Codeforces Round #301 (Div. 2)A B C D 水 模拟 bfs 概率dp
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Scrooge McDuck keeps his most treasured savings in a home safe with a combination lock. Each time he wants to put there the treasures that he's earned fair and square, he has to open the lock.

The combination lock is represented by n rotating disks with digits from 0 to 9 written on them. Scrooge McDuck has to turn some disks so that the combination of digits on the disks forms a secret combination. In one move, he can rotate one disk one digit forwards or backwards. In particular, in one move he can go from digit 0 to digit 9 and vice versa. What minimum number of actions does he need for that?
The first line contains a single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 1000) — the number of disks on the combination lock.
The second line contains a string of n digits — the original state of the disks.
The third line contains a string of n digits — Scrooge McDuck's combination that opens the lock.
Print a single integer — the minimum number of moves Scrooge McDuck needs to open the lock.
5
82195
64723
13
In the sample he needs 13 moves:
- 1 disk:

- 2 disk:
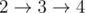
- 3 disk:

- 4 disk:

- 5 disk:
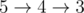
题意:长度为n的10位锁 给你初始状态与密码 问最少需要旋转多少步
题解:水
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll __int64
using namespace std;
int n;
char a[];
char b[];
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
scanf("%s",a);
scanf("%s",b);
int ans=;
for(int i=;i<n;i++)
{
int aa=a[i]-'';
int bb=b[i]-'';
if(aa<bb)
swap(aa,bb);
ans=ans+min(aa-bb,bb+(-aa));
}
printf("%d\n",ans);
return ;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Little Vova studies programming in an elite school. Vova and his classmates are supposed to write n progress tests, for each test they will get a mark from 1 to p. Vova is very smart and he can write every test for any mark, but he doesn't want to stand out from the crowd too much. If the sum of his marks for all tests exceeds value x, then his classmates notice how smart he is and start distracting him asking to let them copy his homework. And if the median of his marks will be lower than y points (the definition of a median is given in the notes), then his mom will decide that he gets too many bad marks and forbid him to play computer games.
Vova has already wrote k tests and got marks a1, ..., ak. He doesn't want to get into the first or the second situation described above and now he needs to determine which marks he needs to get for the remaining tests. Help him do that.
The first line contains 5 space-separated integers: n, k, p, x and y (1 ≤ n ≤ 999, n is odd, 0 ≤ k < n, 1 ≤ p ≤ 1000, n ≤ x ≤ n·p, 1 ≤ y ≤ p). Here n is the number of tests that Vova is planned to write, k is the number of tests he has already written, p is the maximum possible mark for a test, x is the maximum total number of points so that the classmates don't yet disturb Vova, y is the minimum median point so that mom still lets him play computer games.
The second line contains k space-separated integers: a1, ..., ak (1 ≤ ai ≤ p) — the marks that Vova got for the tests he has already written.
If Vova cannot achieve the desired result, print "-1".
Otherwise, print n - k space-separated integers — the marks that Vova should get for the remaining tests. If there are multiple possible solutions, print any of them.
5 3 5 18 4
3 5 4
4 1
5 3 5 16 4
5 5 5
-1
The median of sequence a1, ..., an where n is odd (in this problem n is always odd) is the element staying on (n + 1) / 2 position in the sorted list of ai.
In the first sample the sum of marks equals 3 + 5 + 4 + 4 + 1 = 17, what doesn't exceed 18, that means that Vova won't be disturbed by his classmates. And the median point of the sequence {1, 3, 4, 4, 5} equals to 4, that isn't less than 4, so his mom lets him play computer games.
Please note that you do not have to maximize the sum of marks or the median mark. Any of the answers: "4 2", "2 4", "5 1", "1 5", "4 1", "1 4" for the first test is correct.
In the second sample Vova got three '5' marks, so even if he gets two '1' marks, the sum of marks will be 17, that is more than the required value of 16. So, the answer to this test is "-1".
