numElements >= initialCapacity) {
initialCapacity = numElements;
initialCapacity |= (initialCapacity >>> 1);
initialCapacity |= (initialCapacity >>> 2);
initialCapacity |= (initialCapacity >>> 4);
initialCapacity |= (initialCapacity >>> 8);
initialCapacity |= (initialCapacity >>> 16);
initialCapacity++;
if (initialCapacity < 0) // Too many elements, must back off
initialCapacity >>>= 1;// Good luck allocating 2 ^ 30 elements
}
elements = new Object[initialCapacity];
}
分析:这个计算方法参考下面这个链接,讲的挺好
/**
* Constructs an empty array deque with an initial capacity
* sufficient to hold 16 elements.
*
* 无参构造函数初始化数组长度为16
*/
public ArrayDeque() {
elements = new Object[16];
}
/**
* Constructs an empty array deque with an initial capacity
* sufficient to hold the specified number of elements.
*
* @param numElements lower bound on initial capacity of the deque
*
* 传入长度,构造函数
*/
public ArrayDeque(int numElements) {
allocateElements(numElements);
}
分析:传入长度,初始为数组长度为大于等于numElements最小2次幂
/**
* Constructs a deque containing the elements of the specified
* collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's
* iterator. (The first element returned by the collection's
* iterator becomes the first element, or <i>front</i> of the
* deque.)
*
* @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into the deque
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*
* 传入集合,构造函数
*/
public ArrayDeque(Collection<? extends E> c) {
allocateElements(c.size());
addAll(c);
}
分析:初始化数组长度为大于等于集合长度的最小2次幂,调用addAll()方法
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
* <p>This implementation iterates over the specified collection, and adds
* each object returned by the iterator to this collection, in turn.
*
* <p>Note that this implementation will throw an
* <tt>UnsupportedOperationException</tt> unless <tt>add</tt> is
* overridden (assuming the specified collection is non-empty).
*
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws IllegalArgumentException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws IllegalStateException {@inheritDoc}
*
* @see #add(Object)
*/
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
boolean modified = false;
for (E e : c)
if (add(e))
modified = true;
return modified;
}
分析:遍历集合,一个个add添加
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the end of this deque.
*
* @param e the element to add
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Deque#offerLast})
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null
*
* 添加到队尾
*/
public boolean offerLast(E e) {
addLast(e);
return true;
}
分析:传入元素,调用addLast()方法
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the end of this deque.
*
* <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #add}.
*
* @param e the element to add
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null
*
*/
public void addLast(E e) {
//判空
if (e == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
//根据下标,队尾值为e
elements[tail] = e;
if ( (tail = (tail + 1) & (elements.length - 1)) == head)
doubleCapacity();
}
分析:这里直接在队尾里添加了元素e,因为ArrayDeque是一个循环队列,所以当队尾和队头重合说明,队列满了,需要进行扩容。
tail = (tail + 1) & (elements.length - 1)) == head
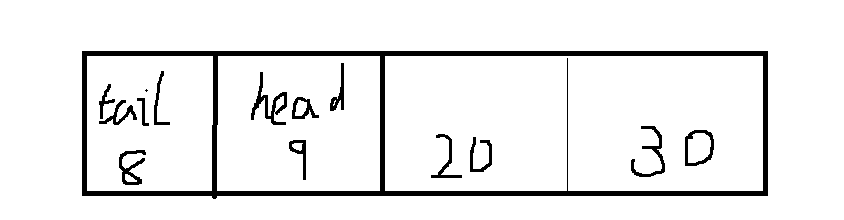
public void addFirst(E e) {
if (e == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
elements[head = (head - 1) & (elements.length - 1)] = e;
if (head == tail)
doubleCapacity();
}
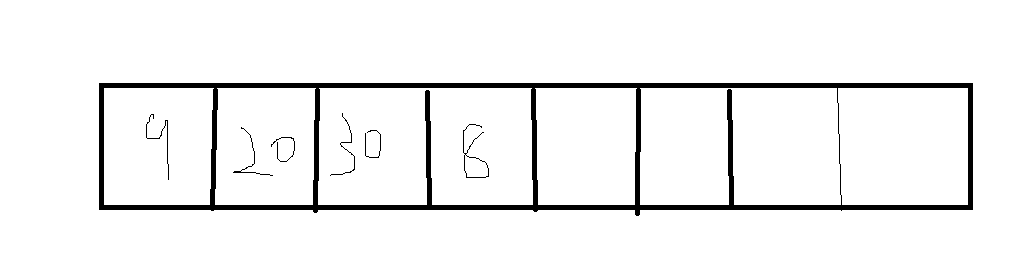
/**
* Doubles the capacity of this deque. Call only when full, i.e.,
* when head and tail have wrapped around to become equal.
