python-静态方法staticmethod、类方法classmethod、属性方法property
Python的方法主要有3个,即静态方法(staticmethod),类方法(classmethod)和实例方法
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
def foo(x): print "executing foo(%s)"%(x) class A(object): def foo(self,x): print "executing foo(%s,%s)"%(self,x) @classmethod def class_foo(cls,x): print "executing class_foo(%s,%s)"%(cls,x) @staticmethod def static_foo(x): print "executing static_foo(%s)"%x a=A() |
这个self和cls是对类或者实例的绑定,对于一般的函数来说我们可以这么调用foo(x),这个函数就是最常用的,它的工作跟任何东西(类,实例)无关.对于实例方法,我们知道在类里每次定义方法的时候都需要绑定这个实例,就是foo(self, x),为什么要这么做呢?因为实例方法的调用离不开实例,我们需要把实例自己传给函数,调用的时候是这样的a.foo(x)(其实是foo(a, x)).类方法一样,只不过它传递的是类而不是实例,A.class_foo(x).注意这里的self和cls可以替换别的参数,但是python的约定是这俩,还是不要改的好.
对于静态方法其实和普通的方法一样,不需要对谁进行绑定,唯一的区别是调用的时候需要使用a.static_foo(x)或者A.static_foo(x)来调用.
| \ | 实例方法 | 类方法 | 静态方法 |
|---|---|---|---|
| a = A() | a.foo(x) | a.class_foo(x) | a.static_foo(x) |
| A | 不可用 | A.class_foo(x) | A.static_foo(x) |
类的普通方法
class Animal(object):
def __init__(self,name):
self.name = name
def intro(self):
print('there is a %s'%(self.name))
cat = Animal('cat')
cat.intro()- 静态类方法
class Animal(object):
def __init__(self,name):
self.name = name
@staticmethod
def intro(self):
print('there is a %s'%(self.name))
cat = Animal('cat')
cat.intro()- 加上装饰器后运行会报错,原因是方法变为一个普通函数,脱离的与类的关系,不能引用构造函数中的变量了。
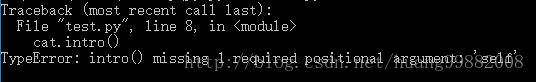
使用场景举例:python内置方法os中的方法,可以直接使用的工具包,跟类没关系。
class Animal(object):
def __init__(self,name):
self.name = name
@classmethod
def intro(self):
print('there is a %s'%(self.name))
cat = Animal('cat')
cat.intro()- 报错信息
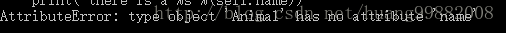
如果换成
class Animal(object):
name = 'cat'
def __init__(self,name):
self.name = name
@classmethod
def intro(self):
print('there is a %s'%(self.name))
cat = Animal('cat')
cat.intro()- 可以正常运行。
结论:类方法只能调用类变量,不能调用实例变量
属性方法@property 把一个方法变为(伪装成)类属性。因为类属性的实质是一个类变量,用户可以调用变量就可以修改变量。某些特定场景要限制用户行为,就用到静态方法。
@property广泛应用在类的定义中,可以让调用者写出简短的代码,同时保证对参数进行必要的检查,这样,程序运行时就减少了出错的可能性。(摘自廖雪峰的博客)
class Animal(object):
def __init__(self,name):
self.name = name
@property
def intro(self,food):
print('there is a %s eating %s'%(self.name,food))
cat = Animal('cat')
cat.intro()- 报错:
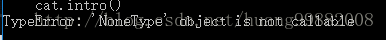
- 方法不能正常调用。如果要调用,如下:
cat.intro- 是这样的话,方法就没办法单独传入参数。如果要传入参数,如下:
class Animal(object):
def __init__(self,name):
self.name = name
@property
def intro(self):
print('there is a %s eating %s'%(self.name,food))
@intro.setter
def intro(self,food):
pass
cat = Animal('cat')
cat.intro- cat.intro还有其他操作getter deleter等等。
一:staticmethod
class Singleton(object):
instance = None def __init__(self):
raise SyntaxError('can not instance, please use get_instance') @staticmethod
def get_instance():
if Singleton.instance is None:
Singleton.instance = object.__new__(Singleton)
return Singleton.instance a = Singleton.get_instance()
b = Singleton.get_instance()
print('a id=', id(a))
print('b id=', id(b))
该方法的要点是在__init__抛出异常,禁止通过类来实例化,只能通过静态get_instance函数来获取实例;因为不能通过类来实例化,所以静态get_instance函数中可以通过父类object.__new__来实例化。
二:classmethod
class Singleton(object):
instance = None def __init__(self):
raise SyntaxError('can not instance, please use get_instance') @classmethod
def get_instance(cls):