题意:要求构造一个长度为n的序列 数字范围为[1,p] 现在已经给你k个数 构造剩下的n-k个数 使得n个数的和不大于x 中位数不小于y 如果无法构造输出-1
题解:细节模拟 具体看代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll __int64
using namespace std;
int n,k,p,x,y;
int a[];
int main()
{
scanf("%d %d %d %d %d",&n,&k,&p,&x,&y);
int sum=;
for(int i=; i<=k; i++){
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
sum+=a[i];
}
int gg=k;
if(x-sum<(n-k)){
printf("-1\n");
return ;
}
else{
int j;
if(k>){
sort(a+,a++k);
for(j=; j<=k; j++){
if(a[j]>=y)
break;
}
if(j==k+){
if(j>n){
printf("-1\n");
return ;
}
else{
a[j]=y;
k++;
}
}
}
else{
a[]=y;
k++;
j=;
sum+=y;
if(y>x){
printf("-1\n");
return ;
}
}
int exm=n/+;
if(k-j+>=exm){
for(int i=k+; i<=n; i++)
a[i]=;
}
else{
int jishu=k+;
int all=;
all=(exm-(k-j+))*y+(n-k-(exm-(k-j+)));
if(((exm-(k-j+))+k)>n||all+sum>x){
printf("-1\n");
return ;
}
else{
for(int i=; i<=exm-(k-j+); i++)
a[jishu++]=y;
for(int j=jishu; j<=n; j++)
a[j]=;
}
}
}
for(int i=gg+; i<=n; i++)
printf("%d ",a[i]);
printf("\n");
return ;
}
/*
5 3 5 18 4
3 5 4 5 3 5 1 4
3 5 4 5 4 5 10 1
1 2 2 2 1 0 3 2 3 5 3 5 17 4
5 5 5
*/
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
You play a computer game. Your character stands on some level of a multilevel ice cave. In order to move on forward, you need to descend one level lower and the only way to do this is to fall through the ice.
The level of the cave where you are is a rectangular square grid of n rows and m columns. Each cell consists either from intact or from cracked ice. From each cell you can move to cells that are side-adjacent with yours (due to some limitations of the game engine you cannot make jumps on the same place, i.e. jump from a cell to itself). If you move to the cell with cracked ice, then your character falls down through it and if you move to the cell with intact ice, then the ice on this cell becomes cracked.
Let's number the rows with integers from 1 to n from top to bottom and the columns with integers from 1 to m from left to right. Let's denote a cell on the intersection of the r-th row and the c-th column as (r, c).
You are staying in the cell (r1, c1) and this cell is cracked because you've just fallen here from a higher level. You need to fall down through the cell (r2, c2) since the exit to the next level is there. Can you do this?
The first line contains two integers, n and m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 500) — the number of rows and columns in the cave description.
Each of the next n lines describes the initial state of the level of the cave, each line consists of m characters "." (that is, intact ice) and "X" (cracked ice).
The next line contains two integers, r1 and c1 (1 ≤ r1 ≤ n, 1 ≤ c1 ≤ m) — your initial coordinates. It is guaranteed that the description of the cave contains character 'X' in cell (r1, c1), that is, the ice on the starting cell is initially cracked.
The next line contains two integers r2 and c2 (1 ≤ r2 ≤ n, 1 ≤ c2 ≤ m) — the coordinates of the cell through which you need to fall. The final cell may coincide with the starting one.
If you can reach the destination, print 'YES', otherwise print 'NO'.
4 6
X...XX
...XX.
.X..X.
......
1 6
2 2
YES
5 4
.X..
...X
X.X.
....
.XX.
5 3
1 1
NO
4 7
..X.XX.
.XX..X.
X...X..
X......
2 2
1 6
YES
In the first sample test one possible path is:

After the first visit of cell (2, 2) the ice on it cracks and when you step there for the second time, your character falls through the ice as intended.
