HTTP methods 与 RESTful API
Note
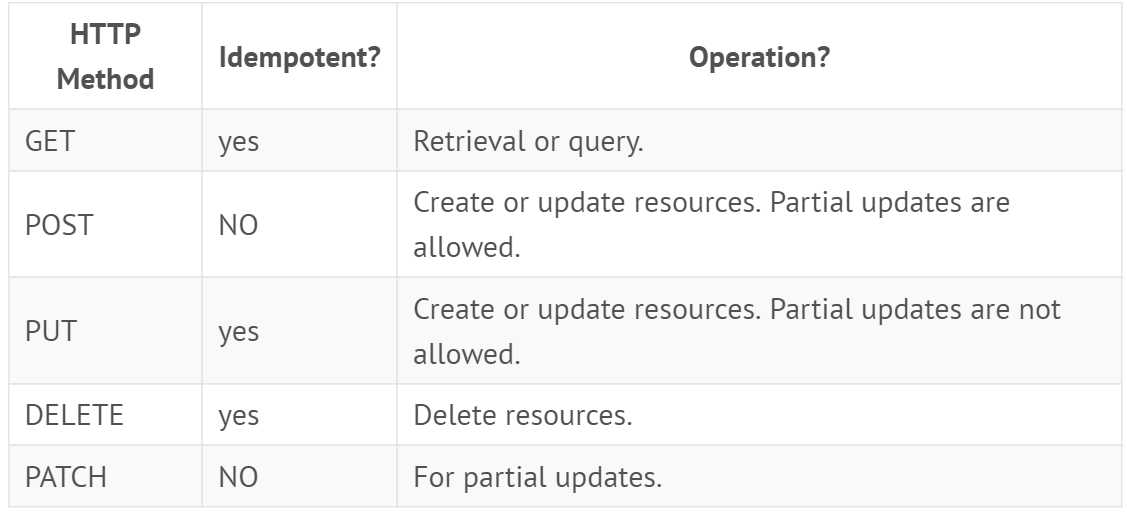
GET, primarily used to select resources.
Other options for an API method include:
POST, primarily used to create child resources.
PUT, primarily used to update existing resources (and, although not recommended, can be used to create child resources).
DELETE, used to delete resources.
PATCH, used to update resources.
HEAD, primarily used in testing scenarios. It is the same as GET but does not return the resource representation.
OPTIONS, which can be used by callers to get information about available communication options for the target service.
The method created is not yet integrated with the back end. The next step sets this up.
目录:
- RESTful 是什么
- JSON-server (提供 RESTful API 接口 + JSON 返回数据)
- 如何选择 REST 方法
- HTTP verbs / method (安全 | 幂等)
- HTTP POST V.S. PUT
- REST POST | PUT | PATCH
RESTful 是什么 阮一峰:理解RESTful架构
- Representational State Transfer 表征状态转移
- 核心:resource。representation 指的是 resource 的表现层。
resource,资源,即一个实体(文本/图片/服务),可以用一个 URI 唯一标识。 - representation,表现层
资源,是一个实体,可以有多种外在表现形式。这个表现形式,即 representation 表现层。
e.g. 文本可以用txt表示,也可以用 HTML/ XML/ JSON。 State Transfer,状态转移
client <-> server,这个交互涉及到数据和状态的变化。
client 操作 server,即通过某种手段(HTTP method),使 server 发生状态转移。目前对 REST 的理解:(2016-8-20)
- 每个 URI 代表一种资源。用名词表示。
- HTTP method 表示对资源进行了哪种类型的操作。
HTTP verbs 推荐返回的状态码
- TOP10 HTTP Status Code in REST
200 OK201 Created204 No Content304 Not Modified400 Bad Request401 Unauthorized403 Forbidden404 Not Found409 Conflict500 Internal Server Error
- 水很深,现在还理解不了
- Richardson Maturity Model
- Level 1 - Resources
- Level 2 - HTTP Verbs
- Level 3 - Hypermedia Controls
- Fielding's paper
- Learn REST: A RESTful Tutorial
- What exactly is RESTful programming?