if Singleton.instance is None:
Singleton.instance = object.__new__(Singleton)
return Singleton.instance a = Singleton.get_instance()
b = Singleton.get_instance()
print('a id=', id(a))
print('b id=', id(b))
该方法的要点是在__init__抛出异常,禁止通过类来实例化,只能通过静态get_instance函数来获取实例;因为不能通过类来实例化,所以静态get_instance函数中可以通过父类object.__new__来实例化。
三:类属性方法
class Singleton(object):
instance = None def __init__(self):
raise SyntaxError('can not instance, please use get_instance') def get_instance():
if Singleton.instance is None:
Singleton.instance = object.__new__(Singleton)
return Singleton.instance a = Singleton.get_instance()
b = Singleton.get_instance()
print(id(a))
print(id(b))
该方法的要点是在__init__抛出异常,禁止通过类来实例化,只能通过静态get_instance函数来获取实例;因为不能通过类来实例化,所以静态get_instance函数中可以通过父类object.__new__来实例化。
四:__new__
常见的方法, 代码如下:
class Singleton(object):
instance = None def __new__(cls, *args, **kw):
if not cls.instance:
# cls.instance = object.__new__(cls, *args)
cls.instance = super(Singleton, cls).__new__(cls, *args, **kw)
return cls.instance a = Singleton()
b = Singleton()
print(id(a))
print(id(b))
五:装饰器
代码如下:
def Singleton(cls):
instances = {} def getinstance():
if cls not in instances:
instances[cls] = cls()
return instances[cls]
return getinstance @Singleton
class MyClass:
pass a = MyClass()
b = MyClass()
c = MyClass() print(id(a))
print(id(b))
print(id(c))
六:元类
class Singleton(type):
def __init__(cls, name, bases, dct):
super(Singleton, cls).__init__(name, bases, dct)
cls.instance = None def __call__(cls, *args):
if cls.instance is None:
cls.instance = super(Singleton, cls).__call__(*args)
return cls.instance class MyClass(object):
__metaclass__ = Singleton a = MyClass()
b = MyClass()
c = MyClass()
print(id(a))
print(id(b))
print(id(c))
print(a is b)
print(a is c)
或者:
class Singleton(type):
def __new__(cls, name, bases, attrs):
attrs["_instance"] = None
return super(Singleton, cls).__new__(cls, name, bases, attrs) def __call__(cls, *args, **kwargs):
if cls._instance is None:
cls._instance = super(Singleton, cls).__call__(*args, **kwargs)
return cls._instance class Foo(object):
__metaclass__ = Singleton x = Foo()
y = Foo()
print(id(x))
print(id(y))
class Singleton(type):
def __new__(cls, name, bases, attrs):
attrs['instance'] = None
return super(Singleton, cls).__new__(cls, name, bases, attrs) def __call__(cls, *args, **kwargs):
if cls.instance is None:
cls.instance = super(Singleton, cls).__call__(*args, **kwargs)
return cls.instance class Foo(metaclass=Singleton):
pass x = Foo()
y = Foo()
print(id(x))
print(id(y))
七:名字覆盖
class Singleton(object):
def foo(self):
print('foo') def __call__(self):
return self Singleton = Singleton() Singleton.foo() a = Singleton()
b = Singleton()
print(id(a))
print(id(b))
python-静态方法staticmethod、类方法classmethod、属性方法property的更多相关文章
- Python 静态方法、类方法和属性方法
Python 静态方法.类方法和属性方法 静态方法(staticmethod) staticmethod不与类或者对象绑定,类和实例对象都可以调用,没有自动传值效果,Python内置函数staticm ...
- Python 静态方法,类方法,属性方法
方法的使用 静态方法 - 只是名义上归类管理,实际上在静态方法里访问不了类或实例中的任何属性. class Dog(object): def __init__(self,name): self.nam ...
- Python静态方法、类方法、属性方法
静态方法 使用静态方法以后,相当于把下面的函数和类的关系截断了,它的作用相当于是类下面的一个独立函数,不会自动传入参数self. class people:..... @staticmethod de ...