*/
private void doubleCapacity() {
//断言头和尾是不是重,也就是队列是否满了
assert head == tail;
//头部索引p
int p = head;
//队列长度n
int n = elements.length;
//头部元素右边有多少个元素r包括头部
int r = n - p; // number of elements to the right of p
//队列长度扩大为2倍
int newCapacity = n << 1;
//如果扩大两倍后长度超过了int大小变为负数,则抛错
if (newCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException("Sorry, deque too big");
//new一个新的数组长度为原来的两倍
Object[] a = new Object[newCapacity];
//旧数组elements 从p头部开始, 新数组a,从0开始, 长度为r。所以是拷贝原数组p右侧数据包括p
System.arraycopy(elements, p, a, 0, r);
//旧数组elements 从下标0开始, 新数组a,从下标r开始, 长度为p。所以是拷贝原数组p左侧数据
System.arraycopy(elements, 0, a, r, p);
//旧数组等于新数组a
elements = a;
//队头索引等于0
head = 0;
//队尾索引等于n,n为旧数组的长度不是最新的数组
tail = n;
}
分析:这里看上面的注释已经将得很清晰了,但是我们这里需要注意一个问题
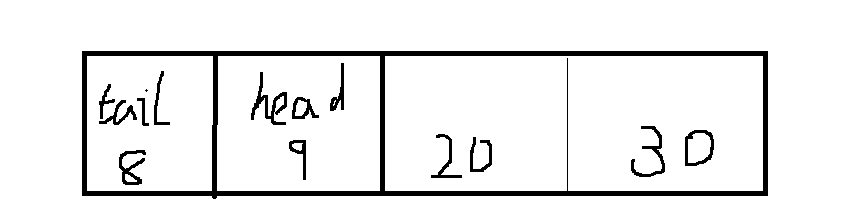
public E pollFirst() {
//头部索引等于h
int h = head;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
//检查头部是否有元素
E result = (E) elements[h];
// Element is null if deque empty
if (result == null)
return null;
//令当前位置为null
elements[h] = null; // Must null out slot
//队头索引向递增方向退一位
head = (h + 1) & (elements.length - 1);
return result;
}
jdk1.8-ArrayDeque的更多相关文章
- 给jdk写注释系列之jdk1.6容器(11)-Queue之ArrayDeque源码解析
前面讲了Stack是一种先进后出的数据结构:栈,那么对应的Queue是一种先进先出(First In First Out)的数据结构:队列. 对比一下Stack,Queue是一种先进先出的容 ...
- 学习JDK1.8集合源码之--ArrayDeque
1. ArrayDeque简介 ArrayDeque是基于数组实现的一种双端队列,既可以当成普通的队列用(先进先出),也可以当成栈来用(后进先出),故ArrayDeque完全可以代替Stack,Arr ...
- 给jdk写注释系列之jdk1.6容器(13)-总结篇之Java集合与数据结构
是的,这篇blogs是一个总结篇,最开始的时候我提到过,对于java容器或集合的学习也可以看做是对数据结构的学习与应用.在前面我们分析了很多的java容器,也接触了好多种常用的数据结构,今天 ...