- Richardson Maturity Model
JSON-Server
- JSON-Server 是一款前端测试工具,可提供 REST API + JSON 服务。
来看一组 JSON-Server 提供的 RESTful API 接口:
GET /posts //获取posts下的所有资源
GET /posts/1 //获取posts下id为1的资源
GET /posts?title=json-server&author=typicode //获取posts下title=json-server&author=typicode的资源
POST /posts //posts添加操作
PUT /posts/1 //对posts下id为1的资源进行修改操作:完全替换
PATCH /posts/1 //对posts下id为1的资源进行修改操作:局部更新
DELETE /posts/1 //对posts下id为1的资源进行删除操作
- 有这两个明显的特点:
- 每个 URI 代表一种资源。用名词表示。
- HTTP method 表示对资源进行了哪种类型的操作。
使用时需注意:
get
将查询的参数用 & 拼接成查询字符串
if(data && Object.prototype.toString.call(data) == "[object Object]") {
for (var i in data) {
dataStr += i + "=" + data[i] + "&";
}
} lastPos = dataStr.lastIndexOf("&");
dataStr = dataStr.slice(0, lastPos);
在
postputpatch请求中,content-type的值必须为application/json
相应的,需要将提交的数据,由 JS对象 -> JSON JSON.stringify()xhr.setRequestHeader("content-type", "application/json");
xhr.send(data ? JSON.stringify(data) : null);
RESTful
RESTful 只是一种 architectural style,意思是如果大家都依此行事的话,沟通成本会很低,开发效率就高。
那么只要前后台约定好,就可以随意选取方法了么?
This is wrong because a request passes through many intermediaries and middleware applications which perform optimizations based on the HTTP method type. These optimizations depend on two key characteristics of HTTP methods: idempotency and safety, which are defined in the HTTP specification.
Code Ahoy: REST Design - Choosing the Right HTTP Method从这个角度来说,对哪种操作使用哪种方法,取决于
HTTP 方法本身的特性和前后台交互接口的约定。HTTP 方法的两个关键特性:
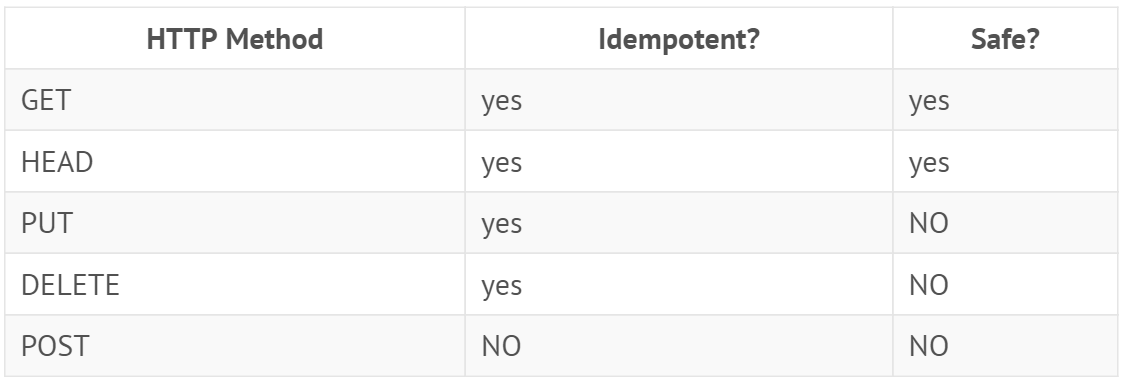
安全|幂等(safe|idempotent)safe
安全的方法被期望不会产生任何副作用(side effects)。这些操作是只读的。e.g. 查询数据库。idempotent
幂等的方法保证了重复进行一个请求和一次请求的效果相同。(并不是指返回 client 的响应总是相同的;而是指 server 上资源的状态从第一次请求后就不再改变)
在数学中,幂等性指N次变换和一次变换的结果相同。x = 1; /* 幂等 */
x++; /* 非幂等 */
安全|幂等是由 HTTP 标准定义的契约:开发者在实现 RESTful API 时必须遵守。- 如果一个操作没有以幂等的方式实现,那么即使它是通过 GET 方法调用的,它也不会自动变成 幂等的/ 安全的。
当使用 HTTP 构建 RESTful 程序时,对HTTP method 的实现应该满足其安全性和幂等性,来使 client 和中间件能自由地按契约优化,并增强用户体验。
e.g. 浏览器并不确切知道某个特定的 form 用途,但如果这个 form 是通过 HTTP GET 提交的,浏览器就会知道当出现网络异常的时候,它可以安全的、自动再次尝试提交。 而通过 HTTP POST 提交的 form,如果浏览器不先向用户确认就重复提交,会是不安全的。
RESTful 下的
postputpatchpost- 非幂等:两次相同的POST请求会在服务器端创建两份资源,它们具有不同的URI。
- POST 所对应的URI并非创建的资源本身,而是资源的接收者。比如:POST xx/articles 的语义是在 xx/articles下创建一篇帖子。
从另一个角度理解 POST 如何设计下单的接口?
post /orders?本来 POST 就是被设计来提交表单这样的事务型操作的。所以 POST 可以理解为执行服务器的一个事务。POST 请求服务器执行一个动作,多次发起请求可能导致动作多次执行:非幂等。
put- 幂等:对同一URI进行多次PUT的副作用和一次PUT是相同的。
- PUT 所对应的URI是要创建或更新的资源本身。比如:PUT xx/articles/4231 的语义是创建或更新ID为4231的帖子。
patch- 非幂等 e.g.
patch可以对资源进行逻辑判断增量修改,如每次加3,那么执行多次,就会造成额外影响。 - 对已有资源的局部更新(而不用指定整个资源)。
- 非幂等 e.g.
