Fragment详解及举例
1.为什么用Fragment(Android3.0提出)来替代TabActivity(Android4.0以后正式被弃用)?
因为Fragment可以适应各种不同屏幕大小,也就是适应不同屏幕的分辨率。例如:
当开发的应用程序同时适用于平板电脑和手机时,可以利用Fragment实现灵活的布局,改善用户体验。
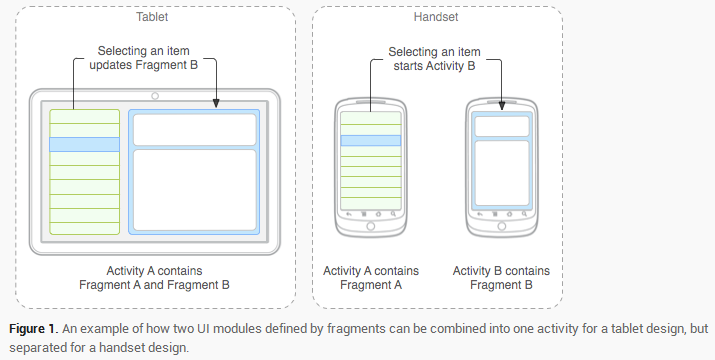
2.Fragment的特征:
- Fragment是Activity中的一部分,或者说值一种行为。Fragment可以调用getActivity()方法获取它所在的Activity,Activity可调用FragmentManager的findFragmentById()或者findFragmentByTag()方法来获取Fragment。
- 一个Activity可以同时组合多个Fragment;反过来,一个Fragment也可被多个Activity复用。
- 在Activity的运行过程中,可调用FragmentManager的add()、remove()、replace()方法动态的添加,删除或者替换Fragment。可以将一个Fragment事务添加到栈中,被activity管理,有了这个栈可以返回执行Fragment事务,可以支持fragment级别的返回。在activity中添加fragment时它必须置于ViewGroup中,并且需要定义fragment自己的界面。
- Fragment可以响应自己的输入事件,并拥有自己的生命周期,但它们的生命周期直接被其所属的Activity的生命周期控制。
3.Fragment的生命周期:
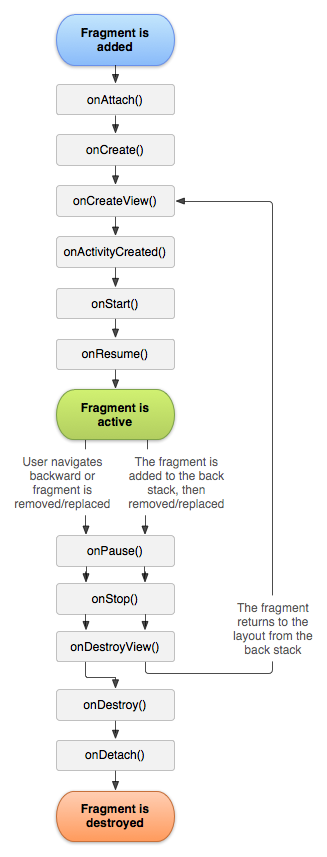
OnAttach():当该fragment被添加到Activity时被回调,该方法值会被调用一次。
onCreate(Bundle savedStatus):创建Fragment时被回调,该方法只会被调用一次。
onCreateView():每次创建、绘制该Fragment的View组件时,回调该方法,Fragment将会显示该方法返回的View组件。
onActivityCreated():当Fragment所在的Activity被启动完成后回调该方法。
onStart():启动Fragment时被回调。
OnResume():恢复Fragment时被回调,onStart()方法后一定会回调onResume()方法。
onPause():暂停Fragment时被回调。
onStop():停止Fragment时被回调。
onDestroyView():销毁Fragment所包含的View组件时调用。
onDestroy():销毁Fragment时被回调,该方法只会被调用一次。
onDetach():将该Fragment从Activity中被删除、被替换完成时回调该方法,onDestroy()方法后一定会回调onDetach()方法,该方法只会被调用一次。
4.将Fragment添加到Activity中的两种方式:
- 在布局中使用<fragment.../>元素添加到Fragment,<fragment.../>元素的Android:name属性指定为Fragment的实现类。
- 在Java代码中通过FragmentTransaction对象的add()方法来添加Fragment。
5.Fragment与Activity之间的通信:
- Activity向Fragment传递数据,在Activity中创建Bundle数据包,并调用Fragment的SetArguments(Bundle bundle)方法即可将绑定的数据包传递给Fragment。
- Fragment向Activity传递数据或Activity需要在Fragment运行中进行实时通信,在Fragment中定义一个内部回调接口,再让包含该Fragment的Activity事项该回调接口,这样Fragment即可调用改回调方法将数据传给Activity。
实例:
定义布局文件fragment_book_detail.xml,展示书的标题和描述
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<!--定义一个TextVew来显示图书标题--> <TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceLarge"
android:text="Large Text"
android:id="@+id/book_title"
android:padding="16dp"/>
<!--定义一个TextView来显示图书描述-->
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceMedium"
android:text="Medium Text"
android:id="@+id/book_desc"
android:padding="16dp"/> </LinearLayout>
定义布局文件activity_book_twopane.xml,左边展示书名,单击后右边展示书名和书描述。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_marginLeft="16dp"
android:layout_marginRight="16dp"
android:divider="?android:attr/dividerHorizontal"
android:showDividers="middle">
<!--添加一个Fragment-->
<fragment
android:name="fragment.BookListFragment"
android:id="@+id/book_list"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"/>
<!--添加一个FrameLayout容器--> <FrameLayout
android:id="@+id/book_detail_container"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="3"
/>
</LinearLayout>
定义一个BookContent实体类:
package bean; import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map; /**
* Created by xiaoping on 2015/8/10.