- 给jdk写注释系列之jdk1.6容器(12)-PriorityQueue源码解析
PriorityQueue是一种什么样的容器呢?看过前面的几个jdk容器分析的话,看到Queue这个单词你一定会,哦~这是一种队列.是的,PriorityQueue是一种队列,但是它又是一种什么样的队 ...
- JDK1.8源码阅读系列之三:Vector
本篇随笔主要描述的是我阅读 Vector 源码期间的对于 Vector 的一些实现上的个人理解,用于个人备忘,有不对的地方,请指出- 先来看一下 Vector 的继承图: 可以看出,Vector 的直 ...
- jdk1.8.0_45源码解读——Set接口和AbstractSet抽象类的实现
jdk1.8.0_45源码解读——Set接口和AbstractSet抽象类的实现 一. Set架构 如上图: (01) Set 是继承于Collection的接口.它是一个不允许有重复元素的集合.(0 ...
- JDK7集合框架源码阅读(七) ArrayDeque
基于版本jdk1.7.0_80 java.util.ArrayDeque 代码如下 /* * ORACLE PROPRIETARY/CONFIDENTIAL. Use is subject to li ...
- 【Java源码】集合类-ArrayDeque
一.类继承关系 ArrayDeque和LinkedList一样都实现了双端队列Deque接口,但它们内部的数据结构和使用方法却不一样.根据该类的源码注释翻译可知: ArrayDeque实现了Deque ...
- 【集合系列】- 深入浅出分析 ArrayDeque
一.摘要 在 jdk1.5 中,新增了 Queue 接口,代表一种队列集合的实现,咱们继续来聊聊 java 集合体系中的 Queue 接口. Queue 接口是由大名鼎鼎的 Doug Lea 创建,中 ...
- 学习JDK1.8集合源码之--HashMap
1. HashMap简介 HashMap是一种key-value结构存储数据的集合,是map集合的经典哈希实现. HashMap允许存储null键和null值,但null键最多只能有一个(HashSe ...
随机推荐
- Linux之RPM 软件管理程序
RPM RPM是软件管理程序,提供软件的安装.升级.查询.反安装的功能.优点:a.安装方便,软件中所有数据都经过编译和打包b.查询.升级.反安装方便缺点:a.缺乏灵活性b.存在相依属性 用法: rpm ...
- CSS基础学习-10.CSS伸缩盒(老版本)
- Mac修改显示器使支持原生缩放
教程 直接搬运没有意义,直接放链接.地址:https://bbs.feng.com/read-htm-tid-11677019.html 若无法访问请使用网页截图备份.地址:https://img20 ...
- 【leetcode】1215.Stepping Numbers
题目如下: A Stepping Number is an integer such that all of its adjacent digits have an absolute differen ...
- ajax上传文件(javaweb)
前台:FormData, formData.append("fileName",$("#file")[0].files[0];); https://ww ...
- hdu 5723 Abandoned country 最小生成树+子节点统计
Abandoned country Time Limit: 8000/4000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/Others ...
- 关于windows 设备驱动重要的事实
1. windows采用设备树描述所有挂在系统总线上的设备,每个设备对应一个节点. 2.每个设备有自己的device object stack/driver stack. 一个物理上的设备对应多个de ...
- From 7.22 To 7.28
From 7.22 To 7.28 大纲 竞赛 我们好像要跟队爷考试... 考试的时候做题吧 学科 还是跟之前一样吧, 完型和阅读几乎没做过... 运动 踢足球!!!!!! 可惜bb他们去上海了... ...
- BZOJ3331压力
码量略大. 题意就是求路径必经点. tarjan缩点,所有的非割点只有是起点终点时才必经,直接开个ans数组就OK了. 至于割点,因为缩完点之后的图是vDcc和割点共同组成的,而且题目说连通,那就是棵 ...
- 2018-2019-2 20165215《网络对抗技术》Exp7 网络欺诈防范
目录 实验目的 实验内容 实验步骤 (一)简单应用SET工具建立冒名网站 (二)ettercap DNS spoof (三)结合应用两种技术,用DNS spoof引导特定访问到冒名网站 基础问题回答 ...