有人认为应该用 POST 来创建新资源,用 PUT 来更新已有资源。如果用 POST 来做更新操作,就不符合 RESTful 风格。
实际并非如此。
The REST standard doesn’t stop us from using POST requests for updates. In fact, it doesn’t even talk about it because idempotency and safety guarantees are properties of the HTTP protocol, not of the REST standard.
作者 Code Ahoy 又引用了 Roy Fielding 的话, 大意是,例如 RESTful 不使用 GET 来进行不安全的操作,是因为这会违反 HTTP 中对 GET 方法的定义,反过来就会影响中间件和搜索引擎。由 HTTP 定义的方法是 Web's architecture definition 的一部分,而不属于 REST architecture style.
因此,使用 POST 还是 PUT 归结于:这些方法的幂等性保证。
因为 PUT 是幂等的,所以当第一个请求的响应没有及时到达的时候,clients 或者中间件可以重复发送 PUT 请求,而不用考虑 server 是否已经处理了第一个请求。 而为了保证幂等性,PUT 请求必须替换整个资源,因此必须发送所有属性。 如果要进行局部更新,就必须使用 POST 或者 PUT 这些非幂等的方法。
- 既然选择 POST 还是 PUT 不属于 REST architecture style 的范围,而属于 HTTP 的设计,那我们来看看两者在 HTTP 中分别应用于什么场景。
HTTP 中的 POST V.S. PUT
The fundamental difference between the POST and PUT requests is reflected in the different meaning of the Request-URI. The URI in a POST request identifies the resource that will handle the enclosed entity. That resource might be a data-accepting process, a gateway to some other protocol, or a separate entity that accepts annotations. In contrast, the URI in a PUT request identifies the entity enclosed with the request – the user agent knows what URI is intended and the server MUST NOT attempt to apply the request to some other resource. Method Definitions RFC2616
POST 和 PUT 最根本的区别反映在 request URI 的含义上:
- POST 请求中的 URI,标识了要处理所附实体的资源。
- PUT 请求的的 URI,标识了所附实体。
PUT
PUT puts a file or resource at a specific URI, and exactly at that URI.
如果这个这个 URI 所指定的位置上已有资源,PUT 就会替换掉这个资源;如果没有, PUT 会创建一个。
但是 PUT 请求的响应不会被缓存。POST
POST sends data to a specific URI and expects the resource at that URI to handle the request.
POST 请求的响应的是可以缓存的,只要 server 设置了合适的 Cache-Control 和 Expires 首部。
HTTP RFC 指定 POST 用来:
- Annotation of existing resources;
- Posting a message to a bulletin board, newsgroup, mailing list, or similar group of articles;
- Providing a block of data, such as the result of submitting a form, to a data-handling process;
- Extending a database through an append operation.
使用 REST 的好处之一就是促进了 HTTP verbs/methods 的正确使用。
- What's the difference between a POST and a PUT HTTP REQUEST?
最后来归纳一下:
POSTto a URL creates a child resource at a server defined URL.PUTto a URL creates/replaces the resource in its entirety at the client defined URL.PATCHto a URL updates part of the resource at that client defined URL.postput创建的对象,其URL是由 client 命名,还是 server?server 决定 -
post;client 命名 -put.如果只是知道这个资源的父级类别的 URL,用
post;(比如说创建的资源id是数据库中自增长的);POST /expense-report
换句话说,如果知道将要创建的资源的 URL,用
put;PUT /expense-report/10929
put是创建时的一个候选方法:当 client 在资源创建前就已经知道了它的URL。putpatchput用来对已知资源做完全替换,要求前端提供一个完整的资源对象,缺了的字段会被清空。patch做局部更新,后台只会更新接收到的字段。【节省带宽】
- ref:
http://www.cnblogs.com/xhz-dalalala/p/5791631.html
HTTP methods 与 RESTful API的更多相关文章
- Meteor 前端 RESTful API 通过后端 API 下载文件
Meteor 下载文件 问题场景 后端 HTTP server提供一个下载接口,可是须要前端 Meteor 可以给浏览器用户开一个URL来下载这个文件. 举例:在线的Meteor Logo文件就好比后 ...