*/
public class BookContent {
//定义一个内部类,作为系统的业务对象
public static class Book {
public Integer id;
public String title;
public String desc; public Book(Integer id, String title, String desc) {
this.id = id;
this.title = title;
this.desc = desc; } @Override
public String toString() {
return title;
}
}
//使用List集合记录系统所包含的Book对象
public static List<Book> ITEMS=new ArrayList<Book>();
//使用Map集合来记录系统所包含的Book对象
public static Map<Integer,Book> ITEM_MAP=new HashMap<Integer,Book>();
static {
//使用静态的初始化代码,将Book对象添加到List集合,Map集合中
addItem(new Book(1,"疯狂的Java讲解","一本好书!"));
addItem(new Book(2,"Java 特种兵","一本好书好书中的好书!"));
addItem(new Book(3,"小明同学","一本即将出版的书"));
} private static void addItem(Book book) {
ITEMS.add(book);
ITEM_MAP.put(book.id,book);
} }
创建在activity_book_twopane.xml布局中BookListFragment类直接activity中Bundle中获取数据。
package fragment;
import android.app.Fragment;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.TextView;
import bean.BookContent;
import whushare.cn.whu.fragment.R;
/**
* Created by xiaoping on 2015/8/10.
*/
public class BookDetailFragment extends Fragment {
public static final String ITEM_ID="item_id";
BookContent.Book book;//保存改Fragment显示的对象 @Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
//如果启动该Fragment时包含了ITEM_ID参数
if(getArguments().containsKey(ITEM_ID)){ book=BookContent.ITEM_MAP.get(getArguments().getInt(ITEM_ID)); }
} @Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
//加载布局文件 fragment_book_detail.xml布局文件
View rootView=inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_book_detail,container,false);
initView(rootView);
return rootView; } private void initView(View rootView) {
if(book!=null){
TextView bookTitle= (TextView) rootView.findViewById(R.id.book_title);
bookTitle.setText(book.title);
TextView bookDesc= (TextView) rootView.findViewById(R.id.book_desc);
bookDesc.setText(book.desc);
}
} }
activity的具体实现类SelectBookActivity,在这个里面创建了数据包,并将数据包中的数据当做参数传递个BookDetailFragment。
package whushare.cn.whu.fragment;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.FragmentManager;
import android.app.FragmentTransaction;
import android.support.v7.app.ActionBarActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.KeyEvent;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.MenuItem;
import fragment.BookDetailFragment;
import fragment.BookListFragment;
import fragment.Callbacks; public class SelectBookActivity extends Activity implements Callbacks {
private FragmentManager mFragmentManager;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
//加载activity_book_twopane布局
setContentView(R.layout.activity_book_twopane);
}
//实现Callbacks接口必须实现的方法
@Override
public void onItemSelected(Integer id) {
//创建Bundle,准备向Fragment传人参数
Bundle arguments=new Bundle();
arguments.putInt(BookDetailFragment.ITEM_ID,id);
//创建BookDetailFragment 对象 BookDetailFragment fragment=new BookDetailFragment();
//向Fragment传入参数
fragment.setArguments(arguments);
//使用fragment替换book_detail_container容器当前显示的Fragment
mFragmentManager=getFragmentManager();
FragmentTransaction transaction= mFragmentManager.beginTransaction();
transaction.replace(R.id.book_detail_container,fragment);
transaction.commit(); }
}
在上面的代码执行加载activity_book_twopane布局setContentView(R.layout.activity_book_twopane);时,BookListFragment被添加到activity中。activity通过实现BookListFragment中的Callbacks接口来获取BookListFragment中的数据。
BookListFragment类的具体实现:
package fragment; import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.ListFragment;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.ArrayAdapter;
import android.widget.ListAdapter;
import android.widget.ListView; import bean.BookContent; /**
* Created by xiaoping on 2015/8/10.