- Python的3个方法:静态方法(staticmethod),类方法(classmethod)和实例方法
Python的方法主要有3个,即静态方法(staticmethod),类方法(classmethod)和实例方法,如下: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 ...
- Python面向对象静态方法,类方法,属性方法
Python面向对象静态方法,类方法,属性方法 属性: 公有属性 (属于类,每个类一份) 普通属性 (属于对象,每个对象一份) 私有属性 (属于对象,跟普通属性相似,只是不能通过对象直接访问) 方法: ...
- python中静态方法、类方法、属性方法区别
在python中,静态方法.类方法.属性方法,刚接触对于它们之间的区别确实让人疑惑. 类方法(@classmethod) 是一个函数修饰符,表是该函数是一个类方法 类方法第一个参数是cls,而实例方法 ...
- Python的程序结构[1] -> 方法/Method[1] -> 静态方法、类方法和属性方法
静态方法.类方法和属性方法 在 Python 中有三种常用的方法装饰器,可以使普通的类实例方法变成带有特殊功能的方法,分别是静态方法.类方法和属性方法. 静态方法 / Static Method 在 ...
- 面向对象【day08】:静态方法、类方法、属性方法(九)
本节内容 概述 静态方法 类方法 属性方法 总结 一.概述 前面我们已经讲解了关于类的很多东西,今天讲讲类的另外的特性:静态方法(staticmethod).类方法(classmethod).属性方法 ...
- Python笔记_第四篇_高阶编程_实例化方法、静态方法、类方法和属性方法概念的解析。
1.先叙述静态方法: 我们知道Python调用类的方法的时候都要进行一个实例化的处理.在面向对象中,一把存在静态类,静态方法,动态类.动态方法等乱七八糟的这么一些叫法.其实这些东西看起来抽象,但是很好 ...
- python 面向对象静态方法、类方法、属性方法、类的特殊成员方法
静态方法:只是名义上归类管理,实际上在静态方法里访问不了类或实例中的任何属性. 在类中方法定义前添加@staticmethod,该方法就与类中的其他(属性,方法)没有关系,不能通过实例化类调用方法使用 ...
随机推荐
- ArcGIS ArcMap 问题(ArcMap闪退、cx_oracle安装不上)
一.问题描述 1.ArcMap闪退 2.安装32位cx_oracle提示python目录不存在 二.解决方案 1.修改pythoncore的文件目录,指向C:\Python27\ArcGIS10.3\ ...
- will-change
目的: 让GPU分担CPU的工作,从而优化和分配内存,告知浏览器做好动画的准备. 背景: 注意事项: 1,will-change虽然可以加速,但是,一定一定要适度使用: 2,使用伪元素,独立渲染: 不 ...
- PHP 开发环境的搭建和使用02--整合让apache处理php
PHP5.3.5直接下载解压即可.但是怎样才能让apache处理php呢? 1/ 在apache 的conf目录下 的 httpd.conf(用于指定apache的设置)加入如下代码: Load ...
- 160524、Linux下如何启动、关闭Oracle以及打开关闭监听
1. linux下启动oraclesu - oraclesqlplus /nologconn /as sysdbastartupexitlsnrctl startexit2. linux下关闭orac ...
- Linux 磁盘管理的命令
Linux 磁盘管理 磁盘分区及挂载: 先查询系统的使用情况: 使用fdisk -l语句 查询结果: 进行磁盘的新建:***添加磁盘时系统必须处于关机状态** 在进行对系统磁盘的使用情况的查询 查 ...
- ORACLE内存结构之SGA
SGA的管理: SQL> show parameter sga NAME TYPE VALUE ---------- ...
- LeetCode—Unique Paths
题目: A robot is located at the top-left corner of a m x n grid (marked 'Start' in the diagram below). ...
- windows中的进程和线程
今天咱们就聊聊windows中的进程和线程 2016-09-30 在讨论windows下的进程和线程时,我们先回顾下通用操作系统的进程和线程.之所以称之为通用是因为一贯的本科或者其他教材都是这么说的: ...
- JavaScript闭包和this绑定
本文最主要讲讲JavaScript闭包和this绑定相关的我的小发现,鉴于这方面的基础知识已经有很多很好的文章讲过了,所以基本的就不讲了,推荐看看[酷壳](http://coolshell.cn/)上 ...
- mysql 约束条件 auto_increment 自动增长 创建表时设置自增字段
auto_increment mysql) )auto_increment; Query OK, rows affected (0.01 sec) mysql> show create tabl ...
