Java Vertor详细介绍和使用示例
①对Vector有个整体认识
Vector是向量类,继承于AbstractList,实现了List,RandomAccess,Clonable这些接口。
Vector继承于AbstractList,实现了List,它是一个队列,支持相关的添加、删除、修改、遍历等功能
Vector实现了RandomAccess接口,即提供了随机访问功能。RandomAccess是Java中来被List实现,为List提供快速访问功能的,在Vecor中,我们可以通过元素的序号快速获取元素对象,这就是快速随机访问。
Vector实现了Cloneable接口,即clone()函数
②Vector的构造函数
//默认构造函数
Vector() //capacity是Vector()的默认容量大小,当由于增加数据导致容量增加时,每次容量会增加一倍。
Vector(int capacity) // capacity是Vector()的默认容量大小,capacityIncrement是每次Vector容量增加时的增量值。
Vector(int capacity,int capacityIncrement) //创建一个包含包含collection的Vector
Vector(Collection<? Extends E> collection)
③Vector的API
synchronized boolean add(E object)
void add(int location, E object)
synchronized boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> collection)
synchronized boolean addAll(int location, Collection<? extends E> collection)
synchronized void addElement(E object)
synchronized int capacity()
void clear()
synchronized Object clone()
boolean contains(Object object)
synchronized boolean containsAll(Collection<?> collection)
synchronized void copyInto(Object[] elements)
synchronized E elementAt(int location)
Enumeration<E> elements()
synchronized void ensureCapacity(int minimumCapacity)
synchronized boolean equals(Object object)
synchronized E firstElement()
E get(int location)
synchronized int hashCode()
synchronized int indexOf(Object object, int location)
int indexOf(Object object)
synchronized void insertElementAt(E object, int location)
synchronized boolean isEmpty()
synchronized E lastElement()
synchronized int lastIndexOf(Object object, int location)
synchronized int lastIndexOf(Object object)
synchronized E remove(int location)
boolean remove(Object object)
synchronized boolean removeAll(Collection<?> collection)
synchronized void removeAllElements()
synchronized boolean removeElement(Object object)
synchronized void removeElementAt(int location)
synchronized boolean retainAll(Collection<?> collection)
synchronized E set(int location, E object)
synchronized void setElementAt(E object, int location)
synchronized void setSize(int length)
synchronized int size()
synchronized List<E> subList(int start, int end)
synchronized <T> T[] toArray(T[] contents)
synchronized Object[] toArray()
synchronized String toString()
synchronized void trimToSize()
④Vector的继承关系
java.lang.Object
↳ java.util.AbstractCollection<E>
↳ java.util.AbstractList<E>
↳ java.util.Vector<E> public class Vector<E>
extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable {}
⑤Vector与Collection关系
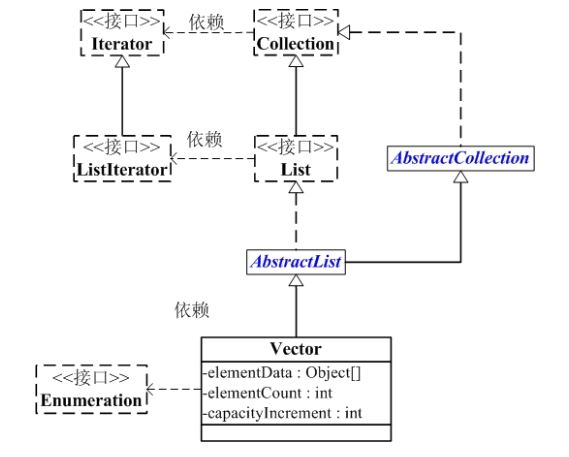
⑥Vector的数据结构
Vector的数据结构包含了3个成员变量:elementData,elementCount,capacityIncrement
elementData是Object[]类型的数组,它保存了添加到Vector中的元素。elementData是个动态数组,如果初始化Vector时,没有指定动态数组的大小,则使用默认大小10。随着Vector中元素的增加,Vector的容量也会动态增长,capacityIncrement是与容量增长相关的增长指数,具体的增长方式请参考源码分析中的ensureCapacity()函数。
elementCount是动态数组的实际大小
capacityIncrement是动态数组的增长系数。如果在创建Vector时,指定了capacityIncrement的大小,则每次Vector中动态数组容量增加时,增加的大小都是capacityIncrement.
