Codeforces 895.E Eyes Closed
2.5 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Vasya and Petya were tired of studying so they decided to play a game. Before the game begins Vasya looks at array a consisting of n integers. As soon as he remembers all elements of a the game begins. Vasya closes his eyes and Petya does q actions of one of two types:
1) Petya says 4 integers l1, r1, l2, r2 — boundaries of two non-intersecting segments. After that he swaps one random element from the [l1, r1]segment with another random element from the [l2, r2] segment.
2) Petya asks Vasya the sum of the elements of a in the [l, r] segment.
Vasya is a mathematician so he answers Petya the mathematical expectation of the sum of the elements in the segment.
Your task is to write a program which will answer the second type questions as Vasya would do it. In other words your program should print the mathematical expectation of the sum of the elements of a in the [l, r] segment for every second type query.
The first line contains two integers n, q (2 ≤ n ≤ 105, 1 ≤ q ≤ 105) — the number of elements in the array and the number of queries you need to handle.
The second line contains n integers ai (1 ≤ ai ≤ 109) — elements of the array.
The next q lines contain Petya's actions of type 1 or 2.
If it is a type 1 action then the line contains 5 integers 1, l1, r1, l2, r2 (1 ≤ l1 ≤ r1 ≤ n, 1 ≤ l2 ≤ r2 ≤ n).
If it is a type 2 query then the line contains 3 integers 2, l, r (1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n).
It is guaranteed that there is at least one type 2 query and segments [l1, r1], [l2, r2] don't have common elements.
For each type 2 query print one real number — the mathematical expectation of the sum of elements in the segment.
Your answer will be considered correct if its absolute or relative error doesn't exceed 10 - 4 — formally, the answer is correct if 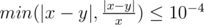 where x is jury's answer and y is yours.
where x is jury's answer and y is yours.
4 4
1 1 2 2
1 2 2 3 3
2 1 2
1 1 2 3 4
2 1 2
3.0000000
3.0000000
10 5
1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 2
1 1 5 6 10
2 1 5
1 1 5 6 10
1 1 5 6 10
2 6 10
6.0000000
8.0400000
10 10
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
1 1 5 6 10
1 1 5 6 10
2 1 5
1 1 3 6 9
2 1 3
1 5 7 8 10
1 1 1 10 10
2 1 5
2 7 10
2 1 10
23.0000000
14.0000000
28.0133333
21.5733333
55.0000000
大致题意:两种操作。
1. [l1, r1]之间随机一个数,[l2, r2]之间随机一个数,把两个交换
2. 问[l, r]区间和的数学期望是多少。
分析:直接分析每个数对整体的影响很难,先分析个体.设len1 = r1 - l1 + 1,len2 = r2 - l2 + 1.那么对于第一个区间的数x,有1/len1的概率随机到.还有(len1 - 1)/len1的概率不会随机到.右边有1/len2的概率随机到y,那么既随机到x又随机到y的概率为1/(len1*len2),枚举第二个区间的每一个数y,那么x对第一个区间的期望的贡献就变成了[(len1 - 1)/len1] * x + sum2 / (len1 * len2).整个区间的期望和就是把所有x的期望加起来.可以利用线段树来维护:区间乘,区间加,区间求和,对于第二个区间也是差不多这样的.
对期望的概念理解的还不是非常深入.直接算整体的不好算可以先考虑算局部的贡献.
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm> using namespace std; const int maxn = ; int n,q,L[maxn << ],R[maxn << ];
double sum[maxn << ],add[maxn << ],mul[maxn << ]; void pushup(int o)
{
sum[o] = sum[o * ] + sum[o * + ];
} void pushdown(int o)
{
sum[o * ] = sum[o * ] * mul[o] + add[o] * (R[o * ] - L[o * ] + );
sum[o * + ] = sum[o * + ] * mul[o] + add[o] * (R[o * + ] - L[o * + ] + );
add[o * ] = add[o * ] * mul[o] + add[o];
add[o * + ] = add[o * + ] * mul[o] + add[o];
mul[o * ] = mul[o * ] * mul[o];
mul[o * + ] = mul[o * + ] * mul[o];
mul[o] = ;
add[o] = ;
} void build(int o,int l,int r)
{
L[o] = l;
R[o] = r;
add[o] = ;
mul[o] = ;
if (l == r)
{
cin >> sum[o];
return;
}
int mid = (l + r) >> ;
build(o * ,l,mid);
build(o * + ,mid + ,r);
pushup(o);
} double query(int o,int l,int r,int x,int y)
{
if (x <= l && r <= y)
return sum[o];
pushdown(o);
int mid = (l + r) >> ;
double res = 0.0;
if (x <= mid)