题意:给你一个n*m的矩阵 ‘X’代表破碎的冰块 不能踩 ‘.’代表冰块 可以踩一次 给你起点与终点 问你是否能从终点落下去 每次只能移动到周围的冰块
题解:bfs
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll __int64
using namespace std;
int n,m;
char mp[][];
int visit[][];
int x1,y1,x2,y2;
struct node
{
int x,y;
}now,exm;
queue<node> q;
int dis[][]={{,},{-,},{,},{,-}};
bool bfs()
{
while(!q.empty())
q.pop();
now.x=x1;
now.y=y1;
visit[x1][y1]=;
q.push(now);
while(!q.empty())
{
now=q.front();
q.pop();
if(visit[x2][y2]>=){
return true;
}
for(int i=;i<;i++)
{
int aa=now.x+dis[i][];
int bb=now.y+dis[i][];
if((aa>=&&aa<=n&&bb>=&&bb<=m)&&(mp[aa][bb]=='.'&&visit[aa][bb]==)||(aa==x2&&bb==y2))
{
exm.x=aa;
exm.y=bb;
q.push(exm);
visit[aa][bb]++;
}
}
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
memset(visit,,sizeof(visit));
scanf("%d %d",&n,&m);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++){
scanf("%s",mp[i]+);
}
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
for(int j=;j<=m;j++)
{
if(mp[i][j]=='X')
visit[i][j]++;
}
}
scanf("%d %d",&x1,&y1);
scanf("%d %d",&x2,&y2);
if(bfs())
printf("YES\n");
else
printf("NO\n");
return ;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
The Bad Luck Island is inhabited by three kinds of species: r rocks, s scissors and p papers. At some moments of time two random individuals meet (all pairs of individuals can meet equiprobably), and if they belong to different species, then one individual kills the other one: a rock kills scissors, scissors kill paper, and paper kills a rock. Your task is to determine for each species what is the probability that this species will be the only one to inhabit this island after a long enough period of time.
The single line contains three integers r, s and p (1 ≤ r, s, p ≤ 100) — the original number of individuals in the species of rock, scissors and paper, respectively.
Print three space-separated real numbers: the probabilities, at which the rocks, the scissors and the paper will be the only surviving species, respectively. The answer will be considered correct if the relative or absolute error of each number doesn't exceed 10 - 9.
2 2 2
0.333333333333 0.333333333333 0.333333333333
2 1 2
0.150000000000 0.300000000000 0.550000000000
1 1 3
0.057142857143 0.657142857143 0.285714285714 题意:
题解:
//ing
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll __int64
using namespace std;
double dp[][][];
double a,b,c;
int main()
{
int r,s,p;
scanf("%d %d %d",&r,&s,&p);
dp[r][s][p]=;
for(int i=r;i>=;i--)
{
for(int j=s;j>=;j--)
{
for(int k=p;k>=;k--)
{
double all=i*j*1.0+j*k*1.0+i*k*1.0;
if(all==) continue;
if(k>=) dp[i][j][k-]+=dp[i][j][k]*(double)(j*1.0*k)/all;
if(j>=) dp[i][j-][k]+=dp[i][j][k]*(double)(j*1.0*i)/all;
if(i>=) dp[i-][j][k]+=dp[i][j][k]*(double)(i*1.0*k)/all;
}
}
}
for(int i=;i<=r;i++) a+=dp[i][][];
for(int i=;i<=s;i++) b+=dp[][i][];
for(int i=;i<=p;i++) c+=dp[][][i];
printf("%.9f %.9f %.9f\n",a,b,c);
return ;
}
Codeforces Round #301 (Div. 2)A B C D 水 模拟 bfs 概率dp的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #374 (Div. 2) A B C D 水 模拟 dp+dfs 优先队列
A. One-dimensional Japanese Crossword time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabyt ...
- DFS/BFS Codeforces Round #301 (Div. 2) C. Ice Cave
题目传送门 /* 题意:告诉起点终点,踩一次, '.'变成'X',再踩一次,冰块破碎,问是否能使终点冰破碎 DFS:如题解所说,分三种情况:1. 如果两点重合,只要往外走一步再走回来就行了:2. 若两 ...