⑦ 源码及解析
package java.util; public class Vector<E>
extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{ // 保存Vector中数据的数组
protected Object[] elementData; // 实际数据的数量
protected int elementCount; // 容量增长系数
protected int capacityIncrement; // Vector的序列版本号
private static final long serialVersionUID = -2767605614048989439L; // Vector构造函数。默认容量是10。
public Vector() {
this(10);
} // 指定Vector容量大小的构造函数
public Vector(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, 0);
} // 指定Vector"容量大小"和"增长系数"的构造函数
public Vector(int initialCapacity, int capacityIncrement) {
super();
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
// 新建一个数组,数组容量是initialCapacity
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
// 设置容量增长系数
this.capacityIncrement = capacityIncrement;
} // 指定集合的Vector构造函数。
public Vector(Collection<? extends E> c) {
// 获取“集合(c)”的数组,并将其赋值给elementData
elementData = c.toArray();
// 设置数组长度
elementCount = elementData.length;
// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, elementCount, Object[].class);
} // 将数组Vector的全部元素都拷贝到数组anArray中
public synchronized void copyInto(Object[] anArray) {
System.arraycopy(elementData, 0, anArray, 0, elementCount);
} // 将当前容量值设为 =实际元素个数
public synchronized void trimToSize() {
modCount++;
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
if (elementCount < oldCapacity) {
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, elementCount);
}
} // 确认“Vector容量”的帮助函数
private void ensureCapacityHelper(int minCapacity) {
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
// 当Vector的容量不足以容纳当前的全部元素,增加容量大小。
// 若 容量增量系数>0(即capacityIncrement>0),则将容量增大当capacityIncrement
// 否则,将容量增大一倍。
if (minCapacity > oldCapacity) {
Object[] oldData = elementData;
int newCapacity = (capacityIncrement > 0) ?
(oldCapacity + capacityIncrement) : (oldCapacity * 2);
if (newCapacity < minCapacity) {
newCapacity = minCapacity;
}
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
} // 确定Vector的容量。
public synchronized void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) {
// 将Vector的改变统计数+1
modCount++;
ensureCapacityHelper(minCapacity);
} // 设置容量值为 newSize
public synchronized void setSize(int newSize) {
modCount++;
if (newSize > elementCount) {
// 若 "newSize 大于 Vector容量",则调整Vector的大小。
ensureCapacityHelper(newSize);
} else {
// 若 "newSize 小于/等于 Vector容量",则将newSize位置开始的元素都设置为null
for (int i = newSize ; i < elementCount ; i++) {
elementData[i] = null;
}
}
elementCount = newSize;
} // 返回“Vector的总的容量”
public synchronized int capacity() {
return elementData.length;
} // 返回“Vector的实际大小”,即Vector中元素个数
public synchronized int size() {
return elementCount;
} // 判断Vector是否为空
public synchronized boolean isEmpty() {
return elementCount == 0;
} // 返回“Vector中全部元素对应的Enumeration”
public Enumeration<E> elements() {
// 通过匿名类实现Enumeration
return new Enumeration<E>() {
int count = 0; // 是否存在下一个元素
public boolean hasMoreElements() {
return count < elementCount;
} // 获取下一个元素
public E nextElement() {
synchronized (Vector.this) {
if (count < elementCount) {
return (E)elementData[count++];
}
}
throw new NoSuchElementException("Vector Enumeration");
}
};
} // 返回Vector中是否包含对象(o)
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return indexOf(o, 0) >= 0;
} // 从index位置开始向后查找元素(o)。
// 若找到,则返回元素的索引值;否则,返回-1
public synchronized int indexOf(Object o, int index) {
if (o == null) {
// 若查找元素为null,则正向找出null元素,并返回它对应的序号
for (int i = index ; i < elementCount ; i++)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
// 若查找元素不为null,则正向找出该元素,并返回它对应的序号
for (int i = index ; i < elementCount ; i++)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
} // 查找并返回元素(o)在Vector中的索引值
public int indexOf(Object o) {
return indexOf(o, 0);
} // 从后向前查找元素(o)。并返回元素的索引
public synchronized int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
return lastIndexOf(o, elementCount-1);
} // 从后向前查找元素(o)。开始位置是从前向后的第index个数;
// 若找到,则返回元素的“索引值”;否则,返回-1。
public synchronized int lastIndexOf(Object o, int index) {
if (index >= elementCount)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= "+ elementCount); if (o == null) {
// 若查找元素为null,则反向找出null元素,并返回它对应的序号
for (int i = index; i >= 0; i--)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
// 若查找元素不为null,则反向找出该元素,并返回它对应的序号
for (int i = index; i >= 0; i--)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
} // 返回Vector中index位置的元素。
// 若index月结,则抛出异常
public synchronized E elementAt(int index) {
if (index >= elementCount) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= " + elementCount);
} return (E)elementData[index];
} // 获取Vector中的第一个元素。
// 若失败,则抛出异常!
