关于 tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits 及 tf.clip_by_value
In order to train our model, we need to define what it means for the model to be good. Well, actually, in machine learning we typically define what it means for a model to be bad. We call this the cost, or the loss, and it represents how far off our model is from our desired outcome. We try to minimize that error, and the smaller the error margin, the better our model is.
One very common, very nice function to determine the loss of a model is called "cross-entropy." Cross-entropy arises from thinking about information compressing codes in information theory but it winds up being an important idea in lots of areas, from gambling to machine learning. It's defined as:
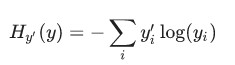
Where y is our predicted probability distribution, and y′ is the true distribution (the one-hot vector with the digit labels). In some rough sense, the cross-entropy is measuring how inefficient our predictions are for describing the truth. Going into more detail about cross-entropy is beyond the scope of this tutorial, but it's well worthunderstanding.
To implement cross-entropy we need to first add a new placeholder to input the correct answers:
y_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 10])
Then we can implement the cross-entropy function, 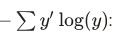
cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(-tf.reduce_sum(y_ * tf.log(y), reduction_indices=[1]))
First, tf.log computes the logarithm of each element of y. Next, we multiply each element of y_ with the corresponding element of tf.log(y). Then tf.reduce_sum adds the elements in the second dimension of y, due to the reduction_indices=[1] parameter. Finally, tf.reduce_mean computes the mean over all the examples in the batch.
Note that in the source code, we don't use this formulation, because it is numerically unstable. Instead, we apply tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits on the unnormalized logits (e.g., we call softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits on tf.matmul(x, W) + b), because this more numerically stable function internally computes the softmax activation. In your code, consider usingtf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits instead.
大意是:如果使用 cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(-tf.reduce_sum(y_ * tf.log(y), reduction_indices=[1]))
来计算交叉熵,则需要使用 tf.clip_by_value 来使某些求 log 的值,因为 log 会产生 none (如 log-3 ), 用它来限定不出现none,具体使用方式如下:
cross_entropy = -tf.reduce_sum(y_*tf.log(tf.clip_by_value(y_conv, 1e-10, 1.0)))但后来有人用了一个更好的方法来避免none:
cross_entropy = -tf.reduce_sum(y_*tf.log(y_conv + 1e-10))具体参见 http://stackoverflow.com/questions/33712178/tensorflow-nan-bug 的讨论。
而如果直接用 tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits 则你再没有上面的后顾之忧了,它自动解决了上面的问题。
关于 tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits 及 tf.clip_by_value的更多相关文章
- 【TensorFlow】tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits的用法
在计算loss的时候,最常见的一句话就是 tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits ,那么它到底是怎么做的呢? 首先明确一点,loss是代价值,也就是我们要最小化 ...
- 深度学习原理与框架-Tensorflow卷积神经网络-卷积神经网络mnist分类 1.tf.nn.conv2d(卷积操作) 2.tf.nn.max_pool(最大池化操作) 3.tf.nn.dropout(执行dropout操作) 4.tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(交叉熵损失) 5.tf.truncated_normal(两个标准差内的正态分布)
1. tf.nn.conv2d(x, w, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME') # 对数据进行卷积操作 参数说明:x表示输入数据,w表示卷积核, stride ...
- [TensorFlow] tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits的用法
在计算loss的时候,最常见的一句话就是tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits,那么它到底是怎么做的呢? 首先明确一点,loss是代价值,也就是我们要最小化的值 ...
- tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits的用法
http://blog.csdn.net/mao_xiao_feng/article/details/53382790 计算loss的时候,最常见的一句话就是tf.nn.softmax_cross_e ...
- tf.nn.softmax & tf.nn.reduce_sum & tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits
tf.nn.softmax softmax是神经网络的最后一层将实数空间映射到概率空间的常用方法,公式如下: \[ softmax(x)_i=\frac{exp(x_i)}{\sum_jexp(x_j ...
- tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits()函数的使用方法
import tensorflow as tf labels = [[0.2,0.3,0.5], [0.1,0.6,0.3]]logits = [[2,0.5,1], [0.1,1,3]] a=tf. ...
- 1、求loss:tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits, labels, name=None))
1.求loss: tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits, labels, name=None)) 第一个参数log ...
- tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits 分类
tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits, labels, name=None) 参数: logits:就是神经网络最后一层的输出,如果有batch ...
- 深度学习原理与框架-图像补全(原理与代码) 1.tf.nn.moments(求平均值和标准差) 2.tf.control_dependencies(先执行内部操作) 3.tf.cond(判别执行前或后函数) 4.tf.nn.atrous_conv2d 5.tf.nn.conv2d_transpose(反卷积) 7.tf.train.get_checkpoint_state(判断sess是否存在
1. tf.nn.moments(x, axes=[0, 1, 2]) # 对前三个维度求平均值和标准差,结果为最后一个维度,即对每个feature_map求平均值和标准差 参数说明:x为输入的fe ...
随机推荐
- js arguments 内置对象
1.arguments是js的内置对象. 2.在不确定对象是可以用来重载函数. 3.用法如下: function goTo() { var i=arguments.length; alert(i); ...
- iOS UITableViewHeaderFooterView设置背景色为透明
给UITableViewHeaderFooterView设置背景色分2种情况 1.tableView在group模式下,UITableViewHeaderFooterView的背景色默认是透明的,此时 ...
- Link-based Classification相关数据集
Link-based Classification相关数据集 Datasets Document Classification Datasets: CiteSeer: The CiteSeer dat ...
- Easyui datebox单击文本框显示日期选择
Easyui默认是点击文本框后面的图标显示日期,为了更进一步优化体验 修改为单击文本框显示日期选择框 修改jquery.easyui.min.js(作者用的是1.3.6版本,其他版本或有区别) 可 c ...
- Vector类与Enumeration接口
Vector类用于保存一组对象,由于java不支持动态数组,Vector可以用于实现跟动态数组差不多的功能.如果要将一组对象存放在某种数据结构中,但是不能确定对象的个数时,Vector是一个不错的选择 ...
- Java线程工作内存与主内存变量交换过程及volatile关键字理解
Java线程工作内存与主内存变量交换过程及volatile关键字理解 1. Java内存模型规定在多线程情况下,线程操作主内存变量,需要通过线程独有的工作内存拷贝主内存变量副本来进行.此处的所谓内存模 ...
- cout顺序,i++和++i
先看下以下代码 #include<iostream> using namespace std; ; int f1() { x = ; return x; } int f2() { x = ...
- UIImagePickerController在UIPopoverController中 旋屏问题
1弧度=180/π度1度=π/180弧度今天遇到了 一个问题.UIImagePickerController在UIPopoverController中 旋屏问题. 在查找了许多资料后方知,此乃iOS系 ...
- CentOS7.0 安装 Nginx
记录下,方便以后查阅. 1.安装依赖库 yum install gcc-c++ yum install pcre pcre-devel yum install zlib zlib-devel yum ...
- 【BZOJ4557】[JLoi2016]侦察守卫 树形DP
[BZOJ4557][JLoi2016]侦察守卫 Description 小R和B神正在玩一款游戏.这款游戏的地图由N个点和N-1条无向边组成,每条无向边连接两个点,且地图是连通的.换句话说,游戏的地 ...