- 贪心 Codeforces Round #301 (Div. 2) B. School Marks
题目传送门 /* 贪心:首先要注意,y是中位数的要求:先把其他的都设置为1,那么最多有(n-1)/2个比y小的,cnt记录比y小的个数 num1是输出的1的个数,numy是除此之外的数都为y,此时的n ...
- 贪心 Codeforces Round #301 (Div. 2) A. Combination Lock
题目传送门 /* 贪心水题:累加到目标数字的距离,两头找取最小值 */ #include <cstdio> #include <iostream> #include <a ...
- Codeforces Round #297 (Div. 2)A. Vitaliy and Pie 水题
Codeforces Round #297 (Div. 2)A. Vitaliy and Pie Time Limit: 2 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MBSubmit: xxx ...
- Codeforces Round #301 (Div. 2) D. Bad Luck Island 概率DP
D. Bad Luck Island Time Limit: 1 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://codeforces.com/contest/540/pr ...
- 「日常训练」Bad Luck Island(Codeforces Round 301 Div.2 D)
题意与分析(CodeForces 540D) 是一道概率dp题. 不过我没把它当dp做... 我就是凭着概率的直觉写的,还好这题不算难. 这题的重点在于考虑概率:他们喜相逢的概率是多少?考虑超几何分布 ...
- Codeforces Round #396 (Div. 2) A B C D 水 trick dp 并查集
A. Mahmoud and Longest Uncommon Subsequence time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 ...
- Codeforces Round #301 (Div. 2)(A,【模拟】B,【贪心构造】C,【DFS】)
A. Combination Lock time limit per test:2 seconds memory limit per test:256 megabytes input:standard ...
随机推荐
- div不设置高度背景颜色或外边框不能显示的解决方法
在使用div+css进行网页布局时,如果外部div有背景颜色或者边框,而不设置其高度,在浏览时出现最外层Div的背景颜色和边框不起作用的问题. 大体结构<div class="oute ...
- 【转】PHPCMS v9 自定义表单添加验证码验证
1. 在 \phpcms\templates\default\formguide\show.html 中添加验证码显示 <input type="text" id=&quo ...
- Windows操作系统C盘占用空间过多
Windows操作系统C盘占用空间过多 大部分的windows电脑用户在长时间使用PC时都会遇到一个问题,就是C盘占用的空间会越来越多,乃至占满整个C盘. 后来在百度了一波,发现各种方法都试过了,也不 ...
- rest_framework组件
认证组件 局部认证 在需要认证的视图类里加上authentication_classes = [认证组件1类名,认证组件2类名....] 示例如下: seralizers.py from rest_f ...
- linux下svn操作(专)
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/clicli/p/5913330.html svn命令在linux下的使用SVN软件版本管理 1.将文件checkout到本地目录svn ch ...
- 欢迎来怼—第二次Scrum会议
一.小组信息 队名:欢迎来怼小组成员队长:田继平成员:李圆圆,葛美义,王伟东,姜珊,邵朔,冉华小组照片 二.开会信息 时间:2017/10/14 18:30~18:47,总计17min.地点:东北师范 ...
- Thunder——互评beta版本
基于NABCD和spec评论作品 Hello World!:http://www.cnblogs.com/vector121/p/7922989.html 欢迎来怼:http://www.cnblog ...
- winform界面之固定大小随dpi
场景: 已经更改成大小可随dpi改变,可是在用applyresoures()之后(添加更改语言功能),发现控件大小失真. 分析:applyresoures()是把该控件的属性改为程序设计的固定大小,不 ...
- Saver 保存与读取
tensorflow 框架下的Saver 功能,用以保存和读取运算数据 Saver 保存数据 代码 import tensorflow as tf # Save to file #remember t ...
- iOS- 关于AVAudioSession的使用——后台播放音乐
1.前言 •AVAudioSession是一个单例,无需实例化即可直接使用.AVAudioSession在各种音频环境中起着非常重要的作用 •针对不同的音频应用场景,需要设置不同的音频会话分类 1 ...