public synchronized E firstElement() {
if (elementCount == 0) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
return (E)elementData[0];
} // 获取Vector中的最后一个元素。
// 若失败,则抛出异常!
public synchronized E lastElement() {
if (elementCount == 0) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
return (E)elementData[elementCount - 1];
} // 设置index位置的元素值为obj
public synchronized void setElementAt(E obj, int index) {
if (index >= elementCount) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= " +
elementCount);
}
elementData[index] = obj;
} // 删除index位置的元素
public synchronized void removeElementAt(int index) {
modCount++;
if (index >= elementCount) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= " +
elementCount);
} else if (index < 0) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
} int j = elementCount - index - 1;
if (j > 0) {
System.arraycopy(elementData, index + 1, elementData, index, j);
}
elementCount--;
elementData[elementCount] = null; /* to let gc do its work */
} // 在index位置处插入元素(obj)
public synchronized void insertElementAt(E obj, int index) {
modCount++;
if (index > elementCount) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index
+ " > " + elementCount);
}
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1, elementCount - index);
elementData[index] = obj;
elementCount++;
} // 将“元素obj”添加到Vector末尾
public synchronized void addElement(E obj) {
modCount++;
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
elementData[elementCount++] = obj;
} // 在Vector中查找并删除元素obj。
// 成功的话,返回true;否则,返回false。
public synchronized boolean removeElement(Object obj) {
modCount++;
int i = indexOf(obj);
if (i >= 0) {
removeElementAt(i);
return true;
}
return false;
} // 删除Vector中的全部元素
public synchronized void removeAllElements() {
modCount++;
// 将Vector中的全部元素设为null
for (int i = 0; i < elementCount; i++)
elementData[i] = null; elementCount = 0;
} // 克隆函数
public synchronized Object clone() {
try {
Vector<E> v = (Vector<E>) super.clone();
// 将当前Vector的全部元素拷贝到v中
v.elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, elementCount);
v.modCount = 0;
return v;
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
// this shouldn't happen, since we are Cloneable
throw new InternalError();
}
} // 返回Object数组
public synchronized Object[] toArray() {
return Arrays.copyOf(elementData, elementCount);
} // 返回Vector的模板数组。所谓模板数组,即可以将T设为任意的数据类型
public synchronized <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {
// 若数组a的大小 < Vector的元素个数;
// 则新建一个T[]数组,数组大小是“Vector的元素个数”,并将“Vector”全部拷贝到新数组中
if (a.length < elementCount)
return (T[]) Arrays.copyOf(elementData, elementCount, a.getClass()); // 若数组a的大小 >= Vector的元素个数;
// 则将Vector的全部元素都拷贝到数组a中。
System.arraycopy(elementData, 0, a, 0, elementCount); if (a.length > elementCount)
a[elementCount] = null; return a;
} // 获取index位置的元素
public synchronized E get(int index) {
if (index >= elementCount)
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index); return (E)elementData[index];
} // 设置index位置的值为element。并返回index位置的原始值
public synchronized E set(int index, E element) {
if (index >= elementCount)
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index); Object oldValue = elementData[index];
elementData[index] = element;
return (E)oldValue;
} // 将“元素e”添加到Vector最后。
public synchronized boolean add(E e) {
modCount++;
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
elementData[elementCount++] = e;
return true;
} // 删除Vector中的元素o
public boolean remove(Object o) {
return removeElement(o);
} // 在index位置添加元素element
public void add(int index, E element) {
insertElementAt(element, index);
} // 删除index位置的元素,并返回index位置的原始值
public synchronized E remove(int index) {
modCount++;
if (index >= elementCount)