*/
public class BookListFragment extends ListFragment {
//定义一个回调接口,该Fragment所在Activity需要实现该接口,该Fragment将通过该接口与它所在的Activity交互
private Callbacks mCallbacks;
public interface Callbacks {
public void onItemSelected(Integer id);
}
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState){
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
ListAdapter listAdapter=new ArrayAdapter<BookContent.Book>(getActivity(),android.R.layout.simple_list_item_activated_1,android.R.id.text1,BookContent.ITEMS);
setListAdapter(listAdapter);
}
//当该Fragment被添加,显示到Activity时,回调该方法
@Override
public void onAttach(Activity activity){
super.onAttach(activity);
//如果Activity没有实现Callbacks接口,抛出异常
if(!(activity instanceof Callbacks)){
throw new IllegalStateException("BookListFragment 所在的Activity必须实现Callbacks接口!");
}
mCallbacks=(Callbacks)activity;
}
//当Fragment从它所属的Activity中被删除时回调该方法
@Override
public void onDetach(){
super.onDetach();
mCallbacks=null;
} @Override
public void onListItemClick(ListView listView, View view, int position, long id) {
super.onListItemClick(listView,view,position,id);
//激发mCallbacks的onItemSelected方法
mCallbacks.onItemSelected(BookContent.ITEMS.get(position).id);
}
public void setActivateOnItemClick(boolean activateOnItemClick){
getListView().setChoiceMode(activateOnItemClick?ListView.CHOICE_MODE_SINGLE:ListView.CHOICE_MODE_NONE);
} }
上述代码并不能实现适应不同屏幕的分辨率,我们将上面的SelectBookActivity换成如下两个Activity即可。而且还要定义一个名为refs.xml的引用资源文件。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<!--定义activity_book_list 实际应用了@layout/activity_book_twopane资源-->
<item name="activity_book_list" type="layout">
@layout/activity_book_twopane</item>
</resources>
定义一个activity_book_list布局
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!--添加一个Fragment-->
<fragment xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:name="fragment.BookListFragment"
android:id="@+id/book_list"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_marginLeft="16dp"
android:layout_marginRight="16dp"/>
同过BookListActivity操作来确定为平板电脑的显示模式,还是手机。
package fragment; import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.FragmentManager;
import android.app.FragmentTransaction;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle; import whushare.cn.whu.fragment.R; /**
* Created by xiaoping on 2015/8/11.
*/
public class BookListActivity extends Activity implements Callbacks {
//定义一个旗标,用于标记该应用是否支持大屏幕
private boolean mTwoPane;
@Override
public void onItemSelected(Integer id) {
if(mTwoPane){
//创建bundle准备向fragment中传递参数
Bundle bundle=new Bundle();
bundle.putInt(BookDetailFragment.ITEM_ID,id);
//创建BookDetailActivity对象
BookDetailFragment fragment=new BookDetailFragment();
//向fragment中传递参数
fragment.setArguments(bundle);
//使用当前的fragment替换book_detail_container容器显示当前的fragment
FragmentTransaction transaction=getFragmentManager().beginTransaction();
transaction.replace(R.id.book_detail_container,fragment);
//将事务添加到back栈,允许用户按下Back按键时返回到替换fragment之前的状态
transaction.addToBackStack(null);
transaction .commit();
}
else
{
//创建启动BookDetailActivity的Intent
Intent intent=new Intent(this,BookDetailActivity.class);
//设置传递给BookDetailActivity的参数
intent.putExtra(BookDetailFragment.ITEM_ID,id);
//启动Activity
startActivity(intent); }
} @Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
//指定加载的R.layout.activity_book_list对应的界面布局文件
//但实际上该应用会根据屏幕的分辨率加载不同的界面布局文件
setContentView(R.layout.activity_book_list);
if(findViewById(R.id.book_detail_container)!=null)
{
mTwoPane=true;
((BookListFragment)getFragmentManager().findFragmentById(R.id.book_list)).setActivateOnItemClick(true);
}
}
}
如果为手机模式则用BookDetailActivity来显示图书的详情。
package fragment; import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.FragmentTransaction;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.MenuItem; import whushare.cn.whu.fragment.R; /**
* Created by xiaoping on 2015/8/11.