- Restful API和传统的API的区别
一.功能区别 Restful API是当作资源的唯一标识符,而传统是实现某某功能 如:/api/getList/1 and /api/getList?page=1 二.methods多样性 Restf ...
- HTTP Methods 和 RESTful Service API 设计
含义: HTTP Methods:也叫 HTTP Verbs,HTTP Methods 可以翻译成 HTTP 方法.它们是 HTTP 协议的一部分,主要规定了 HTTP 如何请求和操作服务器上的资源, ...
- http methods & restful api methods
http methods & restful api methods 超文本传输协议(HTTP)是用于传输超媒体文档(例如HTML)的应用层协议 https://developer.moz ...
- Restful Api 最佳实践
Web APIs has become an very important topic in the last year. We at M-Way Solutions are working ever ...
- 使用Flask设计带认证token的RESTful API接口[翻译]
上一篇文章, 使用python的Flask实现一个RESTful API服务器端 简单地演示了Flask实的现的api服务器,里面提到了因为无状态的原则,没有session cookies,如果访问 ...
- RESTful API URI 设计的一些总结
非常赞的四篇文章: Resource Naming Best Practices for Designing a Pragmatic RESTful API 撰写合格的 REST API JSON 风 ...
- 【转】最佳Restful API 实践
原文转自:https://bourgeois.me/rest/ REST APIs are a very common topic nowaday; they are part of almost e ...
- 利用 Django REST framework 编写 RESTful API
利用 Django REST framework 编写 RESTful API Updateat 2015/12/3: 增加 filter 最近在玩 Django,不得不说 rest_framewor ...
随机推荐
- vs2010 sp1 创建silverlight 时,提示我 “在创建silverlight项目之前,您需要安装最新的silverlight Developer运行时
---恢复内容开始--- Silverlight 5 Developer Rumtime (32bit): http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=229323 ...
- 《图解HTTP》 第11章 web的攻击技术
11.1 针对Web的攻击技术 简单的HTTP协议本身并不存在安全性问题,所以协议本身几乎不会成为攻击的对象. 11.1.1 HTTP不具备必要的安全功能 11.1.2 在客户端即可篡改请求 在HTT ...
- Java 截取反斜杠--java使用split拆分特殊字符
Java 截取反斜杠 replaceAll和split (“\”) 问题解决办法 xxx.split("\\") 显然得不到想要的结果 正确方法 xxx.split("\ ...
- hibernate 一对多操作(级联操作)
一对多级联操作 1. 级联保存 复杂写法 Company company = new Company(); company.setcName("Hello"); company. ...
- (转)关于Android的nodpi,xhdpi,hdpi,mdpi,ldpi
首先是几个基本概念:1.屏幕尺寸Screen size即显示屏幕的实际大小,按照屏幕的对角线进行测量.为简单起见,Android把所有的屏幕大小分为四种尺寸:小,普通,大,超大(分别对应:small, ...
- android .9.png ”点九” 图片制作方法
“点九”是andriod平台的应用软件开发里的一种特殊的图片形式,文件扩展名为:.9.png 智能手机中有自动横屏的功能,同一幅界面会在随着手机(或平板电脑)中的方向传感器的参数不同而改变显示的方向, ...
- 使用spring @Scheduled注解运行定时任务、
曾经框架使用quartz框架运行定时调度问题. 老大说这配置太麻烦.每一个调度都须要多加在spring的配置中. 能不能降低配置的量从而提高开发效率. 近期看了看spring的 scheduled的使 ...
- 设计模式14---设计模式之命令模式(Command)(行为型)
1.场景模拟 请用软件模拟开机过程 按下启动按钮 然后电源供电 主板开始加电自检 BIOS依次寻找其他设备的BIOS并且让他们初始化自检 开始检测CPU,内存,光盘,硬盘,光驱,串口,并口,软驱即插即 ...
- jsPlumb开发入门教程(实现html5拖拽连线)
jsPlumb是一个强大的JavaScript连线库,它可以将html中的元素用箭头.曲线.直线等连接起来,适用于开发Web上的图表.建模工具等.它同时支持jQuery+jQuery UI.MooTo ...
- 利用ESLint检查代码质量
1. ESLint ESLint 是一个插件化的 javascript 代码检测工具,它可以用于检查常见的 JavaScript 代码错误,也可以进行代码风格检查,这样我们就可以根据自己的喜好指定一套 ...