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
Object oldValue = elementData[index]; int numMoved = elementCount - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--elementCount] = null; // Let gc do its work return (E)oldValue;
} // 清空Vector
public void clear() {
removeAllElements();
} // 返回Vector是否包含集合c
public synchronized boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c) {
return super.containsAll(c);
} // 将集合c添加到Vector中
public synchronized boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
modCount++;
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + numNew);
// 将集合c的全部元素拷贝到数组elementData中
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, elementCount, numNew);
elementCount += numNew;
return numNew != 0;
} // 删除集合c的全部元素
public synchronized boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) {
return super.removeAll(c);
} // 删除“非集合c中的元素”
public synchronized boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) {
return super.retainAll(c);
} // 从index位置开始,将集合c添加到Vector中
public synchronized boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
modCount++;
if (index < 0 || index > elementCount)
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index); Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + numNew); int numMoved = elementCount - index;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + numNew, numMoved); System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, index, numNew);
elementCount += numNew;
return numNew != 0;
} // 返回两个对象是否相等
public synchronized boolean equals(Object o) {
return super.equals(o);
} // 计算哈希值
public synchronized int hashCode() {
return super.hashCode();
} // 调用父类的toString()
public synchronized String toString() {
return super.toString();
} // 获取Vector中fromIndex(包括)到toIndex(不包括)的子集
public synchronized List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
return Collections.synchronizedList(super.subList(fromIndex, toIndex), this);
} // 删除Vector中fromIndex到toIndex的元素
protected synchronized void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
modCount++;
int numMoved = elementCount - toIndex;
System.arraycopy(elementData, toIndex, elementData, fromIndex,
numMoved); // Let gc do its work
int newElementCount = elementCount - (toIndex-fromIndex);
while (elementCount != newElementCount)
elementData[--elementCount] = null;
} // java.io.Serializable的写入函数
private synchronized void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException {
s.defaultWriteObject();
}
}
Vector实际上是通过一个数组去保存数据的。当我们构造Vecotr时;若使用默认构造函数,则Vector的默认容量大小是10。
当Vector容量不足以容纳全部元素时,Vector的容量会增加。若容量增加系数 >0,则将容量的值增加“容量增加系数”;否则,将容量大小增加一倍。
Vector的克隆函数,即是将全部元素克隆到一个数组中。
⑧Vector遍历方式
通过迭代器遍历
Integer value=null;
Int size=vec.size();
For(int i=0;i<size;i++){
Value=(Integer)vec.get(i);
}
随机访问,通过索引值去遍历
Integer value=null;
Int size =vec.size();
For(int i=0;i<size;i++){
Value=(Integer)vec.get(i);
}
另一种for循环
Integer value=null;
For(Integer integ:vec){
Value=integ;
}
Enumeration遍历
Integer enu=vec.elements();
While (enu.hasMoreElements()){
Value=(Integer)enu.nextElement();
}
⑨ 测试这些遍历方式效率的代码如下
import java.util.*; /*
* @desc Vector遍历方式和效率的测试程序。
*
* @author skywang
*/
public class VectorRandomAccessTest { public static void main(String[] args) {
Vector vec= new Vector();
for (int i=0; i<100000; i++)
vec.add(i);
iteratorThroughRandomAccess(vec) ;
iteratorThroughIterator(vec) ;
iteratorThroughFor2(vec) ;
iteratorThroughEnumeration(vec) ; } private static void isRandomAccessSupported(List list) {
if (list instanceof RandomAccess) {
System.out.println("RandomAccess implemented!");
} else {
System.out.println("RandomAccess not implemented!");
} } public static void iteratorThroughRandomAccess(List list) { long startTime;