*/
public class BookDetailActivity extends Activity{
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_book_detail);
// getActionBar().setDisplayHomeAsUpEnabled(true);
if(savedInstanceState==null){
//创建BookDetailFragment对象
BookDetailFragment fragment=new BookDetailFragment();
//创建Bundle对象
Bundle arguments=new Bundle();
arguments.putInt(BookDetailFragment.ITEM_ID,getIntent().getIntExtra(BookDetailFragment.ITEM_ID,0));
//向Fragment中传递参数
fragment.setArguments(arguments);
//将指定的fragment添加到book_detail_container中
FragmentTransaction transaction=getFragmentManager().beginTransaction();
transaction.replace(R.id.book_detail_container,fragment);
transaction.addToBackStack(null);
transaction.commit();
}
} @Override
public boolean onOptionsItemSelected(MenuItem item) {
if(item.getItemId()==android.R.id.home){
//创建启动BookListActivity的Intent
Intent intent=new Intent(this,BookListActivity.class);
//添加额外的Flag,将Activity栈中处于FirstActivity之上的Activity弹出
intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TOP);
//启动intent对应的Activity
startActivity(intent);
return true;
}
return super.onOptionsItemSelected(item);
}
}
Fragment详解及举例的更多相关文章
- Linux防火墙iptables学习笔记(三)iptables命令详解和举例[转载]
Linux防火墙iptables学习笔记(三)iptables命令详解和举例 2008-10-16 23:45:46 转载 网上看到这个配置讲解得还比较易懂,就转过来了,大家一起看下,希望对您工作能 ...
- Fragment详解之三——管理Fragment(1)
相关文章: 1.<Fragment详解之一--概述>2.<Fragment详解之二--基本使用方法>3.<Fragment详解之三--管理Fragment(1)>4 ...
- iptables命令详解和举例
网上看到这个配置讲解得还比较易懂,就转过来了,大家一起看下,希望对您工作能有所帮助.网管员的安全意识要比空喊Linux安全重要得多. iptables -Fiptables -Xiptables -F ...
- Android Fragment 详解(一)
Android从3.0开始引入fragment,主要是为了支持更动态更灵活的界面设计,比如在平板上的应用.平板机上拥有比手机更大的屏幕空间来组合和交互界面组件们.Fragment使你在做那样的设计时, ...
- Android Fragment详解(三): 实现Fragment的界面
为fragment添加用户界面: Fragment一般作为activity的用户界面的一部分,把它自己的layout嵌入到activity的layout中. 一个 要为fragment提供layout ...
- android——fragment详解
在android开发过程中,如果使用到了导航栏.那么不可避免的就需要使用fragment来处理界面.闲着没事,就详解一下Framgent的使用方法吧. 难得写一次.本人 shoneworn shone ...
- Android面试收集录4 Fragment详解
1.什么是Fragment? 你可以简单的理解为,Fragment是显示在Activity中的Activity. 它可以显示在Activity中,然后它也可以显示出一些内容. 因为它拥有自己的生命周期 ...
- Android 开发 之 Fragment 详解
本文转载于 : http://blog.csdn.net/shulianghan/article/details/38064191 本博客代码地址 : -- 单一 Fragment 示例 : http ...
- 5. Fragment详解
onCreateView是Fragment生命周期方法中最重要的一个.因为在该 方法中会创建在Fragment中显示的View. public View onCreateView(LayoutInfl ...
随机推荐
- MySQL-5.7设置InnoDB表数据文件存储位置
1.表空间 Innodb存储引擎可将所有数据存放于ibdata*的共享表空间,也可将每张表存放于独立的.ibd文件的独立表空间. 共享表空间以及独立表空间都是针对数据的存储方式而言的. 共享表空间: ...
- oracle时间的获取,前一天,上一个星期,上一个月
–前一天的开始时刻 SELECT to_date(to_char(TRUNC(SYSDATE-1),’yyyy-mm-dd’) || ‘00:00:00’,’yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss ...
- 2 Powershell与Cmd以及Unix/Linux Shell
上篇文章我说道,windows为了改变用户对其console界面的诟病,于是就从windows vista开始,计划要改变这种局面,于是就有 了Powershell的出现. 1.兼容shell命令 ...
- 安装 SPRING TOOL SUITE
- Spring注解(事务)
spring操作数据库 jdbc <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-jdbc --> & ...
- eclipse中的错误解决——Servlet cannot be resolved to a type
问题如图 解决问题方法
- SpringBoot配置文件 application.properties详解
SpringBoot配置文件 application.properties详解 本文转载:https://www.cnblogs.com/louby/p/8565027.html 阅读过程中若发现 ...
- CocoaPods学习系列2——使自己的项目支持CocoaPods管理
该篇记录使自己的项目支持CocoaPods管理. 要达到这一目的,需要如下步骤: 1.将自己的项目提交到github,添加开源协议license 2.添加podspec文件 3.验证podspec,成 ...
- scala学习手记18 - Any和Nothing
Any 前面已经有两次提到过:在scala中,Any类是所有类的超类. Any有两个子类:AnyVal和AnyRef.对应Java直接类型的scala封装类,如Int.Double等,AnyVal是它 ...
- Matlab操作矩阵的相关方法
Matlab操作矩阵的相关方法 下面这篇文章主要是对吴恩达老师机器学习中matlab操作的一个整理和归纳 一.基本操作 1.生成矩阵(ones.zeros) A = [1 2;3 4;5 6] ...