res += query(o * ,l,mid,x,y);
if (y > mid)
res += query(o * + ,mid + ,r,x,y);
return res;
} void update1(int o,int l,int r,int x,int y,double v)
{
if (x <= l && r <= y)
{
sum[o] += v * (r - l + );
add[o] += v;
return;
}
pushdown(o);
int mid = (l + r) >> ;
if (x <= mid)
update1(o * ,l,mid,x,y,v);
if (y > mid)
update1(o * + ,mid + ,r,x,y,v);
pushup(o);
} void update2(int o,int l,int r,int x,int y,double v)
{
if (x <= l && r <= y)
{
add[o] *= v;
sum[o] *= v;
mul[o] *= v;
return;
}
pushdown(o);
int mid = (l + r) >> ;
if (x <= mid)
update2(o * ,l,mid,x,y,v);
if (y > mid)
update2(o * + ,mid + ,r,x,y,v);
pushup(o);
} int main()
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&q);
build(,,n);
while (q--)
{
int l1,r1,l2,r2;
int id;
scanf("%d",&id);
if (id == )
{
scanf("%d%d%d%d",&l1,&r1,&l2,&r2);
double sum1 = query(,,n,l1,r1),sum2 = query(,,n,l2,r2);
double len1 = r1 - l1 + ,len2 = r2 - l2 + ;
update2(,,n,l1,r1,(len1 - ) / len1);
update2(,,n,l2,r2,(len2 - ) / len2);
update1(,,n,l1,r1,1.0 / len1 * (sum2 / len2));
update1(,,n,l2,r2,1.0 / len2 * (sum1 / len1));
}
else
{
scanf("%d%d",&l1,&r1);
printf("%.7lf\n",query(,,n,l1,r1));
}
} return ;
}
Codeforces 895.E Eyes Closed的更多相关文章
- Codeforces 895.D String Mark
D. String Mark time limit per test 4 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard inpu ...
- Codeforces 895.C Square Subsets
C. Square Subsets time limit per test 4 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard i ...
- Codeforces 895.B XK Segments
B. XK Segments time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard input ...
- Codeforces 895.A Pizza Separation
A. Pizza Separation time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard ...
- Codeforces 895E Eyes Closed(线段树)
题目链接 Eyes Closed 题意 两个人玩一个游戏,现在有两种操作: 1.两个人格子挑选一个区间,保证两个的区间不相交.在这两个区间里面各选出一个数,交换这两个数. 2.挑选一个区间,求这个 ...
- Codeforces GYM 100114 B. Island 水题
B. Island Time Limit: 1 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://codeforces.com/gym/100114 Description O ...
- Codeforces Gym 100338C C - Important Roads tarjan
C - Important RoadsTime Limit: 20 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://acm.hust.edu.cn/vjudge/contes ...
- Codeforces Round #257 (Div. 1)A~C(DIV.2-C~E)题解
今天老师(orz sansirowaltz)让我们做了很久之前的一场Codeforces Round #257 (Div. 1),这里给出A~C的题解,对应DIV2的C~E. A.Jzzhu and ...
- Codeforces Round #426 (Div. 2)【A.枚举,B.思维,C,二分+数学】
A. The Useless Toy time limit per test:1 second memory limit per test:256 megabytes input:standard i ...
随机推荐
- leetcode-每个节点的右向指针(填充同一层的兄弟节点)
给定一个二叉树 struct TreeLinkNode { TreeLinkNode *left; TreeLinkNode *right; TreeLinkNode *next; } 填充它的每个 ...
- vue中的样式
一.使用class样式: CSS部分: <style> .green{ color:green; } .italic{ font-style:italic; } .thin{ ; } .a ...
- [ Continuously Update ] This is an *Index Page*.
The links below present papers in certain fields. Despite overlaps exist, their emphasis is markedly ...
- 基于C#的机器学习--面部和动态检测-图像过滤器
在本章中,我们将展示两个独立的例子,一个用于人脸检测,另一个用于动态检测,以及如何快速地将这些功能添加到应用程序中. 在这一章中,我们将讨论: 面部检测 动态检测 将检测添加到应用程序中 面部检测 人 ...
- 微软职位内部推荐-Software Engineer II-Data Mining
微软近期Open的职位: Are you looking for a big challenge? Do you know why Big Data is the next frontier for ...
- npm 常用指令
npm install <name>安装nodejs的依赖包 例如npm install express 就会默认安装express的最新版本,也可以通过在后面加版本号的方式安装指定版本, ...
- Masha and Bears(翻译+思维)
Description A family consisting of father bear, mother bear and son bear owns three cars. Father bea ...
- Android开发第二阶段(1)
今天:总结第一阶段的冲刺成果,第一阶段就是主要是学习andriod开发,参考文件有<黑马教学视频><Mars教学视频>...结果在看的过程遇到很多问题特别是对java的一些理解 ...
- 【转】nodeJs学习之项目结构
新建的项目结构应该是这样 bin:项目的启动文件,也可以放其他脚本. node_modules:用来存放项目的依赖库. public:用来存放静态文件(css,js,img). routes:路由控制 ...
- div跟随鼠标移动
1.目标是实现div跟随鼠标而移动,分三种情况进行实现 a)首先获取div,进行绑定鼠标移动事件,给div开启定位功能 第一种实现方式,假如body的大小跟页面大小一样,则可以用这个方法. 1)获取鼠 ...