long endTime;
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i=0; i<list.size(); i++) {
list.get(i);
}
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
long interval = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println("iteratorThroughRandomAccess:" + interval+" ms");
} public static void iteratorThroughIterator(List list) { long startTime;
long endTime;
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(Iterator iter = list.iterator(); iter.hasNext(); ) {
iter.next();
}
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
long interval = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println("iteratorThroughIterator:" + interval+" ms");
} public static void iteratorThroughFor2(List list) { long startTime;
long endTime;
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(Object obj:list)
;
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
long interval = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println("iteratorThroughFor2:" + interval+" ms");
} public static void iteratorThroughEnumeration(Vector vec) { long startTime;
long endTime;
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(Enumeration enu = vec.elements(); enu.hasMoreElements(); ) {
enu.nextElement();
}
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
long interval = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println("iteratorThroughEnumeration:" + interval+" ms");
}
}
⑩Vector示例
import java.util.Vector;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Enumeration; /**
* @desc Vector测试函数:遍历Vector和常用API
*
* @author skywang
*/
public class VectorTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 新建Vector
Vector vec = new Vector(); // 添加元素
vec.add("1");
vec.add("2");
vec.add("3");
vec.add("4");
vec.add("5"); // 设置第一个元素为100
vec.set(0, "100");
// 将“500”插入到第3个位置
vec.add(2, "300");
System.out.println("vec:"+vec); // (顺序查找)获取100的索引
System.out.println("vec.indexOf(100):"+vec.indexOf("100"));
// (倒序查找)获取100的索引
System.out.println("vec.lastIndexOf(100):"+vec.lastIndexOf("100"));
// 获取第一个元素
System.out.println("vec.firstElement():"+vec.firstElement());
// 获取第3个元素
System.out.println("vec.elementAt(2):"+vec.elementAt(2));
// 获取最后一个元素
System.out.println("vec.lastElement():"+vec.lastElement()); // 获取Vector的大小
System.out.println("size:"+vec.size());
// 获取Vector的总的容量
System.out.println("capacity:"+vec.capacity()); // 获取vector的“第2”到“第4”个元素
System.out.println("vec 2 to 4:"+vec.subList(1, 4)); // 通过Enumeration遍历Vector
Enumeration enu = vec.elements();
while(enu.hasMoreElements())
System.out.println("nextElement():"+enu.nextElement()); Vector retainVec = new Vector();
retainVec.add("100");
retainVec.add("300");
// 获取“vec”中包含在“retainVec中的元素”的集合
System.out.println("vec.retain():"+vec.retainAll(retainVec));
System.out.println("vec:"+vec); // 获取vec对应的String数组
String[] arr = (String[]) vec.toArray(new String[0]);
for (String str:arr)
System.out.println("str:"+str); // 清空Vector。clear()和removeAllElements()一样!
vec.clear();
// vec.removeAllElements(); // 判断Vector是否为空
System.out.println("vec.isEmpty():"+vec.isEmpty());
}
}
out
vec:[100, 2, 300, 3, 4, 5]
vec.indexOf(100):0
vec.lastIndexOf(100):0
vec.firstElement():100
vec.elementAt(2):300
vec.lastElement():5
size:6
capacity:10
vec 2 to 4:[2, 300, 3]
nextElement():100
nextElement():2
nextElement():300
nextElement():3
nextElement():4
nextElement():5
vec.retain():true
vec:[100, 300]
str:100
str:300
vec.isEmpty():true
Java Vertor详细介绍和使用示例的更多相关文章
- Java linkedList详细介绍及使用示例
①LinkedList简单介绍 是一个继承于AbstractSequentialList的双向链表.它可以被当成堆栈.队列或双端队列进行操作. 实现了List接口,能对它进行队列操作. 实现了Dequ ...
- Java ArrayList详细介绍和使用示例
①对ArrayList的整体认识 ArrayList是一个数组队列,相当于动态数组.与Java中的数组相比,它的容量能动态增长.它继承了AbstractList,实现了List,RandomAcces ...
- Java TreeMap详细介绍和使用示例
①对TreeMap有个整体认识 TreeMap是一个有序的key-value集合,它是通过红黑树实现的. TreeMap继承于AbstractMap,所以它是一个Map,即key-value集合. T ...
- Java Hashtable详细介绍和使用示例
①对Hashtable有个整体认识 和HashMap一样,Hashtable 也是一个散列表,它存储的内容是键值对(key-value)映射.Hashtable 继承于Dictionary,实现了Ma ...
- Java HashMap详细介绍和使用示例
①对HashMap的整体认识 HashMap是一个散列表,它存储的内容是键值对(key-value)映射. HashMap继承于AbstractMap,实现了Map.Cloneable.java.io ...
- java agent 详细介绍 -javaagent参数
java agent 详细介绍 简介 java agent是java命令的一个参数.参数 javaagent 可以用于指定一个 jar 包,并且对该 java 包有2个要求: 这个 jar 包的MAN ...
- JAVA HashMap详细介绍和示例
http://www.jb51.net/article/42769.htm 我们先对HashMap有个整体认识,然后再学习它的源码,最后再通过实例来学会使用HashMap. 第1部分 HashMa ...
- Java反射详细介绍
反射 目录介绍 1.反射概述 1.1 反射概述 1.2 获取class文件对象的三种方式 1.3 反射常用的方法介绍 1.4 反射的定义 1.5 反射的组成 1.6 反射的作用有哪些 2.反射的相关使 ...
- java jodd框架介绍及使用示例
Jodd是一个普通开源Java包.你可以把Jodd想象成Java的"瑞士军刀",不仅小,锋利而且包含许多便利的功能.Jodd 提供的功能有: 提供操作Java bean, 可以 ...
随机推荐
- 总结界面框架_UI_Adapter
本人定期更新经典案例及解决方案如有疑问请联系我QQ1822282728 -- 277627117 下面是常用到的ui Demo 安卓三级筛选菜单listview(非常经典) http://dow ...
- c#基础 第六讲
烧开水 先询问:“是否要烧开水(Y/N)” 是的话执行--0°--100°(30°---水温了,50°---水热了,80°---水快开了,100°---水已经开了, 结束.) 判断 循环 选择 跳转 ...
- 【BZOJ2792】[Poi2012]Well 二分+双指针法
[BZOJ2792][Poi2012]Well Description 给出n个正整数X1,X2,...Xn,可以进行不超过m次操作,每次操作选择一个非零的Xi,并将它减一. 最终要求存在某个k满足X ...
- 加载CDN加速服务地址
Jquery是个非常流行的JS前端框架,在很多网站都能看到它的身影.很多网站都喜欢采用一些Jquery CDN加速服务,这样网站加载jquery会更快.之前火端网络的一些网站都是使用Google的jq ...
- 获取 js DOM元素中绑定的所有事件,模仿 chrome getEventListeners
偶尔看到了这个问题,如何用JS获取元素某一事件上绑定的所有Listener? 突然觉得好像是有解决办法的,查了下,在 chrome 下,支持 window.getEventListeners(obj) ...
- Python全栈day13(作业讲解根据用户输入选择输出字典内容)
题目,有一个动植物对应的字典内容如下,请根据用户输入列出对应的动物或者植物,实现字典三级菜单功能 dic = { "植物": {"草本植物": ["牵 ...
- HDU 4417 Super Mario(线段树)
Super Mario Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others) Tota ...
- md5sum检验MD5值
md5sum命令检验MD5值 md5sum命令用于生成和校验文件的md5值.它会逐位对文件的内容进行校验.是文件的内容,与文件名无关,也就是文件内容相同,其md5值相同.md5值是一个128位的二进制 ...
- 病毒侵袭---hdu2896(AC自动机)
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2896 输入的字符是所有可见的ASCII码(共有127个)所以要注意一下: 把结果存到一个数组中,然后输 ...
- Apache mahout 源码阅读笔记-DataModel之UserBaseRecommender
先来看一下使用流程: 1)拿到DataModel 2)定义相似度计算模型 PearsonCorrelationSimilarity 3)定义用户邻域计算模型 NearestNUserNeighborh ...
